propedeutics small animals- locomotor/musculoskeletal system exploration
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1. standing inspection
2. dynamic observation
3. standing palpation
4. lateral decubitus exam
what 4 inspections must we include in our orthopedic exam?
-general condition
-head, neck, and spine position
-limb and joint alignment
-muscle contours (atrophy, tumors, myositis)
-weight support on the ground
conditions:
-on the floor
-quiet environment
-non slippery surfaces
-avoiding support on the owner or wall
what should we assess when performing a standing inspection of an animal?
in what conditions do we perform this exam?
60;40
when standing, an animal should support ____% of his weight with the forelimbs and _____% with its hindlimbs.
-spine deviations
-limb/joint asymmetries
-inflammation, fluid accumulation, tumors
-atrophy
-decreased weight bearing
what are the common abnormalities we can find when doing a standing inspection of an animal?
floor
is it better to perform a standing inspection of an animal on the floor or table?
-limping
-step shortening
-nail dragging
-circular movements
-displacement of the center of gravity
what abnormalities are we looking for when doing a dynamic observation of an animal?
pain in a forelimb
in a dynamic exam, we notice that an animal is lifting his head while stepping, what does this indicate?
its head will lower when it steps with that limb
how will an animal walk if it has pain in a hindlimb?
-with both hands
-proximal to distal and cranial to caudal
-bilaterally
it should be painless for the animal, no increased temperature, symmetric, and smooth
how do we perform a general palpation?
-look at the head, neck, and back position
-superficial and deep palpation (checking for pain)
-passive neck movements (checking mobility, pain, crackling)
how do we examine the spine?
inflammation of a joint
what is synovitis?
a crackling or rattling sound of a joint
what is crepitation?
the collateral ligaments of the elbow
what does the campbell test evaluate?
superficial layer of the bone (periosteum) becomes painfully inflamed in YOUNG animals (while it is still growing)
what is panosteitis?
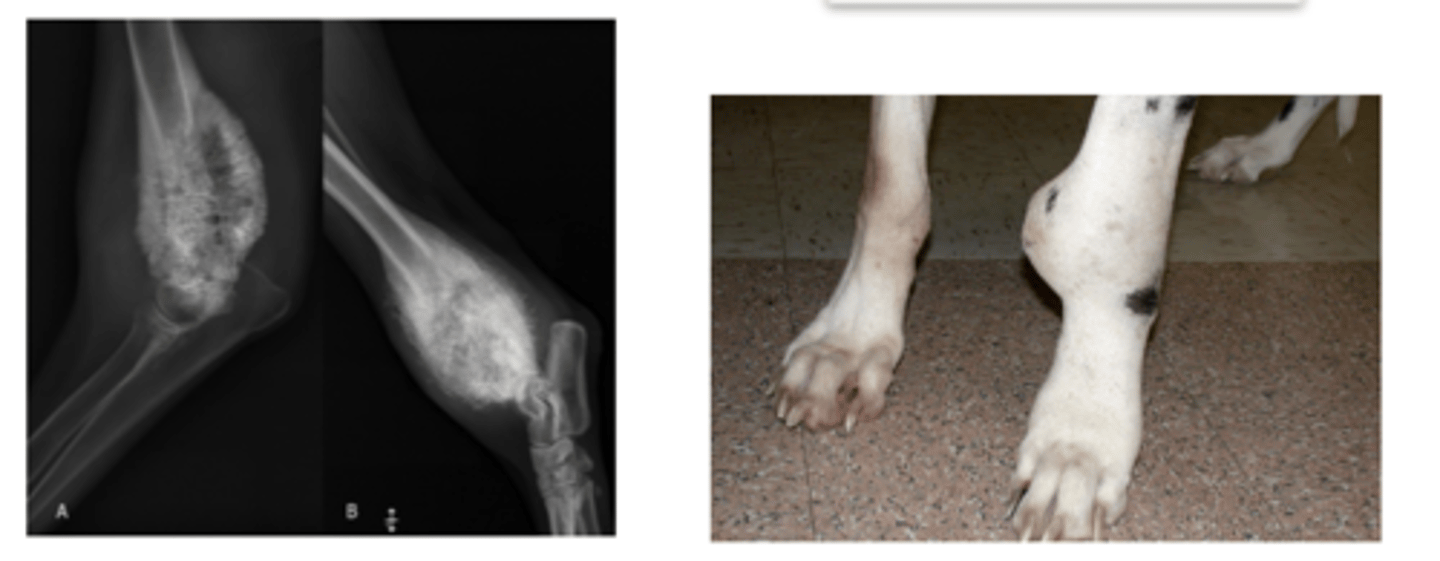
osteosarcoma
what is this called?
