lecture 6: forces and torques of the body
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
force
how objects interact
Push (compression) or pull (tension)
Produces changes in some physical qualities
SI unit = N
1 N = 1kg m/s^2
Is a vector
Forces add as a vector
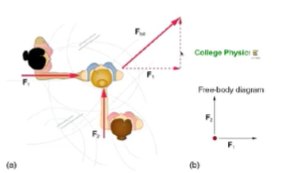
Free body diagram (forces are all pulling)
Force can cause an acceleration of an object

force of gravity
on me by Earth


mass (kg)
mg
g is in 9.8 N.kg
weight (N)
the size (magnitude) of the gravitational force
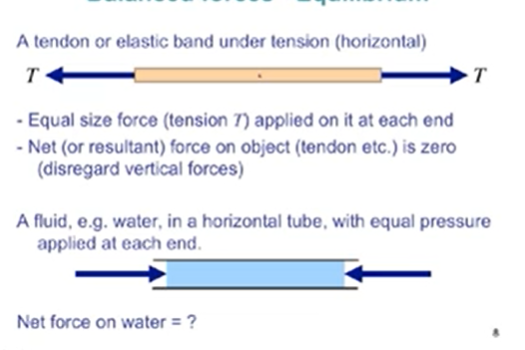
balanced forces
net force on water is zero, thus the water is stationary

natural state of an object
in motion with constant velocity and direction
newtons first law
Every object in a state of uniform motion teds to remain in that state of motion unless acted on by an external force
'law of inertia'
An object stays in its state of rest (or of uniform motion in a straight line) as long as no net force acts on it
Net (or resultant) force means sum of all forces acting on the object. We always consider the direction of the forces
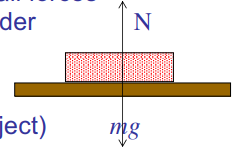
E.g. Book (object) on table
Gravitational force on book by Earth
Contact or Normal force (N) on book by table
Gravitational force actually acts on all parts of the object, but shown as if it acts at one point, the 'centre of mass'
newtons second law
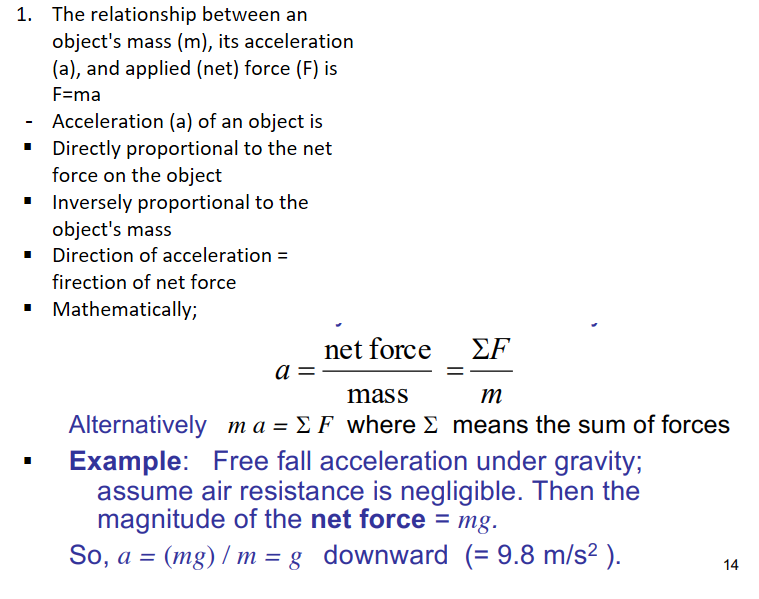
The relationship between an object's mass (m), its acceleration (a), and applied (net) force (F) is F=ma
Acceleration (a) of an object is
Directly proportional to the net force on the object
Inversely proportional to the object's mass
Direction of acceleration = direction of net force
Mathematically;


newtons third law
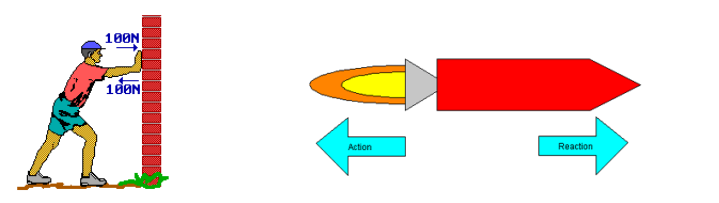
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction

