NAPLEX Sterile Compounding
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
sterile compounding is used to prepare?
Injections (IV, IM, SC)
Eye drops
Irrigations
Pulmonary inhalations
Baths, soaks for live tissues/organs
Implants
USP ____ - sterile
797
SVP define
small volume parenteral
-IV bag with a volume ≤100 ml
LVP define
large volume parenteral
-IV bag with volume >100 ml
PEC define
primary engineering control
-sterile hood that provides ISO 5 air for sterile compounding
LAFW define
laminar airflow workbench
type of open front sterile hood (PEC); air flow in one direction
SEC define
secondary engineering control
-room containing ISO 7 air where sterile hood (PEC) is located; also called buffer room
SCA define
segregated compounding area
-designated space that contains ISO 5 but is not part of cleanroom suite
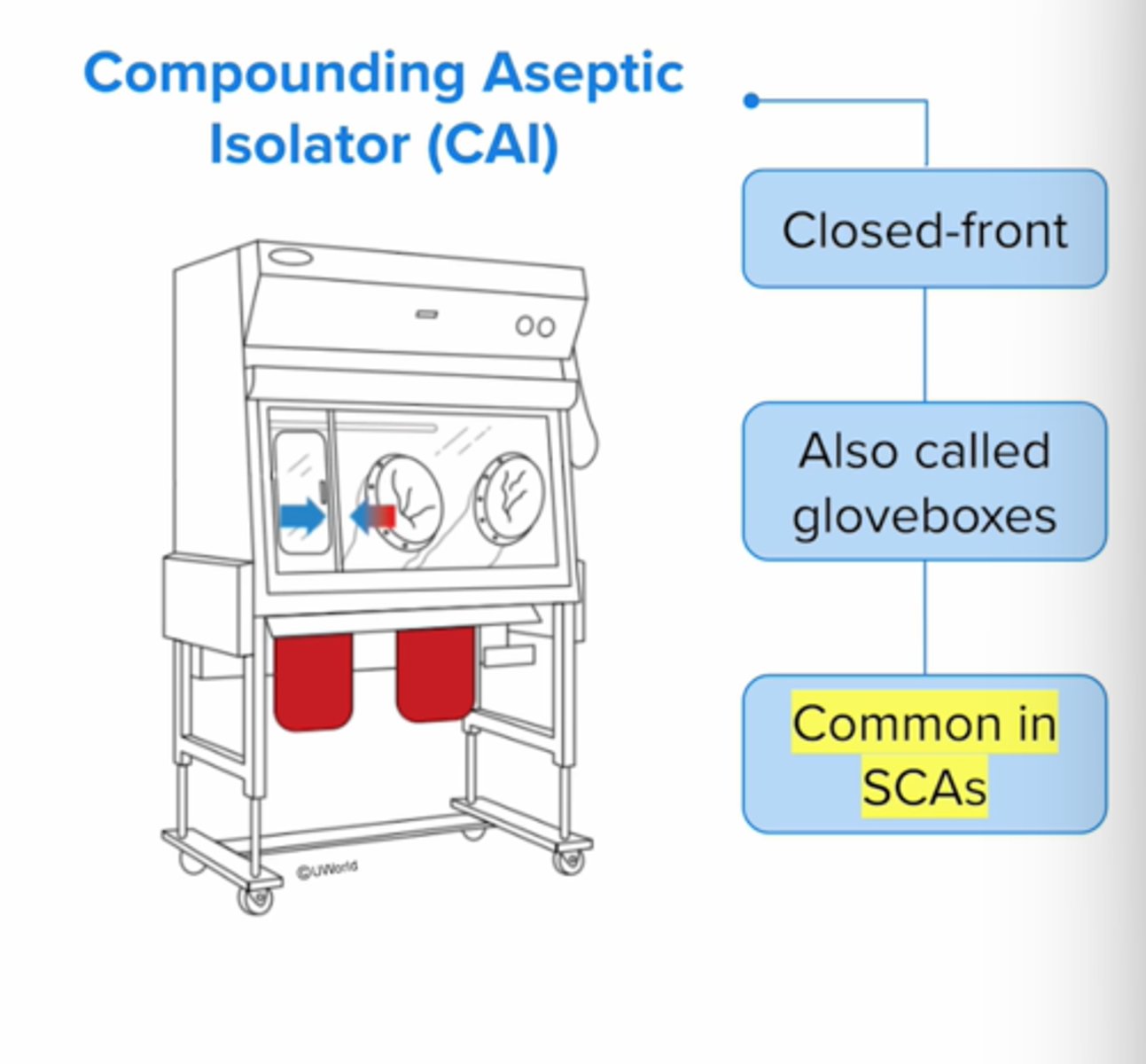
CAI define
compounding aseptic isolator
-type of closed front ISO 5 sterile hood used for nonhazardous drug compounding;
-known as glovebox
RABS define
restricted access barrier system
-any closed front ISO 5 sterile good (includes CAIs)
-referred to as glove box
physical space basics
all surfaces must be smooth, impervious, free from cracks/cabinets for easy cleaning
-stainless steel is often used
-no objects that shed particles (cardboard boxes)
the lower the particle count, the ____ the room
cleaner
the PEC (inside hood) must be at least ISO ___
5
SEC( buffer room) must be at least ISO ___
7
anteroom must be at least ISO ___
7 if negative pressure buffer room (ie. hazardous drug compounding)
8 if opens to positive pressure buffer room
handwashing, garbing, etc.
