Thẻ ghi nhớ: Unit 3: Forces and energy (0893, Stage 7 Science) | Quizlet
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Earth
Third planet from the sun

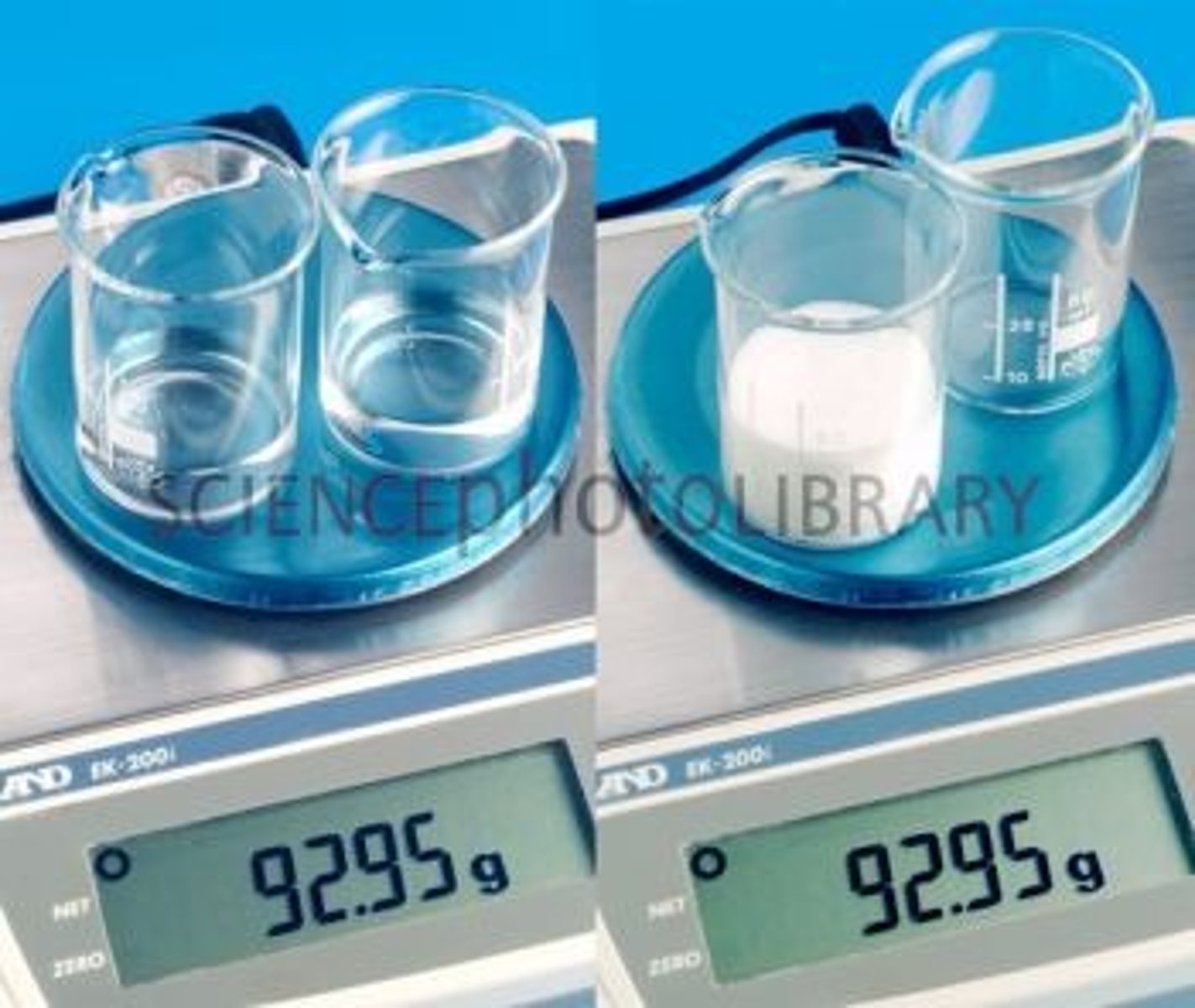
mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object

