B7.2 Digestive system
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the 5 processes that take place in the alimentary canal?
1. Ingestion
2. Digestion
3. Absorption
4. Assimilation
5. Egestion
What is the definition of ingestion?
The taking in of substances (food and drink) into the body through the mouth

What is the definition of digestion?
The breakdown of food into nutrients
What is the definition of absorption?
The movement of small food molecules and ions from the wall of the intestine into the blood
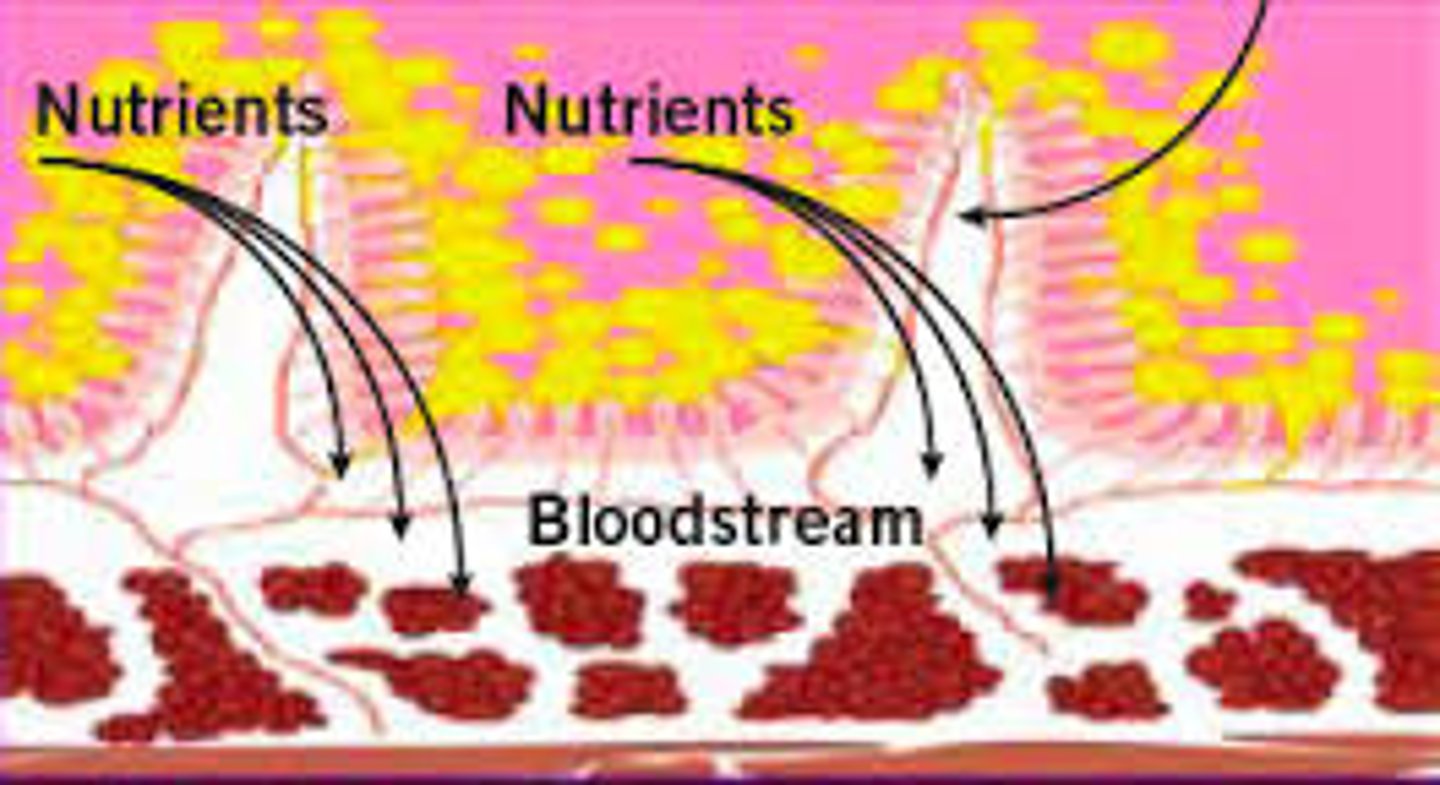
What is the definition of assimilation?
