NURS 245 Ch. 43: Disorders of the Male Reproductive System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
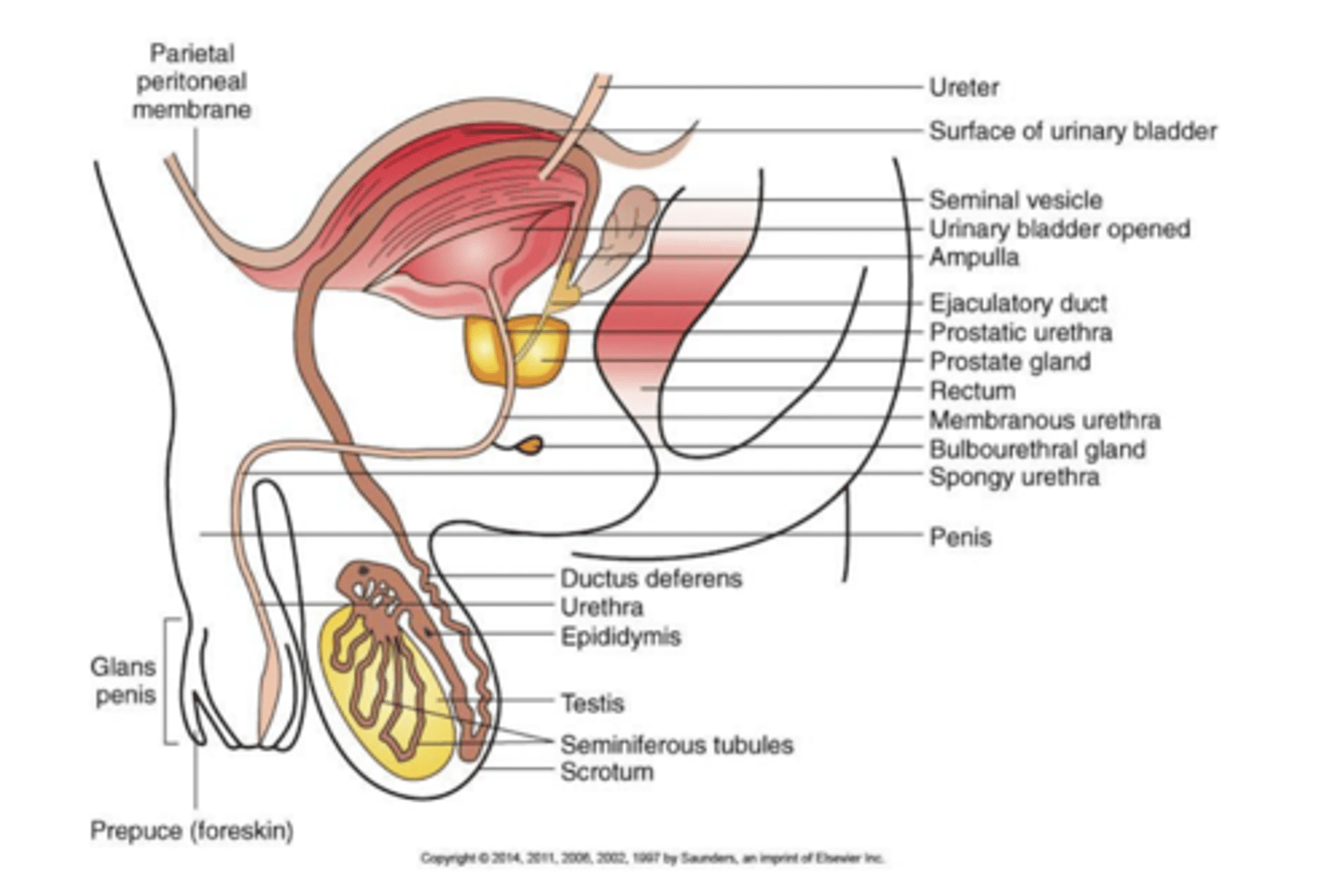
anatomy of the male reproductive system
-Testes.
-Duct system:
• Epididymis.
• Ductus deferens.
• Urethra.
- Accessory organs:
• Seminal vesicle.
• Prostate gland.
• Bulbourethral gland.
-External genitalia:
• Penis.
• Scrotum.
