16. Surgical diseases of the stomach. Foreign body. Dilatation and volvulus. Aetiology, symptoms, diagnosis and therapy. Pericardioperitoneal hernia. Neoplasia of the stomach
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the sections of the stomach?
Cardia
Fundus
Body
Pylorus
The inlet (with sphincters) of the stomach, located right of the midline.
The large middle portion. Has curvatura minor and curvatura major.
The outlet (sphincters) of the stomach, located ventrally.
Mucosa, submucosa, muscle (longitudinal, circular, oblique), and serosa (peritoneum).
Parietal (facing the diaphragm and liver)
Visceral (facing other organs).
Greater omentum (superficial and deep leaf)
Lesser omentum
Gastrosplenic ligament
Hepatogastric ligament.
Foreign objects
Ulcer disease and bleeding
Necrosis
Tumours
Stomach dilatation
GDV.
What are examples of stomach surgeries?
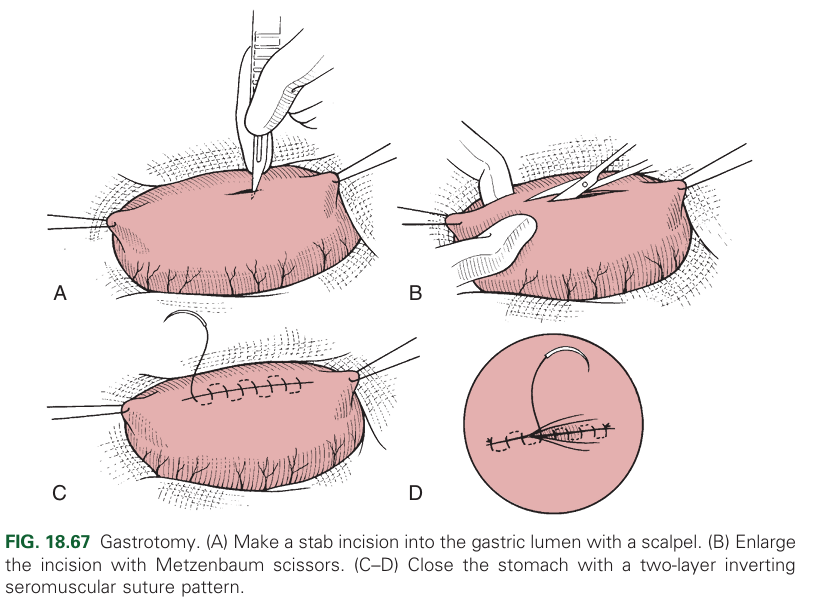
Gastrotomy
Gastrostomy
Gastrectomy
Gastropexy
Billroth I
Billroth II
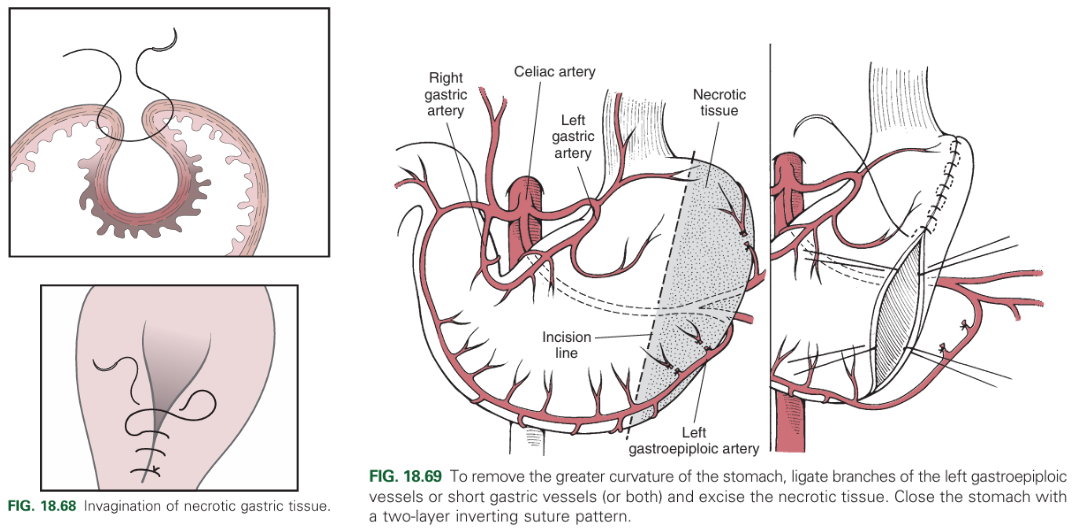
Partial resection of a portion of the stomach. Can be done by invagination or resection.