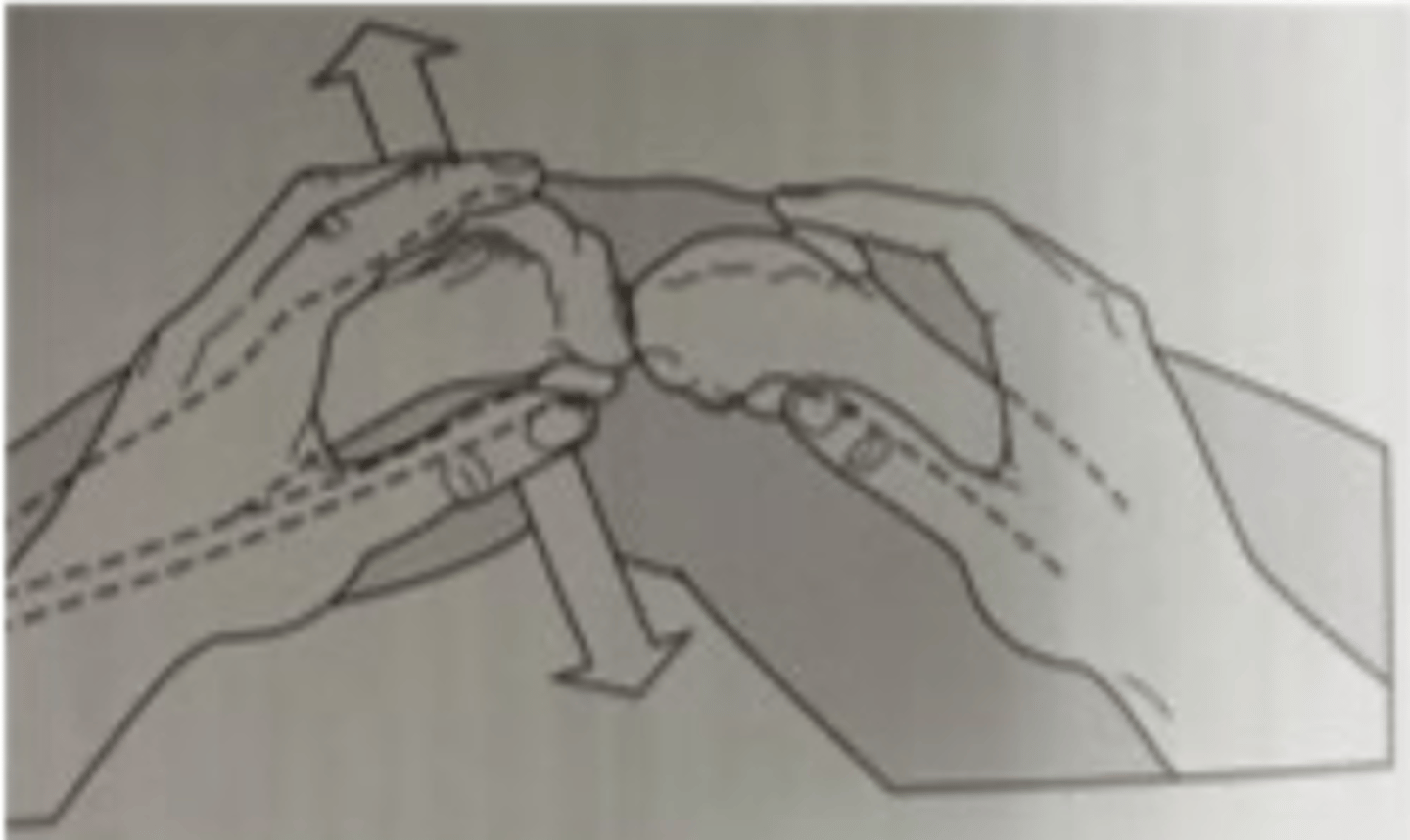
it is used to check for hip dysplasia.