The movement of digested food molecules into the cells where they are used
What is the definition of egestion?
The removal of food that has not been digested or absorbed

What is the alimentary canal?
The tube in which food passes through the body
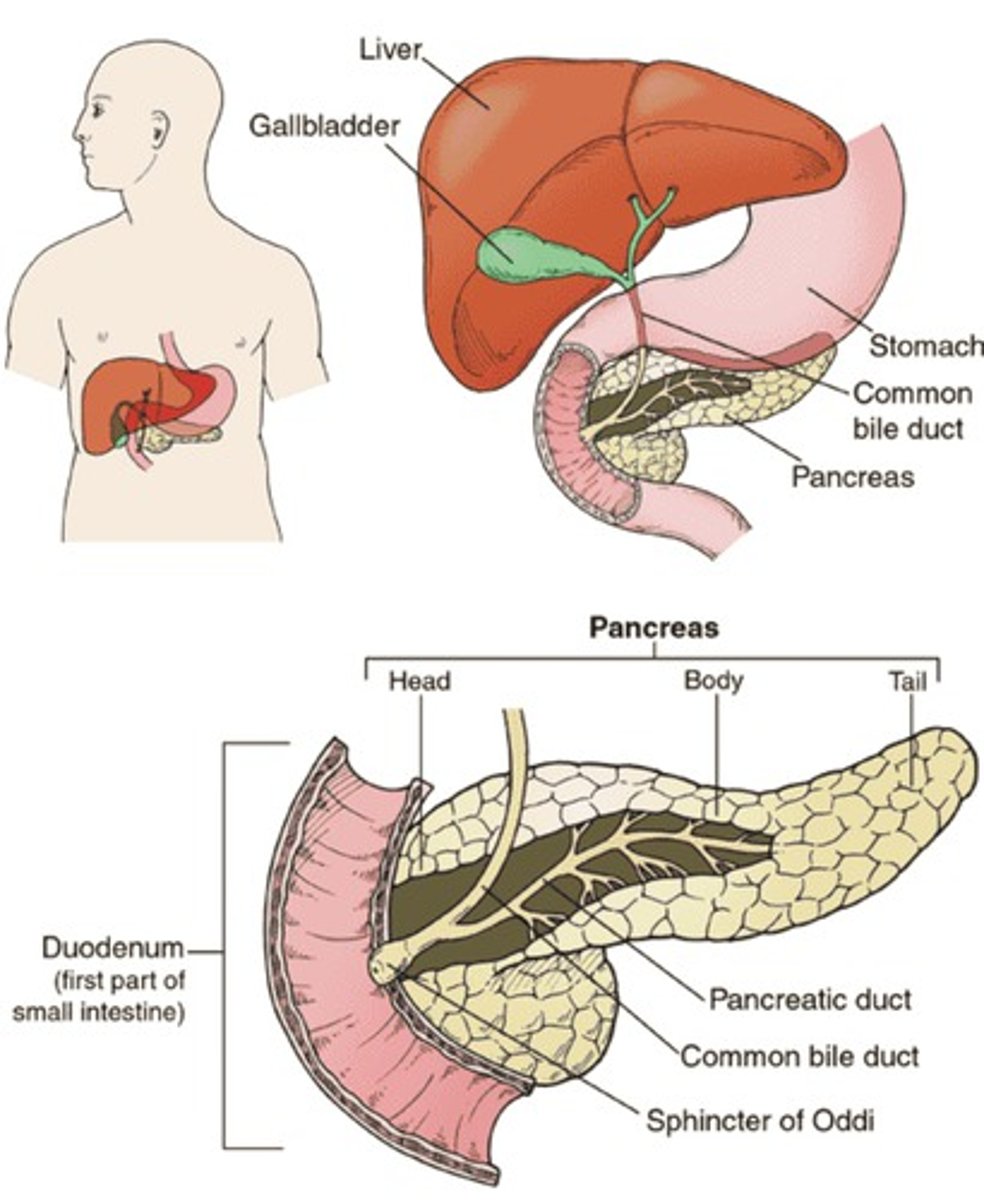
Name each of the main and associated organs of the digestive system
Alimentary canal: mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum), large intestine (colon, rectum, anus)
Associated organs: salivary gland, liver, gallblader, pancreas