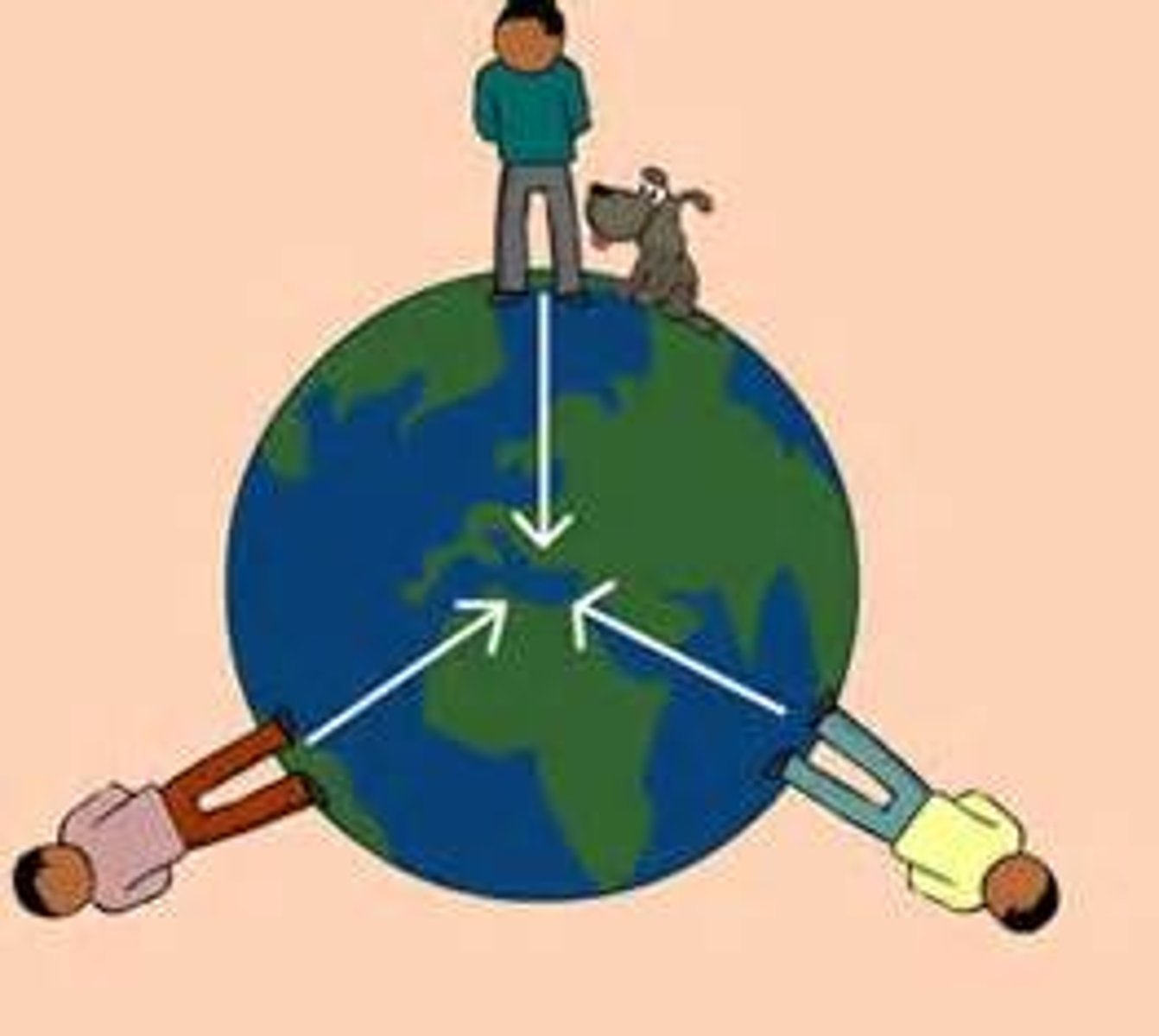
gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.
acts towards the centre
gravity causes a force which pulls objects towards the centre of a planet or star
force of gravity
a force of attraction which is an example of a non-contact force
weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object

newtons
The unit of measurement for force and weight

contact force
a push or pull on one object by another that is touching it
quantity
the amount of something; _________ is preferred in science to "amount"

kilograms
unit for mass

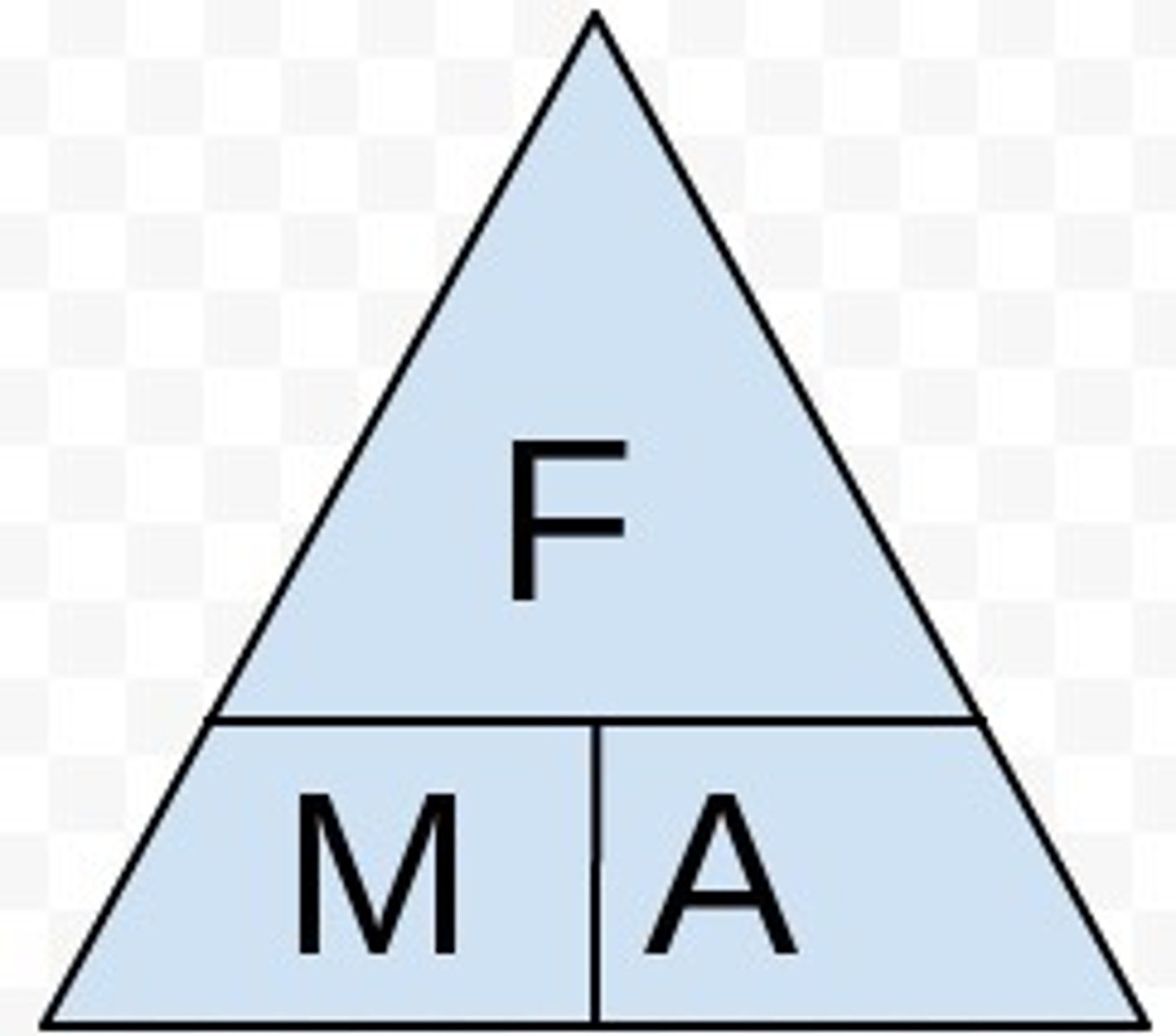
formula triangle
a method of using an equation
accurate
being close to a true value

