HCS 202 Exam 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Pillar 3
Population estimation with confidence intervals
single sample t test
compares a sample mean to a population mean when the population standard deviation is unknown
Variables needed for single sample t test
sample mean and standard deviation, and population mean
Robust Assumtions
must be met in order to proceed with test
Non-robust assumptions
assumptions that can be violated to some degree and still perform the test
4 Common test assumptions
independence of data, appropriate measurement variables, normality of distributions, homogeneity of variance
Independence of data
no score is linked to another, not robust
appropriate measurement variables
the variables of interest must be measured on an appropriate scale, not robust
normality of distributions
the distribution of sample means for each condition must have a normal shape, robust
homogeneity of variance
standard deviations from the sample and population are similar, robust
Null Hypothesis (H0)
states there is no effect
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
States there is an affect
T test null hypothesis
there is no difference between the sample and population mean
t test alternative hypothesis
there is a mean difference between the sample and population mean
if data is not compatible with the null hypothesis
fail to reject the null (insufficicent evidence)
if data is incompatible with the null
reject the null (sufficient data)
one-tailed hypothesis
only one direction of an effect or relationship is predicted in the alternative hypothesis of the test
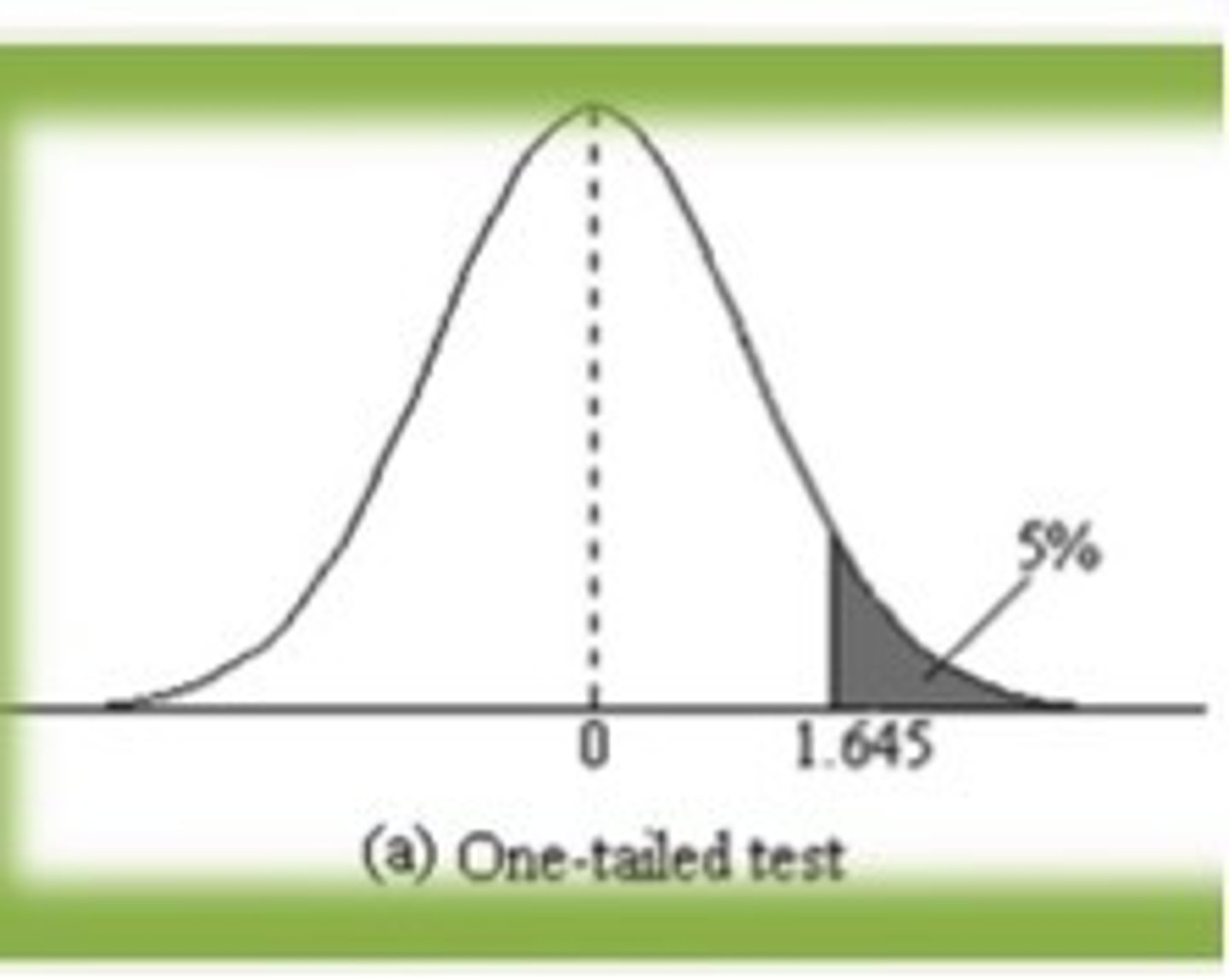
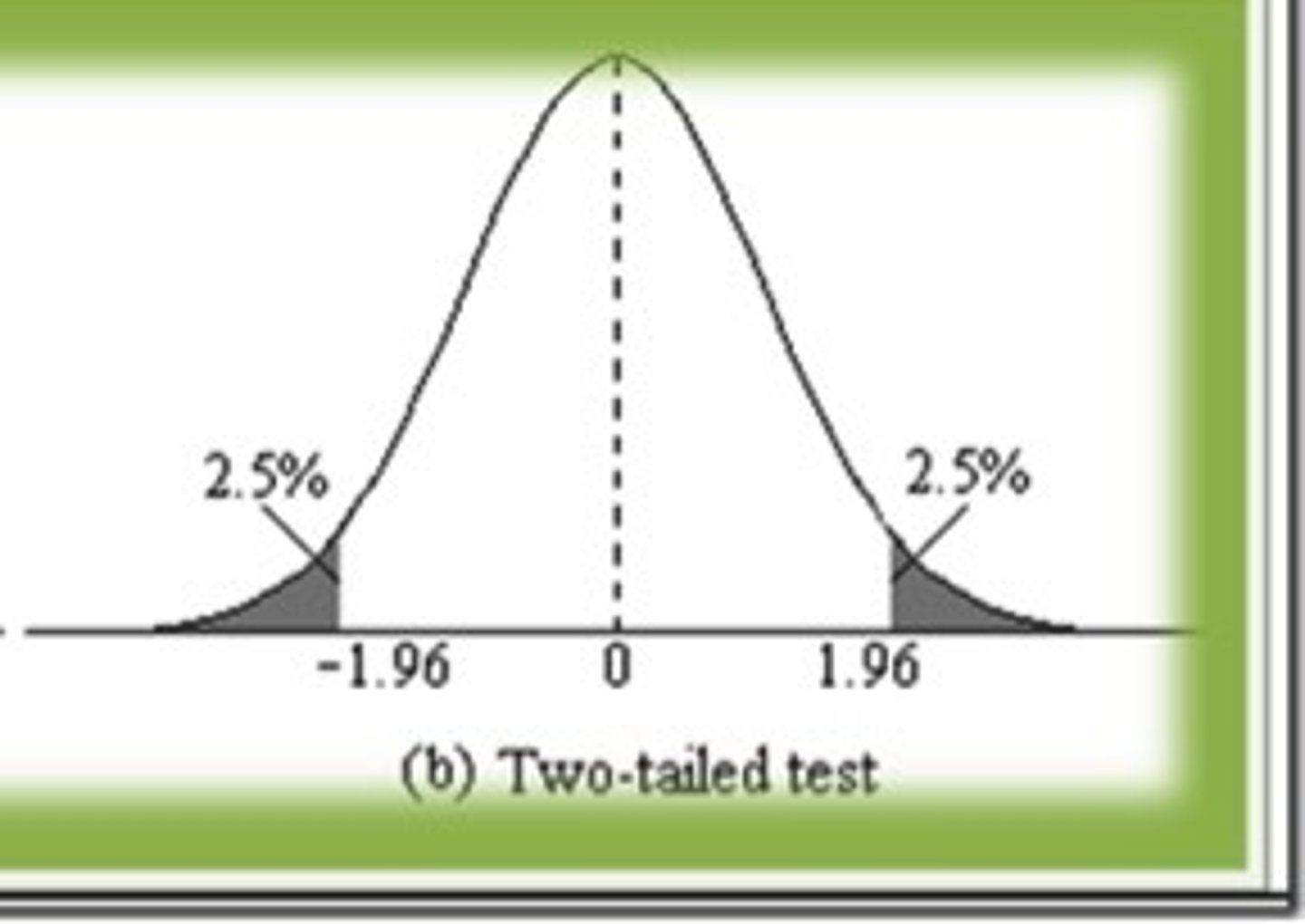
two-tailed hypothesis
both directions of an effect or relationship are considered in the alternative hypothesis of the test
decision rule
the rule that determines when we will reject the null or fail to reject the null