Circumcostal
Belt-loop
Incision
Laparoscopic.
What is a circumcostal gastropexy?
Seromuscular flap that is pulled & fixed behind 11th/12th rib
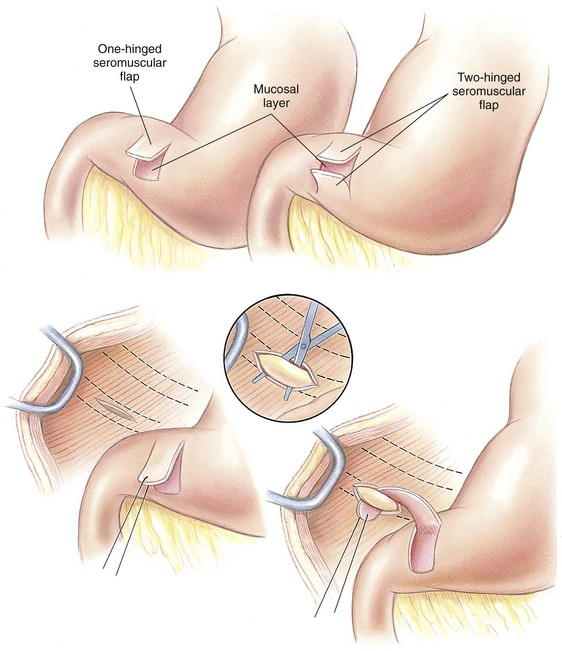
What is a belt-loop gastropexy?
Seromuscular flap pulled through abdominal wall muscle layer & fixed
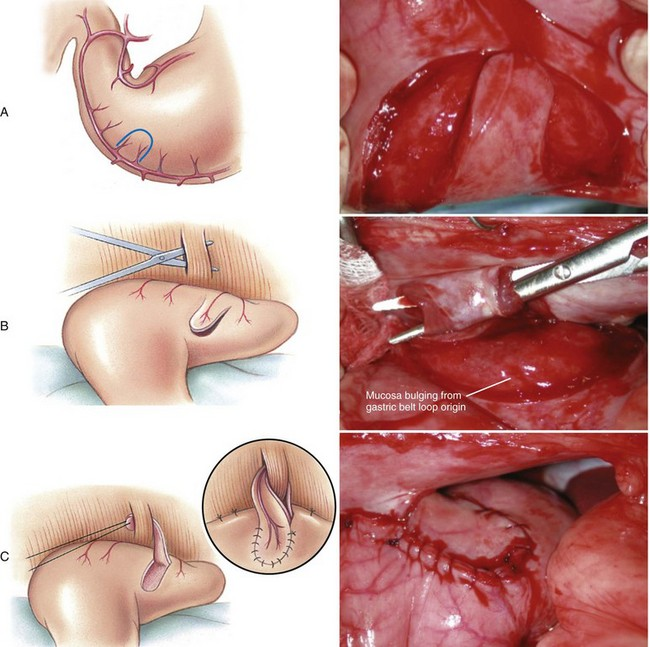
What is an incision gastropexy?