observe
to see; to notice

formed
made or organized

evidence
facts that support or contradict a hypothesis

hypothesis
A testable prediction

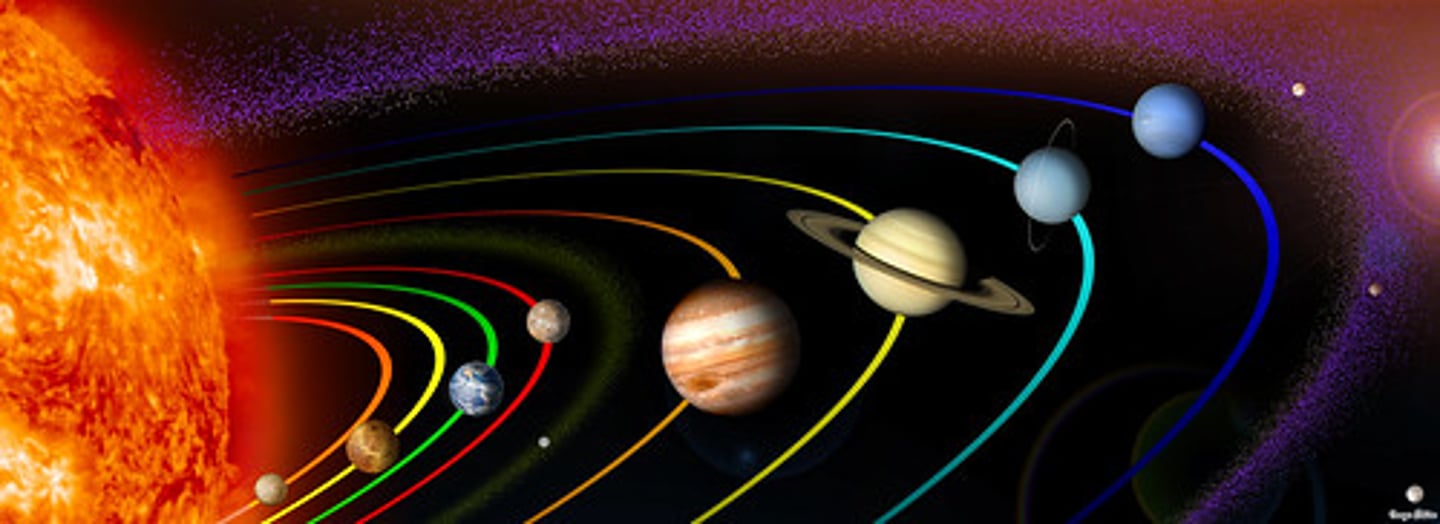
orbit
the path of a planet around the Sun or a satellite (natural or artificial) around a planet
spin
the circular movement of a planet around its own axis, such as causes day and night on Earth

axis
An imaginary line that passes through Earth's center and the North and South poles, about which Earth rotates

planet
A large body in space that orbits a star and does not produce light of its own

nebula
A large cloud of dust and gas in space

model
A representation of an object or event
support
Back up with details

contradict
to speak against; to say the opposite

circular
having the shape of a circle
speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time

