AP psych semester 1 Study guide
1/372
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
373 Terms
Experimental
proves cause and effect
Non-experimental
does not prove cause and effect
Independent variable
variable that is changed
Dependent variable
variable that is measured
confounding variable
factors other than the independent variable that may cause a result
random assignment
every participant having an equal chance of each assignment (control or experimental)
population
number of group of people from a specific group
sample
a sample is the group of people in a large group
random sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population, because each member has an equal chance of being included
representative samples
a sample that matches the representation
convenience samples
a non probaility sample method where data is collected by an easily accessible and available group of people
sampling bias
the sample doesn’t accurately represent the population being studied
generalizability
something that can be applied to a whole population
Experimental group
receives the treatment
control group
does not receive the treatment
placebo group
a group that receives what they think is to be the treatment but is actually a neutral thing that does not contain any treatment
placebo effect
when the brain thinks the individual’s treatment for their mental health or physical health is working after taking a placebo
single blind procedure
researcher knows treatment groups
double blind procedure
neither researcher nor participants know treatment groups
experimenter bias
double blind limits experimenter bias
case study
a person or group being studied for a specific experience or situation
correlation
(Does not cause causation) a measure of the extent to which 2 factors vary together
positive correlation
when both variables increase
negative correlation
both variables have an inverse relationship (one up one down)dir
directionalilty problem
what causes what? ex: does depression cause low self esteem
third variable problem
a confounding variable affects both variables to make them seem causally related when they are not.
scatter plots
scatter of plots showing what happens with one variable when another variable is changed
correlation coefficient
indicates a measure of the direction and strength of a relationship between 2 variables
quantitative measures (e.g. likert scales)
uses numerical data to represent a variable
qualitative measures (e.g. structures interviews)
in depth, narrative data
surveys
a series of questions asked to the respondents in order to understand their processes and mental state f
framing
a type of cognitive bias or error in thinking
social desirability bias
people answer in a way they think will please the researcher
self report bias
when people don’t accurately report or remember their behaviors
meta-analysis
combining the results of multiple studies
naturalistic observation
qualitative research method where you record behavior of the individuals
hypothesis
a guess of what is going to happen
falseifiability
good hypotheses are falsifiable
operational definitions
carefully worded statement of exact procedures
replication
repeating a research study, with different participants in different situations to see if the same finding can be reproduced
peer review
process where research is evaluated before it’s published to the public
ethical guidelines
established for clinical research to protect volunteer (confidentiality, debriefing, informed consent)
institutional review board
IRB, concerned with protecting the welfare, rights and privacy of individuals and animals. Charged with the responsibility of reviewing.
informed consent
agreement to participate in a procedure
informed assent
minors need to get informant assent (parents sign)
protection from harm
ensuring their physical safety, privacy rights, during any psychological research.
confidentiality of participants
keeping results and information from the public and keeping it private
confederates
someone on your side (ally or accomplice)
debriefing
explaing the purpose of the study to the participants after the study
central tendency
mean: average of values
median: middle value
mode: most frequent number
measures of variation
range: difference between high and low values
standard deviation: a measure of how many scores
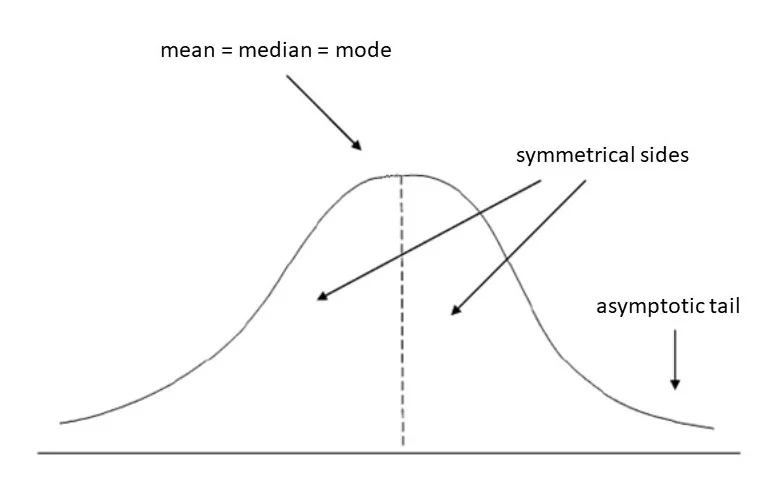
normal curve (percentages and percentiles)
graph with smooth, symmetrical lines.
