combinedd , pharynx+palate+tongue
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
what form the hard palate
1) maxilla ( palatine process )
2) palatine bone (horizontal plate)
what continue posterior to the hard palate?
soft palate
what relations does hard palate form with cavities?
floor of nasal cavity
roof of oral cavity
is the hard palate covered?
yes, by mucous membrane
with inf. median raphe and corrugations on both sides
is the soft palate covered?
yes , by mucous membrane
what the soft palate ends posteriolrly
uvula
what continue with the soft palate on both sides?
lateral walls of pharynx
contents of soft palate (easy)
muscles
palatine aponeurosis
vessels
nerves
lymphoid tissue
WTF is palatine apponeurosis
fibrous sheet attached to post border of hard palate (just for support)
it is an expanded tendon of tensor palati muscle
give attachment to all palatine muscles
what also the palatine apponeurosis do
split to cover the musculus uvala muscle
does the palate contain muscles?
yes , in soft palate
tell me the names of soft palate muscles
tensor palati
levator palati
palato-glossus
palato-pharyngeus
musculas uvala
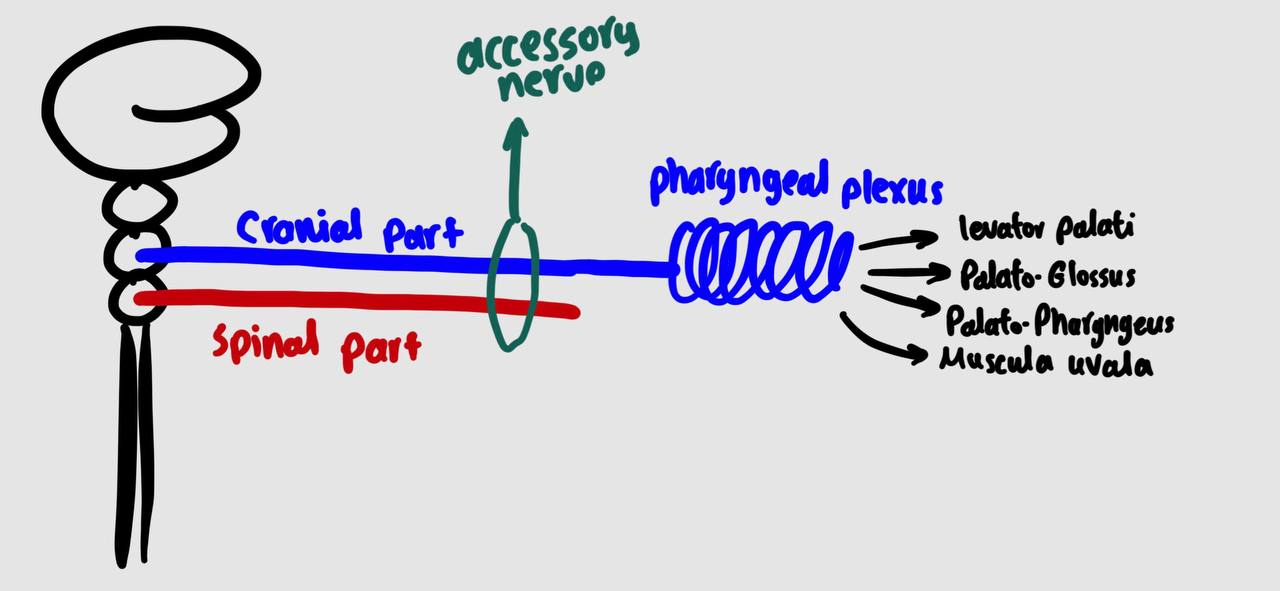
nerve supply of muscles of soft palate
by cranial part of accessory nerve ( through pharyngeal plexus )
EXEPT : tensor palati by trunk of mandibular nerve
action of tensor palati muscle
tense the soft palate
open the auditory tube
action of levator palati
elevate the soft palate
open the auditory tube
what auditory tube need to be open ?
to equalize the pressure between middle ear and nasopharynx
action of palato-glossus muscle
deppress the palate
elevate the root of the tonge
-narrow the oro-pharyngeal isthmus
action of palato-pharyngeous muscle
elevate the pharynx
-narrow the naso-pharyngeal isthmus
action of musculus uvulae
retraction of uvala لورا
elevation of uvula لفوق
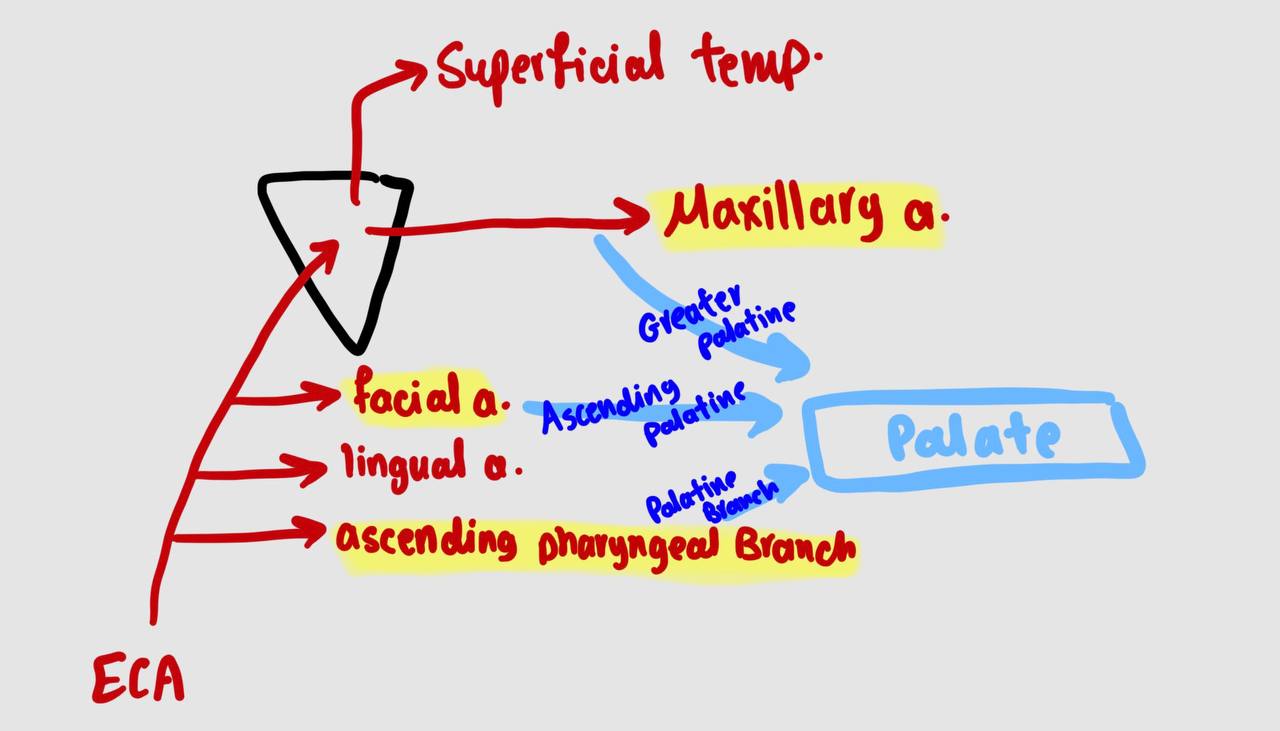
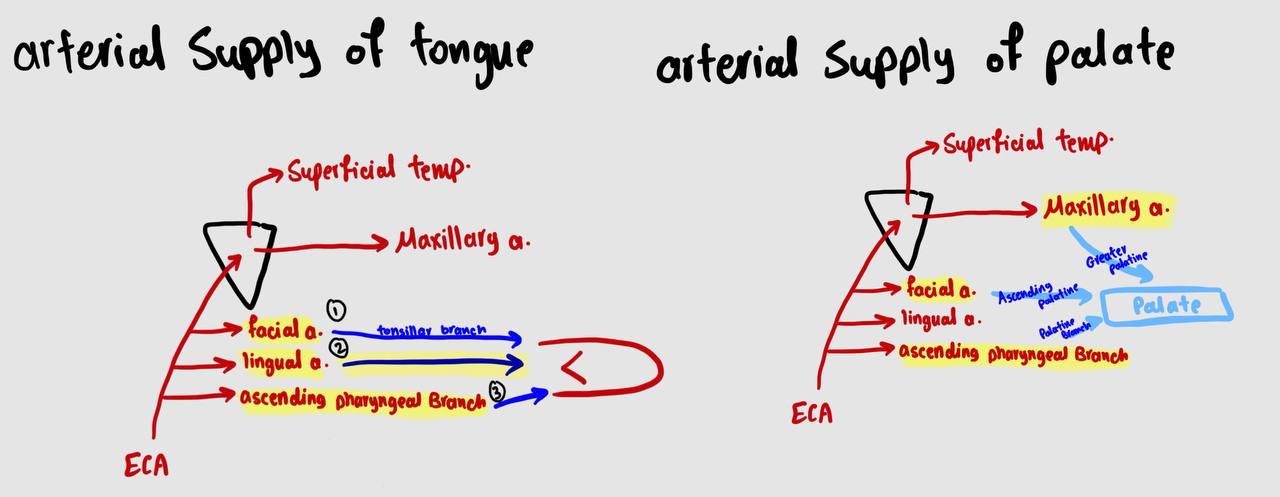
arterial supply of the palate
Greater palatine artery: branch from maxillary a.
2- Ascending palatine artery: branch from facial a.
