PSY 336 FINAL STUDY GUIDE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:51 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
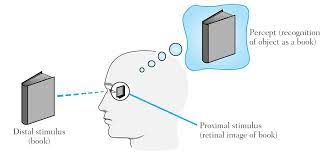
Distal Stimulus
the object/event that can actually exist in the world (Ex: the tree or beeping of your phone)
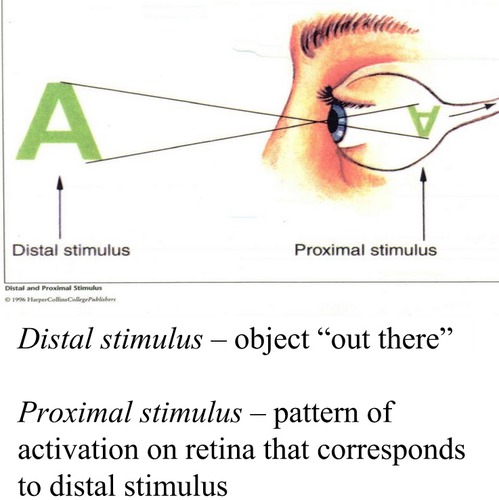
2
New cards
Proximal Stimulus
the physical phenomenon evoked by a distal stimulus that impinges on the specialized cells of the relevant sense.(What activates neurotransmitters, light photons, sound waves, etc. Ex: the reflected light or sound wave. )
3
New cards
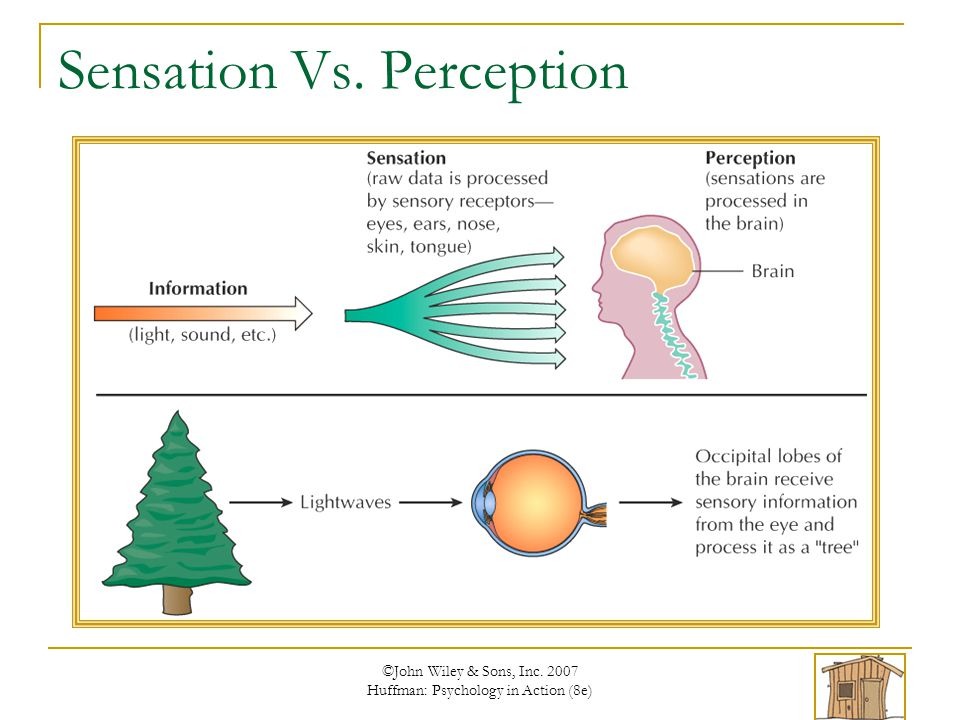
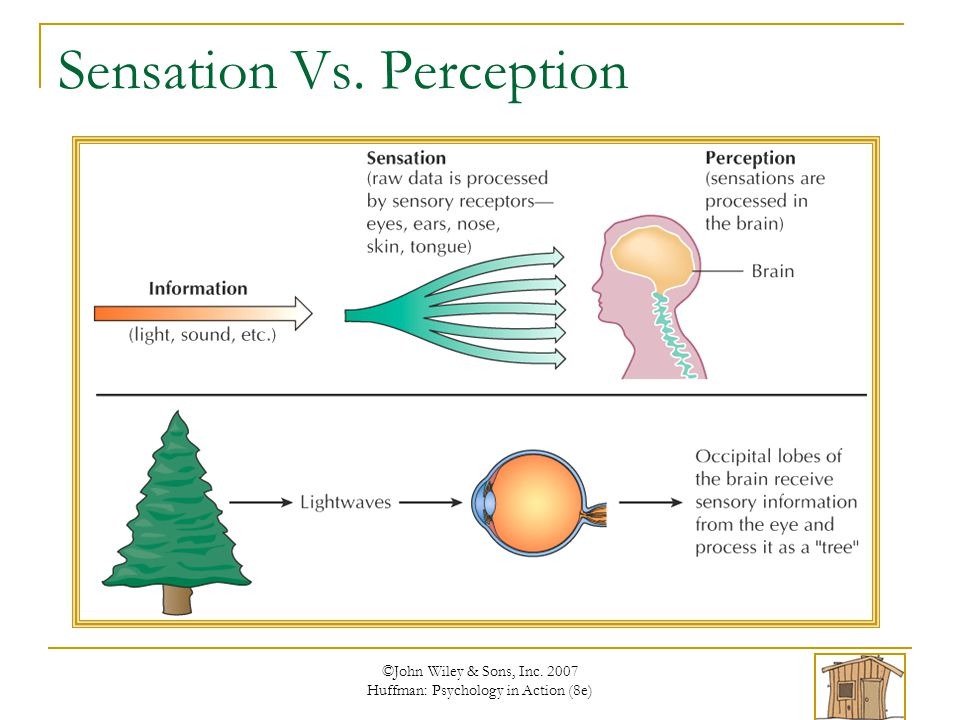
Sensation
Direct measure of some aspect of the environment. Allows you to respond to the world. Measures some property of the external world (Physical Stim)
4
New cards
Perception
Something from the world & our brain reacts to it. (Reflex; How your brain interprets the stimulus)
5
New cards
Absolute Threshold
Minimal intensity to detect a stimulus. Defined as the stimulus intensity leading to a 50/50 balance between "yes" & "no" responses.

6
New cards
Resting Potential
Neuron potential when not firing (-70 mV, 70 less than outside)

7
New cards
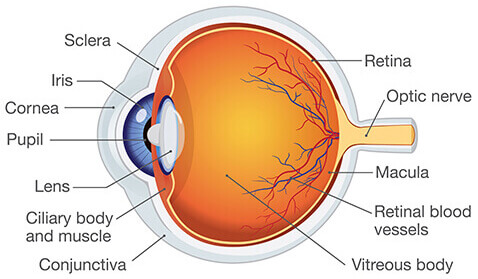
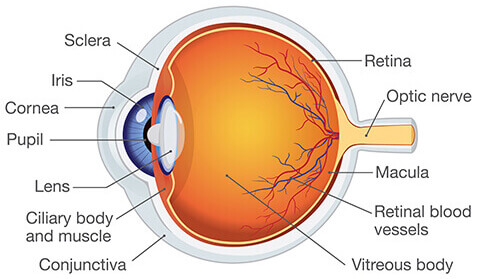
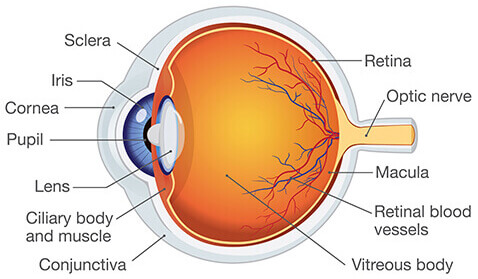
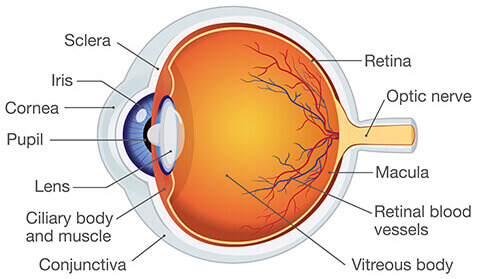
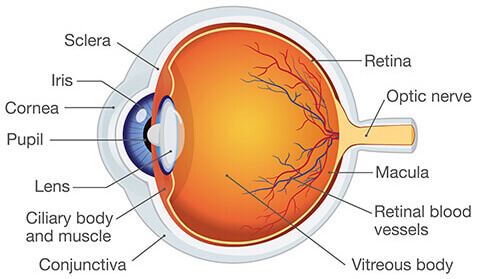
Eye Anatomy
Know Retina, Lens, Fovea, Optic Nerve, and Visual Pathway
8
New cards
Retina
Holds photoreceptors
9
New cards
Lens
Bends to refract light to retina
10
New cards
Fovea
Lots of cones, high acuity.
11
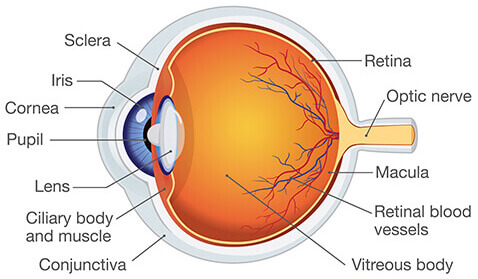
New cards
Optic Nerve
Blindspot where it goes in.