we have one hand on the sacral region, and the other on the greater trochanter of the femur. we apply a dorsal pressure of the femur until we hear a "click" and abduct until we hear a second "click" (this is when the femur head reenters the acetabulum)
what is the ortolani test?
patella luxation (the ability of the patella to pop out of place).
this is measured from degree I to IV.
anterior cruciate ligament (with the drawer test)
when evaluating the knee, we check for...
small
medial luxation of the patella is common in ______ breeds (small/large)
large
lateral luxation of the patella is common in ______ breeds (small/large)
campbell test
what is the test for checking the collateral ligaments of the elbow?
for testing the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. we try to move the tibia cranially and caudally while holding the femur in place. if the ligament is ruptured, we can displace the tibia.
what is the drawer test?
drawer test
anterior cruciate ligament of the knee
what test is being performed? what is evaluated?
tibial compression test
drawer test
what test is performed to evaluate the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee?
for evaluating the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. we flex and extend the tarsus with one hand and hold the femur in place, if the tibia displaces cranially, there is a rupture of the ligament
what is the tibial compression test?
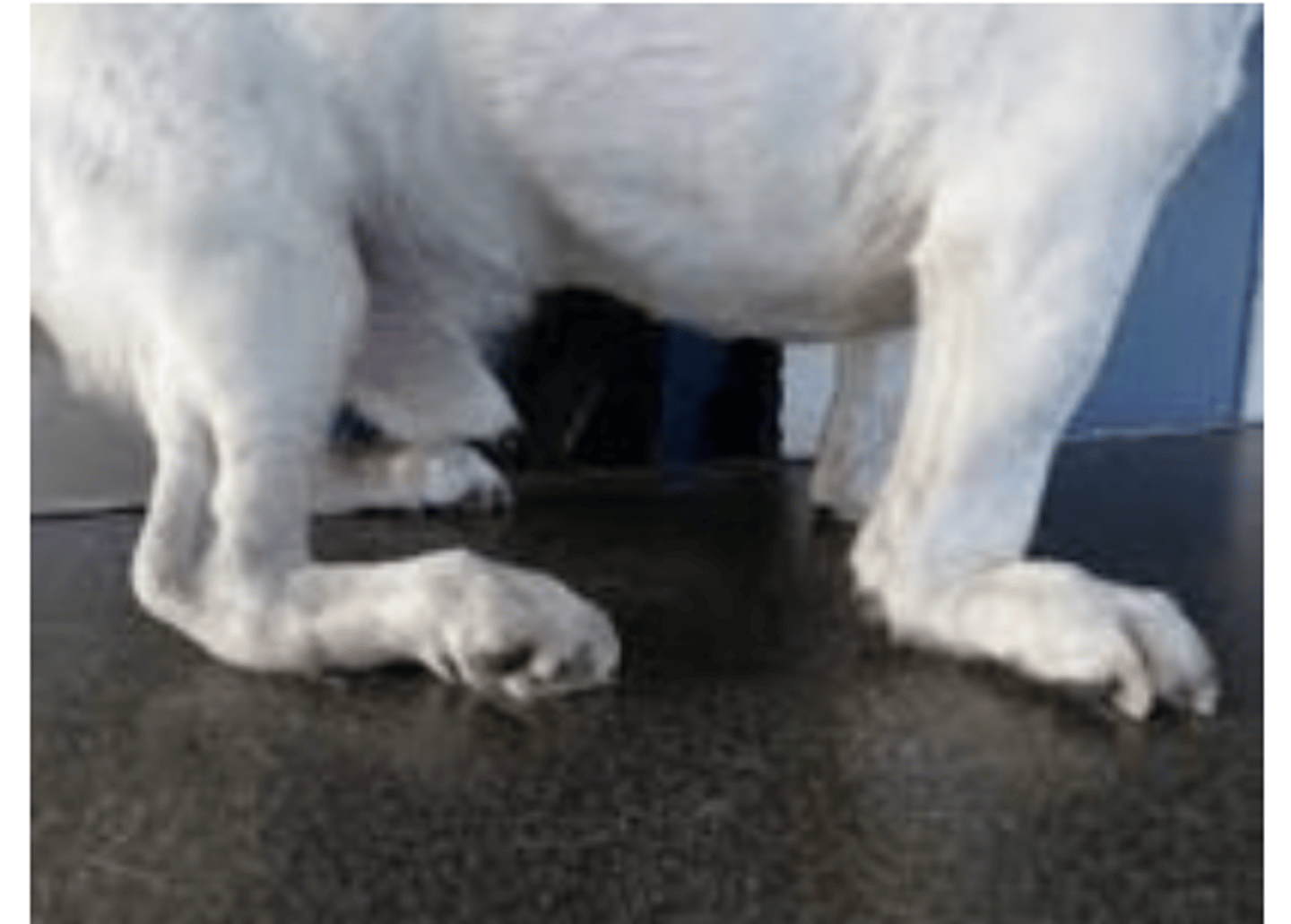
tarsal hyperextension
what is this called?