Identify each of the main and associated organs of the digestive system in a diagram
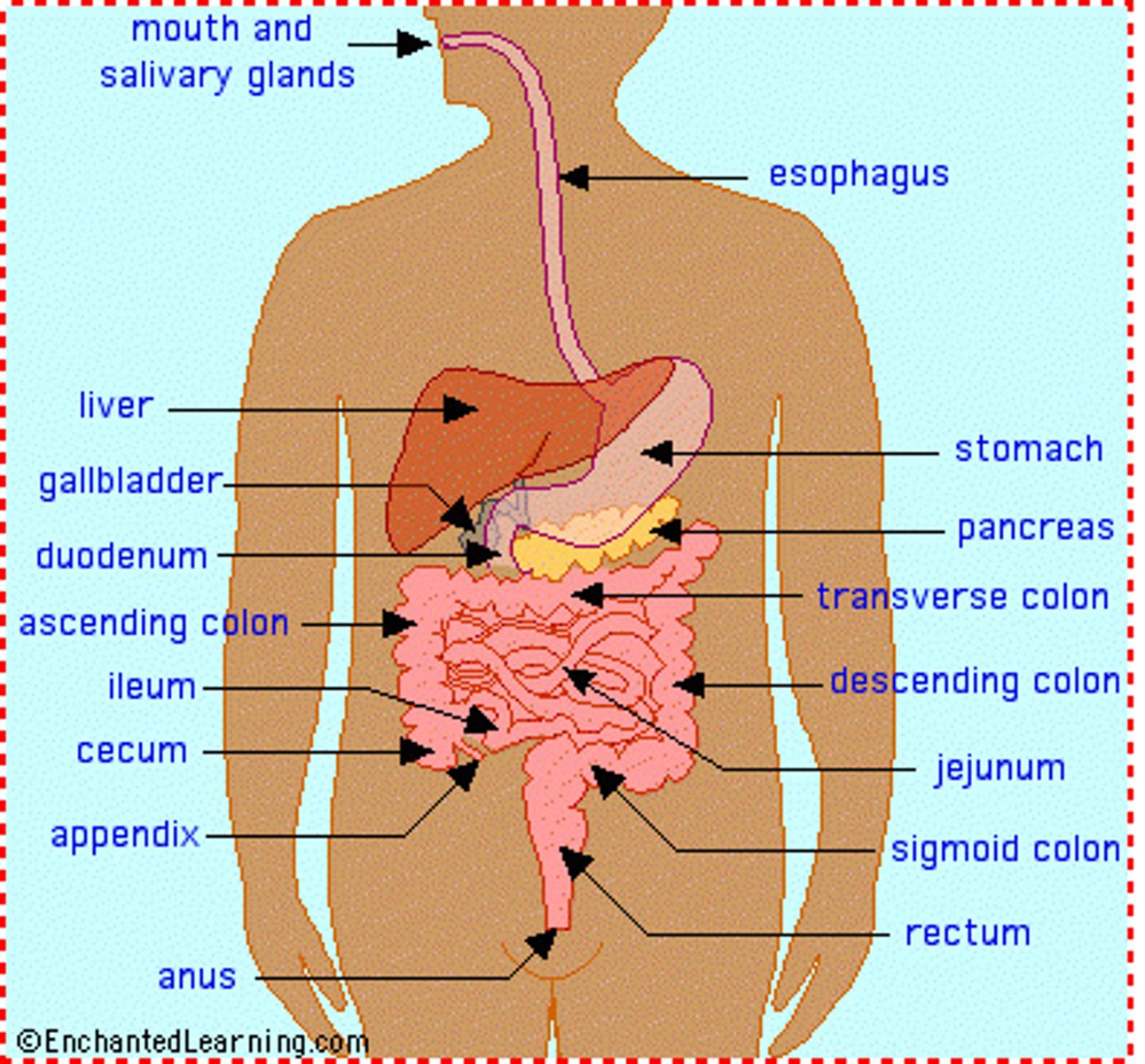
What is the path food takes in the alimentary canal?
mouth -> oesophagus -> stomach -> small intestine -> large intestine -> anus
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
- Mechanical digestion: breakdown of food into smaller pieces without any chemical changes
- Chemical digestion: breakdown of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules with the help of enzymes
Which organs use mechanical digestion?