air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air

vacuum
A space where no particles of matter exist

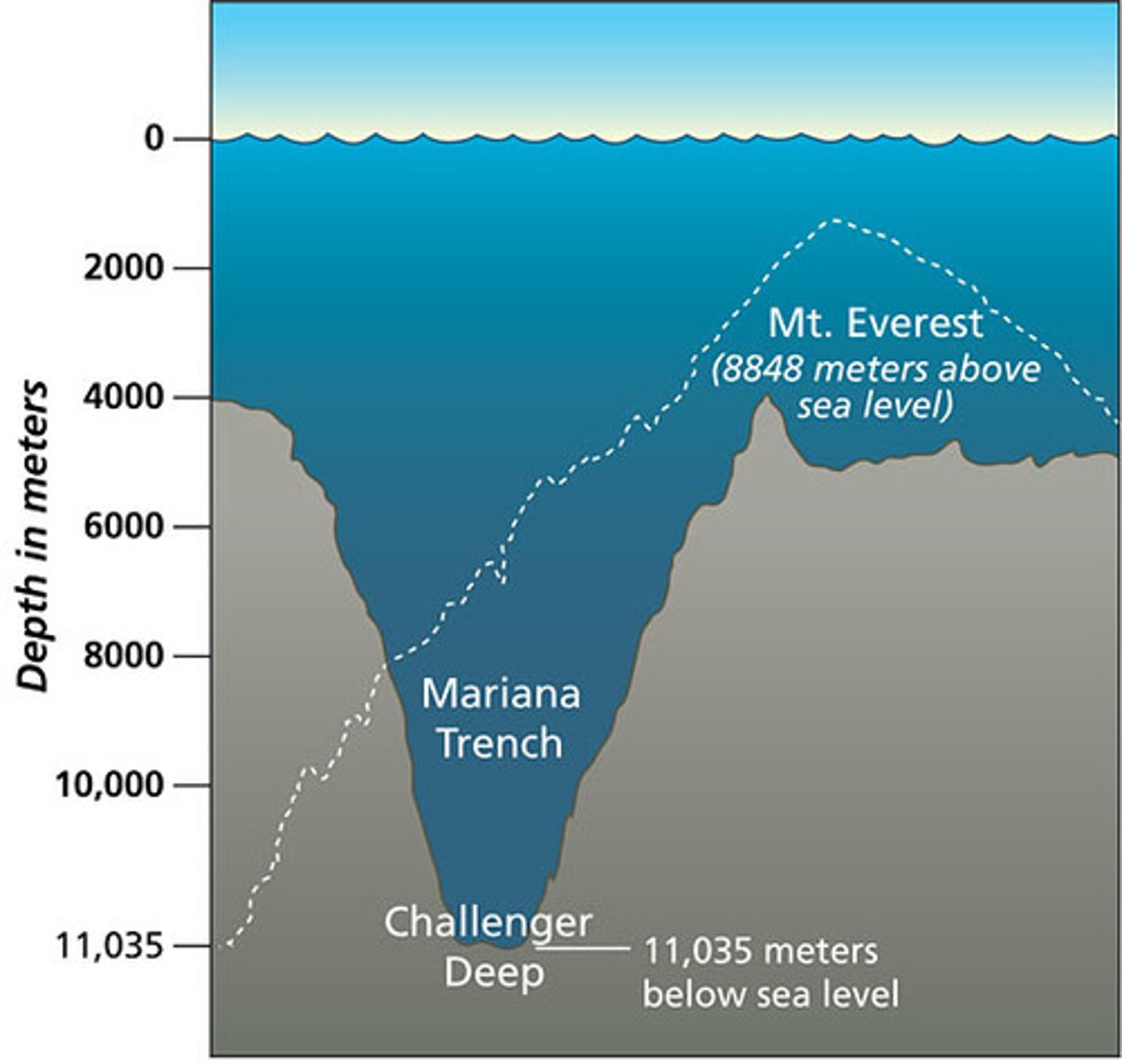
depth
the distance from the bottom of the ocean to the surface of the ocean; how deep the ocean is
harbour
an area of water near the coast where ships are kept and are safe from the sea

coastal
located on or near or bordering on a coast

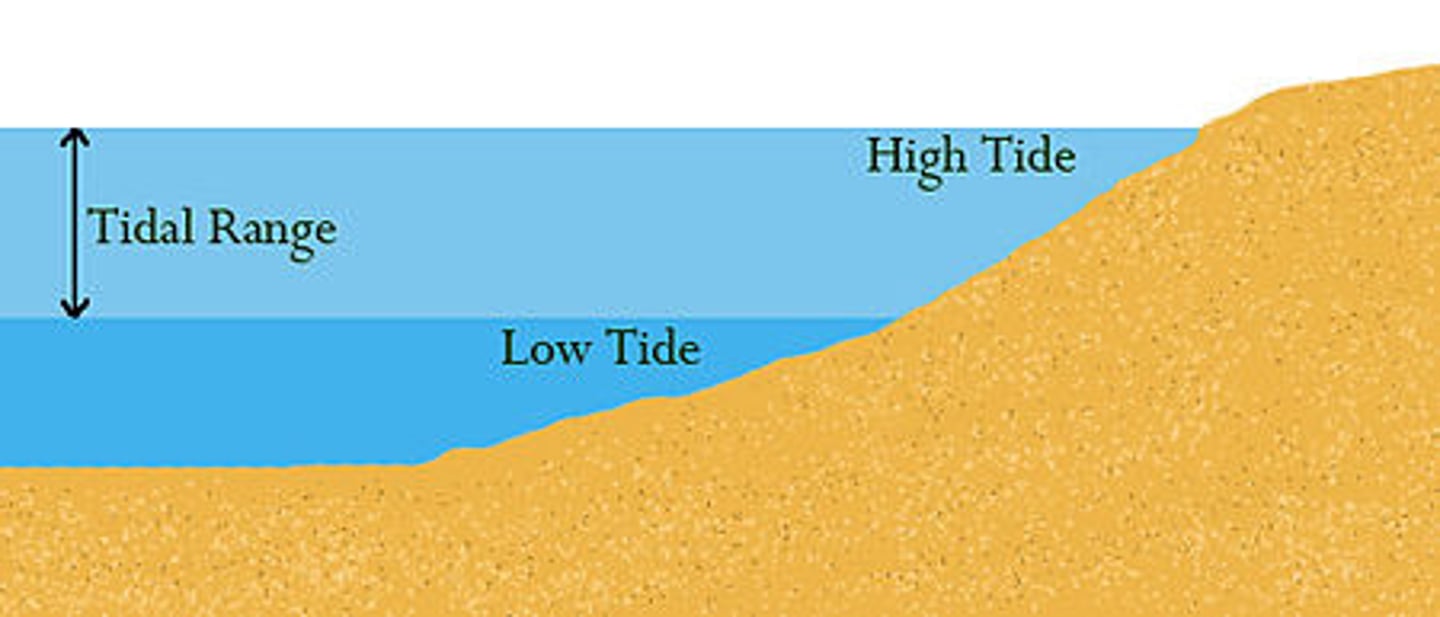
tide
The periodic rise and fall of the level of water in the ocean