12
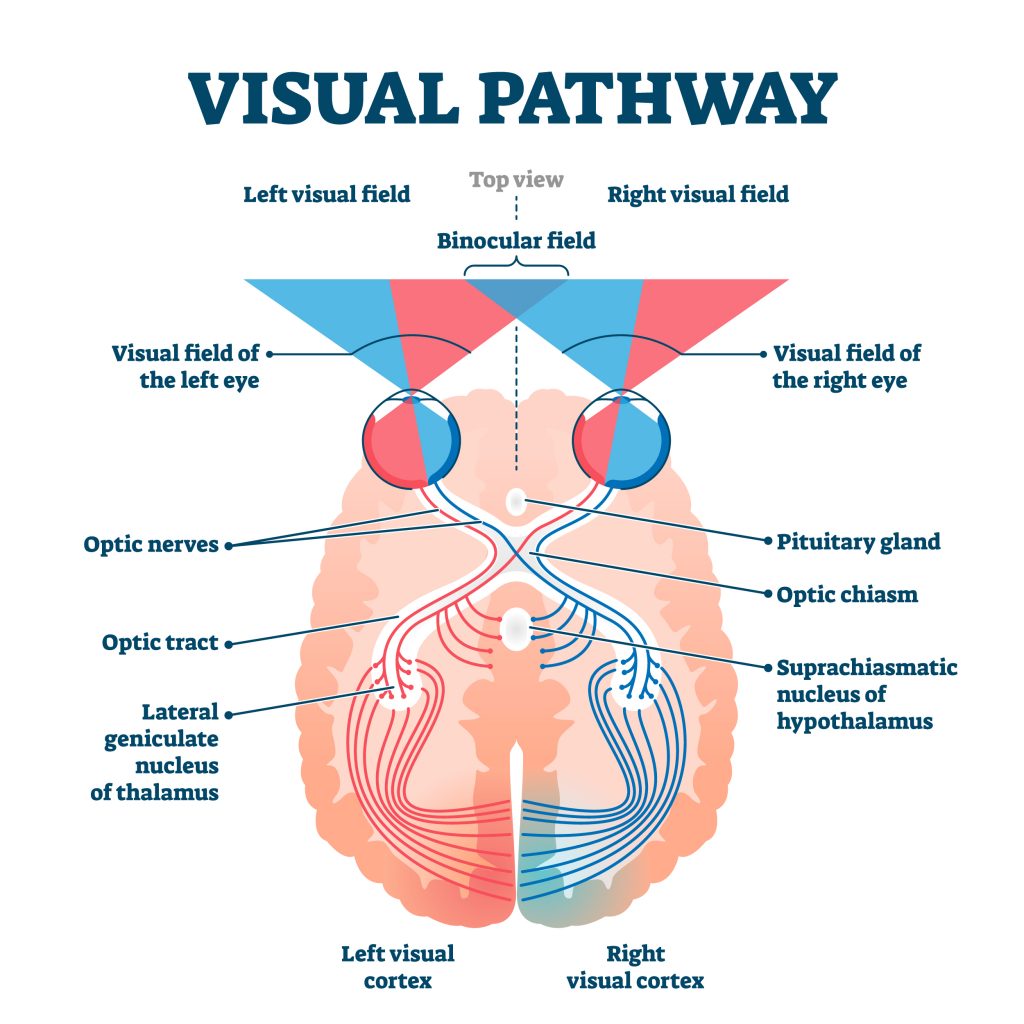
New cards
Visual Pathway
Left hits right retina, crossing over, etc.
13
New cards
Functional Specialization
Areas specialize in what they process. Specific to senses.
14
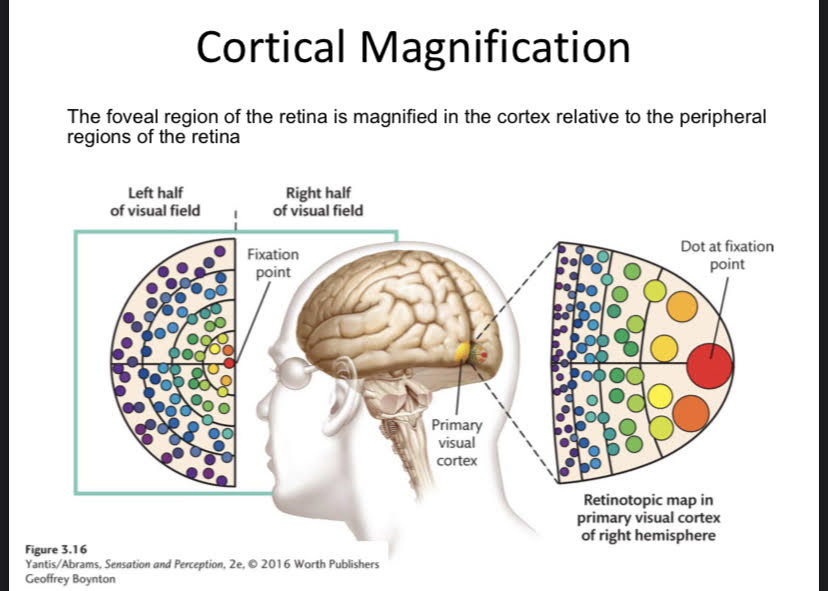
New cards
Cortical Magnification in V1
More space dedicated to foveal RF. The foveal region of the retina is magnified in the cortex relative to the peripheral regions of the retina.
15
New cards
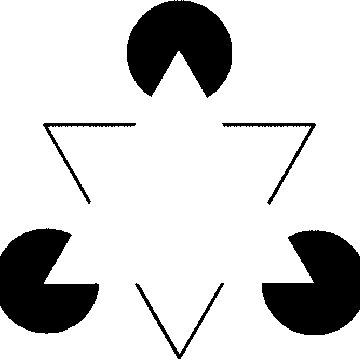
Perceptual Interpolation
Edges and surfaces assumed to perceive objects as whole.
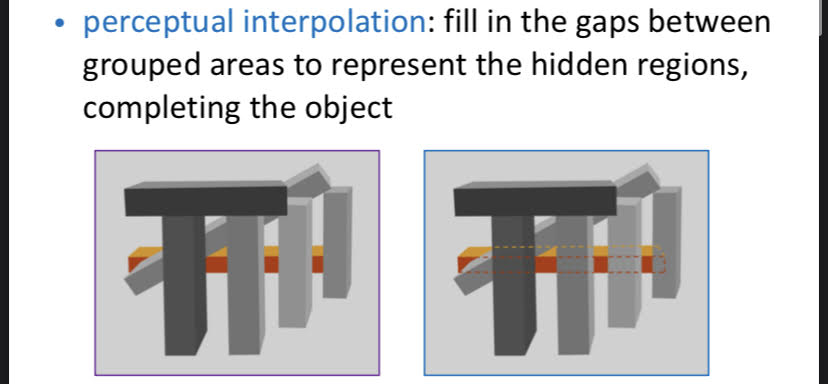
16
New cards
Border Ownership
Assume the border belongs to only one object in our visual field.
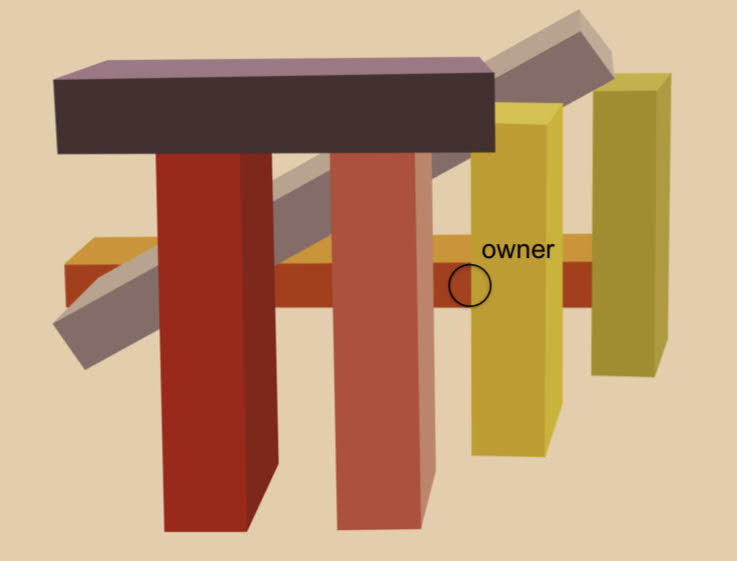
17
New cards
Grandmother Cell
Cell dedicated to grandmother recognition.
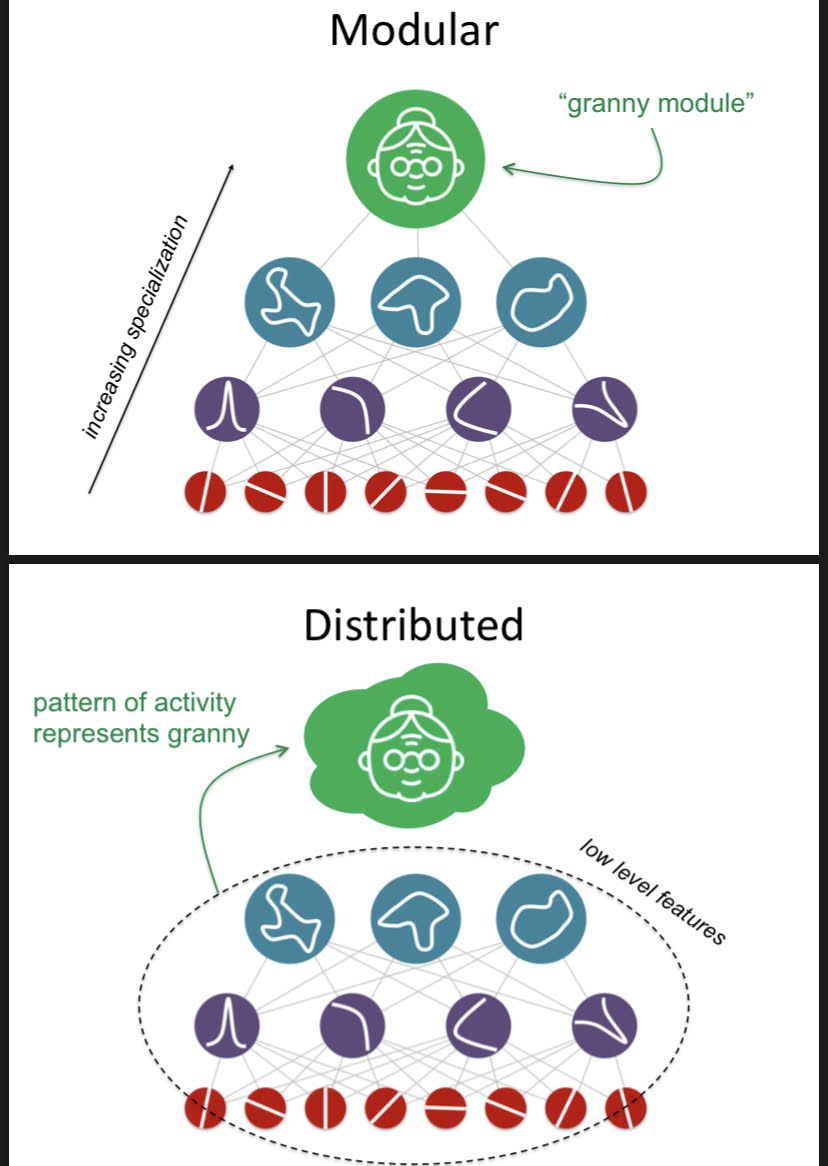
18
New cards
Photopigment Bleaching
When a photopigment absorbs a photon, it takes a bit of time before it’s ready to absorb a new one.
