AP Micro Economics Unit 1
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fuhyuh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Scarcity
The problem of economics (unlimited wants but limited resources)
Incentives
How we make decisions
Opportunity Cost
What is given up when a decision is made (the 2nd choice)
Market Economies
Individuals and Private entities make decisions. (Property rights = incentives)
Command Economies
Governments or Central bodies make decisions
Land
Natural Resources (timber, oil, coal)
Labor
Workers
Capital
Machines, tools, buildings
Entrepreneurship
the owning of a business? idrk
Microeconomics
Small economics (zoomed in)
One single industry, store, person
Macroeconomics
Whole economy
U.S. Unemployment
Normative
based on norms, beliefs
positive
based on positions, facts/reality
What does the Business Cycle Model shows?
Fluctuations in output over time
Economic growth
Increase in capacity to produce
What is economic growth caused by?
More resources
Improving the Quality of Resources
Technology (combination of resources)
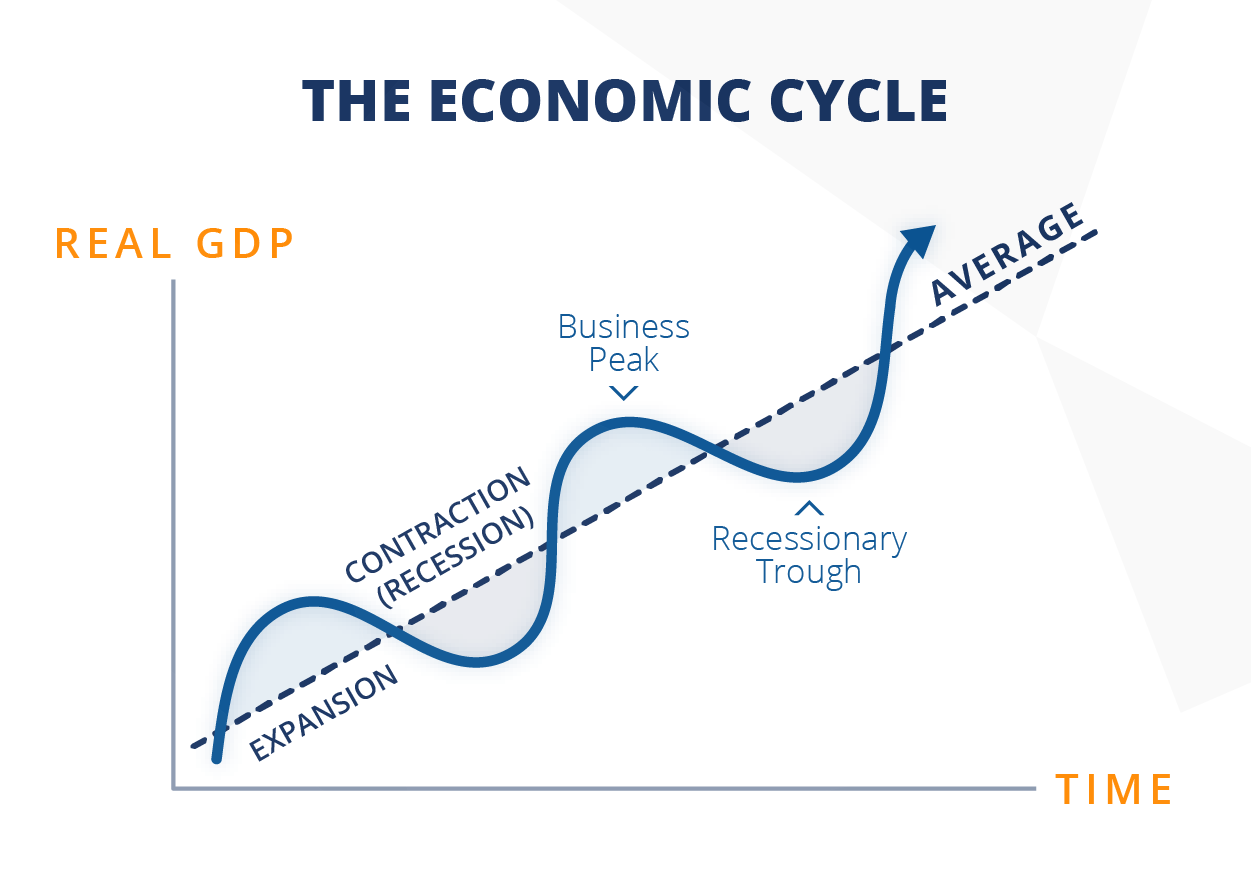
What happens to Unemployment and Price during a recession?
unemployment increases and price decreases
What happens to Unemployment and Price during an expansion?