Mouth, stomach
Which organs use chemical digestion?
Mouth, stomach, small intestine
Where do each of the processes take place in the alimentary canal?
- Ingestion: mouth
- Digestion: mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
- Absorption: small intestine
- Assimilation: small intestine
- Egestion: large intestine (rectum and anus)
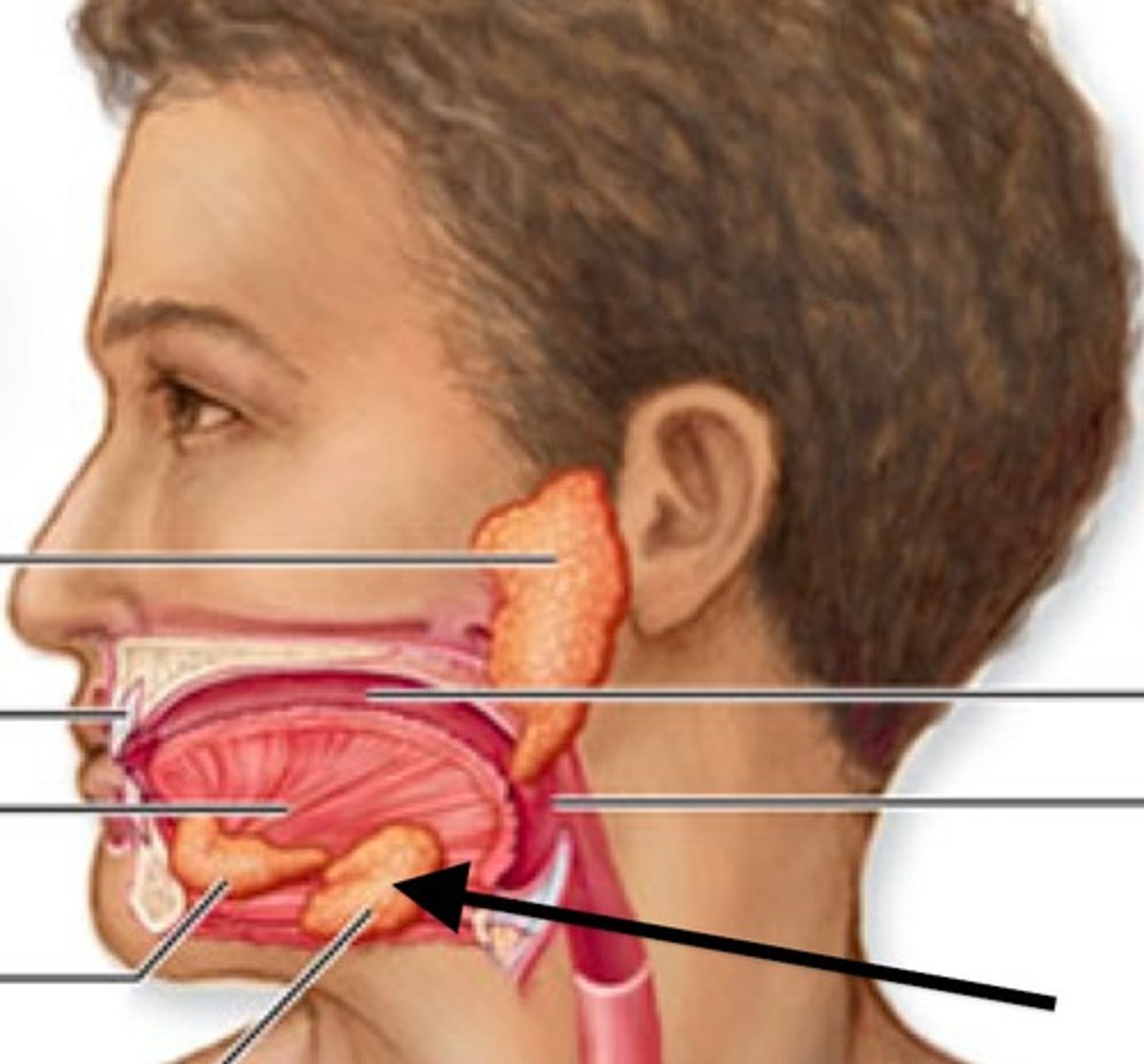
What is the function of the salivary gland?