\
Cell runs out of chemicals to send. Can't send signals, stop seeing color. Stare at bright red light, stare at white screen, green. Causes Afterimage.
\
Cell runs out of chemicals to send. Can't send signals, stop seeing color. Stare at bright red light, stare at white screen, green. Causes Afterimage.

19
New cards
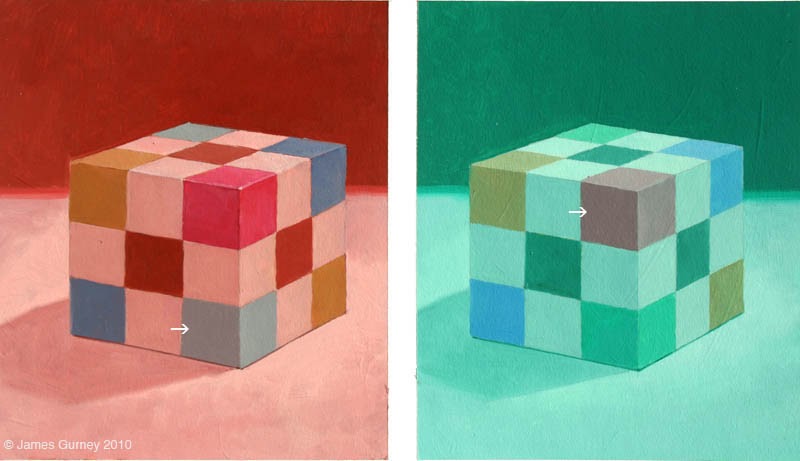
Color Constancy
"We take cues from our surroundings to perceive color." Observed light is the product of the SPD (spectral power distribution) of the illumination & reflectance of the object.
20
New cards
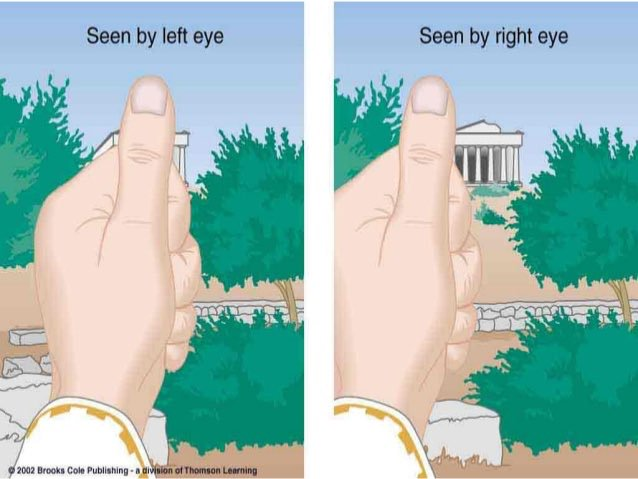
Binocular Disparity
Difference in the relative positions of objects in the retinal images of the two eyes.
21
New cards
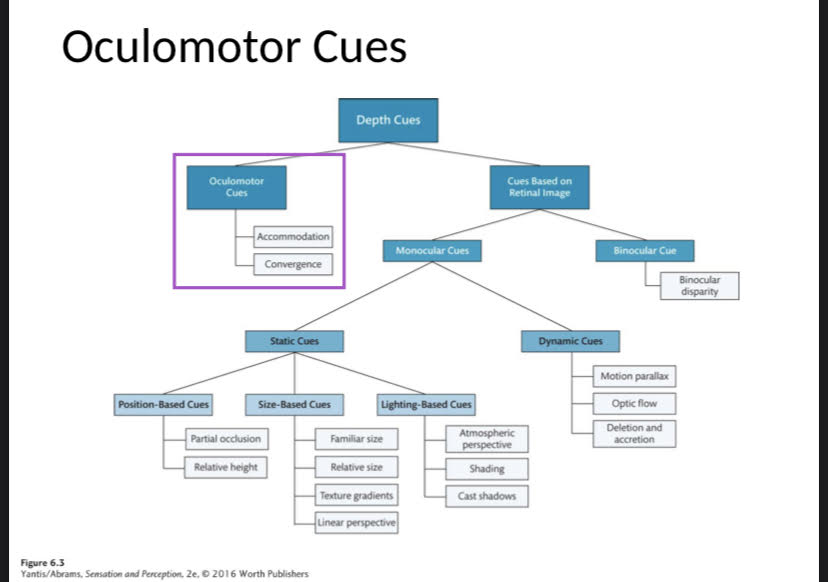
Oculomotor Cues
Feedback from muscles around and within the eye. Cues from eye movement. Include Accommodation and Convergence.
22
New cards
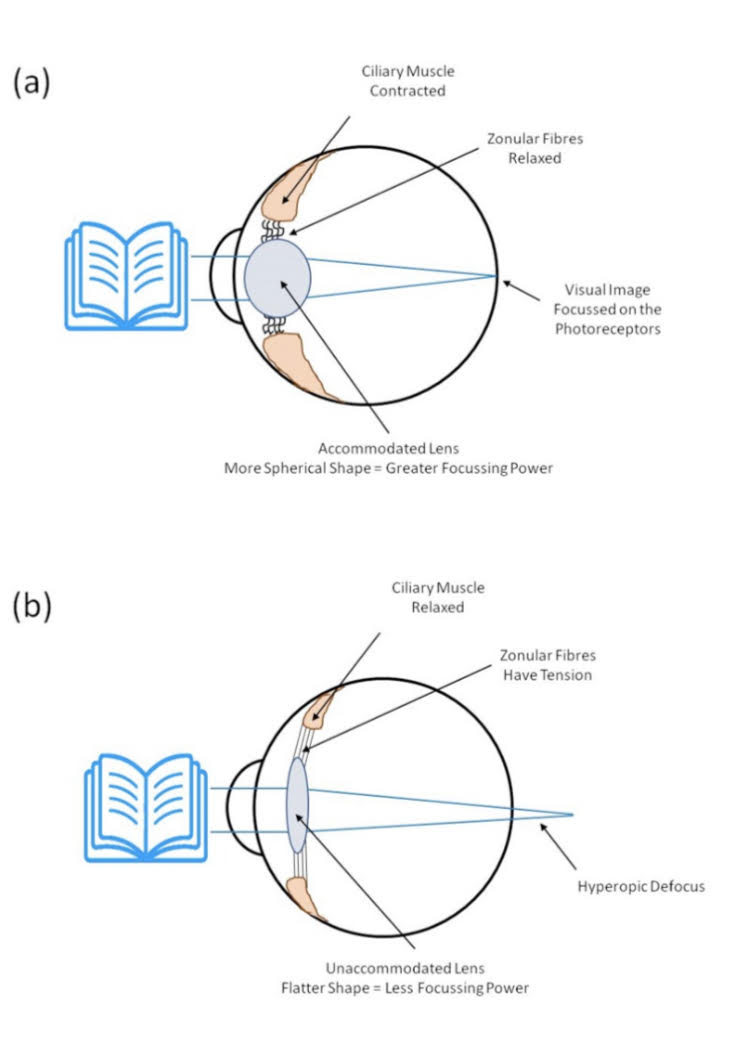
Accommodation
Relaxing (thinner lens, weaker focus, distant objects) and contracting (thicker lens, stronger focus, closer objects) the ciliary muscles changes the shape of the lens. Relays information for objects within about 2 meters.
23
New cards
Convergence
Eyes turn inward to keep objects in focus.

24
New cards
Deletion and Accretion
Objects are occluded (deleted) or revealed from behind occlusion (accreted). Specific distance where eyes do not cross.

25
New cards
Bimodal Neurons
Respond to TWO modalities (kinds of senses such as visual and tactile).
26
New cards
Motion Aftereffect
Cells get tired, perceive things spinning in one direction as spinning in the opposite.

