7217 Anatomy Exam 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
The neurovascular plane is located in which layer of the scalp?
A. skin
B. connective tissue
C. aponeurosis
D. loose areolar CT
E. periosteum
B. connective tissue
Which option represents a likely site for infections to collect due to dental abscess?
a. fascial spaces of the face
b. muscles in the beck
c. fascial spaces around organs
d. tongue
a. fascial spaces of the face
Infections from which of the following teeth normally travel to the prevertebral space?
a. maxillary molars
b. maxillary premoars
c. mandibular molars
d. mandibular premolars
e. none of the above
e. none of the above
Where the infection actually goes: Odontogenic infections (especially from Mandibular Molars or Maxillary Third Molars) that travel posteriorly typically land in the Retro-pharyngeal Space or the Danger Space.
The Barrier: The Prevertebral Space is the compartment contained within the Pre-vertebral Fascia. This fascia is incredibly robust and tightly encases the deep muscles of the neck (like the Longus Colli) and the vertebral column itself.
The Path of Least Resistance: Bacteria are lazy; they prefer the "gaping highways" of potential space. The Danger Space (between the Alar Fascia and Pre-vertebral Fascia) provides a much easier route for fluid to travel down to the diaphragm than trying to penetrate the tough, deep fibers of the Pre-vertebral Fascia to enter the actual vertebral compartment.
Quick Refresher on Posterior Spread
Maxillary M3s: Can spread to the Parapharyngeal Space >> Retro-pharyngeal Space.
Mandibular M2s/M3s: Often spread to the Submandibular Space >> Parapharyngeal Space >>Danger Space.
Infections from the mandible will spread directly to all of the following spaces, except for the:
a. retropharyngeal
b. sublingual
c. buccal
d. mental
a. retropharyngeal
While mandibular infections (especially from the third molars) can reach the back of the throat, they typically must first enter the parapharyngeal space. From there, they can spread into the retropharyngeal space or the danger space. Because there is an intermediary step (the parapharyngeal space), it is not considered a "direct" primary spread from the mandible in the same way the others are.
The buccinator is the lateral border of the:
a. buccal space
b. facial vestibule
c. submandibular space
d. parapharyngeal space
e. sublingual space
b. facial vestibule
In a true Ludwig's angina, infection will be found in all of the following spaces, except for the:
a. submandibular space
b. sublingual space
c. submental space
d. submasseteric space
d. submasseteric space
The anterior border of danger space is the:
a. pharynx
b. carotid sheath
c. prevertebral fascia
d. alar fascia
d. alar fascia
The canine space lies deep to which of the following muscles?
a. orbicularis oris
b. orbicularis oculi
c. zygomaticus major
d. mentalis
e. none of the above
e. none of the above
The Canine Space (the space above the incisors) lies deep to the levator anguli oris and superficial to the levator labii superioris.
Here is why the other options are incorrect:
Orbicularis oris: This is the sphincter muscle of the mouth; the canine space is superior to it.
Orbicularis oculi: The Periorbital Space lies deep to this muscle, not the canine space.
Zygomaticus major: This muscle is more lateral and superficial; it doesn't serve as the primary covering for the canine space.
Mentalis: This is located on the chin (genu), associated with the Mental Space.
Imaging reveals a patient has fluid accumulation in the posterior mediastinum to the level of the diaphragm. The accumulating fluid distends a potential space anterior to the vertebral bodies. Where is this fluid located?
a. retropharyngeal space
b. pretracheal space
c. danger space
d. prevertebral space
e. retrotracheal space
c. danger space
What is not a potential symptom of a cavernous sinus infection?
a. infected cutaneous blemish near the eye
b. an adducted eye
c. a constricted pupil
d. exophalmos
e. beating exophthalmos
f. all are potential symptoms of a cavernous sinus infection
f. all are potential symptoms of a cavernous sinus infection
A patient demonstrates an infection of a first upper premolar tooth. Where do you anticipate the infection to go first?