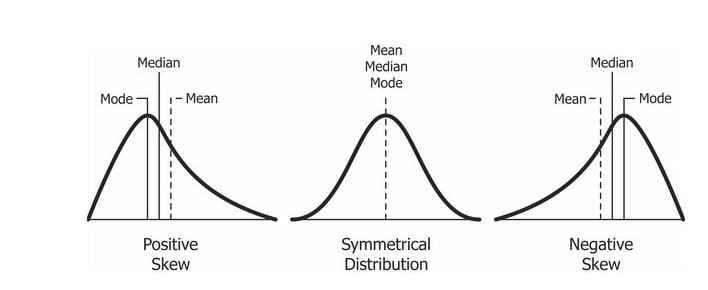
positive and negative skews
positive: skewed to the right
negative: skewed to the left
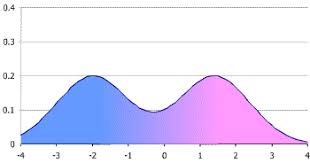
bimodal distributions
type of distribution characterized by 2 distinct peaks
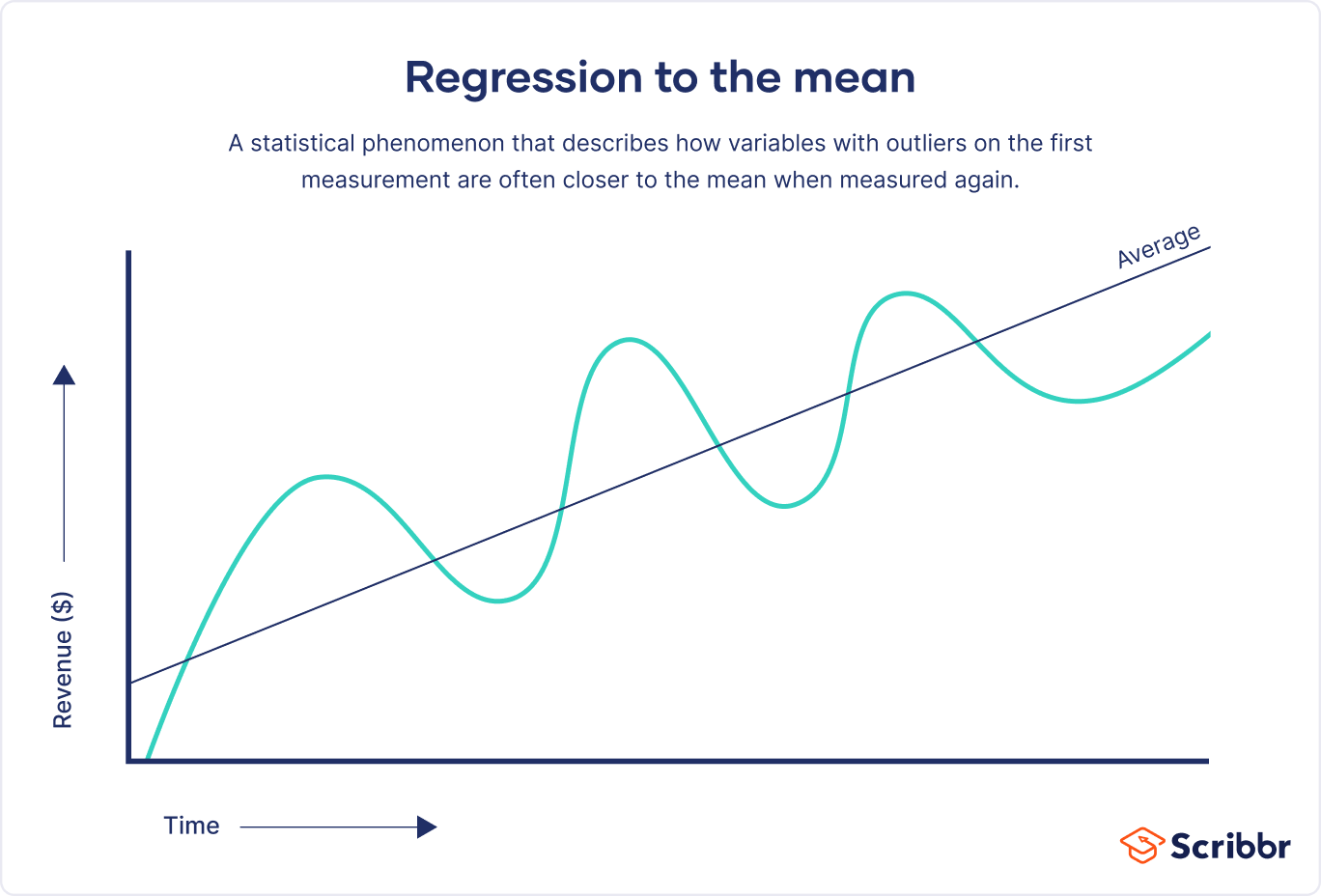
regression towards the mean
statistical phenomenon describing how variables much higher or lower than the mean are closer to the mean measured a second time.