27
New cards
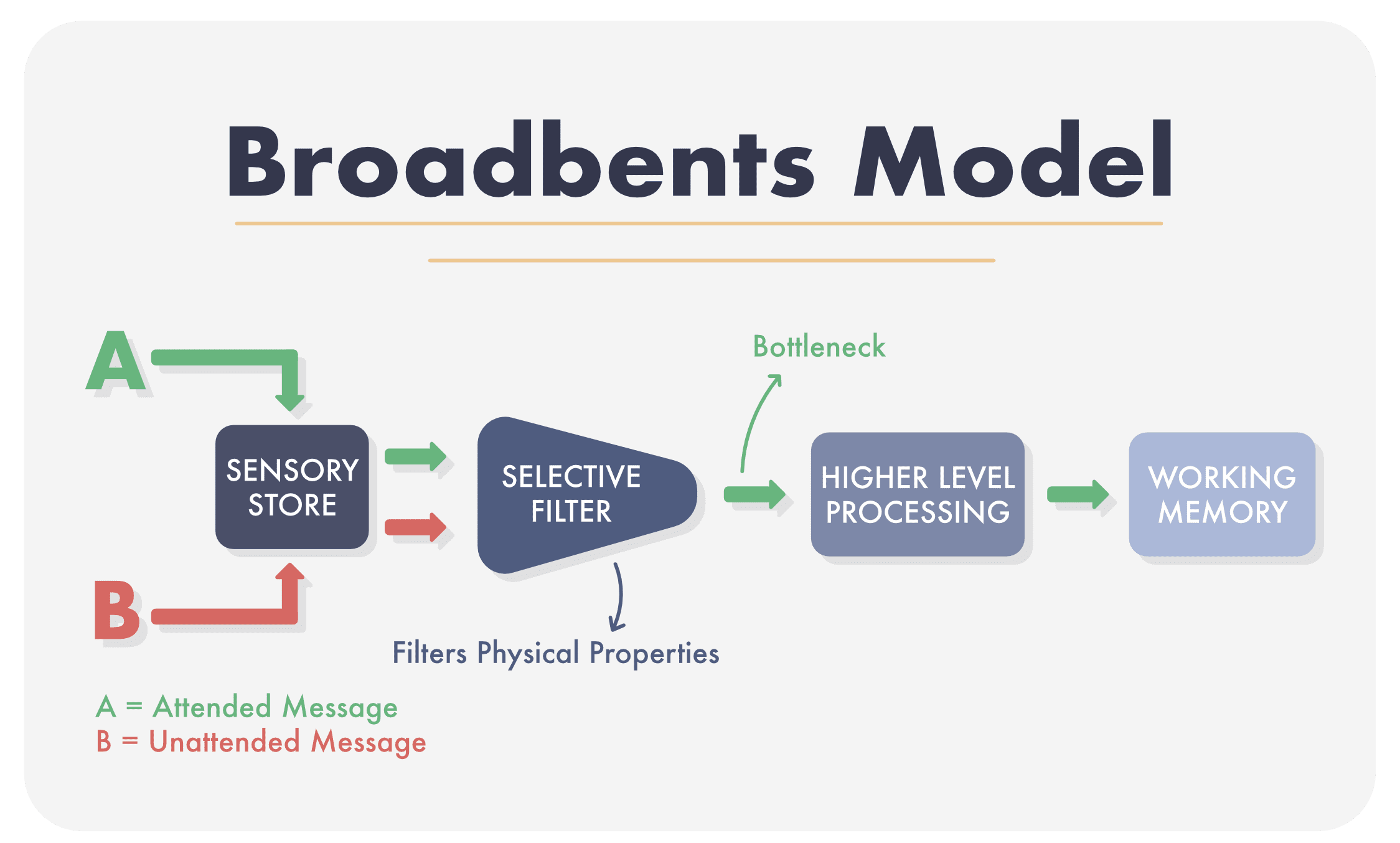
Broadbent's Filter Theory of Attention
"People do not process unattended stimuli beyond basic physical properties." States that Information is unavailable for later recall.
28
New cards
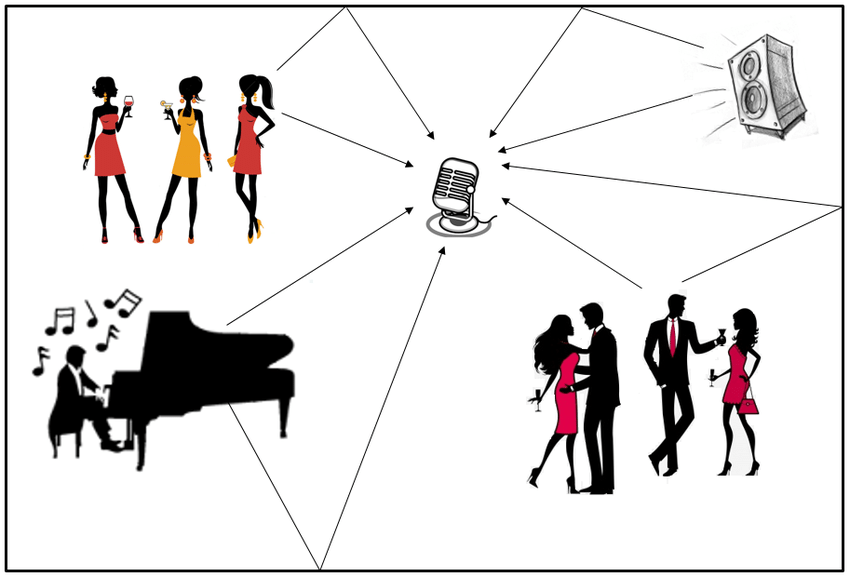
Cocktail Party Problem
Attend to and understand a single convo in a sea of noise. Other conversations are unattended.
29
New cards
Attention Cueing
Response time faster to the area that attention is allocated to.
30
New cards
Divided Attention
Ability to pay attention to more than one thing at once.

31
New cards
Top-Down vs Bottom-Up Attention
Top-Down Control: Voluntary attention, reflects deliberate conscious goals. “Goal-relevant stimuli.”
Bottom-Up Control: When low-level stimuli “capture” attention independent from the observer’s goals or intentions.
\n
\
Top down is effortful conscious focus (trying to take notes at mach 5). Bottom up is whatever grabs your attention against your will (a gunshot). Voluntary vs. Involuntary.
Bottom-Up Control: When low-level stimuli “capture” attention independent from the observer’s goals or intentions.
\n
\
Top down is effortful conscious focus (trying to take notes at mach 5). Bottom up is whatever grabs your attention against your will (a gunshot). Voluntary vs. Involuntary.
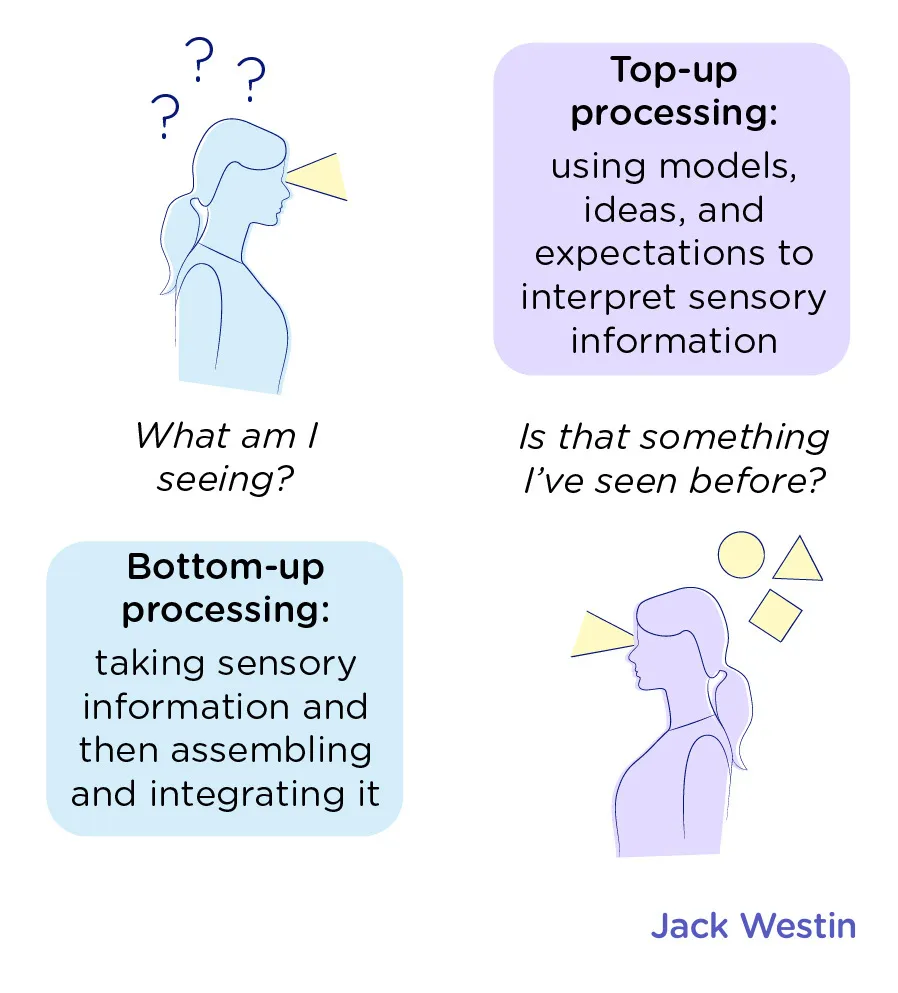
32
New cards
Loudness
Perception of how loud something is, amplitude. Physical pressure of sound.
33
New cards
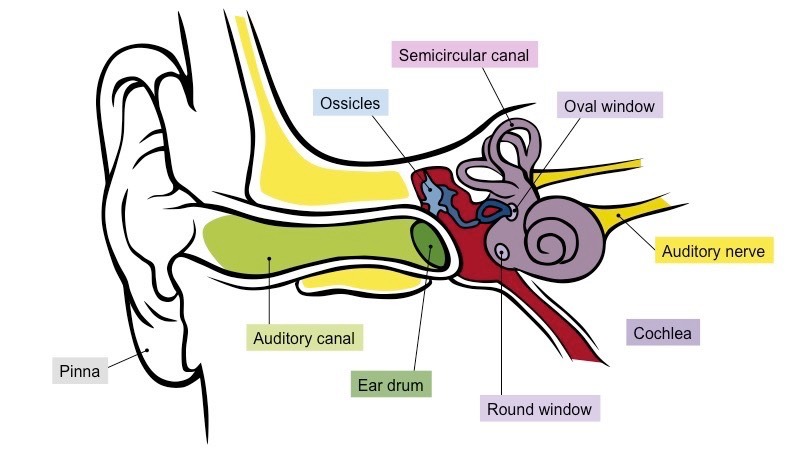
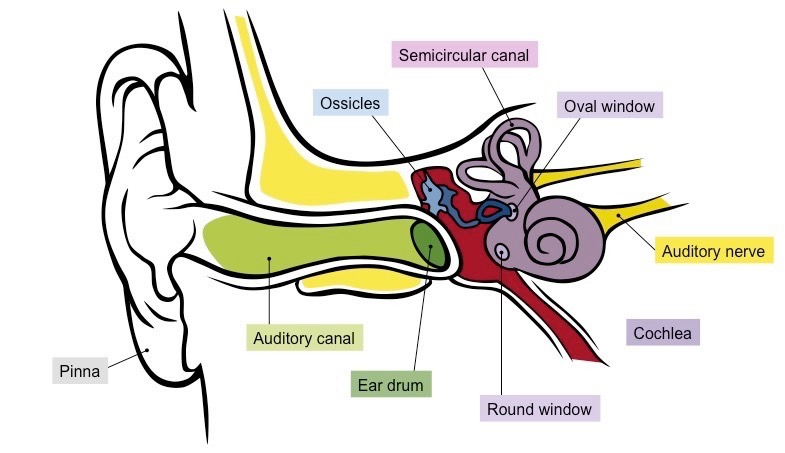
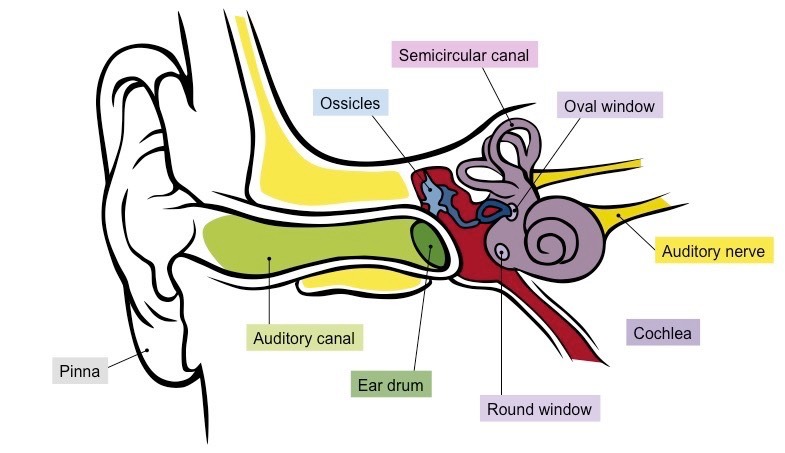
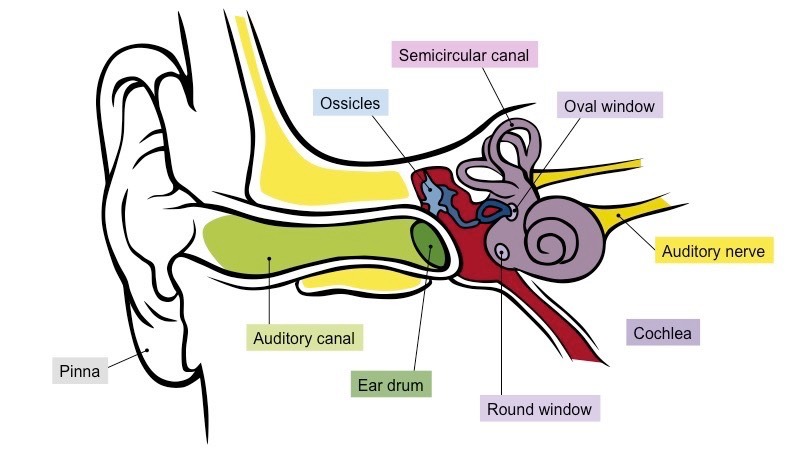
Ear Anatomy
Know Pinna and Cochlea
34
New cards
Pinna
Weird ear wiggle shape. Useful in perceiving elevation.
