Long term memory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the capacity and duration of long-term memory?
No known limit; duration can be lifelong.
What is secondary memory vs primary memory?
Secondary memory: Declarative memory (knowledge of events/facts with awareness of prior experience).
Primary memory: Working memory.
What is the difference between structural and functional views of memory?
Structural: How memory is organized.
Functional: How processes operate and interact.
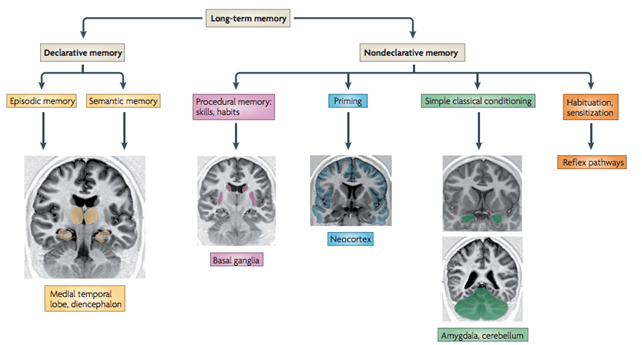
What are the two types of declarative memory?
Episodic: Re-experiencing specific events in time and space; includes sensory and emotional detail; hippocampus-dependent.
medial temporal/hippocampa
Semantic: General knowledge, concepts, language, schemas; based in neocortex.
How does encoding differ between episodic and semantic memory?
Episodic often encoded in one shot; semantic learning is gradual.
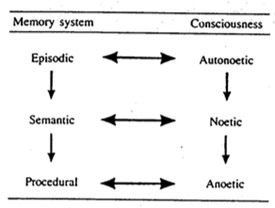
What is anoetic consciousness?
Procedural memory—skills performed without conscious thought. (Tulving forms of conscious experience)
what is retrograde amnesia
loss of older memory’s regarding information that occured before the injury
What did KC’s case show?
Motorcycle accident caused severe episodic retrograde and anterograde loss (damage to medial temporal lobe), but semantic memory was spared—he could identify people but not recall context.
What did patient EL demonstrate?
Semantic dementia (progressive loss of conceptual knowledge) with left anterior temporal atrophy; episodic intact but semantic degraded.
opposite of patient KC → given the same tasks of looking at family photos (EL couldn’t identify faces)
What does Jon’s case reveal?
Hippocampal damage from birth → no episodic memory, but intact semantic knowledge
never been able to equire episodic memories, but knows facts but couldn’t say how he learnt them
shows the clear distinctions in EM and SM (clearer in hippocampal damage studys)
How do recollection and familiarity differ?
Familiarity: Sense of knowing without context; fast and automatic. → can cause initial confusion if you see someone you know outside of context
Recollection: Contextual details; slower and effortful and require attention → can have spontaneous retrieval cues
What triggers spontaneous recollection?
Retrieval cues like music or smell
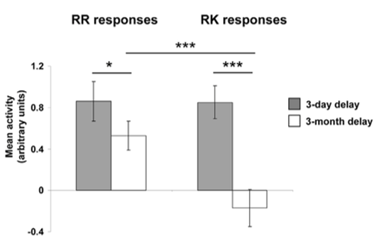
How does hippocampal activity differ in remembering vs knowing?
Remembering (R): Hippocampus active.
Knowing (K): Hippocampus not active—memory has become semanticized.
explain the study that showed this difference in hippocampus for knowing vs remebering
HC amnesic patients impaired on R rather than K is word recognition
Study: with RR the hippocampus is still active
with RK: the hippocampus is not active anymore (the memory has become semanticised)
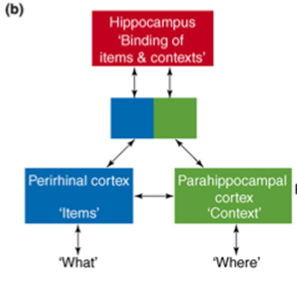
What is binding in episodic memory?