tidal range
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide
Earth tide
the rise and fall of the land surface as a result of tidal forces

tidal force
the force from the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun that causes tides on Earth
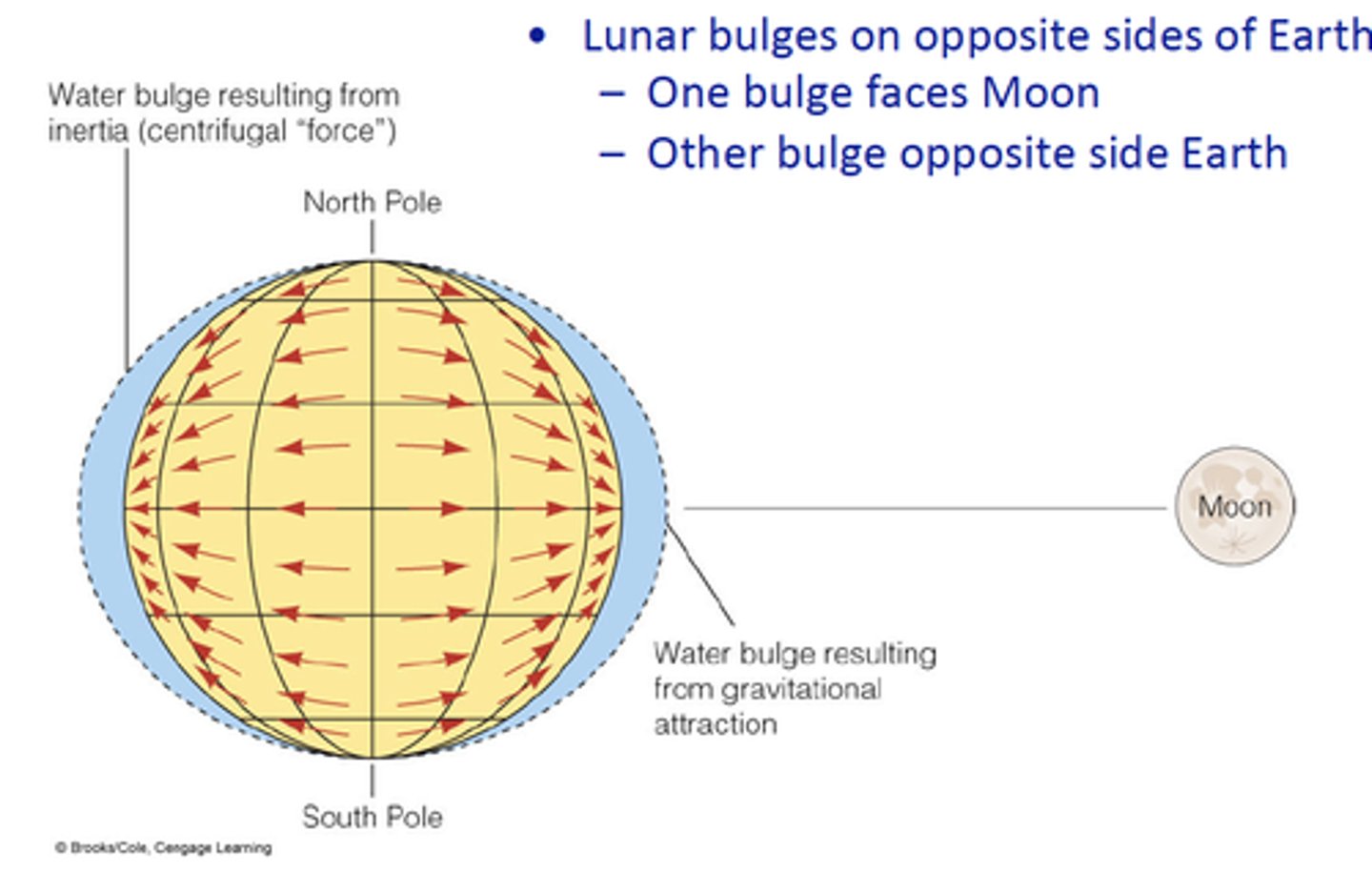
low tide
The time at which the tide reaches its lowest level

high tide
The time at which the tide reaches its highest level

earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.