a. canine space
b. submental space
c. periorbital space
d. infraorbital space
e. sublingual space
d. infraorbital space
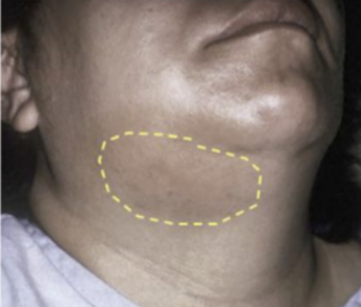
If a patient demonstrates swelling such as that seen in the provided image, where do you anticipate the infection to be located?
a. submental space
b. submandibular space
c. sublingual space
d. mental space
e. cervical space
b. submandibular space
True or False: Infection may enter the fascial space overlying the canine fossa
true
Identify the specific fascial structure (not a fascial layer) that attaches to the styloid process
stylomandibular ligament
Put the following structures/spaces in the correct order, going from anterior to posterior:
- danger space
- retropharyngeal space
- prevertebral fascia
- alar fascia
A: retropharyngeal space > alar fascia > danger space > prevertebral fascia
The alar fascia is an outcropping of which type of fascia?
D: prevertebral
The buccopharyngeal fascia is the name given to a specific location of which type of fascia?
A: visceral (pretracheal)
The axillary sheath is directly continuous with which of the following?
a. prevertebral fascia
b. investing fascia
c. pretracheal fascia
d. superficial fascia
A: prevertebral fascia
A bilateral infection of the sublingual, submental, and submandibular spaces is referred to as:
Ludwig's Angina
Which of the following teeth can cause an osteodontic infection of the submandibular space from only one root?
C: 1st mandibular molar
The ramus of the mandible, the zygomatic arch, and the parotid gland are all boundaries of which fascial space?
A: submasseteric
The maxillary origin of buccinator muscle is on the alveolar process between the apex of the canine eminence and the coronoid process of the mandible. If a patient has an infection in tooth #2 or #15, where will the infection spread first?
D: Vestibular space
Abnormal medial deviation of the eyeball can be a sign that infection has spread to the cavernous sinus and affected the sixth cranial nerve. (T/F)
True
All of the following fascial space infections represent a high risk to the patient except for the:
B: vestibular
Infections of the infraorbital space can start from which teeth? (Select all that apply)
A: central incisors, B: lateral incisors, C: canines, D: first premolars
Organs in the muscular triangle are enveloped in which fascial layer?
A: pretracheal (muscular layer)
The intermediate tendon of the omohyoid muscle is composed of which type of fascia?
C: investing (also includes traps and SCM posteriorly... anterior is the hyoid muscles)
When dissecting a cadaver, in order to see the muscles that comprise the floor of the posterior triangle, which fascial layer(s) must be removed?
D: All of the above (superficial, investing, and prevertebral)
The superficial fascia is also known as the:
A: hypodermis
Which of the following is a boundary between the sublingual and submandibular space?
E: mylohyoid ridge (line)
An infection from a maxillary molar will infect the vestibule if the root is:
A: inferior (to the buccinator attachment)
Reference the attached image. The yellow dashed line represents the maxillary origin of Patient X's buccinator muscle. In the event this patient has an infection associated with M2, where will the infection spread first?
