The layout of the circus maximus
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what was circus maximus
translates to great circle or great racecourse
a roman racecourse constructed in 6 BCE and used continuously until Totila (the Ostrogoth King) held the last official chariot in 549 CE.
where was the circus maximus
located in the valley between the palatine and aventine hills in rome, and is the city’s largest and oldest outdoor space.
roman legends suggest that it was built by the very first kings of rome, but it was julius ceasar who gave it its distinctive oval shape.
what was the circus maximus used for
primarily used for chariot racing.
site of the Ludi Romani (the roman games) which happened over a fifteen day period every september in honour of the god jupiter.
as well as these games, the circus maximus was home to wild animal hunts, gladiator fights and public executions.
some of these events were wildly extravagant.
how big was the circus maximus
the circus was at its biggest in the first century ce, following a rebuilding after the great fire of 64ce. the circus could seat 250000 spectators on banks of seats 30 metres wide and 28 metres high.
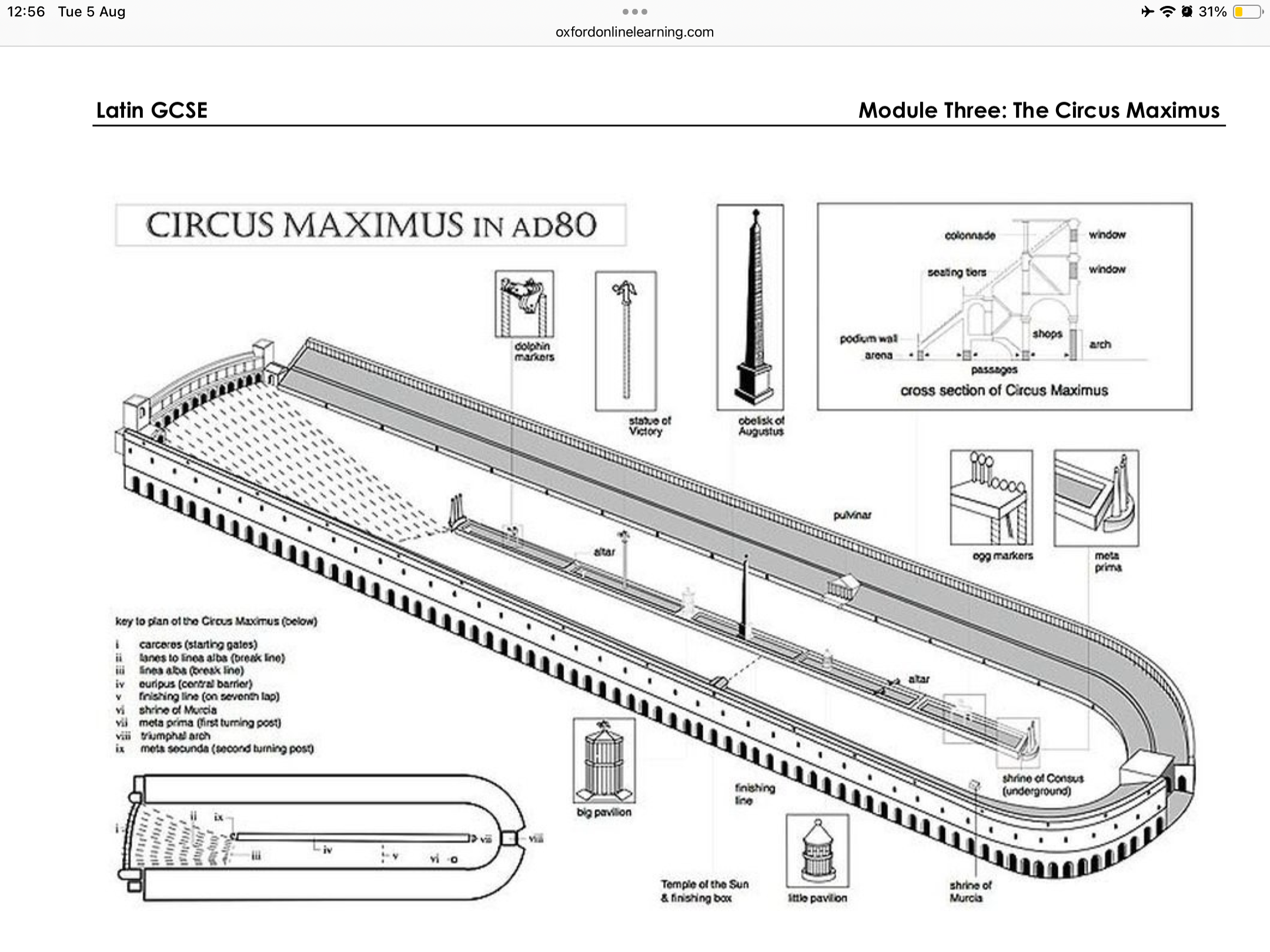
the spina/euripes
was a decorative barrier running down the centre of the track. two of the decorations on the spina are known to have been egyptian obelisks.
one (1280bce) was taken from heliopolis by the emperor augustus in 10 bce.
the other, which stood at the centre, came from temple to the chief egyptian god amun at larnak and dates from around 1500bce
meta (s) metae (pl)
first decl noun meaning cone or pyramid
cone shaped turning posts placed at the end of each side of the track.
the lap markers
shaped like eggs and dolphins, the lap markers were used to signal the completion of each of the seven laps of a typical chariot race.
typical day at the circus maximus
started with the pompa circensis, a progression/parade to launch spectacles of the day.
attended by the sponsor of the day’s games, youth groups, the charioteers, dancers and musicians. followed by a public draw, a bit like the national lottery.
the religious significance of the circus maximus
the turn located at the south east end was located between two shrines, believed to predate construction of the circus itself.
first shrine is dedicated to murcia (goddess of the valley in which the circus stood)
the second was to the god consus who was a minor god of grain stores. roman legend said it was always there and discovered romulus shortly after he founded rome.
lap markers in shapes of eggs and dolphins.
believed twin gods castor and pollux (gods of horses and horsemen) were born from an egg, while the sea god neptune was also a god of horses.