air changes per hour (ACPH) for a room with ISO 7 air
30 ACPH
air pressure inside the PEC and SEC are both ___ for nonhazardous drug compounding
positive - pushes air out to keep away from sterile products
types of sterile compounding areas: cleanroom suite
one or more sterile hoods inside a buffer room that is entered through an adjacent anteroom
contains pec (iso 5) inside sec (buffer room iso 7) and anteroom
types of sterile compounding areas: segregated compounding area (SCA)
a sterile hood, often an isolator (glovebox), with a closed front, located in a segregated space with unclassified air
the space in front of the HEPA filter is called ____ and the air coming directly out of HEPA filter is called the ____
direct compounding area (DCA)
first air
HEPA filter must be recertified by a specialist how often?
every 6 months and any time a PEC has been moved
a ____ is an open-front PEC where air flows in unidirectional lines from the HEPA filter, typically from the back of the hood, known as horizontal laminar flow
LAFW (laminar airflow workbench)
waste buckets underneath a CAI are ____ for sharps and nonhazardous waste
red
what is the line of demarcation
line which separates room into clean/dirty sections (in anteroom)
how are shoe covers applied?
one at a time while stepping over the demarcation line
where can an SCA NOT be?
adjacent to food preparation, warehouses, restrooms, windows/doors that connect to outdoors, high traffic flow areas
____ are useful for satellite pharmacies that are a distance away from main pharmacy in a large hospital, infusion centers, clinic, small hospitals
SCAs
each facility is required to have a ____ who is responsible for training and oversight of compounding staff