3- Palatine branch of ascending pharyngeal a.
venous drainage of palat:
1- pterygoid plexus of veins
2- pharyngeal plexus of veins
lymphatic drainage of the palate
Hard palate : submandibular LN
Soft palate :
upper deep cervical LN
retro pharyngeal LN
motor nerve supply of the palate
all by cranial part of accesory n. exept tensor palati
sensory supply of palate
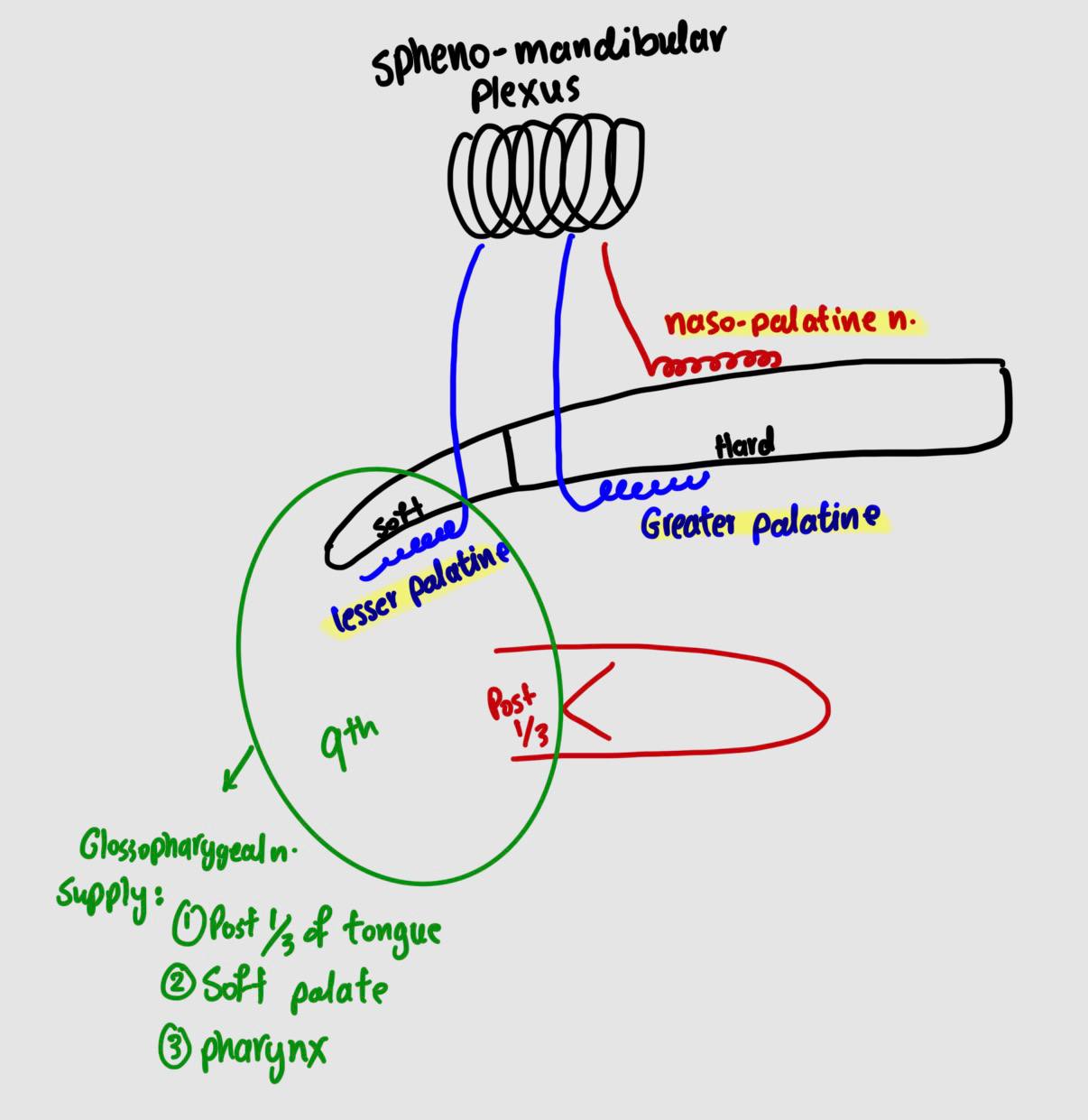
Hard palate :
greater palatine artery
naso palatine nerve
Soft palate :
lesser palatine nerve
glosso pharyngeal nerve
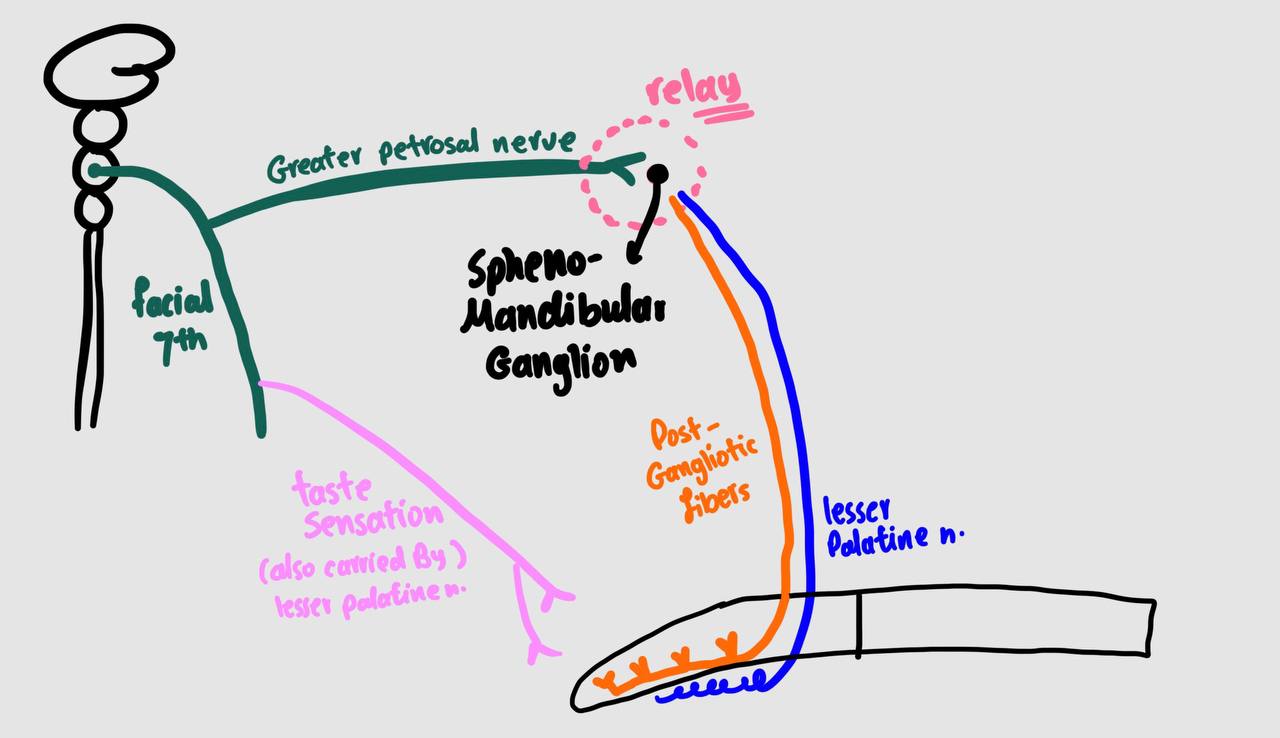
talk about the secretory motor fibers to the palatine glands (autonomic {involantery by ANS} )

draw the secretory motor fibers to the palatine glands (autonomic {involantery by ANS} )
TOUNGUE is consist of:
striated muscles with mucous membrane
parts of tongue
1) tip + root
2) dorsal surface (superior)]
3) ventral surface ((inferior)
dorsal surface of the tingue is seperated to ant and post parts by what ?
sulcus terminalis
what the apex of sulcus marked with?