volcano
A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface

force of attraction
A force that pulls objects together
energy
the ability to do work
transferred
passed from one place or form to another
stored energy
energy contained in one place

kinetic
relating to movement

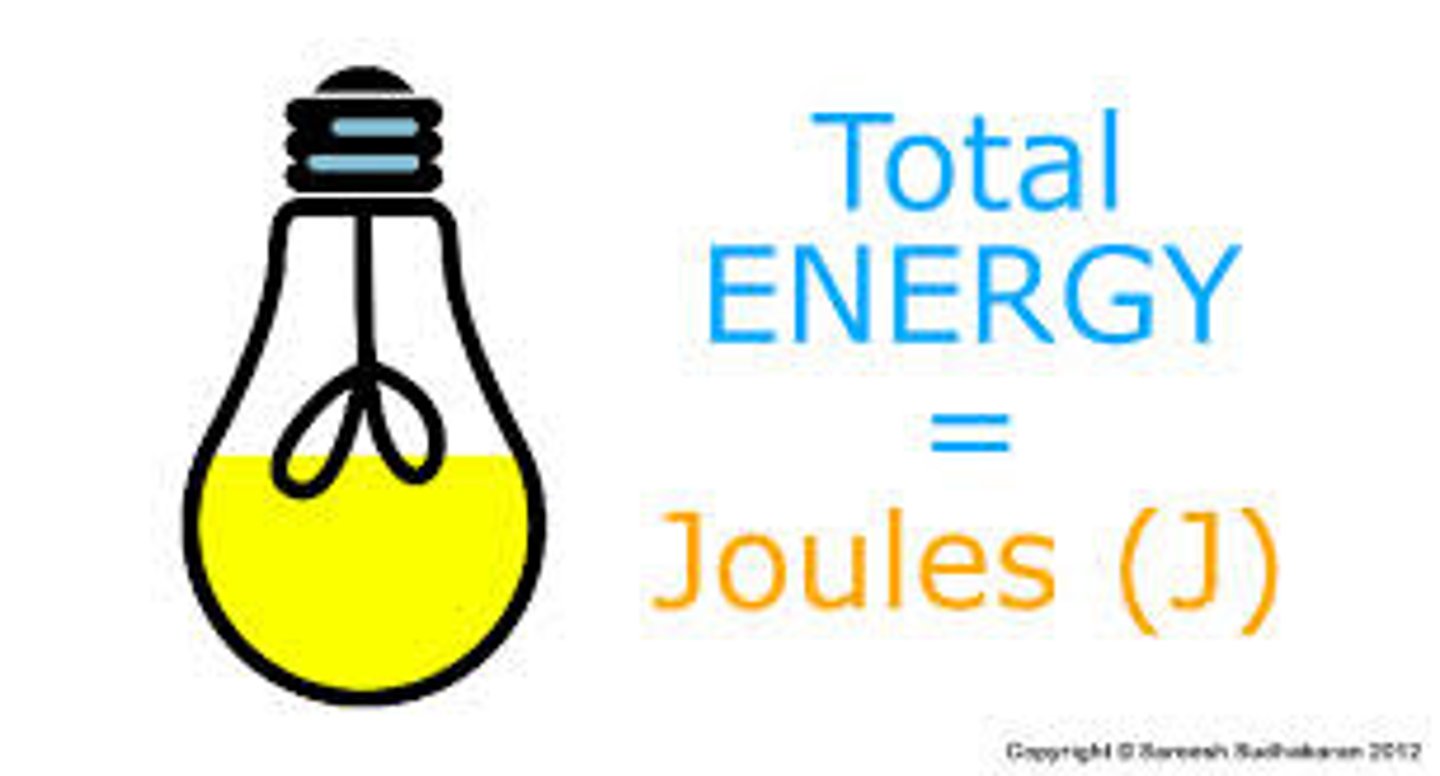
joule
the unit of energy
chemical energy
A form of energy that is stored in food and fuels