35
New cards
Cochlea
In the inner ear. Contains the organ of Corti, produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations.
36
New cards
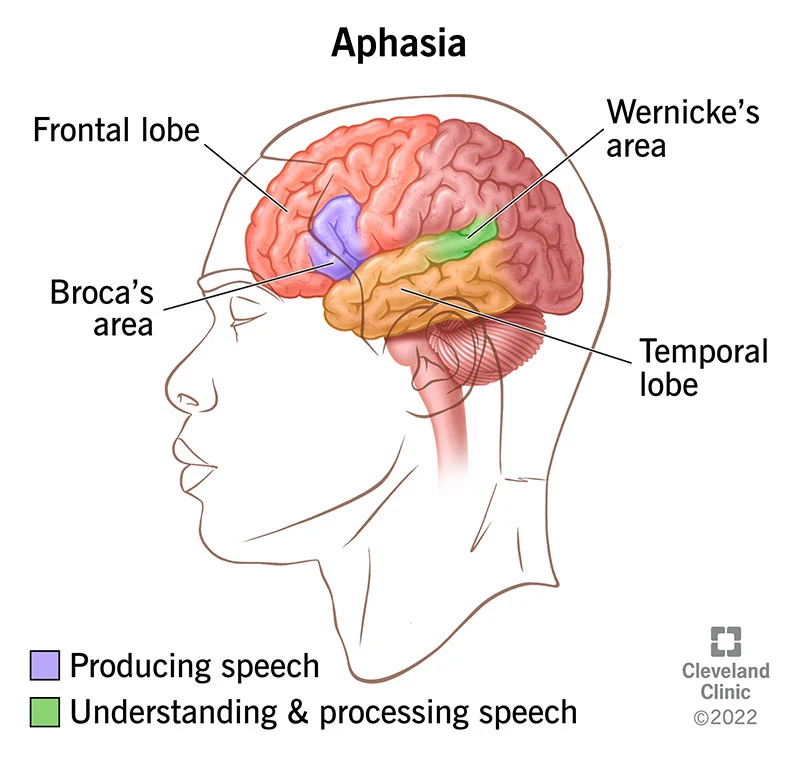
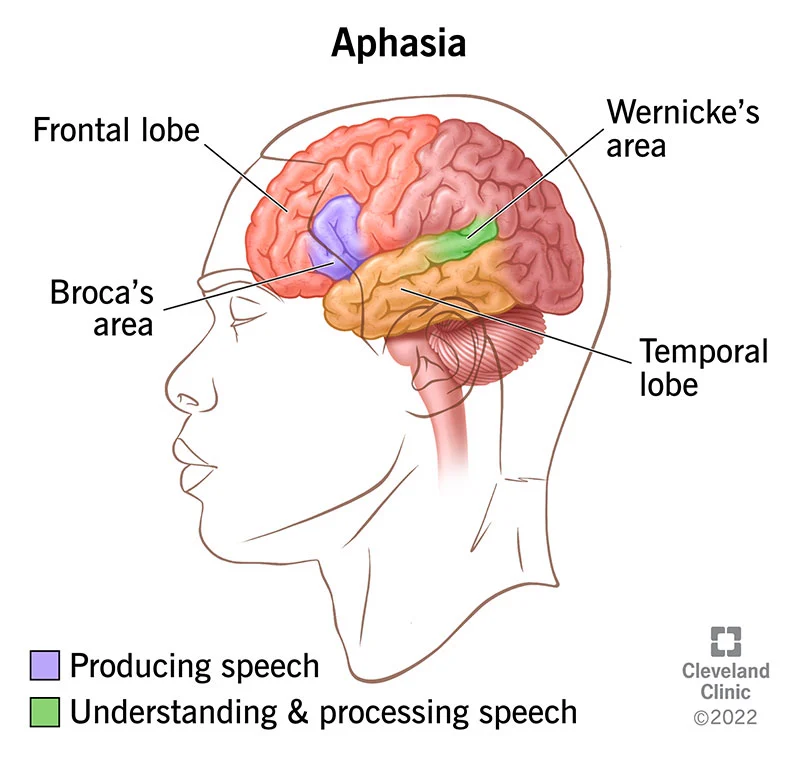
Aphasias
Broca's and Wernicke's
37
New cards
Broca's Aphasia
Frontal lobe damage, impaired production but intact comprehension. (If it’s Broca \[broke-a\], you can’t talk-a)
![Frontal lobe damage, impaired production but intact comprehension. (If it’s Broca \[broke-a\], you can’t talk-a)](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6af8545098ea46db91ce217a3cc23322.jpeg)
38
New cards
Wernicke's Aphasia
Near the temporal junction, impaired comprehension but intact production. Can't read either.
39
New cards
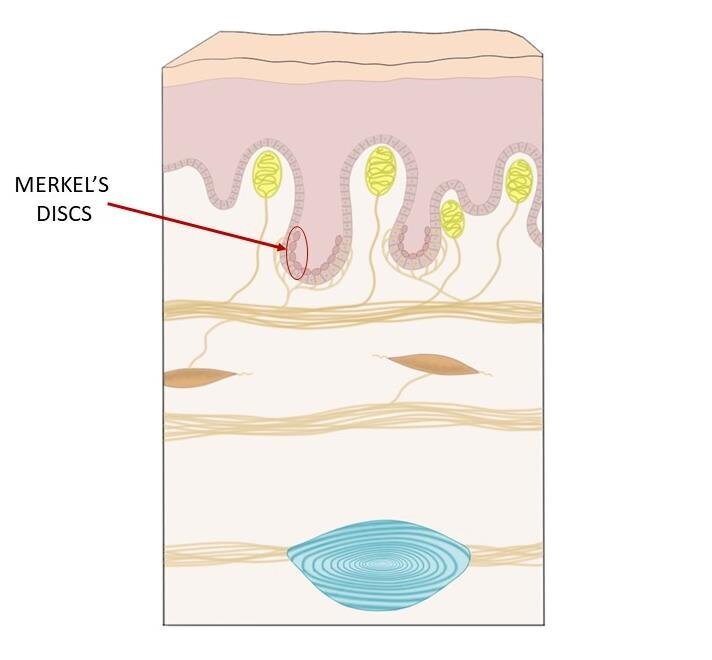
Merkel's Disks
Small RF, high tactile acuity. On fingertips, useful for feeling small textures.
40
New cards
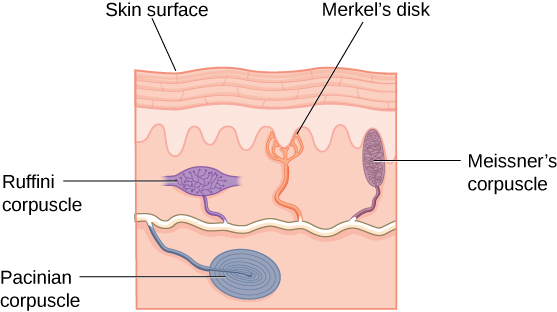
Pacinian Corpuscles
Deep pressure and vibration. Large RFs.
41
New cards
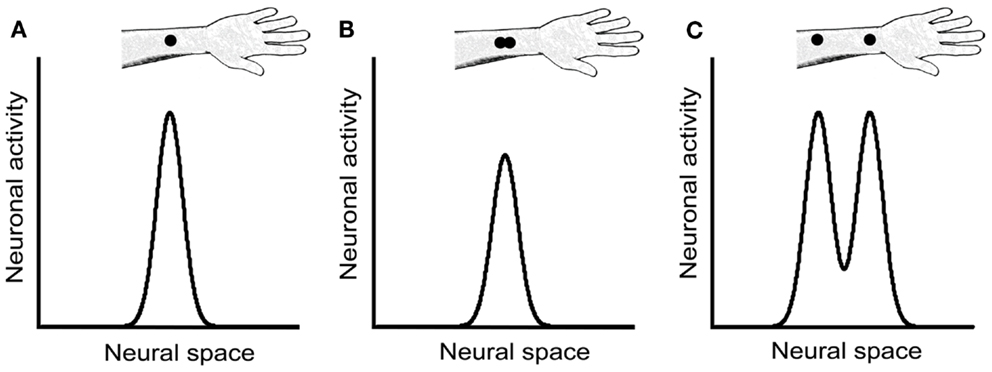
Two-Point Threshold
Smallest distance to be able to tell if 2 stimuli can be detected. Sensitive parts have higher acuity.