foramen caecum
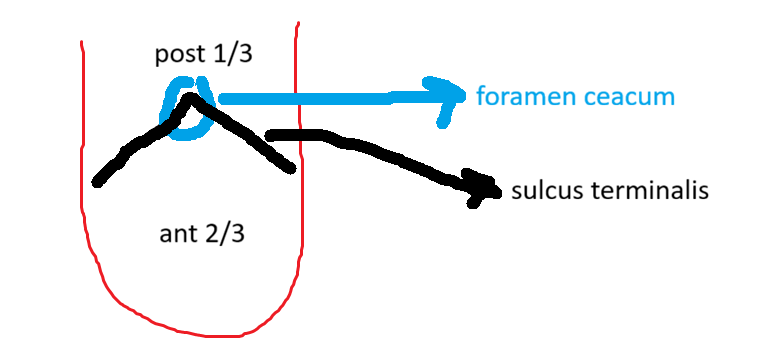
anterior 2/3 is covered by
papilae
posterior 1/3 is covered by:
lingual tonsils
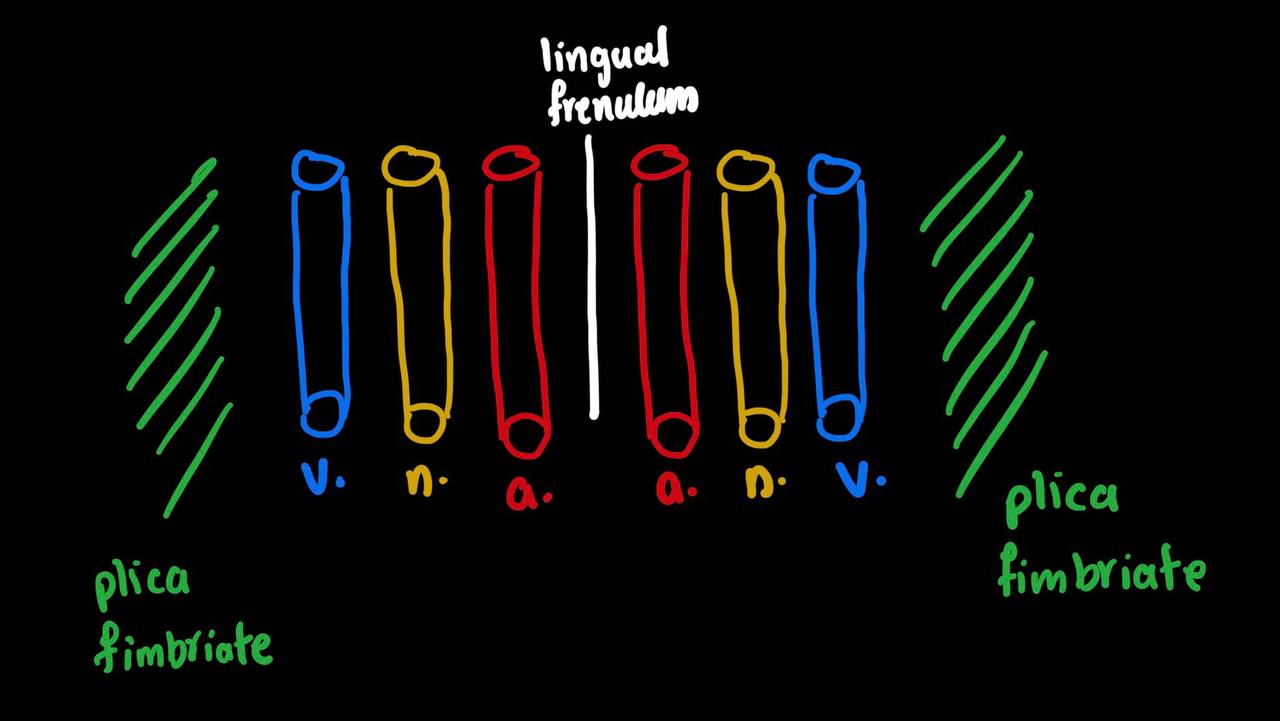
what connect the ventral surface of tongue to the floor of the mouth
lingual frenulum
what structures are present on both sides of lingual frenalum ( from medial to lateral )
ANV
lingual artery
lingual nerve
lingual vein
-then on medial on lingual vein there is the plica fimbriate
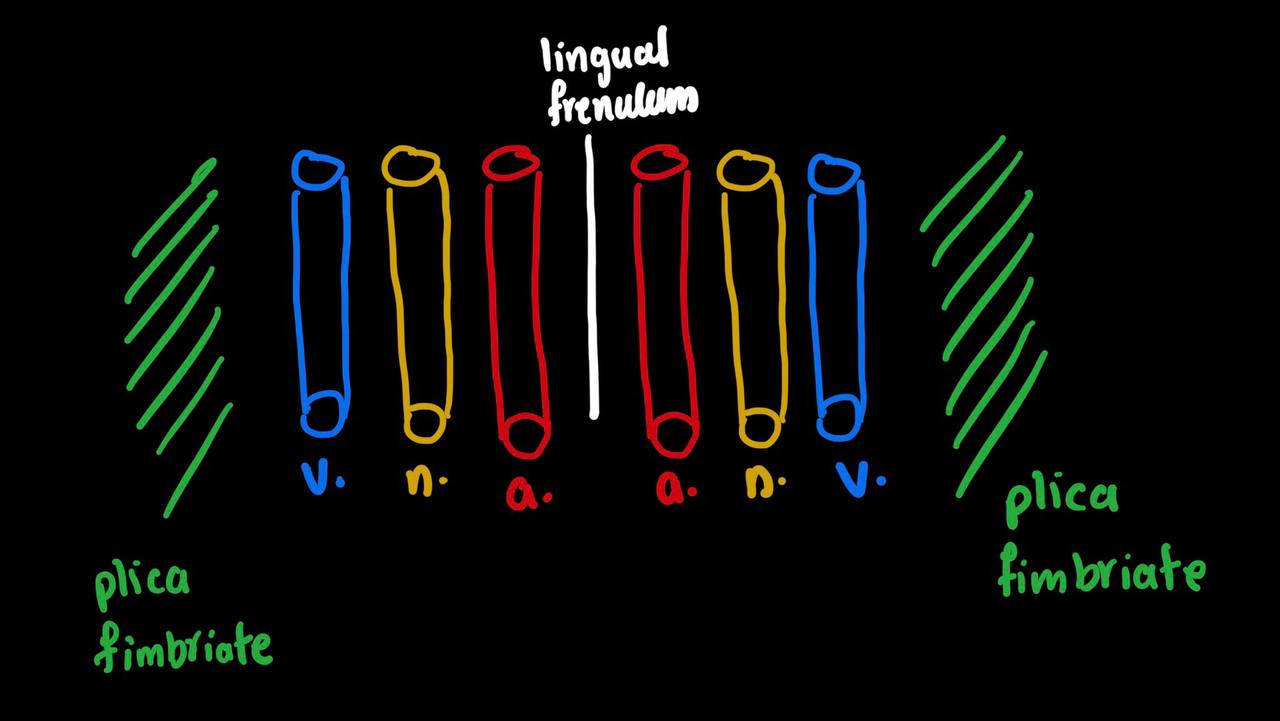
what sturcture is medial to lingual vein
plica fimbrate
what are the muscles of the tongue
intrinsic for shape
extrinsic for position
list the intrinsic tongue muscle
1) transverse m.
2) longitudinal m.