Incision of pyloric antrum & peritoneum w/ muscle -apposition- suture
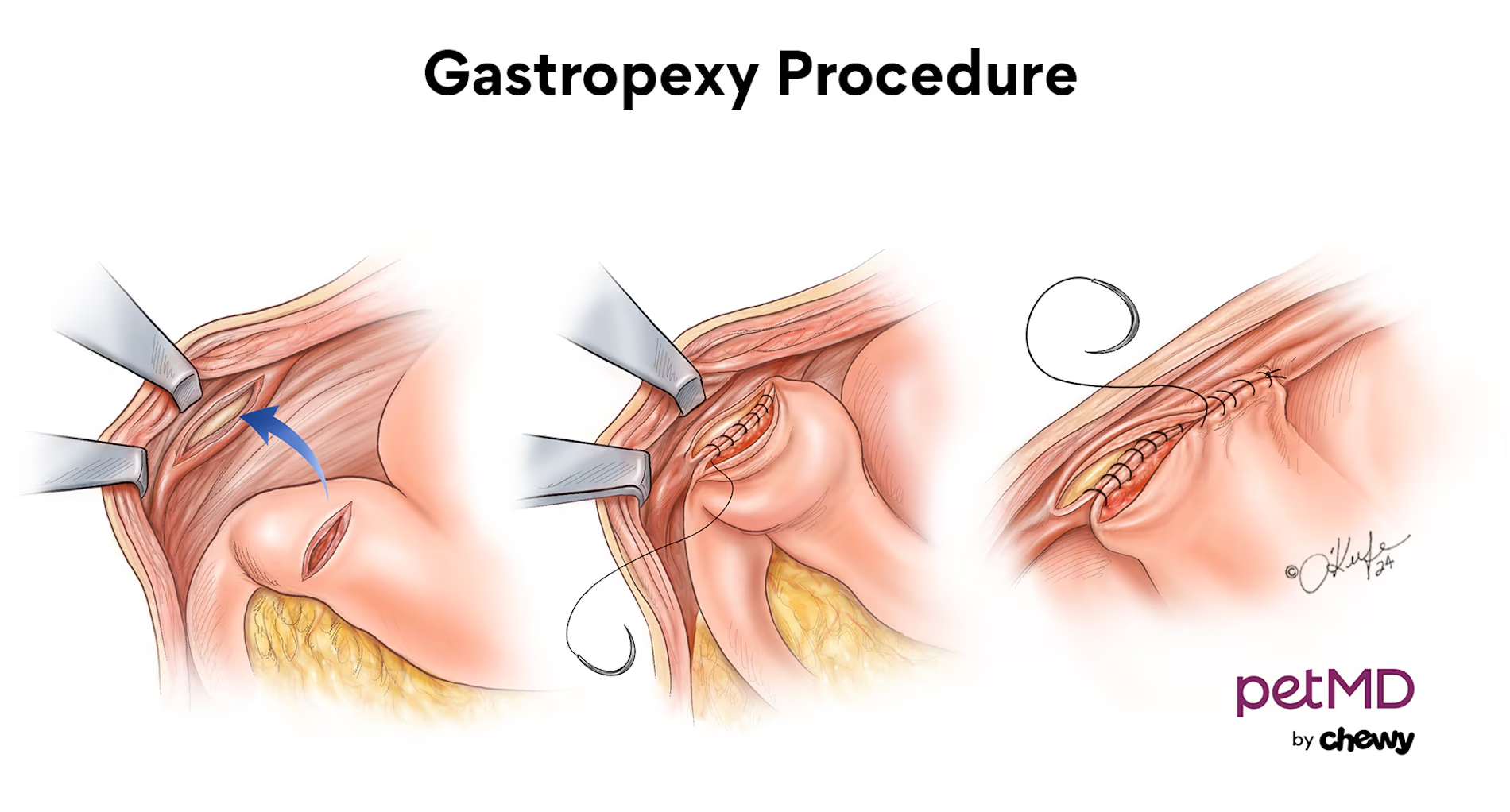
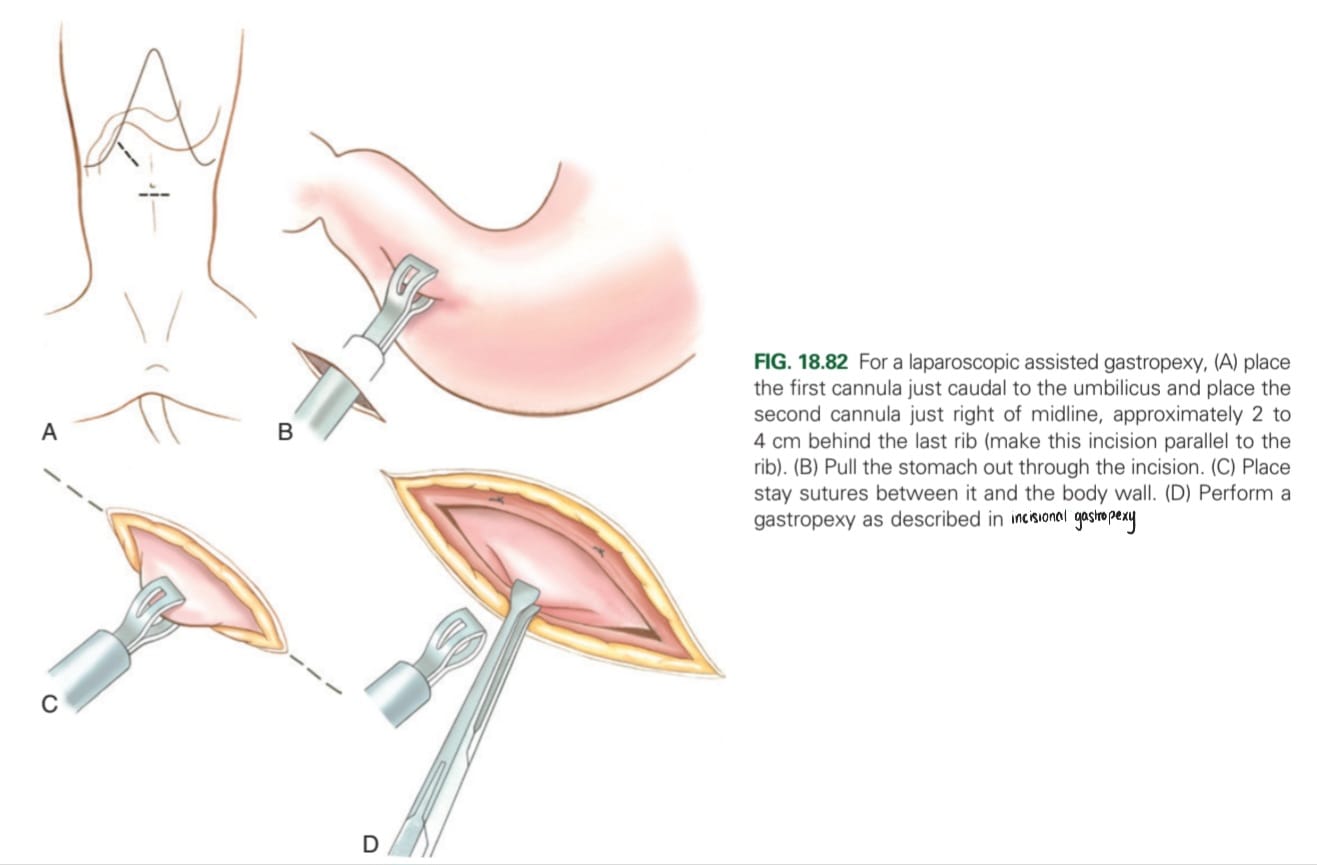
When is a laparoscopy gastropexy carried out?
Prevention
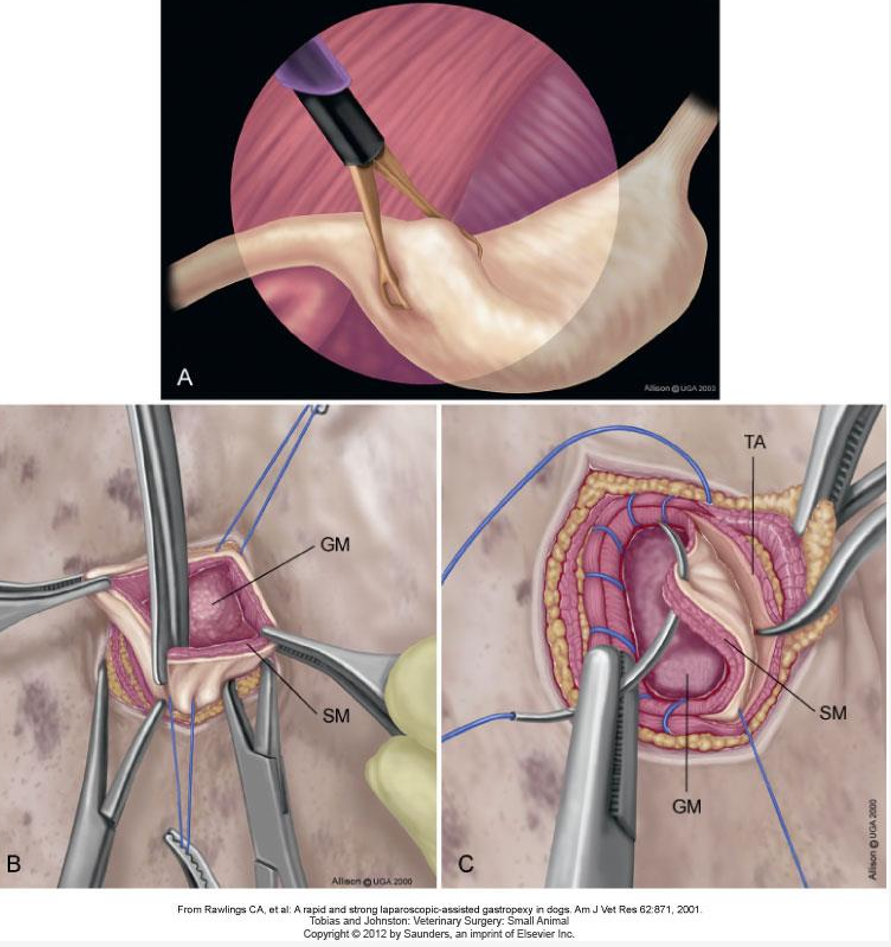
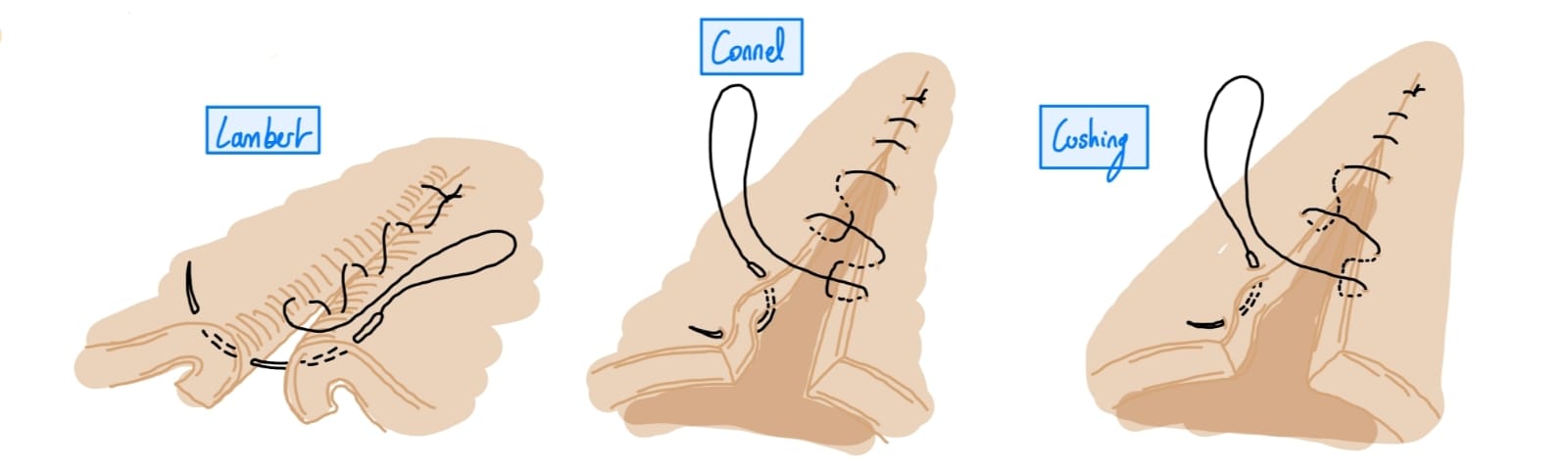
With 2-0 to 3-0 absorbable sutures in two layers using a sero-muscular pattern
1st layer: Cushings, Connell, or simple continuous for muscularis, submucosa
2nd layer: Lambert or Cushing for serosa and muscularis).
What are the surgical approaches for laparoscopy?
Paracostal or midline.
External oblique abdominal muscle
Internal oblique abdominal muscle
Transverse abdominal muscle
Linea alba (sits between rectus abdominis)
1st stage: Dilatation (bloat)
2nd stage: Volvulus (twisting of the stomach so entrance and exit of stomach become blocked → progressive dilatation).