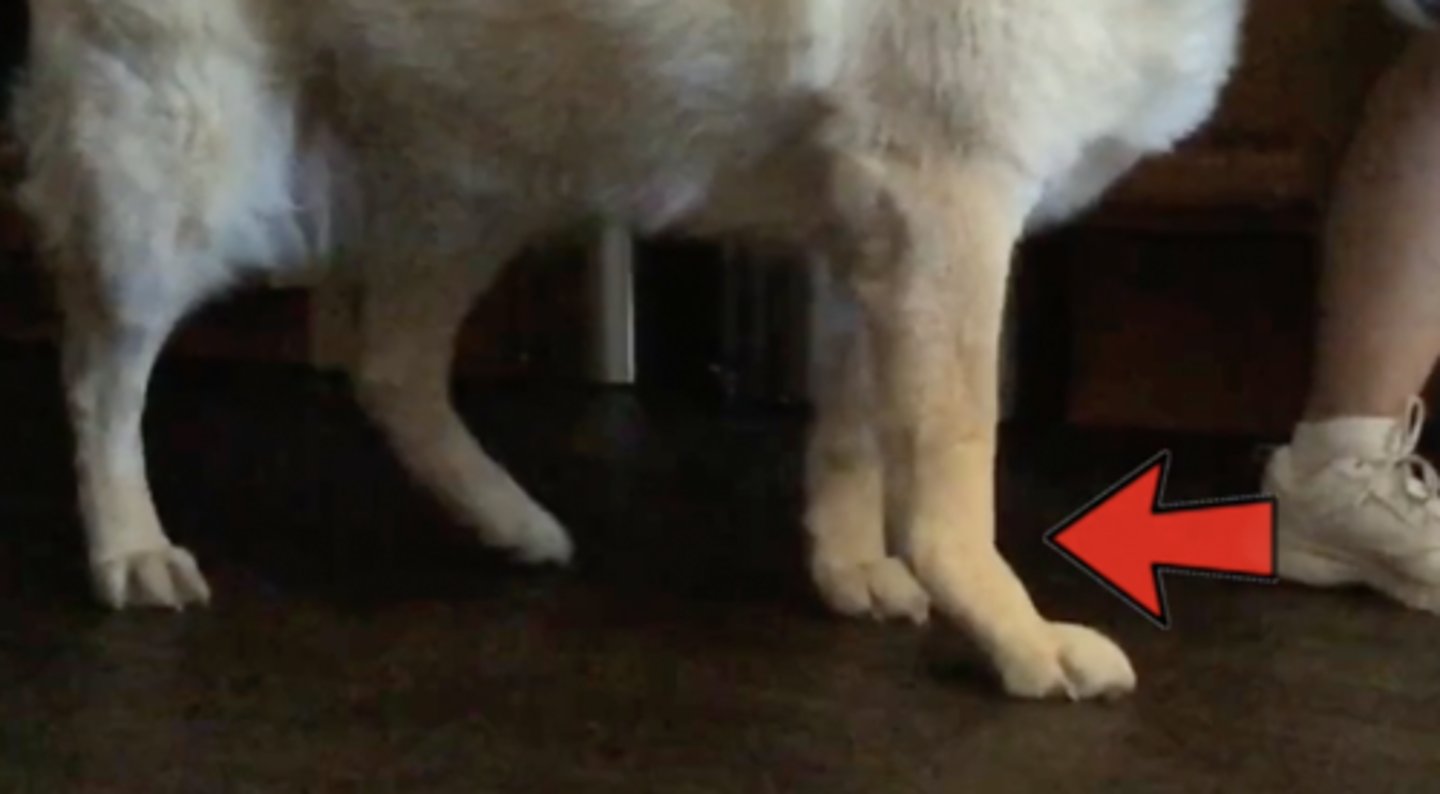

tarsal hyperextension
what is this called?