net force on an object
Newton's 3rd Law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
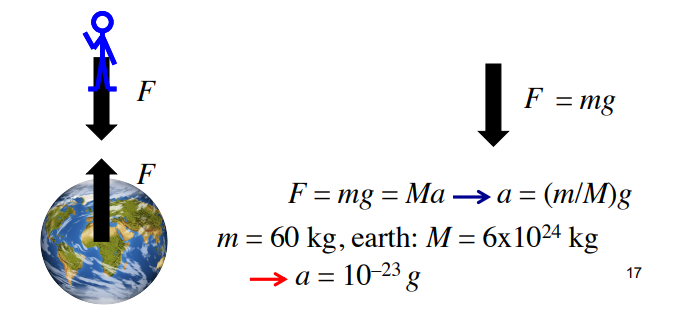
In order to determine the net force on an object, you need to consider the object alone (consider a person falling towards earth)

newtons third law; normal force and tension
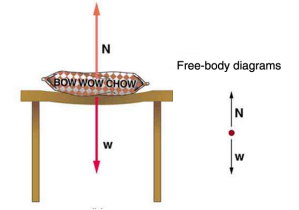
Forces (push or pull)
Only acts perpendicular (normal) to surfaces
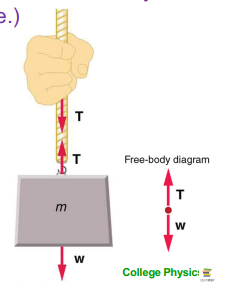
Forces (tension)
The same everywhere along the rope (doesn't matter where you hold the rope)

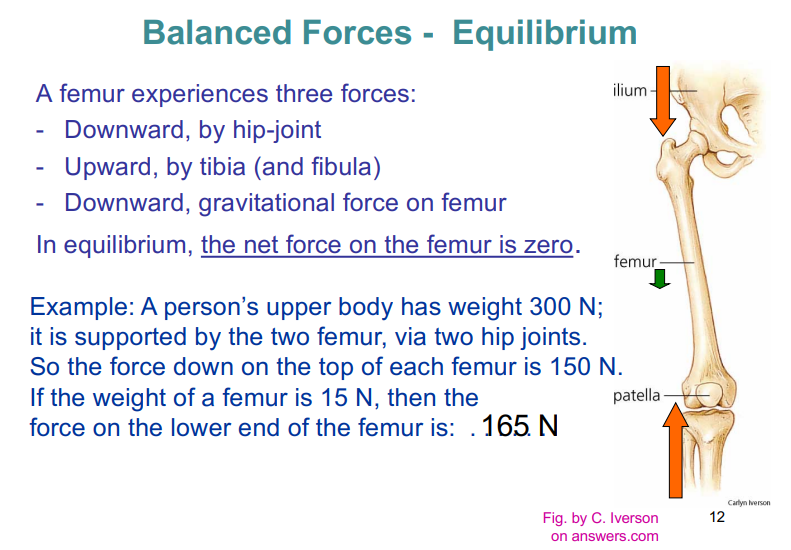
equilibrium and balance
For an object to be in equilibrium, the net force must be zero
In equilibrium an object must also have zero net torque
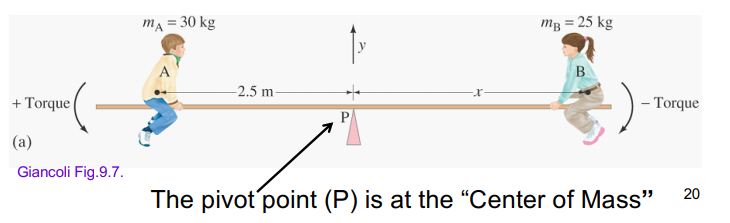
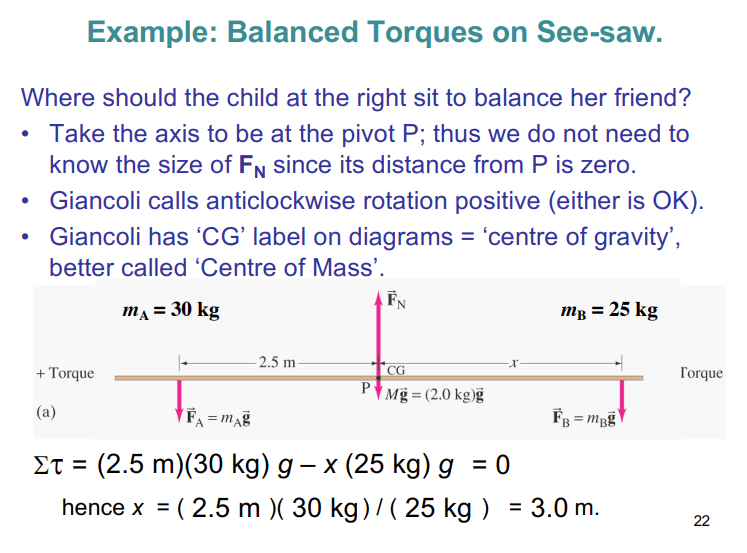
torque (moment of force)
Torque: an application of a force that causes rotation
Unit: Nm
Torque (moment of a force) around a given axis is
τ=LF
L= perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the axis or pivot point (L is also called the lever arm)
Rotational equilibrium requires zero net torque, Στ=0