designated person
ant person who compounds must have documented ____ training and continuous training completed how often?
initial
every 12 months
Staff must demonstrate that they can follow adequate aseptic procedures for each of these items prior to independently compounding:
hand hygiene
garbing/gloving
cleaning/disinfecting
sterile drug preparation
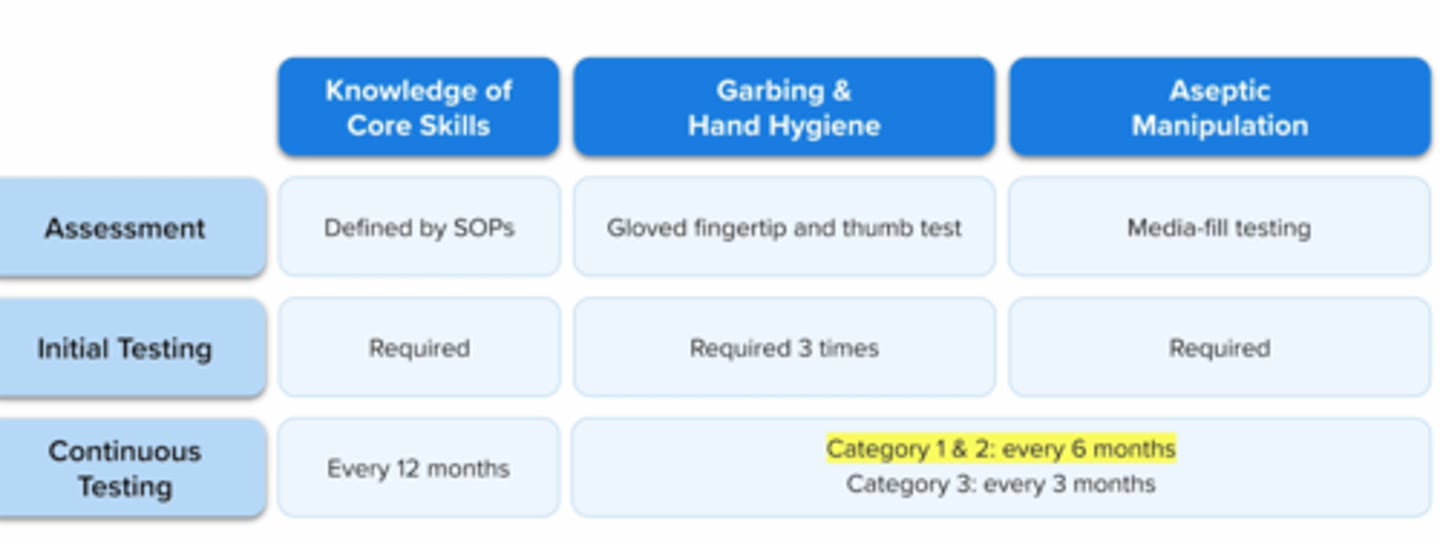
adequate asceptic technique in hand hygiene, garbing, and gloving is demonstrated by
visual obersvation completed >/= 3 times
gloved fingertip and thumb test
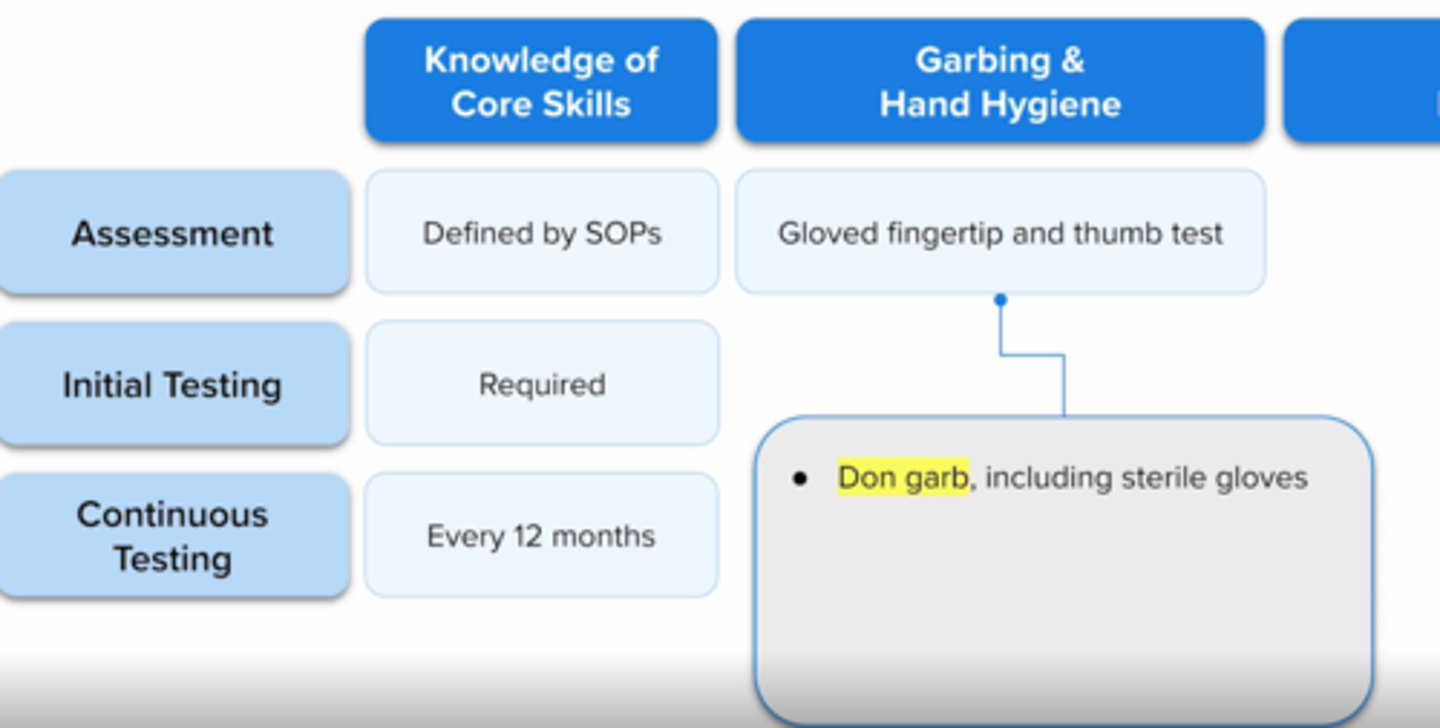
both gloved fingertip test and media fill test must be completed by a compounder initially, then every ___ if compounding only category 1 and 2 CSPs OR every ____ if compounding category 3 CSPs
6 months
3 months
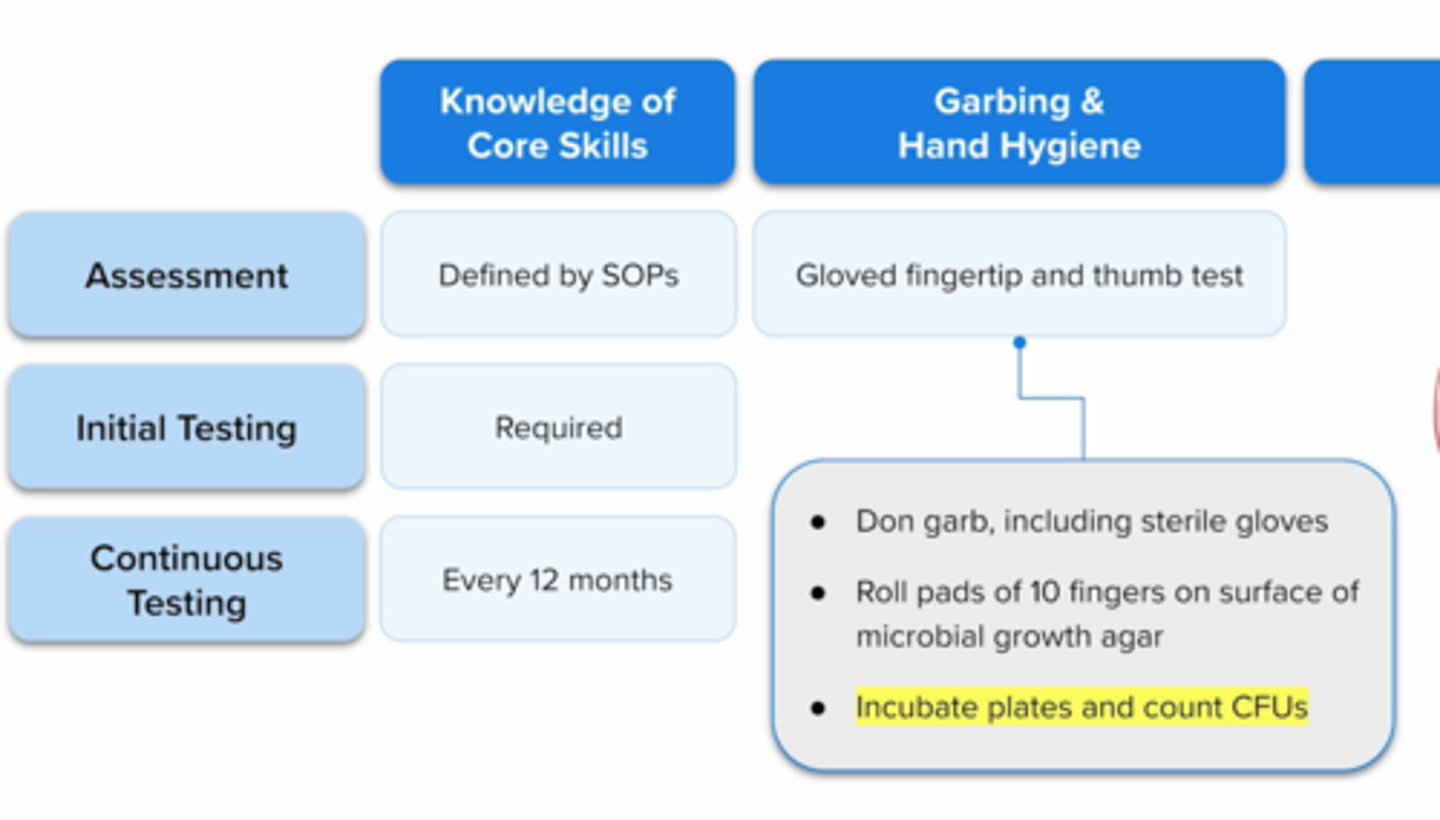
gloved fingertip test
immediately after completing hand hygiene and garbing/gloving, the evaluator collects a gloved fingertip sample from both hands of compounder by rolling pads of fingers and thumb over a plate with microbial growth agar (tryptic soy agar or TSA)
-plates are incubated then inspected after ≥7 days
-if organisms are present, TSA will be used as food source and they will replicate (spots/CFUs/contamination will be seen)
passing a gloved fingertip test:
-after garbing - passing requires ___ consecutive gloved fingertip samples, taken after garbing, with ___ CFUs for both hands
3
zero
passing a gloved fingertip test:
-after media fill testing - passing requires at least ___ sample taken from each hand immediately after completion of media fill test, with ____ CFUs total for both hands
1
≤ 3
media fill test
used to determine if compounder is preparing in aseptic manner