42
New cards
C-Tactile Mechanoreceptors
The Good Feels transmitters. Free nerve endings present only in hair skin, respond to slow gentle touch
43
New cards
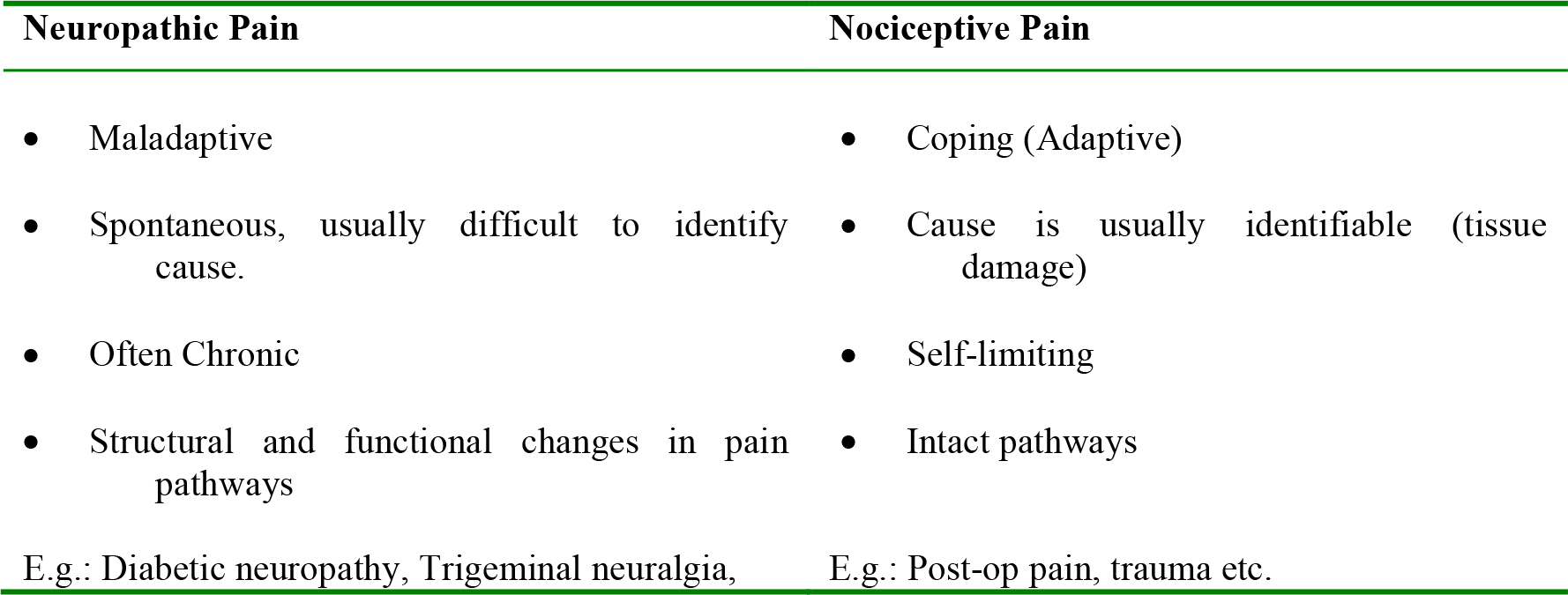
Neuropathic Pain
DMG to peripheral or central nervous system, causes pain in the areas that the nerve is normally linked to. (Arising from damage to the nervous system)
44
New cards
Thermoreceptors
Fire to sudden change in temp, fast
45
New cards
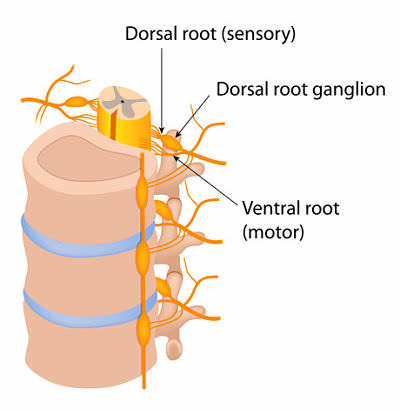
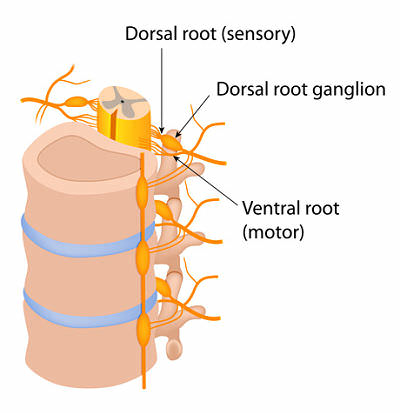
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Sensory info to the dorsal part of the spinal cord. Senses pain, temperature, and touch.
46
New cards
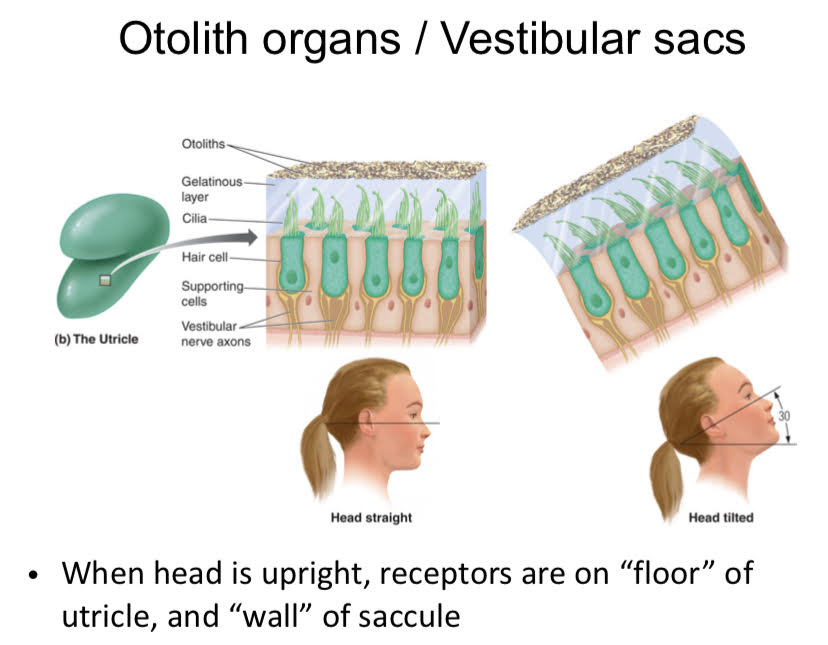
Otolith Organs
The wiggly shit in your ear that helps you understand which way your head is tilted.
47
New cards
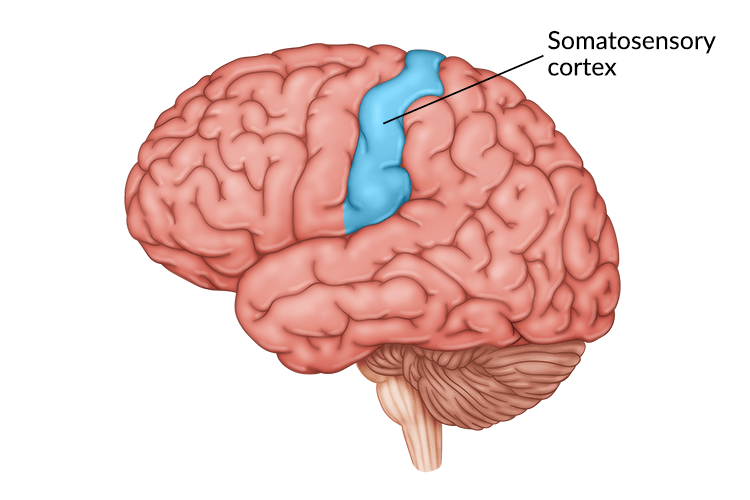
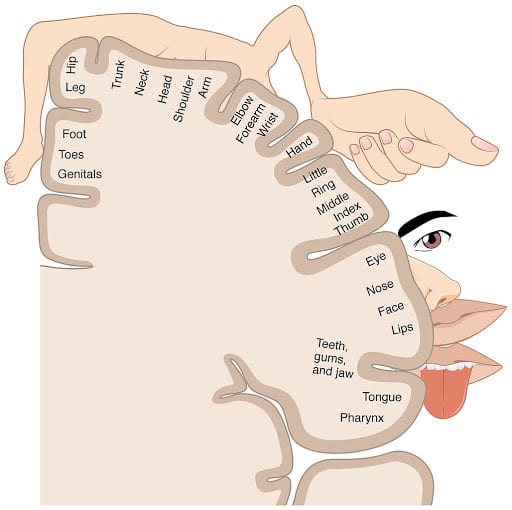
Somatosensory Cortex
Processing tactile info, in anterior parietal lobe. Weird naked homunculus dude. Right next to the motor cortex. There's apparently a motor homunculus. RFs correlated to sensitivity of part they're wired to.
48
New cards
Contextual Info (Smell)
Bad at distinguishing smell alone. Context info used to help perceive it.
49
New cards

Adaptation
Reduced sensitivity to odorants which we are continuously exposed to. (Why you don’t smell your perfume after some time)

50
New cards
Cross Adaptation
Adapt to odorants that are similar. Lemon and Lime smells weaken each other.