Blockage of the stomach entrance and exit, progressive dilatation
Pressure on the diaphragm (dyspnoea)
Compromised circulation ( → shock)
Potential trapping of the spleen.
What is the treatment for GDV?
Stabilisation (fluid therapy [crystalloids], antibiotics, and oxygen therapy).
Gastric decompression
Surgery
Passage of a stomach tube/gastroscopy.
Percutaneous decompression with catheters or trocars
Gastrotomy
Inspection of the stomach and spleen. remove damaged or necrotic tissues
Decompression and correction of malpositioning
Gastropexy to prevent subsequent malpositioning
What is the aetiology of a pericardioperitoneal hernia?
Congenital anomaly with the failure of development or pre-natal injury of septum transversum (thick plate of mesodermal tissue) → formation of thin diaphragmatic tissue, which easily ruptures, allowing herniation of abdominal viscera into pericardial sac
What are clinical signs of pericardialperitoneal hernia
Ascites, muffled heart sounds, murmurs, dyspnoea, shock, pneumothorax, peritonitis (often as a complication)
How are pericardioperitoneal hernias diagnosed?
CS, history, physical exam, X-ray of heart and thorax, USG
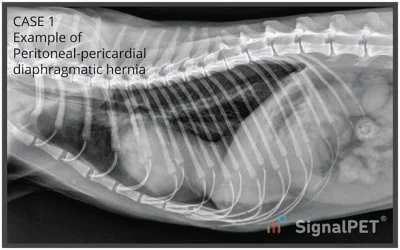
How are pericardioperitoneal hernias treated?
Dyspnoea: oxygen, sternal position, all 4 limbs elevated
Shock: fluids, ATB (if septic or as prophylaxis)
Surgery: ventral incision through the sternum - close defect in the diaphragm and remove air from pleural cavity and pericardial sac - repair sternal and abdominal wall defects
Adenocarcinoma (most common)
Adenoma (polyps)
Leiomyoma (polyps)
Malignant lymphoma
Carcinoma.
What should be done if a dog with GDV comes into the clinic?
Stabilise (ABC, IV fluids, administration of ATB, CCS, O2 mask)
Gastric decompression (Gastric tube, per cutaneous, gastrotomy)
Surgery (Gastropexy)
What type of laparotomy will be carried out in the case of GDV?
Cranial ventral laparotomy
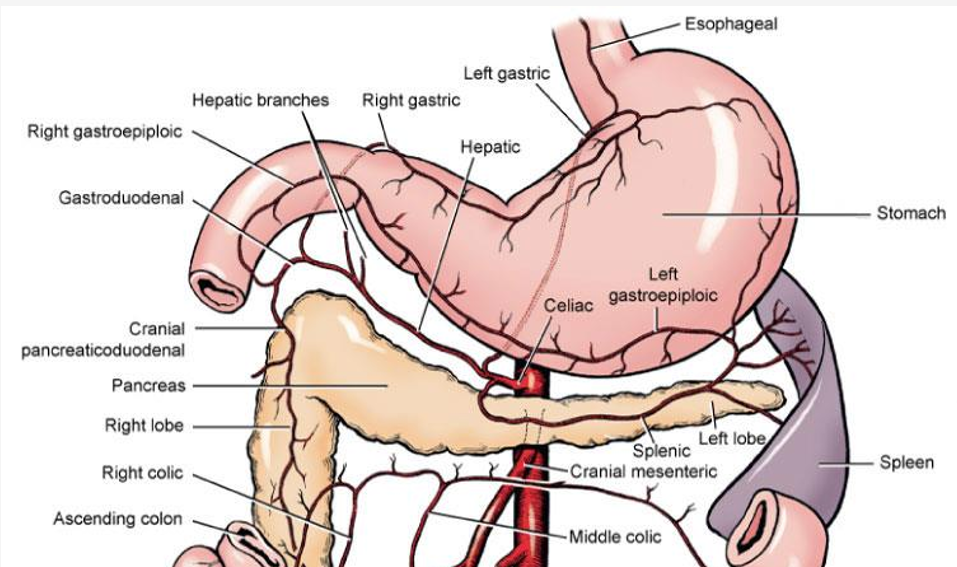
Which veins are important to avoid when opening the stomach?
Right and left gastric arteries
Left gastroepiploic artery
What breeds are predisposed to GDV, and when does it occur?