-compounder prepares small IV bag or vial using tryptic soy broth (TSB) instead of drug. multiple manipulations (transfers with same syringe) are done and product is incubated to check for bacterial growth
____ means contamination is present in a media fill test
turbidity
passing a media fill test:
-if liquid stays clear after ____ days of incubation, compounder has passed
14 days
SEC or buffer room temp should be checked how often? and how should it be maintained? (temp/humidity)
once daily
20C or 68F
humidity at 60% or less
temperature in the CSP storage areas (fridge, freezer) should be monitored at least ____
daily
air sampling (iso) for contaminants is performed at least how often?
every 6 months
surface sampling for contaminants must be performed how often?
-areas touched most frequently, test at end of compounding shift before cleaning/disinfecting
every 30 days at end of compounding shift
air pressure testing is done to confirm the correct ____ between two spaces and ensure airflow is unidirectional
differential
should PECs be kep running at all times?
yes, preferably
what happens if there is a power outage (PEC)
all compounding must stop
clean and disinfect PEC
apply sterile 70% IPA prior to re-starting compounding
the PEC must be on for at least how long after a power outage is fixed before compounding can begin?
30 minutes
cleaning the PEC (products/how often)
daily and anytime contamination is suspected
-use 70% IPA every 30 minutes throughout day
-first PEC is cleaned with detergent, then disinfected, then 70% IPA is applied
-sporicidal disinfectant is required, but less often
sterile, ___ wipes are used to clean PEC
low-lint
order of cleaning for a PEC