Linking what, where, and when; hippocampus critical for source judgments.
HC creates and retains bindings underlying recollective experiences → not just what happened but also where it happened and why it happened
HC is involved in source judgements
how do EM and SM relate
neural connections overlap
episodic memory and the hippocampus support new semantic learning
What is prospective memory?
Remembering to perform future actions.
Event-based: Triggered by external cues (more reliable). e.g. alarm going off
Time-based: Requires self-initiated recall at a specific time.
event based is more reliable as it involves triggering a memory by external cause
what is consolidation
the process by which new memories become stable and long lasting after they are initially aquired
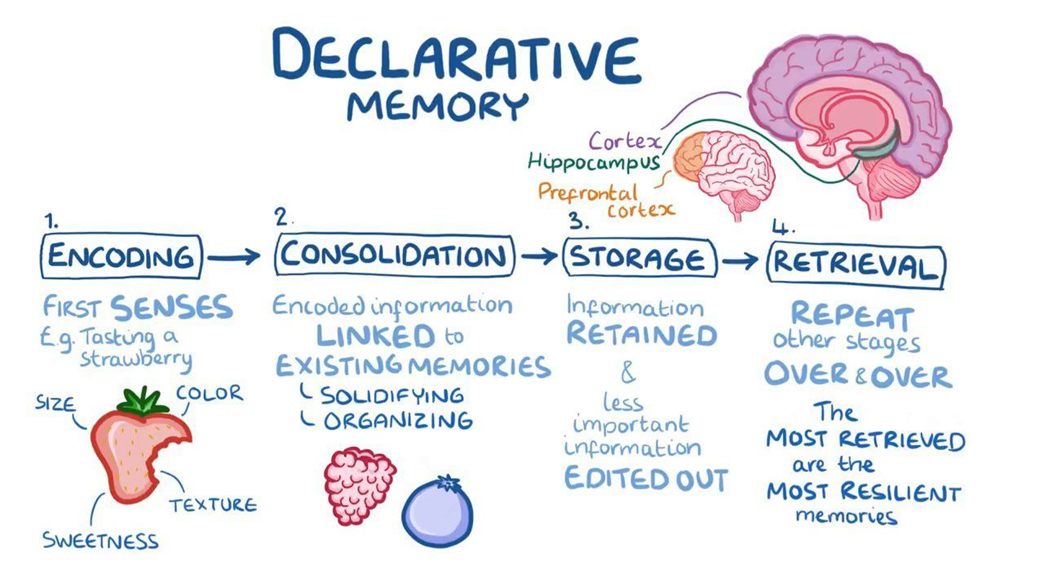
What does multiple trace theory propose?
Episodic memories remain hippocampus-dependent; each retrieval creates new traces, strengthening memory.
accepts gradual development of schematic and non-contextual memory in the neocortex
but contextual memory features are hippocampal dependent forever
Recollective/re-experience leads to re-encoding in new memory traces (every time an episodic memory is retrieved) a new trace is formed across hippocampus -> the more a memory is retrieved, the more traces therefore stronger the memory
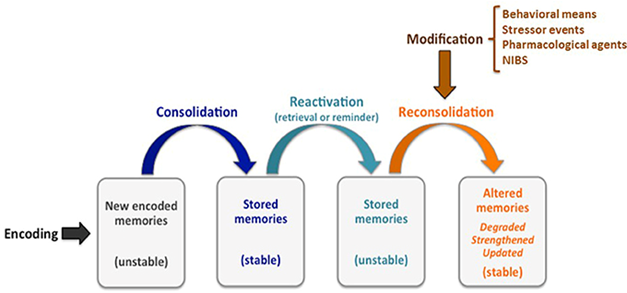
What happens when declarative memories are reactivated?
Increased vulnerability to interference or misinformation.
its called the reconsolidation window - the memory can be changed at any time
What is implicit memory?
Unconscious improvement from experience; not a single system.