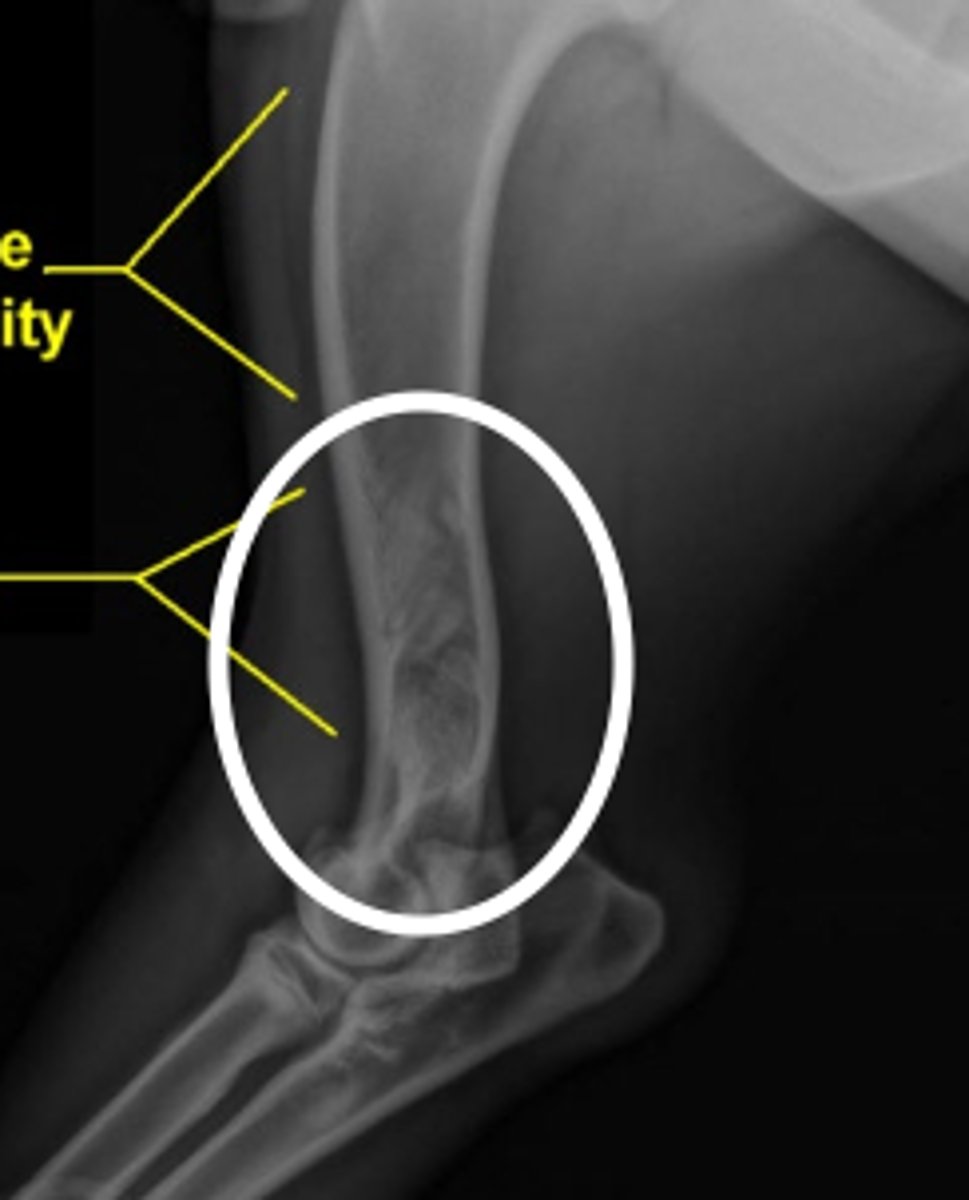
panosteitis
what is the problem here?
a procedure that is performed to obtain synovial fluid from within a joint capsule
what is arthrocentesis?