a. buccal space
b. infraorbital space
c. pterygomandibular space
d. vestibular space
e. infratemporal space
d. vestibular space
Which muscle of mastication is most closely associated with the buccopharyngeal fascia? (recall: pharynx)
a. medial pterygoid muscle
b. lateral pterygoid muscle
a. medial pterygoid muscle
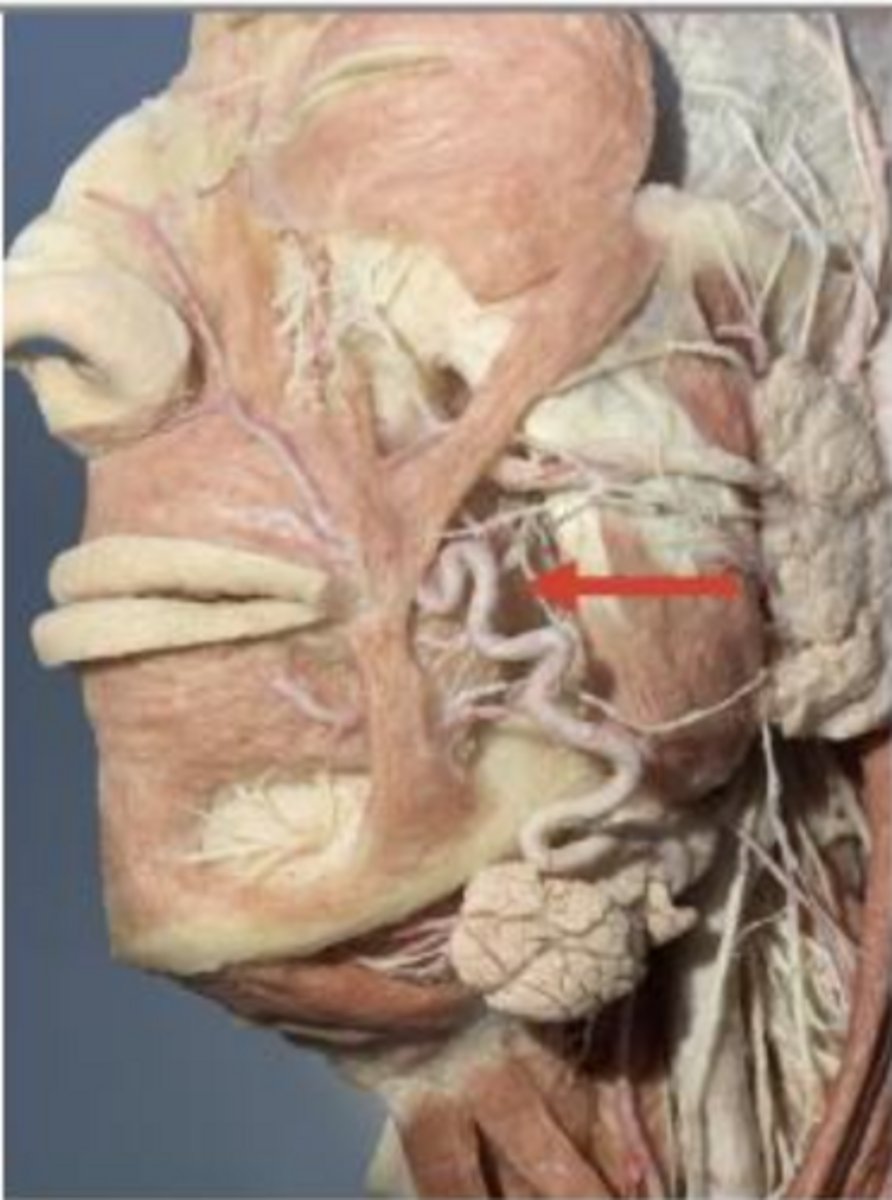
Which fascial space is marked by the red arrow?
a. buccal space
b. parotid space
c. infraorbital space
a. buccal space
The _____ fascia separated the retropharyngeal and danger spaces?
a. pretracheal
b. prevertebral
c. investing
d. superficial
e. alar
e. alar
Muscles directly covered by the investing fascia include the
a. platysma
b. anterior scalene
c. mentalis
d. trapezius
e. levator scapulae
d. trapezius (and SCM posteriorly... also hyoid muscles anteriorly)
The phrenic nerve sits just deep to the
a. superficial fascia
b. prevertebral fascia
c. buccopharyngeal fascia
b. prevertebral fascia
The intermediate tendon of the omohyoid muscle is composed of which type of fascia?"
A: pretracheal B: prevertebral C: investing D: superficial E: alar
C: investing
The __________ fascia separates the retropharyngeal and danger spaces.
