41) gallbladder + metabolismj of liver
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
(CHO metabolism)
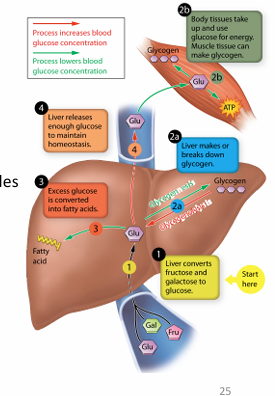
High blood glucose
Glycogenesis
- store glucose → glycogen
via insulin
-convert excess glucose to FA
(CHO metabolism)
Low blood glucose
1) Glycogenolysis
-break glycogen → glucose
via glucagon + epin
2) Gluconeogenesis
-create glucose from AA, lactate, glycerol
via GLUCAGON + cortisol
Lipid metabolism
1) Chylomicrons (big lipids)
→ bypass hepatic portal circulation
→ straight to adipose/muscle tissue
2) FFA
- betaoxidation to produce ATP
OR
-convert to:
triglyceride
cholsterol = create bile
3) bound to albumin = transported
Triglycerides
-stored when high blood glucose
-TG + cholesterol package = lipoproteins (travel through body)
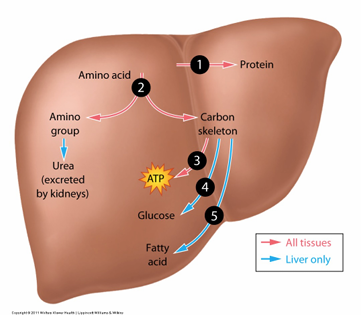
AA metabolism
AA breaks down into:
- ATP
- FA
- glucoseW
What to be careful of for AA metabolism?
deamination (break down AA)
→ forms AMMONIA
(combine with CO2)
→ which is TOXIC
→ ammonia convert to urea for excretion (kidney saliva sweat)
What vitamins and minerals are stored in the liver?
fat soluble vitamins: A,D,E,K
vitamin B12
Fe (for transferrin/ferritin) (used when blood levels low)
additional functions of liver:
-alcohol to acetaldehyde
-inactivate hormones + drug → make them water soluble → flush out through kidney (urine) or bile poop)
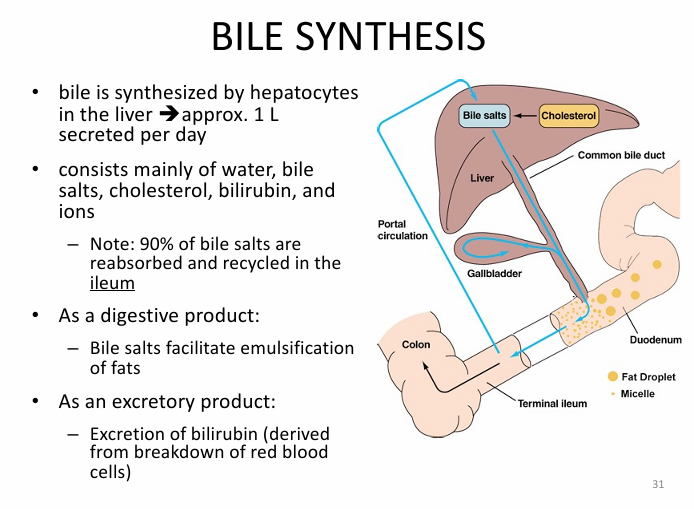
How is bile synthesized?
via hepatocytes in liver (mainly water)W
Where are bile salts reabsorbed and recycled?
ileum
Bile function as a:
1) digestive product
2) excretory product
1) emulsify fat
2) excrete bilirubin (broken down RBC)
What is UNCONJUGATED bilirubin?
-broken down heme
-lipid soluble
→ needs to bind to albumin to transport to liver
What is CONJUGATED bilirubin?
unconjugated bilirubin makes it to liver
→ bilirubin binds to GLUCURONIC ACID
→ forms conjugated bilirubin
(water soluble; able to be excreted in bile (poop) & kidney (pee)
Gallbladder general info: (doubt you need to know)
intraperitoneal
- in fossa on posterior surface of right lobe of liver
What is the path gallbladder bile storage? (see your purple gallbladder drawing)
(Rid of bile)
CCK released from intestinal ENTEOENDOCRINE CELL
→ relax hepatopancreatic sphinter (bile enters SI)
→ contract gallblader (squeezes bile out → to enter SI)
—
(Storing bile)
SI is EMPTY
- no CCK release
- hepatopancreatic sphincter CLOSES
- bile backs up into cystic duct
→ stores into gallbladder
What are gallstones?
cholesterol in bile crystallized = gallstone
- due to excessive cholesterol
OR
→ insufficient bile salts (like soap to breakdown/mix cholsterol)