price increase and unemployment decreases
What is a Production Possibilities model
A model showing the opportunity cost and productive efficiency
Define Productive Effecient
full employment of resources
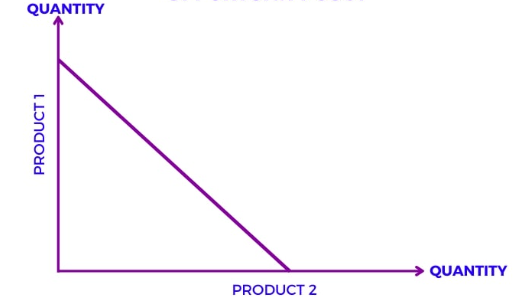
What graph is this
Constant Opportunity Cost Graph
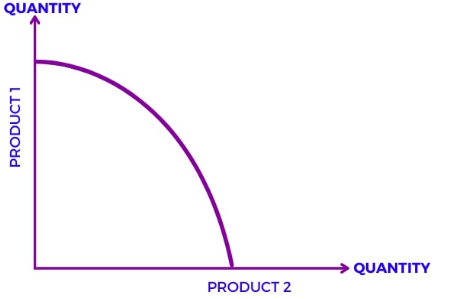
What graph is this
Increasing Opportunity Cost
Where would an inefficient point be on an increasing opportunity cost graph?
Underneath the curve
Where would an infeasible point be on an PPC graph
Above the curve
Trade
Mutually beneficial Exchanges
Absolute Advantage
More output given the same inputC
Comparative Advantage
Lower opportunity cost given the same inputs (impossible to have a comparative advantage in both goods)
What is a seller’s opportunity cost?
The minimum price the seller will accept
What is the buyer's opportunity cost
the maximum price the buyer is paying
What is the benefit of trade?
allows consumption beyond individuals PPC curve
Acceptable terms of trade
Mutually benenficial
Unacceptable terms of trade
below seller’s minimum price OR above buyer’s maximum price
What are the assumptions of a perfect competition market model?
Large # of buyers and sellers
identical products
Quantity Demand
the amount people are willing and able to buy at a specific price
Demand
Relationship between all prices and their respective quantity demanded
Relationship between Market Size and Demand
proportional
Relationship between the expectation of future prices?
proportional
What is the relationship between the price of a complementary good and demand?
Inverse relationship
What is the relationship between the price of a substitute good and demand?
proportional
What is the relationship between income and demand for a normal good?
proportional
What is the relationship between income and demand for an inferior good?
inverse
What is the relationship between preferences for a good and the demand for the good
proportional
Quantity Supplied
The quantity that producers are willing and able to sell at a specific price
Supply
relationship between all prices and respective quantities supplies
Relationship between Quantity supplied and Demand
Proportional
What is the relationship between the number of producers and the supply curve?
proportional
What is the relationship between input costs and the supply?
inverse
What is the relationship between a per unit tax and supply?
inverse
What is the relationship between subsidies and supply?
proportionalwhat
What is the relationship between technology (productivity of each resource) and supply?
proportional
What is the relationship between expectations of future prices and supply?
proportional
Increase in demand causes…
Increase in both quantity and price
Decrease in demand causes…
Decrease in both quantity and price
Increase in supply causes…
increase in quantity but a decrease in demand
Decrease in supply causes…
decrease in quantity but an increase in price
What happens when supply increases and demand decreases
Price decreases
Quantity is indeterminate
What happens when supply decreases and demand increases?
Price increases
Quantity is indeterminate
What happens when supply and demand both increase
quantity increases
price is indeterminate
What happens when both supply and demand decrease?
Quantity decreases
price is indeterminate
What do price ceilings cause?
a shortage
What do price floors cause?
a surplus
What does a tariff do
Decreases the amount of imports necessary. More domestic producers.
What does a quota do?
increases price
What does a per unit tax do?
increases the price for buyers