N4E3
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
therapeutic milieu
the clients environment is organized to assist him to control problematic behavior and use various adaptive skills in coping with self, others, and environment
focus on social relationships and activities
can co-exist in many settings
actual or anticipated loss
the death of a loved one, losing a job, a serious injury resulting in a disability, or a natural disaster destroying your home, while "anticipated loss" could refer to grieving the future loss of a loved one diagnosed with a terminal illness, preparing for the eventual retirement from a job, or knowing a relationship is likely to end soon.
major depressive disorder
lasts at least 2 weeks
mild —→ severe
sleeping issues, weight change, feelings of worthlessness and hopelessness, recurrent thoughts of death
causes impairment in social or occupational functioning
disruptive mood Dysregulation disorder
children and adolescents 6-18 years old
differentiates between children with irritability and episodic bipolar disorder
persistent depressive disroder
feelings of depression nearly all the time
often begins in childhood
This is LESS severe than regular depression. People can continue with ADLs but feel chronically sad, still go day-to-day
premenstrual dysphoric disorder
symptoms occur before/during menstruation
this type of feeling improves when the female moves out of menstruation
ECT/EST
pulses of electrical energy passed through the brain- sufficient to cause a seizure (gran maul- tonic clonic)
used for serious, life - threatening mood disorders
MEDICATIONS: given to reduce secretions, cause anesthesia, and prevent seizure related injuries
side effects for ECT
primarily memory deficits
ECT nurse responsibility
signed consent, no education on procedure
NPO 8 hours prior
have client empty bladder
loose, non-restrictive clothing
offer support
vitals, documentation
milieu management
specific types of verbal techniques
helps client gain insight into causes of depression
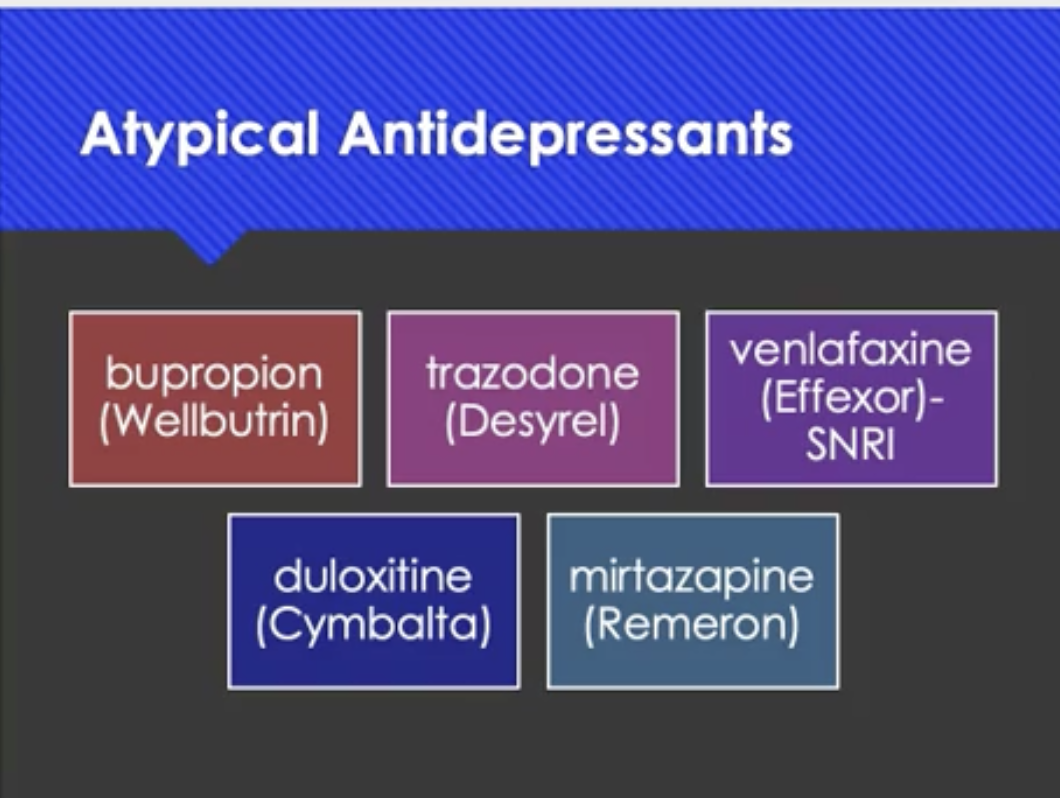
medications for depression
tricyclic antidepressants
take 2-4 weeks for a response
must be tapered off
adverse effects: dry mouth, constipation, difficulty passing urine, orthostatic SE , SEDATION
can help with: improving appetite, and weight.
is FATAL in overdose (do not give to suicidle patients)
SSRI
tx of choice for depression
4-6 weeks to see effects
generally safe in overdose
DO NOT ABRUPTLY WITHDRAWL (headache, vivid dreams, insomnia, confusion)
take in MORNING with food
serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome occurs when the levels of a chemical in your brain called serotonin become too high. It's usually triggered when you take an SSRI in combination with another medicine (MAOI or st johns wart)
serotonin syndrome s/s
mental status change, agitation, hyperreflex, hypertension, fever, sweating, nausea, headache
tx: discontinue, in severe patients may require muscle relaxants
apathy syndrome related to SSRI
Apathy syndrome, also known as SSRI-induced apathy, is a collection of symptoms that can occur when taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). SSRIs are commonly used to treat depression.