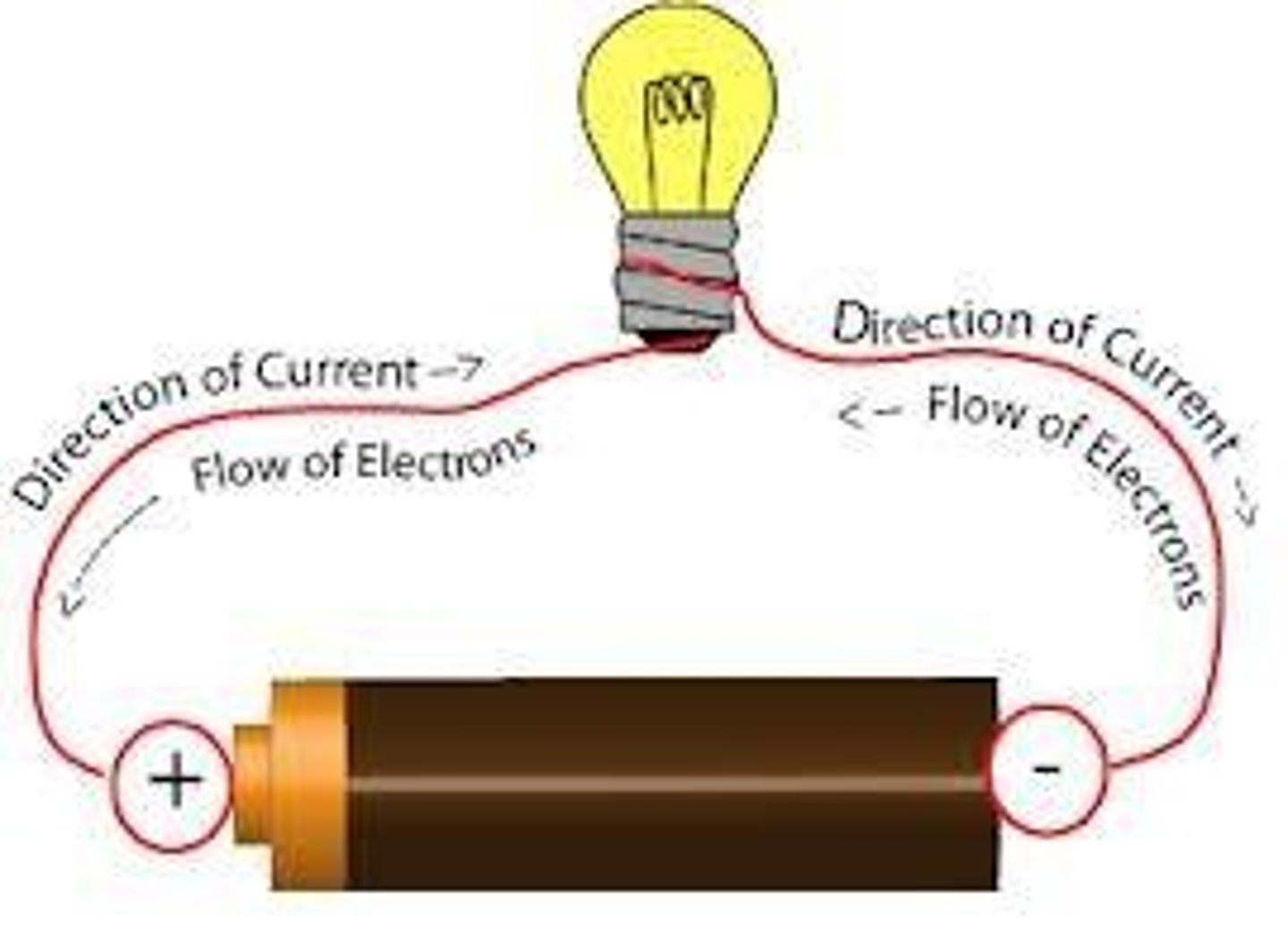
electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
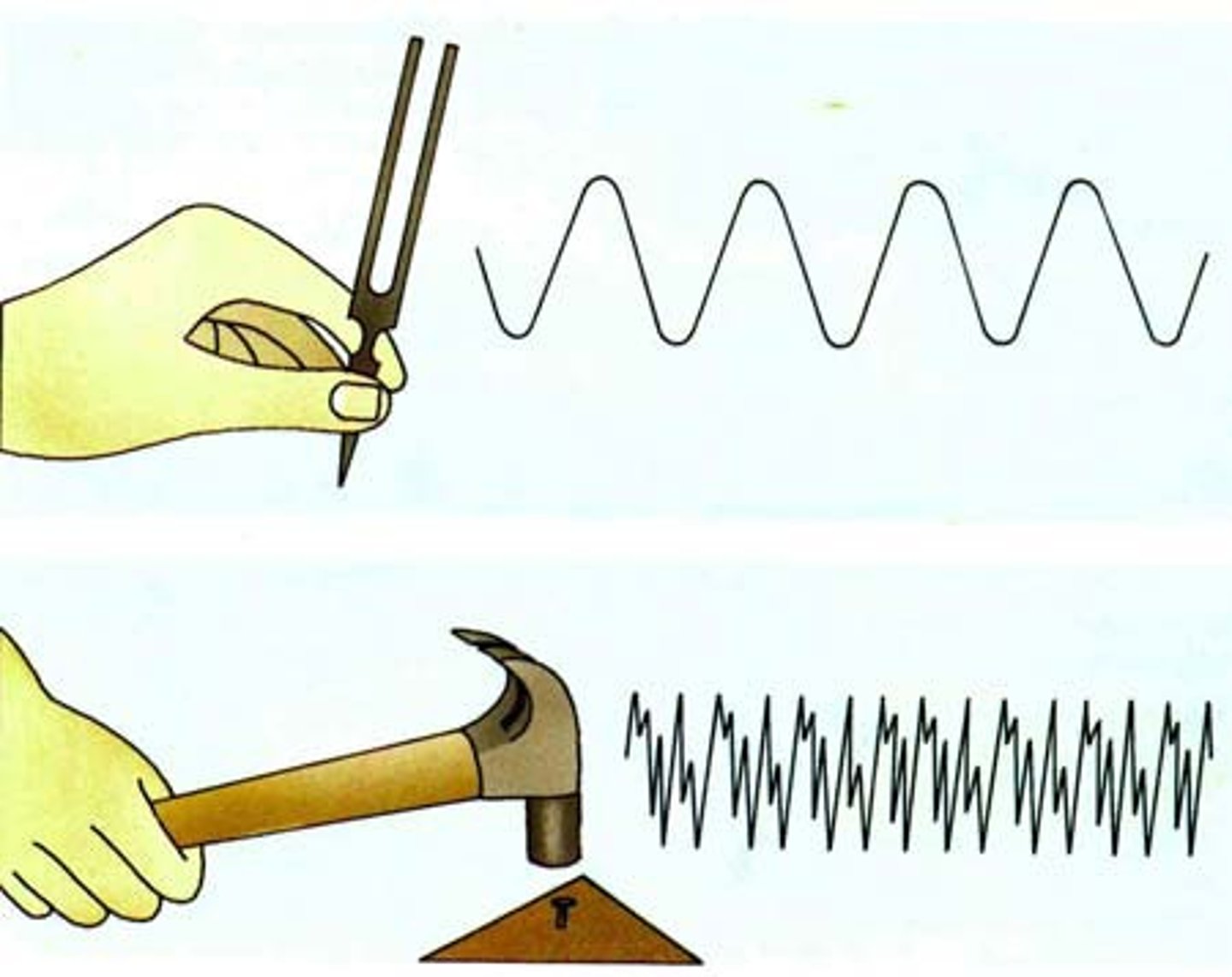
sound energy
Energy caused by an object's vibrations
light energy
Energy in the form of moving waves of light