clean ceiling of hood from back to front
clean back of hood from top to bottom
clean IV bar and hooks
clean side walls from back to front
clean anything kept in the hood (equipment)
clean bottom (work area) surface from back to front
do not start compounding until surfaces have ____
dried
PEC, pass-through chambers, work surfaces outside PEC and floors must be cleaned and disinfected how often?
daily

walls, doors, ceilings, storage shelves/bins, and equipment outside PEC must be cleaning and disinfected how often?
monthly
how often is sopricidal disinfectant used?
monthly
cleaning v disinfecting v sporicidal
removes organics and inorganic contaminants
destroys microbes
destroys vegetative spores
Garbing Technique
-Remove coats/rings/makeup/etc
-Don head, facial covers, face mask, shoe covers while stepping over demarcation line, optional eye shield
-Hand hygiene with soap/warm water, clean fingernails, wash for ≥30 seconds
-Dry hands with low lint towels
-Don low lint gown
-Enter buffer area
-Apply alcohol based hand scrub
-Don sterile, powder free gloves
-Sanitize gloves with 70% IPA
if working in an SCA and it is left for any reason, ____ is required
regarbing
___ syringes are commonly used for sterile compounding to transfer drugs/additives from and onto sterile containers
hypodermic (parenteral)
do not use a syringe the ___ size of the amount needed (plunger can become dislodged)
exact
____ make secure, leak free connections between syringes/needles and IV lines. ends twist together to form a tight seal
luer lock
a ____ or ____ is required when withdrawing liquid from the ampule to remove glass (after snapping the neck)
filter needle
filter straw
why are some drugs available as powders?