3) vertical m.
function of transvese m. of the tongue
narrowing of the tongue
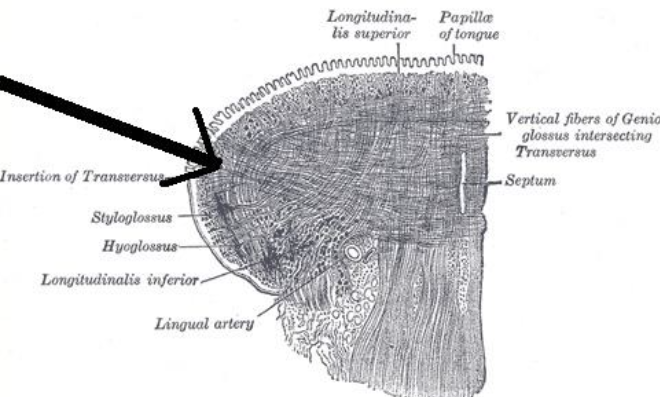
function of the longuitudinal m. of the tongue
shortening ( point A )
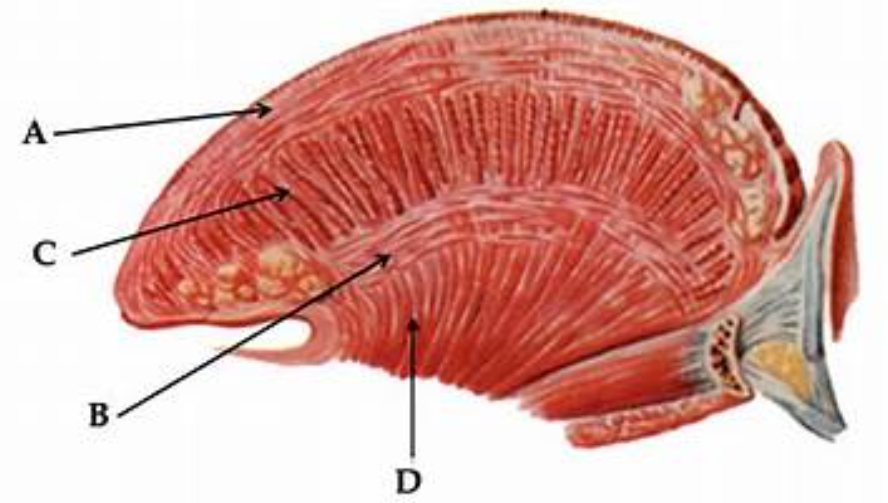
function of the vertical m. of the tongue
thinning (point C)
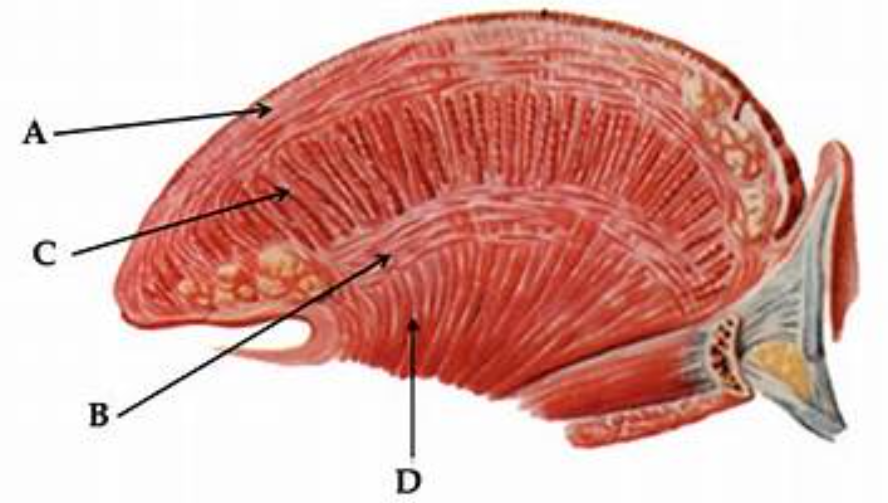
what is the supply of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue
hypoglossal nerve
list the external muscles of the tongue
genio-glossus
stylo-glossus
hyoglossus
palato-glossus
origin of geniogloussus muscle
superior genial tubercle
orgigin of styloglossus muscle
styloid proccess
origin of hyoglossus muscle
hyoid bone
origin of palatoglossus muscle
palatine apponeurosis
it give origin to all muscles of soft palate
palatoglossus muscle is in softpalate and also in the tongue as extrinsic muscle
insertion of all exctrinsic muscles of the tongue
tongue
nerve supply of extrinsic muscles of the tongue
hypoglossal nerve
exept palatoglossus by cranial part of accesory nerve(it is a soft plate muscle)