A: pretracheal B: prevertebral C: investing D: superficial E: alar
E: alar
What is the primary determinant of whether an infection from a third maxillary molar spreads into the facial vestibule or the buccal space?
The position of the root of the tooth in comparison to the attachment of the buccinator on the maxilla.
The axillary sheath is directly continuous with which of the following?
A: prevertebral fascia
B: investing fascia
C: pretracheal fascia
D: superficial fascia
A: prevertebral fascia
Muscles directly covered by the investing fascia include the
A: platysma. B: anterior scalene. C: mentalis. D: trapezius. E: levator scapulae.
D: trapezius
The phrenic nerve sits just deep to the
A: superficial fascia. B: prevertebral fascia. C: buccopharyngeal fascia. D: pretracheal fascia. E: investing fascia.
B: prevertebral fascia
Which option represents a likely site for infections to collect due to dental abscesses?
A. Fascial spaces of the face
B. Muscles in the neck
C. Fascial spaces around organs
D. Tongue
A. Fascial spaces of the face
Organs in the muscular triangle are enveloped in which fascial layer?
A: pretracheal
B: prevertebral
C: investing
D: superficial
A: pretracheal
Put the following structures/spaces in the correct order, going from anterior to posterior
A: retropharyngeal space; alar fascia; danger space; prevertebral fascia
B: danger space; prevertebral fascia; retropharyngeal space; alar fascia
C: alar fascia; retropharyngeal space; prevertebral fascia; danger space
D: prevertebral fascia; danger space; alar fascia; retropharyngeal space
A: retropharyngeal space; alar fascia; danger space; prevertebral fascia
The alar fascia is an outcropping of which type of fascia?
A: visceral
B: superficial
C: investing
D: prevertebral
D: prevertebral
The buccopharyngeal fascia is the name given to a specific location of which type of fascia?
A: visceral B: superficial C: investing D: prevertebral
A: visceral
When dissecting a cadaver, in order to see the muscles that comprise the floor of the posterior triangle, which fascial layer(s) must be removed?
A: superficial B: investing C: prevertebral D: All of the above
D: All of the above
The superficial fascia is also known as the _____________.
A: hypodermis B: dermis C: epidermis
A: hypodermis
Which of the following are branches of the external carotid artery that supply the scalp?
A: supraorbital artery B: supratrochlear artery C: posterior auricular artery D: a and b
C: posterior auricular artery
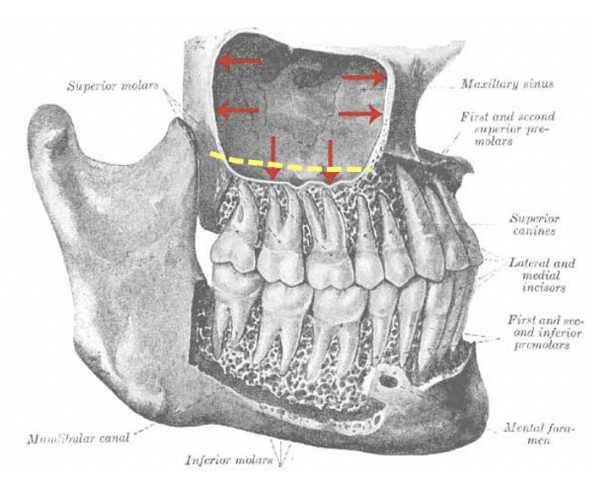
Reference the attached image. The yellow dashed line represents the maxillary origin of Patient X's buccinator muscle. In the event this patient has an infection associated with M2, where will the infection spread first?
A: Buccal space
B: Infraorbital space
C: Pterygomandibular space
D: Vestibular space
E: Infratemporal space
D: Vestibular space
Which muscle of mastication is most closely associated with the buccopharyngeal fascia?