rotational equilibrium
requires zero net torque, Στ=0
requires no angular acceleration
centre of mass
Many objects exhibit translational and rotational motion
Even if the object is rotating, there appears to be a point that follows the path of the translational motional
That point is the centre of mass (axis of rotation)
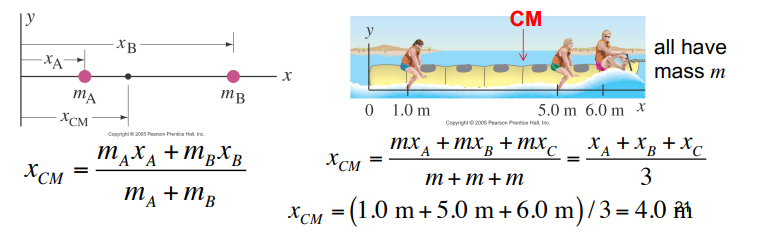
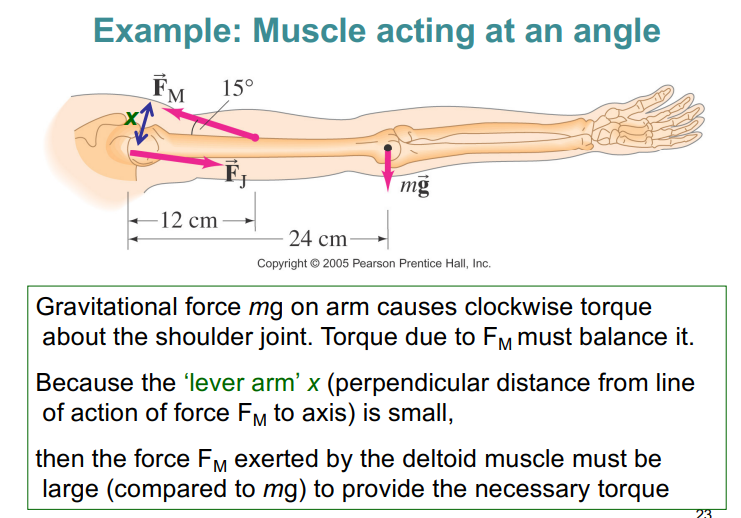
example; muscle acting on an angle

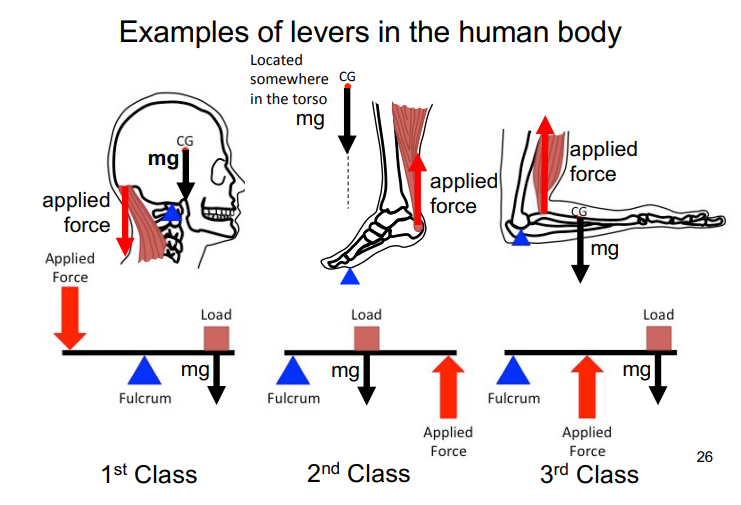
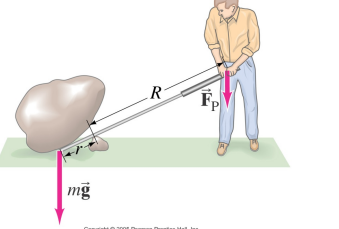
“magnifying” force or distance moved
In common cases of levers, a small force moved through a large distance is changed to a large force moved through a small distance
R/r = "the mechanical advantage"
(mg)r = (Fp)R
Muscles only constact small distances
Levers in the body allow fingers and feet etc., to move further and faster

classes of levers