because they are unstable as a solution
SVPs are often ____ onto a LVP
piggybacked
____ are available as prepared IV bags or prefilled syringes; not compounded
ready to use medications (RTUs)
ready to use vial/bag systems
Add-Vantage
Minibag Plus
what does an automated compounding device (ACD) do?
aseptically transfer ingredients into a sterile final container
automated compounding devices should be interfaced with the EHR to prevent transcription errors
the EHR to prevent transcription errors
what do IV workflow management systems (IVWMS) do?
automate preparation, verification, tracking, and documentation, of CSPs
-barcode scanning, photo capture
all work within the PEC must be performed at least ___ from the front
6 inches
place all items in the sterile hood ____
side by side
the volume of solution drawn into a syringe is measured at the point of ___ between the rubber piston and the side of the syringe barrel
contact
___ occurs when a small piece of rubber from the stopper is aspirated into the needle, and is put into the solution in a vial
coring
look for small ___ pieces floating near the top of the solution during visual inspection of the CSP
cored
what is the syringe pull back method?
occurs when the pharmacist verifies the volume in an empty syringe AFTER compounding is done
this is NOT recommended
terminal sterilization is required for CSPs that are compounded with any ____ ingredients
nonsterile
types of terminal sterilization
steam sterilization (with autoclave)
dry heat sterilization (depyrogenation)
filtration
How can CSPs that are heat-labile be sterilized? (heat sensitive eg. proteins, hormones, insulin)
filtration using sterile 0.22 micron filter
if filtering is used for sterilization, the manufacturer might require a test for filter integrity such as the ?
bubble point test
what is the bubble point test
test that determines the pressure required to see bubbles out of a filter
endotoxins from gram ____ are more potent and represent a serious threat
negative
pyrogens come from using equipment washed with ____ water
tap
how to avoid pyrogens
glassware and utensils should be rinsed with sterile water and depyrogenated using dry-heat (steam) sterilization with an autoclave
category 1 sterile compounding
what
prepared in ISO 5 PEC that is placed in an SCA (unclassified air)
-higher risk of contamination
-shorter BUD, no sterility test needed
RT: ≤12 hours
Fridge: ≤24 hours

category 2 sterile compounding
made in a cleanroom suite
-longer BUD, sterility testing may be needed

category 3 sterile compounding
-specific requirements
-longer BUD, some require sterility testing

category 3 sterile compounding - BUD up to a max of ____
180 days
which has highest risk of contamination: category 1, 2, or 3
1 has higher risk than 3
-to determine appropriate BUD
BUD for products made emergently in suboptimal conditions
BUD: 4 hours
BUD
CSP category
category 1
environment
ISO 5 PEC in SCA
RT: ≤12 hours
Fridge: ≤24 hours
freezer: N/A

BUD
CSP category
category 2
environment
ISO 5 PEC in clean room
RT: 45 days
Fridge: 60 days
freezer: 90 days

BUD
CSP category
category 3
environment
ISO 5, clean room + sterility or other
RT: 90 days
Fridge: 120 days
Freezer: 180 days

sterility testing is required for which category?
3
optional for cat 2 to increase BUD
BUD for single dose container (vial, bag, bottle syringe inside ISO 5)
up to 12 hours from puncture or opening
BUD for single dose container (ampule inside or outside ISO 5)
any used contents left in ampule must be discarded
BUD for multi dose container (inside or outside ISO 5)
up to 28 days from puncture or opening
the ____ is needed for CSPs prepared for more than one patient or from nonsterile ingredients
master formulation record
is a CSP is prepared for more than one patient for from nonsterile ingredients, what must be recorded in the compounding record?
vendor
lot number
expiration date
CSP label requirements
Names of ingredients
Amounts of ingredients
Total volume
BUD
dosage form
Route of administration
Storage requirements
internal identification number (order number, barcode)
QA vs QC
QA ensures compounding process is consistent
QC induces sampling, testing, documentation of results
most CSPs including IV solutions and ophthalmic products, should be ___ to human blood
isotonic
compounded preparations that require a narrow pH range will need a ____ that can resist changes in pH
buffer system