Large, deep chested breeds
Exercise after eating
Which surgery is used to prevent GDV?
Gastropexy (between pyloric antrum and right abdominal wall [11-12th rib])
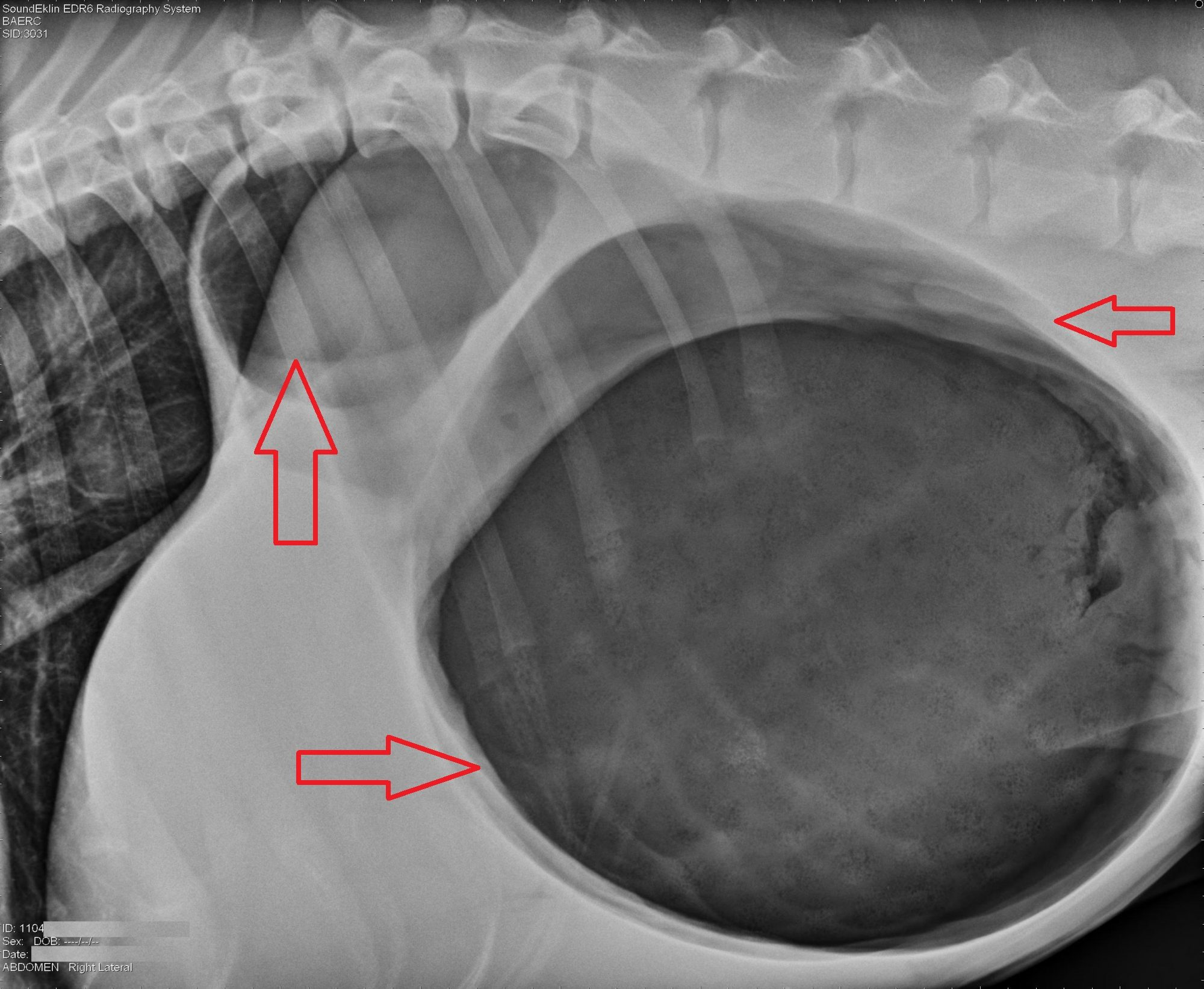
What can be seen on x-rays in the case of GDV?
Distension of the stomach with gas (black)
What is gastroscopy for in the case of GDV?
Gastric decompression