Symptoms Loss of motivation, Lack of curiosity, Anergy, and Decreased emotional responsiveness.
SSRI withdrawal syndrome
do not stop abruptly, can cause lethargy, dizziness, nausea, anxiety, and agitation
SSRI examples
citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paraoxetine, sertraline
MAOI examples
marplan, nardil, parnate
MAOI
strictly reserved for patients who are not response to other medications
orthosatis hypertension is a common effect
numerous drug interactions
what foods do patients on these medications avoid
tyramine - leads to dangerous hypertension
(beer, wine, mature cheese, sour cream, yogurt, processed meat)
psychosis
disruptive mental state where the client struggles to distinguish the external world from the internal perception
can not distinguish between what is real and what is not
have impaired communication
can occur in many diagnosis
positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Positive symptoms refer to excesses or distortions of normal function caused by overactivity of dopamine in the brain.
hallucinations, delusions, loose associations, word salad,
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Negative symptoms refer to a loss or reduction of normal functions, often linked to decreased dopamine activity in certain brain regions.
absense of what should be there
blunted affect, social withdrawal, poor insight
lack of social skills
anergia
abnormal lack of energy
anhedonia
Anhedonia is a symptom characterized by a reduced ability to experience pleasure or interest in previously enjoyable activities
alogia
Alogia, also known as poverty of speech, is a condition that makes it hard for someone to speak.
avolition
a lack of motivation or the inability to start or continue goal-directed activities
does positive or negative symptoms have better prognosis?
positive - negative last longer
schizoaffective disorder
schizophrenic symptoms are dominate but accompanied by major depressive or manic symptoms (affective)
brief psychotic disorder
all psychotic disturbances that last less than 1 month are not related to a mood disorder, medical condition, or substance abuse
delusional disorder
similar to schizophrenia but do not meet criteria for schizophrenia
Milieu management
Maintain a secure and predictable environment
Set clear rules and expectations
Monitor for self-harm or aggressive behaviors
Allow patients to participate in decision-making
Promote responsibility for self-care and daily routines
Empower patients to set personal goals
non stimulating environment
suspicious patients
be matter of fact,
do not laugh or whisper
be consistent and maintain eye contact
antipsychotics (traditional)
most effective on positive symptoms
significant adverse effects (photosensitivity, decreased sweating,
antipsychotics, 2nd generation (atypical)
increased effectiveness on negative symptoms
little to no risk of EPS or TD
antipsychotics, third generation
most effective on negetive symptoms
side effects of traditional
Orthostatic hypotension
constipation, nv
photosensitivity
sexual dysfunction, menstral dysfunction
extrapyramidal side effects
extrapyramidal side effects
Parkinson like symptoms:
Dystonia (Acute Muscle Spasms) 🦴
Oculogyric crisis (upward eye deviation)
Akathisia (Restlessness & Urge to Move) 🏃♂
Parkinsonism (Tremors & Rigidity) 🧓
Tardive Dyskinesia (Late-Onset Involuntary Movements) 👄
Dystonia
Acute Muscle Spasms) 🦴
Torticollis
neck twisting
Oculogyric crisis
upward eye deviation
Akathisia
Intense inner restlessness, pacing, inability to sit stil
Parkinsonism (Tremors & Rigidity) 🧓
Symptoms mimic Parkinson’s disease:
Tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slow movement), shuffling gait
Tardive Dyskinesia
Involuntary, repetitive movements (lip smacking, tongue rolling, blinking
neuroleptic malignant syndrome
NMS is a rare but serious adverse reaction to antipsychotic medications. It is characterized by a triad of symptoms:
fever, muscle rigidity, and altered mental status, tachycardia.
neuroleptic malignant syndrome
dentroline or dopamine antagonist
anticholinergic side effects
Dry mouth (xerostomia)
Blurred vision (due to pupil dilation)
Urinary retention
Constipation
Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
Flushed skin (redness & warmth)
Decreased sweating (anhidrosis), leading to overheating
akathisia
Akathisia is a movement disorder characterized by an intense, uncontrollable urge to move.
akinesia
Akinesia refers to the inability to voluntarily move one's muscles and limbs.
managment if EPS and TD
lowest dose of antipsychotics
vitamin E
benadryl, cogentin, vistril
benzos
haldol (haloperidol)
HIGH potenency (first generation)
2nd generation
clozapine, rispiridone, olanzapine, quetiapine (-PINE and -DONE)
Better for negative symptoms
third generation
Aripiprazole (abilify)
dystonia
sudden and expected muscle spam in neck, face, and mouth
· Understand MAOI’s and food interactions/teaching r/t Rx· Understand MAOI’s and food interactions/teaching r/t Rx
o Interacts with TYRMAINE (aged cheeses, smoked meats, chocolate, overripe fruits, fermented foods)
· Review definition of EPS. Which meds most likely to cause these? How is this treated?

Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) are drug-induced movement disorders that include symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, often caused by antipsychotic medications. Treatment typically involves the use of anticholinergic drugs or beta-blockers.