action of genioglossus muscle
depression of the tongue
protraction of the tongue (protrusion outward)
action of styloglossus muscle
elevation of the tongue
retraction of tongue
action of hyoglossus muscle
depression of the tongue
NO PROTRUSION
action of palato-glossus muscle
depresion of palate
elevation of tongue
narrowing the oro-pharyngeal isthmus
arterial supply of the tongue
1) lingual artery
2) acsending pharyngeal branch
3) tonsillar branch of facial artery
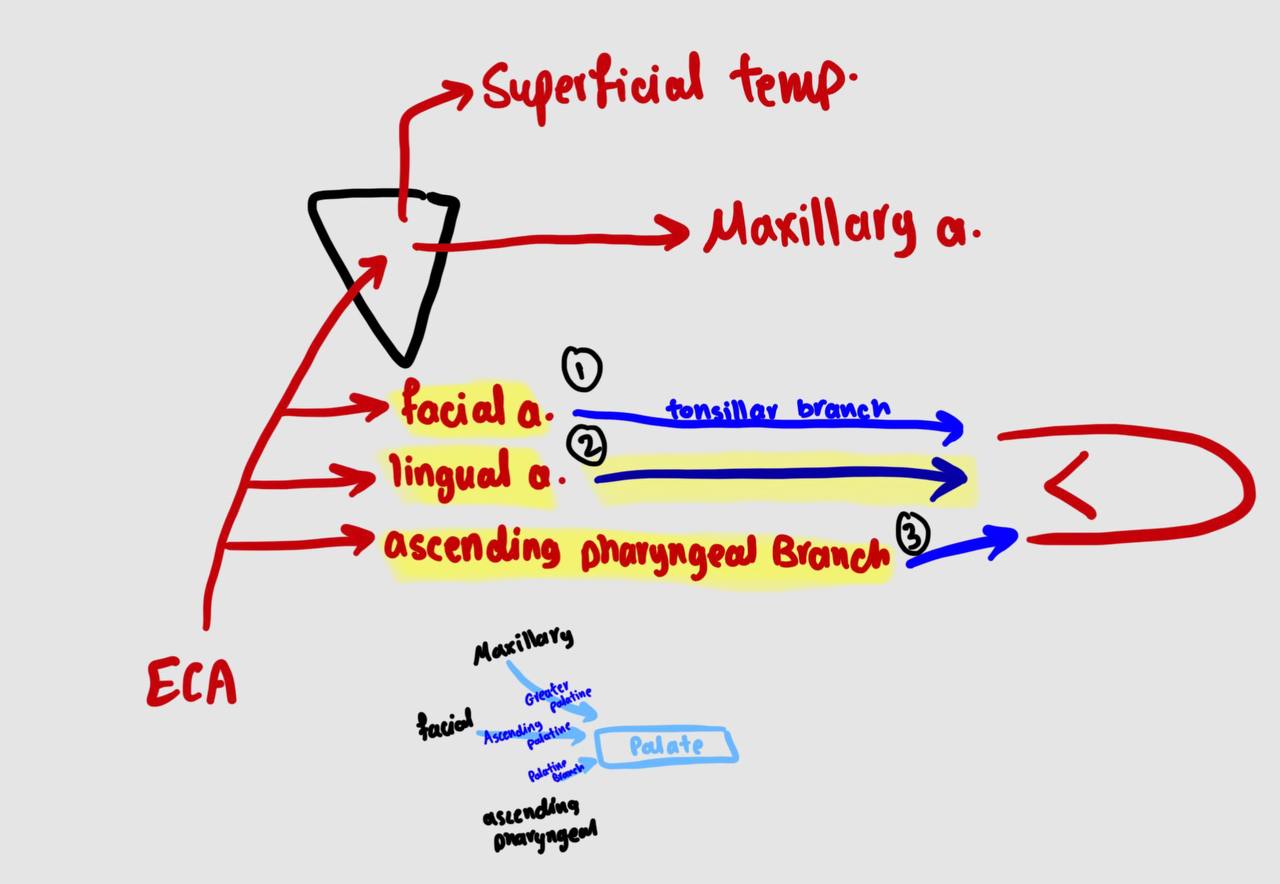
for a revision draw the arterial supply of palate and tongue
venous drainage of the tongue?
into lingual vein
which drain into internal jugular vein
tongue —→ lingual vein —→ internal jugular vein
lymphatic drainage of the tongue

nerve supply of the tongue (motor)
all muscles of tongue are supplied by hypoglossal nerve except palatoglossus which is supplied by cranial part of accessory nerve through pharyngeal plexus
nerve supply of the tongue (sensory)
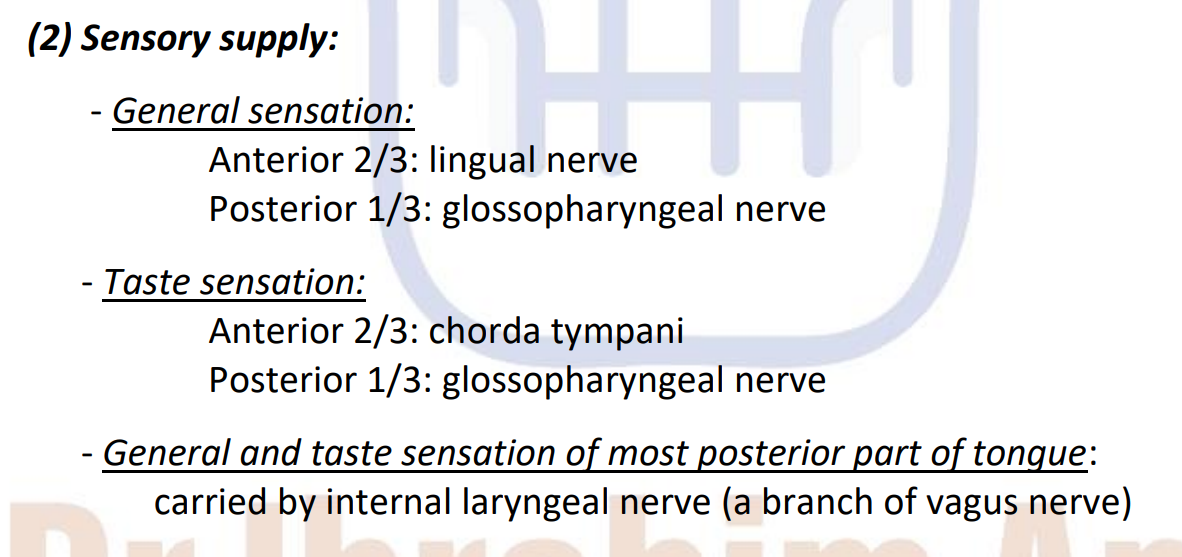
IMP IMP , how many cranial nerves supply the tongue?