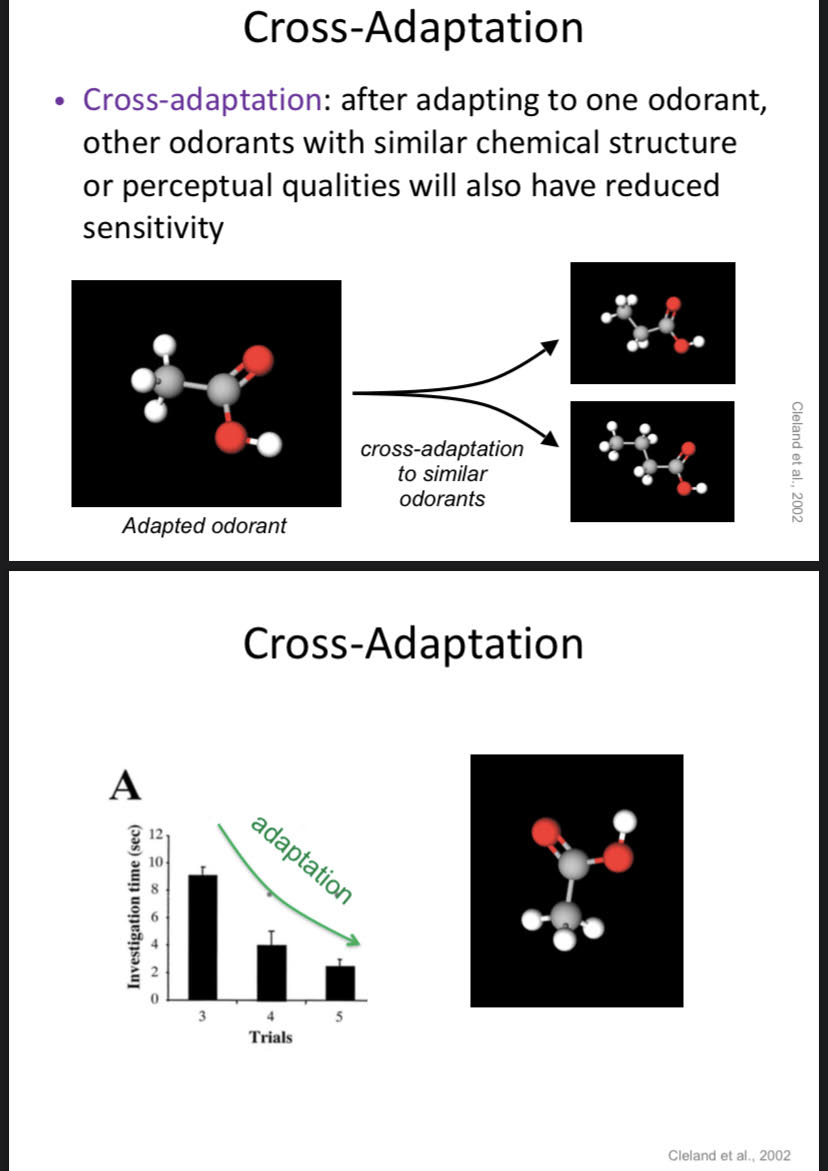
51
New cards
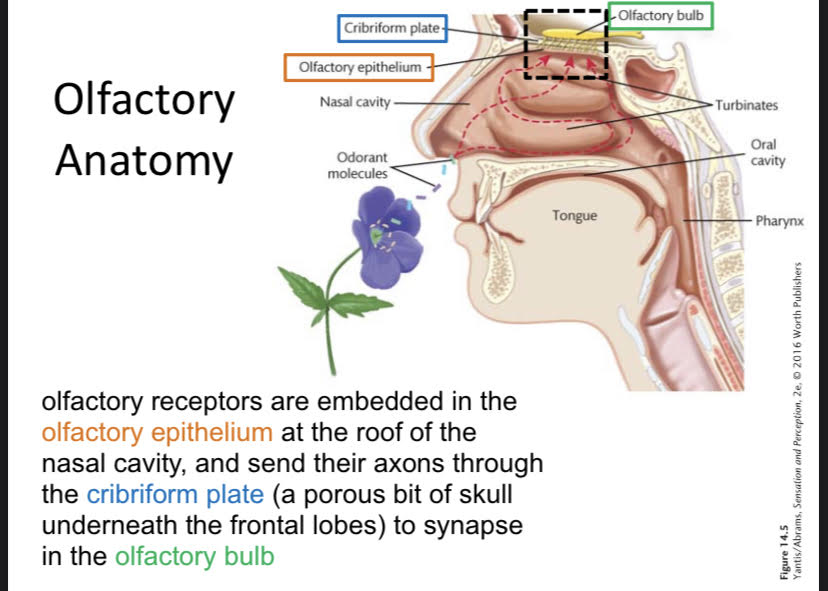
Olfactory System Path
Doesn't go through thalamus, direct paths to olfactory cortex.
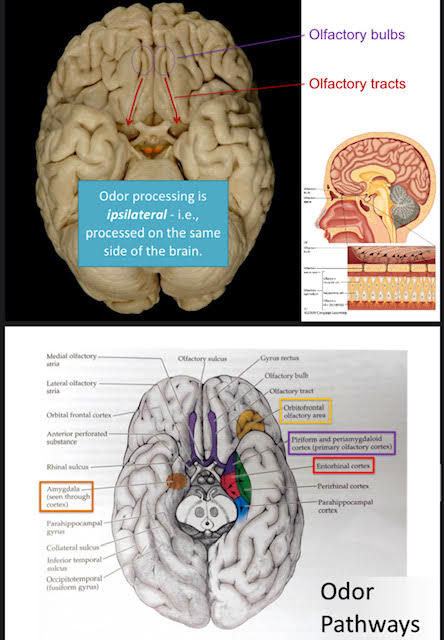
52
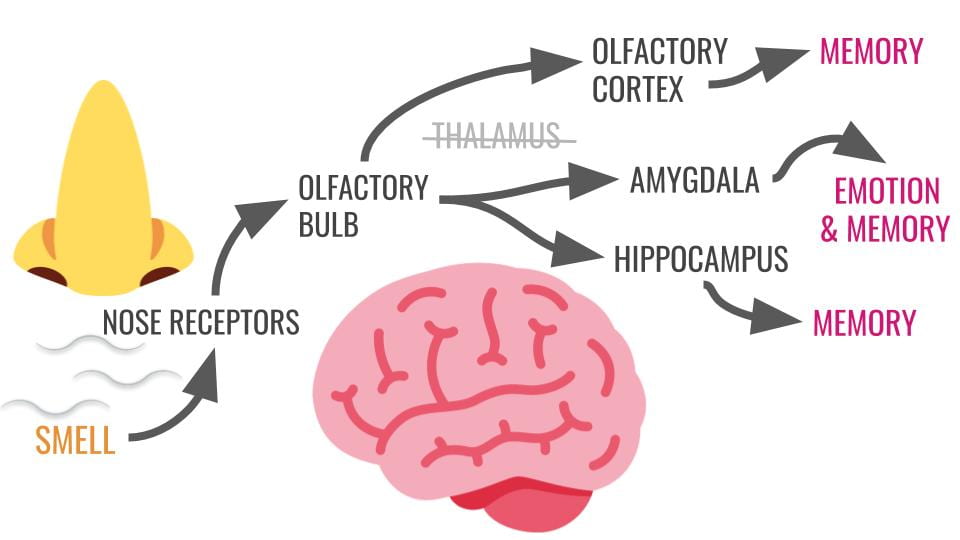
New cards
Smell to Hippocampus
Smells super tied to memories. Tied to amygdala too.
53
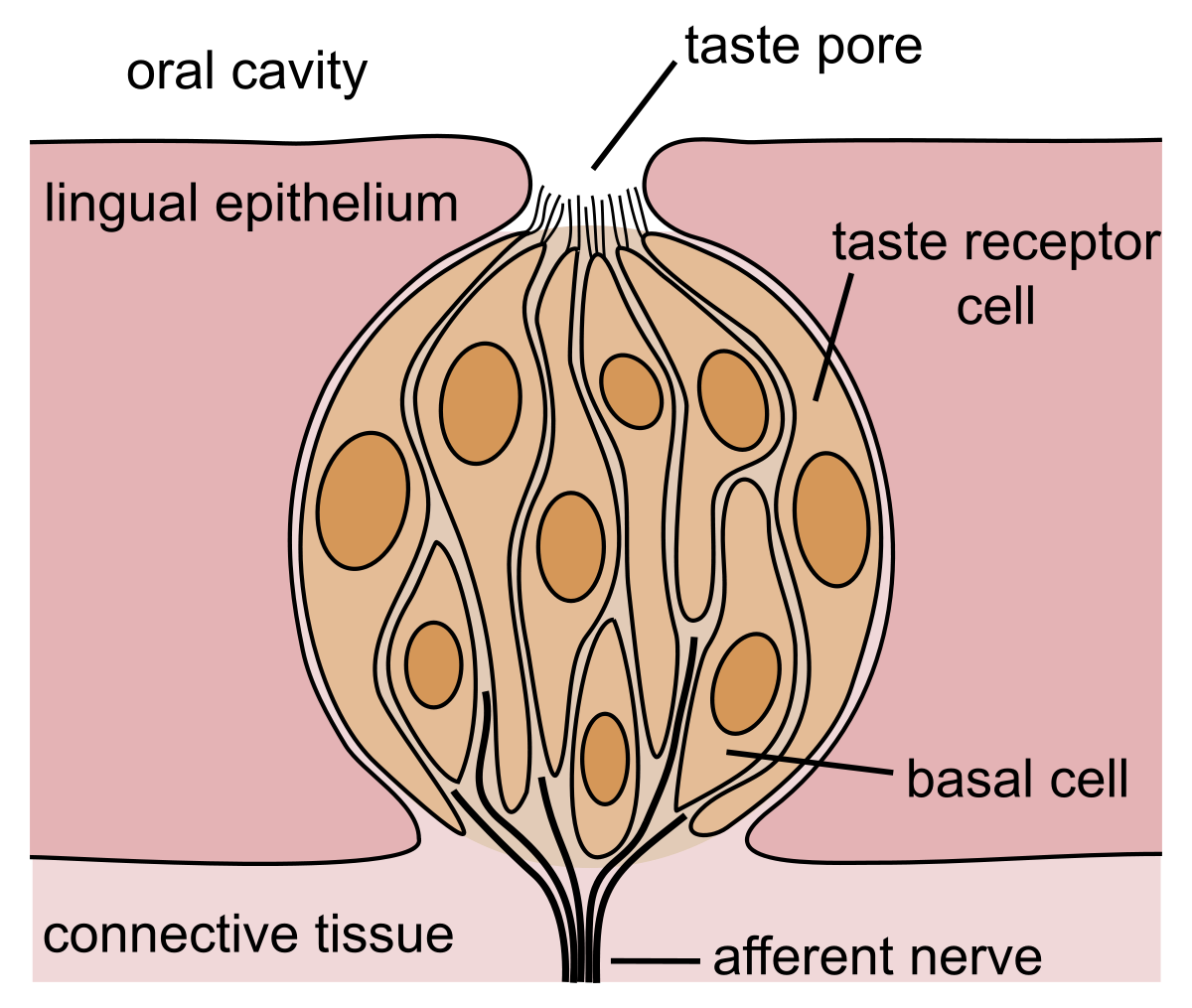
New cards
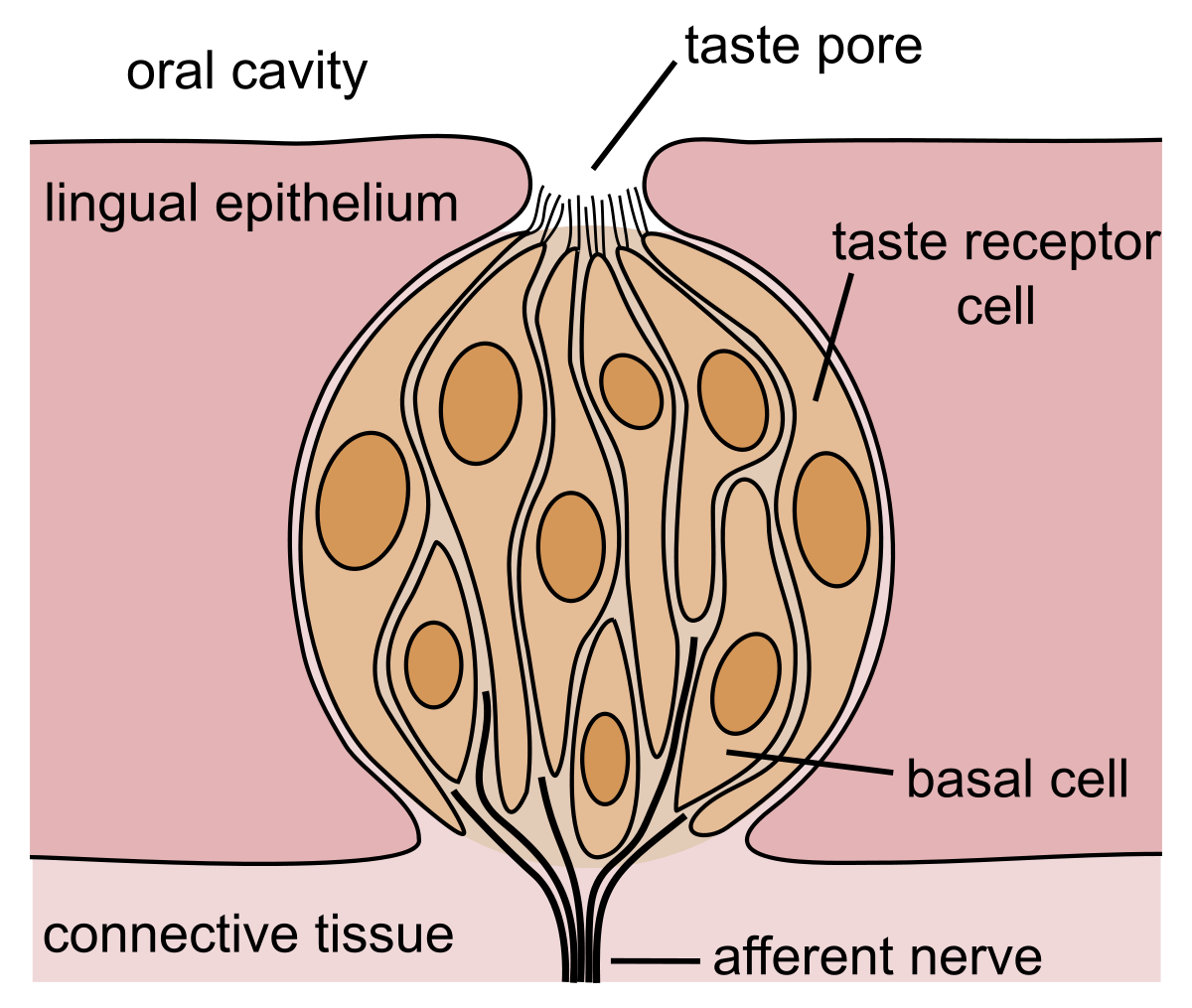
Taste Receptor Cell