thermal energy
The total energy of all the particles of an object.
elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects
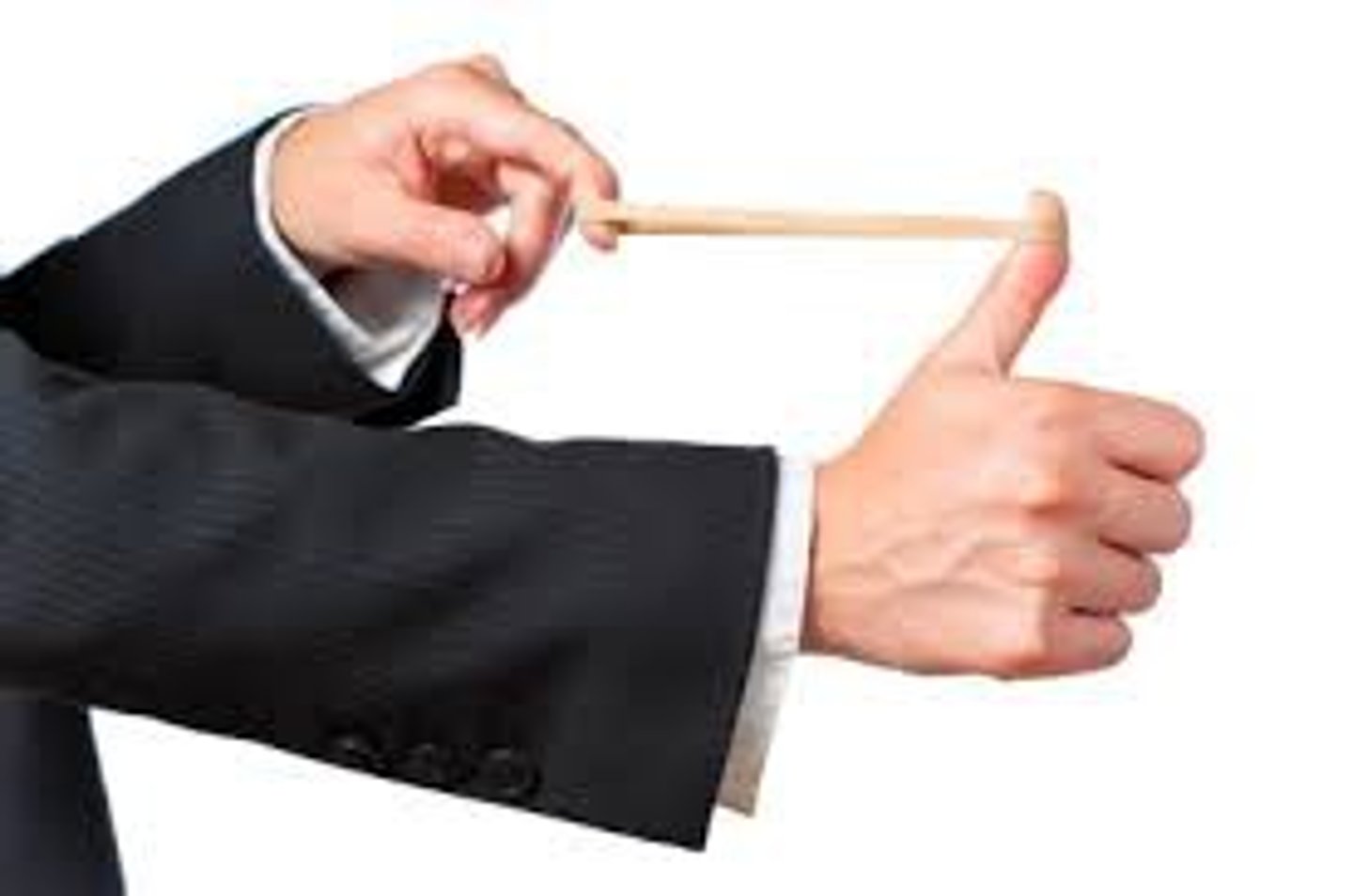

gravitational potential energy
Energy stored by objects due to their position above Earth's surface.

fuel
a material that releases energy when it burns

luminous
giving off light

changes in energy
when energy changes from one state to another

change
to make or become different

process
A series of actions or steps taken to achieve an end
event
anything that happens or is regarded as happening
useful
helpful; energy changed in the way that we want

wasted energy
Energy that is not usefully transferred

dissipated energy
energy used up in a system, typically lost due to work done by friction, 'wasted energy'

recovered
collected and used again