Statistical significance
how likely an experimental results occurred due to chance
effect sizes
strength of a relationship between 2 variables.
larger effect sizes=the more one variable can be explained by another
cognitive biases: hindsight bias
I knew it all alone phenomenon co
cognitive biases: overconfidence
tendency to overestimate our knowledge and abilities in a certain area
cognitive biases: confirmation bias
tendency to process information by looking for or interpreting information that is consistent
nature
genetics, DNA, etc
nurture
external factors that influence physical, behavioral and mental traits
genetic predisposition
means that there is an increased chance that a person will develop a particular disease
evolutionary perspective
how the natural selection of traits contributes to passing on genes.
eugenics
scientifically inaccurate theory that humans can be improved. “In addition to” genetics, how the environment influences gene expression
twin studies
can’t experiment with nature vs nurture. are studies that are conducted on identical or fraternal twins
central nervous system
Brain: controls how we think and learn
Spine: carries messages back and forth between the brain and the nerves that run throughout the body.
peripheral nervous system
connects CNS to limbs and organs, allowing communication
somatic nervous system
skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
controls glands and muscles
sympathetic nervous system
“fight or flight” arouses body in scary situations
parasympathetic nervous system
calms after “fight or flight” called “rest and digest”
Glial cell
-glue cells
-not part of the neuron
-supports the neuron, provide nutrients and myelin
neurons
basic building block of the nervous system
relfex arc
the basic unit of reflex, which involves neural pathways acting on an impulse before that impulse has reached the brain.
sensory neurons
nerve cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment.
motor neurons
cells in the brain and spinal cord that allow us to do movements by sending commands to the brain to the muscles
interneurons
a type of neuron that are located between sensory neurons and motor neurons
Neural transmission: all or nothing principle
you cannot part fire a neuron
More sensation=more neurons firing more often
Action potential
a rapid sequence of changes in voltage across a membrane
depolarization
a change within a cell when it becomes positive pr less negative.
refractory period
refers to the period of time during which the response to a second stimulus is significantly slowed
resting potential
the state of a neuron when its being stimulated or sending signals
reuptake
unused neurotransmitters reabsorbed into the sending neurotransmitter.
Firing threshold
self generating action potential is triggered. causing the membrane potential to reverse and become briefly positive.
dopamine
Excitatory, increase likelihood of action potential (speeds up), rewards and motivation
serotonin
Inhibitory, decrease likelihood of action potential (slows down)
norepinephrine
Excitatory, increase likelihood of action potential (speeds up)
glutamate
Excitatory, increase likelihood of action potential (speeds up)
GABA
Inhibitory, decrease likelihood of action potential (slows down)
endorphins
released in pain or stress block pain signals, endorphins attached to opioid receptors dopamine is released
substance p
related to stress response, immune system, inflammatory response, and pain. (works alongside glutamate)ac
acetycholine
muscle action, learning and memory
hormones
chemical messengers
adreneline
“fight or flight response”
leptin
a hormone your body releases that helps it maintain your normal weight on a long term basis.
ghrelin
a hormone produced by your stomach
melatonin
a hormone that your brain produced in response to darkness, helps you sleep
oxytocin
hormone that produces good feelings, empathy, trust and relationship building.
Minimal deception
to pose no more risk to participants in a study