Transduces taste info.
54
New cards
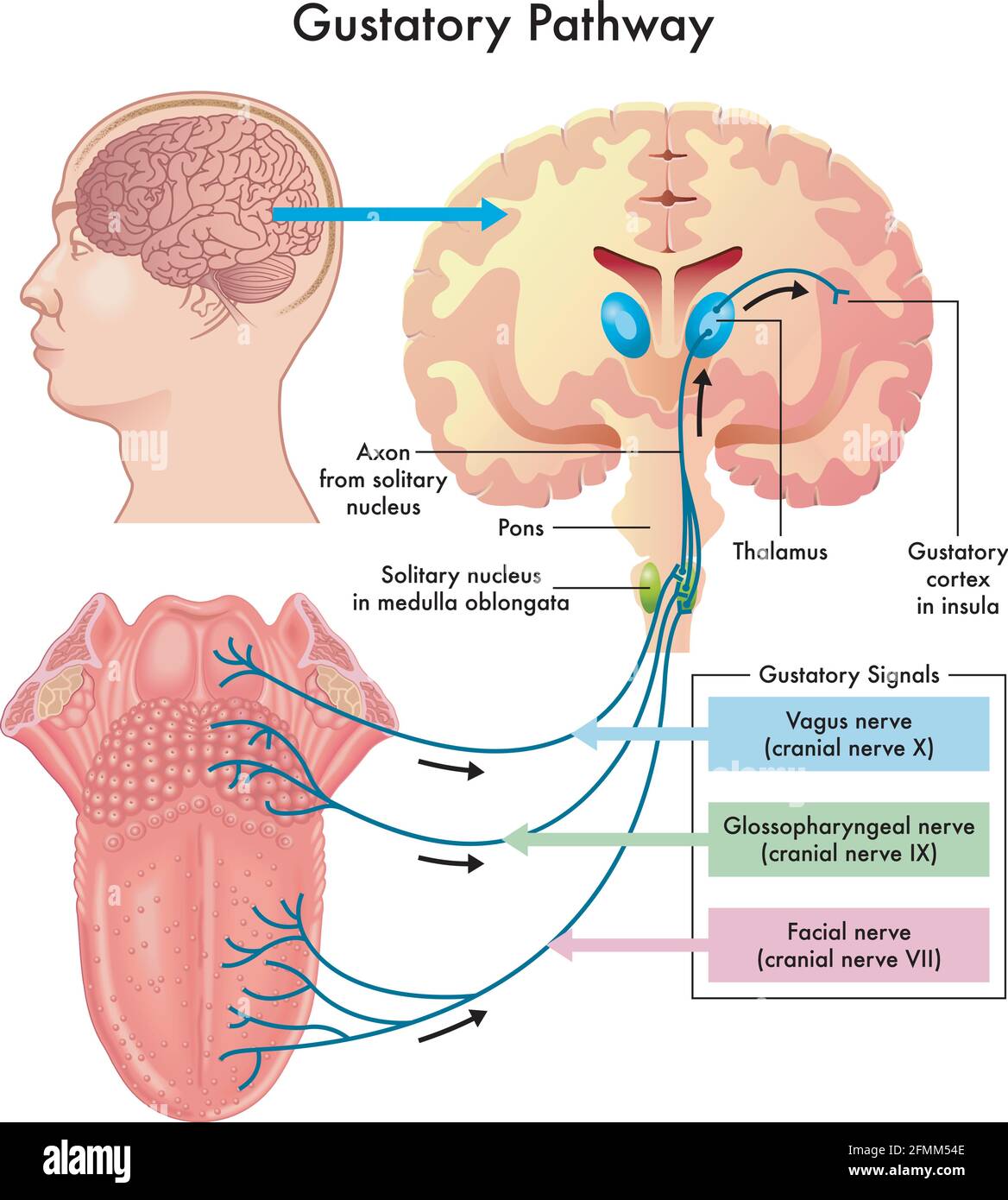
Primary Taste Cortex (Gustatory Cortex)
Where taste quality (elements of flavor and identification) is processed. Parietal lobe.
55
New cards
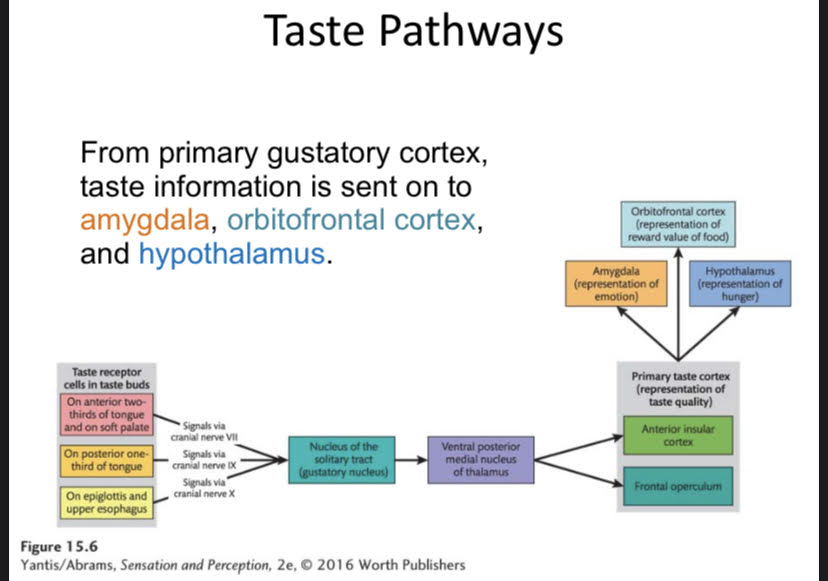
Orbitofrontal Cortex
Where we process the reward value of food.
56
New cards
Lateral Inhibition
Excited neurons reduce activity in their neighbors. Increases contrast. Nearby neurons don't send signals. Not just visual.