6 cranial nerves
5th trigeminal ( for lingual nerve)
7th facial (for chorda tympina)
9th glossopharyngeal
10th vagus (for interal laryngeal n)
11th accessory (cranial part )
location of naso pharynx
from base of the skull to upper surface of saft palate (C1)
what are the contents of nasopharynx
1) pharyngeal opening
2) tubal elevation
3) salpingo-pharyngeal flod
4) salpingo-palatine fold
5) pharyngeal tonsil
6 ) pharyngeal reccess (fossa of Rosen muller)
other name of pharyngeal opening
eustachian or pharyngo-tympanic
location of pharyngeal opening
lateral wall of nasopharynx
function of pharyngeal opening
connect the nasopharynx to the middle ear to equalize pressure on both sides of ear drum
location of tubal elevation
above pharyngeal opening
what form the tubal elevation
1) mucosa covering it {from the cartilaginous end of auditory tube)
2) tubal tonsil
what is the location of salpingo-pharyngeal fold
extend from the tubal eleavtion towards the pharynx
what form the salpngo-pharyngeal fold
1) salpingo-pharngeus muscle
2) mucous membrane covering the muscle
location of salpingo-palatine fold
extend from tubal elevation towards the palate
location of pharyngeal tonsil
posterior wall of nasopharynx near its roof
what happen of the pharyngeal tonsil is enlarged
it will be called ADENOIDS اللحمية
other name for pharyngeal recess
fossa of Rosen Muller
what is the pharyngeal recces
a depression behind the tubal elevation
what is the function of pharyngeal recess
overlies the internal carotid artery
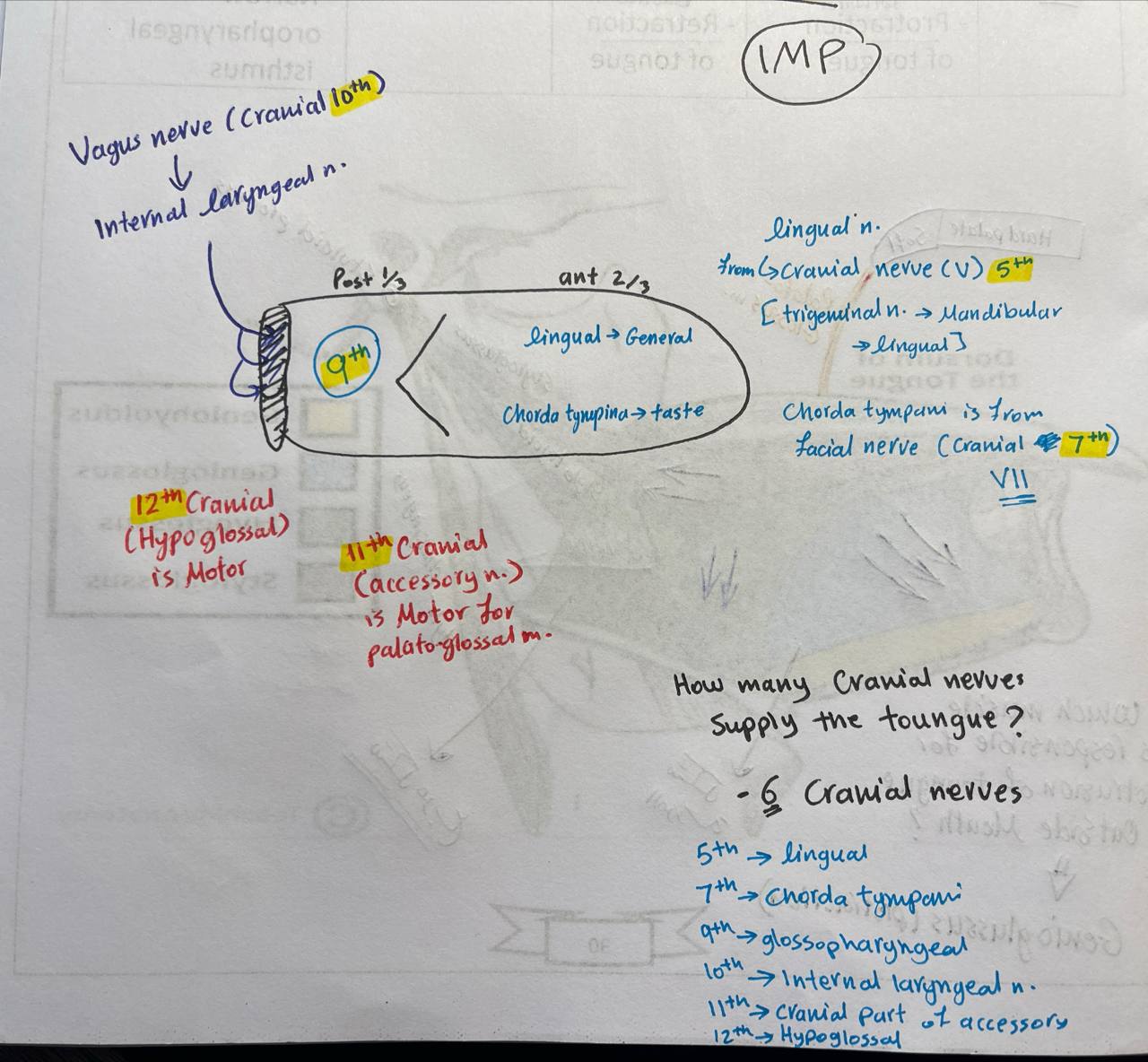
Oropharynx extent
extends from lower surface of soft palate(C1) to upper surface of epiglottis(C3)
Oropharynx communication
Communicates anterior with oral cavity through oropharyngeal isthmus
WHAT closs the oro-pharyngeal isthmus??
palato-glossal muscle
list the contents of the oropharynx
1) palato-glossal arch
2) palato-pharyngeal arch
palatine tonsil between the two arches
3) vallecula
Palatoglossal arch