Produces saliva (which contains amylase: an enzyme used to break down starch into simple reducing sugars) which is secreted into the mouth, which mixes with ingested food to make it easier to swallow.
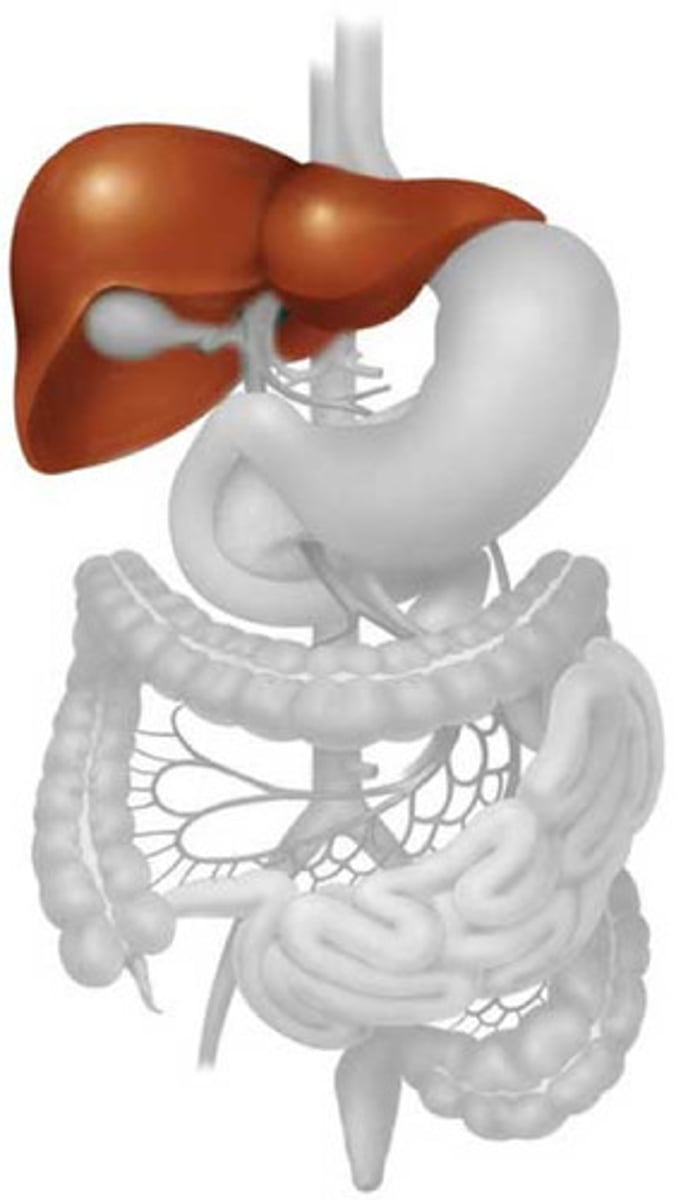
What is the function of the liver and gallbladder?
The liver produces bile, which is an alkaline liquid that neutralises the acidic mixture entering the duodenum from the stomach and emulsifies fat. This bile is then stored in the gallbladder, before it is released into the bile duct in the duodenum.
What is the function of the pancreas?
Secrets pancreatic juice, which helps with chemical digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It is alkaline, meaning it helps neutralise food leaving the stomach.