A: Medial pterygoid muscle
B: Lateral pterygoid muscle
C: Levator veli palatini muscle
D: Tensor veli palatini muscle
A: Medial pterygoid muscle
Imaging reveals a patient has fluid accumulation in the posterior mediastinum to the level of the diaphragm. The accumulating fluid distends a potential space anterior to the vertebral bodies. Where is this fluid located?
A: Retropharyngeal Space
B: Pretracheal Space
C: Danger Space
D: Prevertebral Space
E: Retrotracheal Space
C: Danger Space
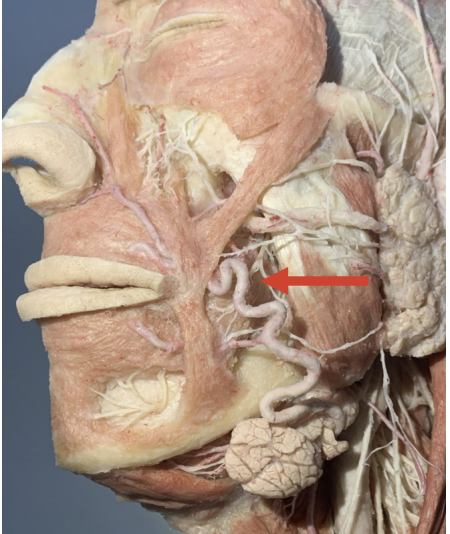
Which fascial space is marked by the red arrow?
Buccal space
Which tooth is most likely to send infection directly to the retropharyngeal space?
A: M3 B: M1 C: Premolar 1 D: Canine
A: M3
The neurovascular plane is located in which layer of the scalp?
A: Skin B: Connective tissue C: Aponeurosis D: Loose areolar connective tissue E: Periosteum
B: Connective tissue
Infections from which of the following teeth normally travel to the prevertebral space?
A: maxillary molars
B: maxillary premolars
C: mandibular molars
D: mandibular premolars
E: none of the above
E: none of the above
Infections from the third mandibular molars will preferentially spread to the
A: mentalis space.
B: buccal space.
C: sublingual space.
D: canine space.
B: buccal space.
Infections from the mandible will spread directly to all of the following spaces, except for the
A: retropharyngeal. B: sublingual. C: buccal. D: mentalis.
A: retropharyngeal.
The buccinator is the lateral border of the
A: buccal space.
B: facial vestibule.
C: submandibular space.
D: parapharyngeal space.
E: sublingual space
B: facial vestibule.
Which of the following is a correct border of the submandibular space?
A: Roof -- Anterior digastric muscle
B: Floor -- Posterior digastric muscle
C: Medial -- mentalis muscle
D: Lateral -- mandible
D: Lateral -- mandible
In a true Ludwig's angina infection will be found in all of the following spaces, except for
A: submandibular space.
B: sublingual space.
C: submental space.
D: submasseteric space.
D: submasseteric space.
The anterior border of danger space number four is the
A: pharynx.
B: carotid sheath.
C: prevertebral fascia.
D: alar fascia
D: alar fascia
Structures found within the retropharyngeal space include
A: an intertwining plexus of veins.
B: lymph nodes.
C: the internal jugular vein.
D: the glossopharyngeal nerve.
B: lymph nodes.
Difficulty in swallowing is consistent with an infection in which of the following spaces?
A: lateral pharyngeal
B: retropharyngeal
C: buccal
D: a and b only
E: a, b and c
D: a and b only
What type of deep fascia has an anesthesiology association?
prevertebral
What layer of the pretracheal deep fascia houses the trachea and the larynx?
visceral layer
What type of fascia is made up of a muscular layer and a visceral layer?
pretracheal
Which fascia of the neck encases the laryngeal cartilages and the thyroid gland?
a. Investing fascia
b. Pretracheal muscular fascia
c. Pretracheal visceral fascia
d. Prevertebral fascia
c. Pretracheal visceral fascia
What is the most superficial fascia of the neck that envelopes the submandibular and parotid glands?
a. Investing fascia
b. Pretracheal fascia
c. Prevertebral fascia
d. Alar fascia
a. Investing fascia