formed of palatoglossal muscle covered with mucous membrane
Palatopharyngeal arch
formed of palate-pharyngeus muscle covered with mucous membrane
Palatine tonsil location
Between palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches, there is palatine tonsil
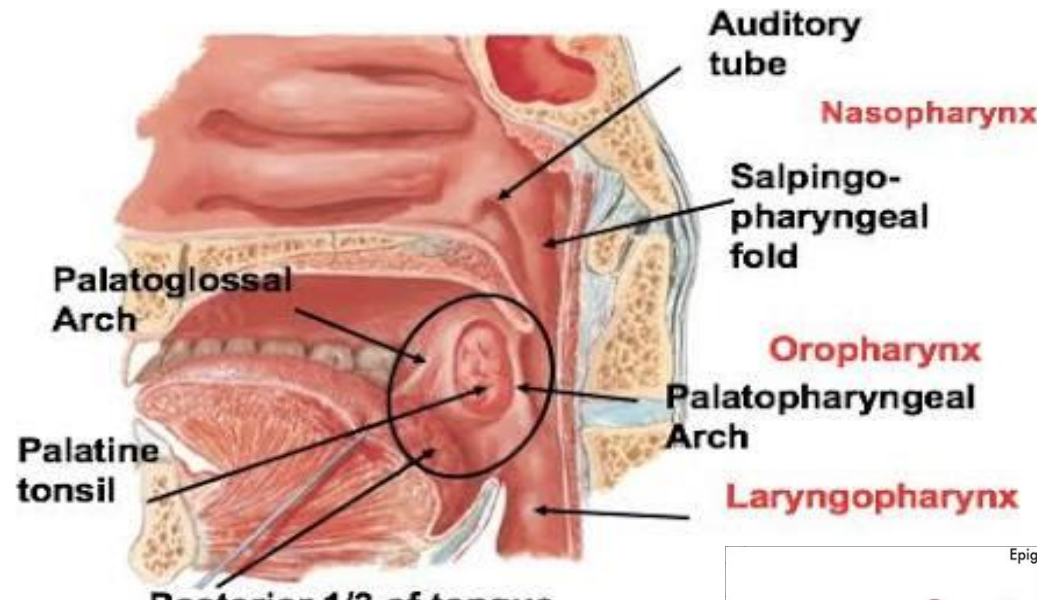
Vallecula
it is a depression between median and lateral glosso-epiglottic folds
glosso-epiglottic folds connect the tongue and epiglottis
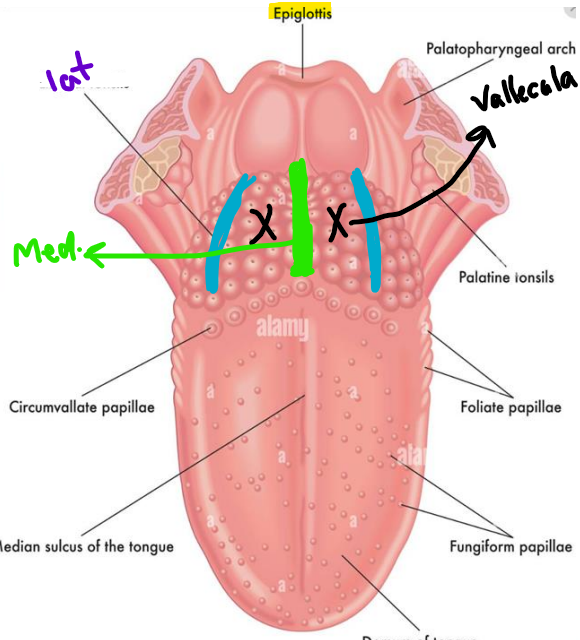
Vallecula nerve supply
it is supplied by internal laryngeal nerve
Palatine tonsil definition
two masses of lymphoid tissue in the lateral wall of oropharynx
Palatine tonsil covering
they are covered by mucous membrane
Palatine tonsil medial surface
its medial surface projects into lumen of oropharynx with many openings which lead to tonsillar crypts
what the upper part of medial side contain
the upper part of medial surface has a deep intra-tonsillar cleft (crypta magna)
Palatine tonsil lateral covering
it is covered on lateral side by a capsule
عشان لما نشيل اللوز بس منروح عنر الكبسول و بنقشر اللوز منها
Palatine tonsil relation anterior
Palato-glossal arch
Palatine tonsil relation posterior
Palato-pharyngeal arch
Palatine tonsil relation superior
Soft palate
Palatine tonsil relation inferior
Posterior third of tongue
Palatine tonsil relation medial
Cavity of oropharynx
Palatine tonsil relation lateral
(Tonsillar bed)
Palatine tonsil lateral side (tonsillar bed ) is formed by ?
Superior constrictor muscle
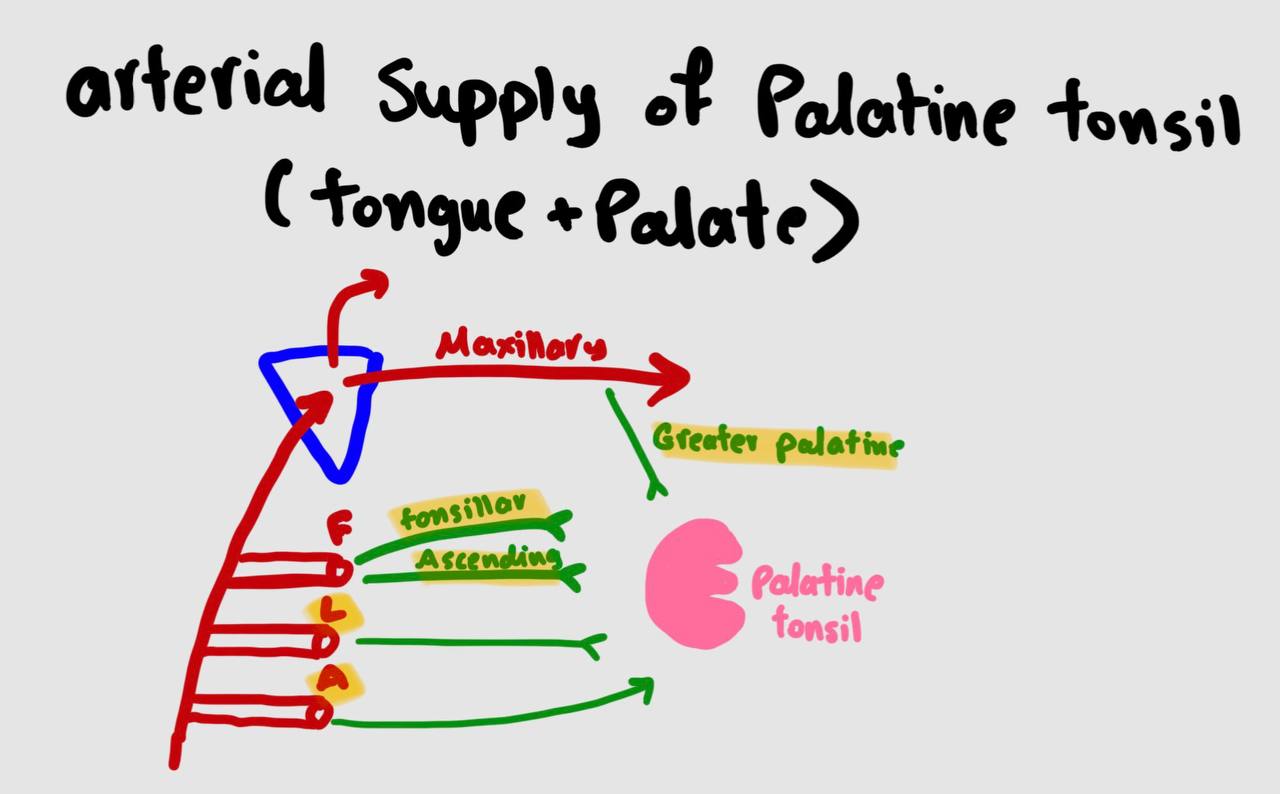
Arterial supply of palatine tonsil
Tonsillar artery (from facial artery) — enter from lateral wall by piercing the tonsillar bed (superior constrictor muscle)
Ascending palatine artery (from facial artery);
Lingual artery (from ECA);
Ascending pharyngeal artery (from ECA);
Greater palatine artery (from maxillary artery)
Venous drainage of palatine tonsil
Paratonsillar vein
para = beside
mention two vessels present lateral to palatine tonsil
1) tonsillar artery
2) paratonsilar vein