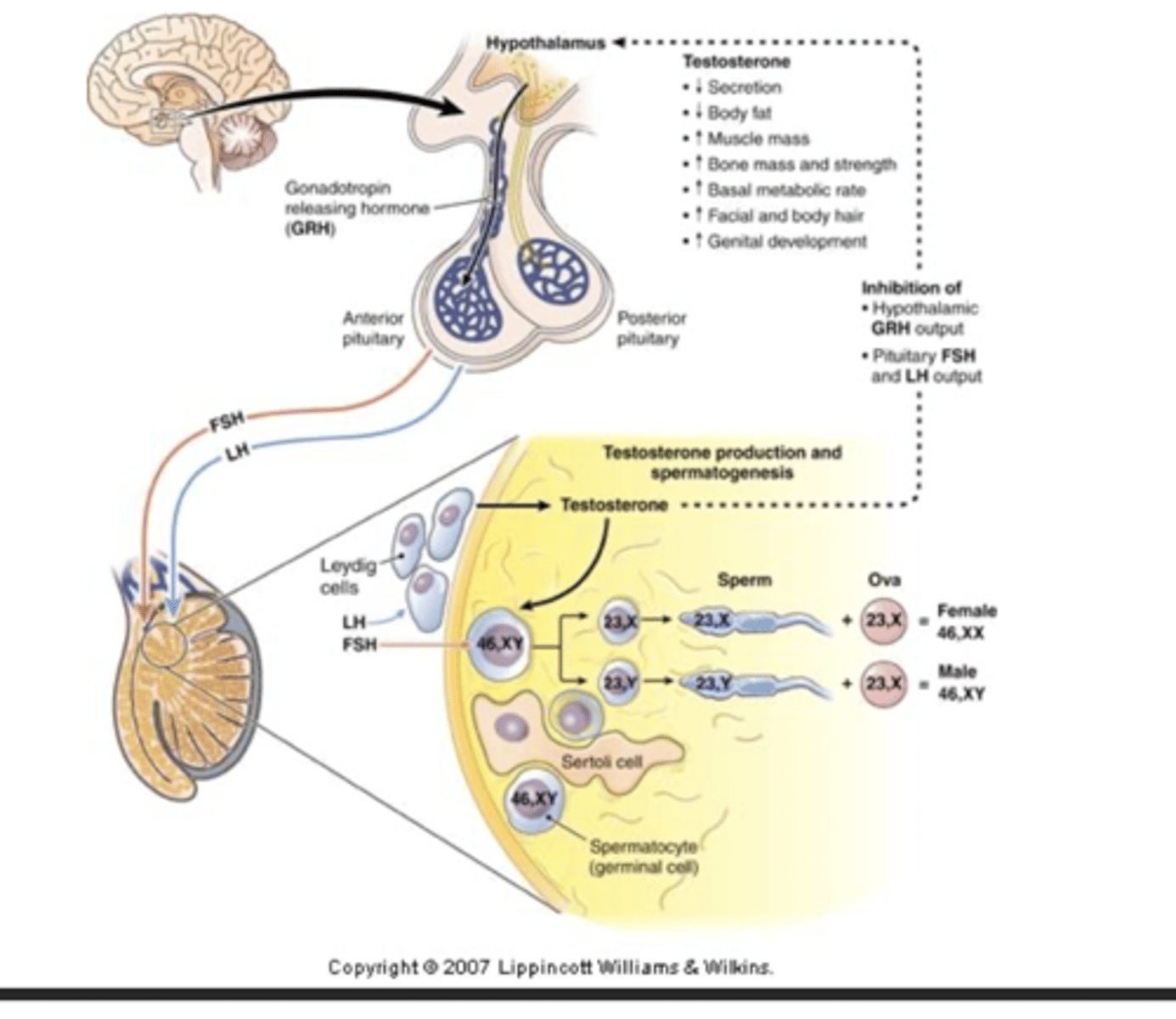
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
initiates spermatogenesis
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
stimulates testosterone production
testosterone
maturation of sperm, sex characteristics, protein metabolism, muscle development
epispadias
congenital defect in which urethral opening on ventral or upper surface of penis
hypospadias
congenital defect in which urethral opening is on dorsal surface of the penis which can result in incontinence or infection
how do you treat congenital abnormalities?
congenital reconstruction
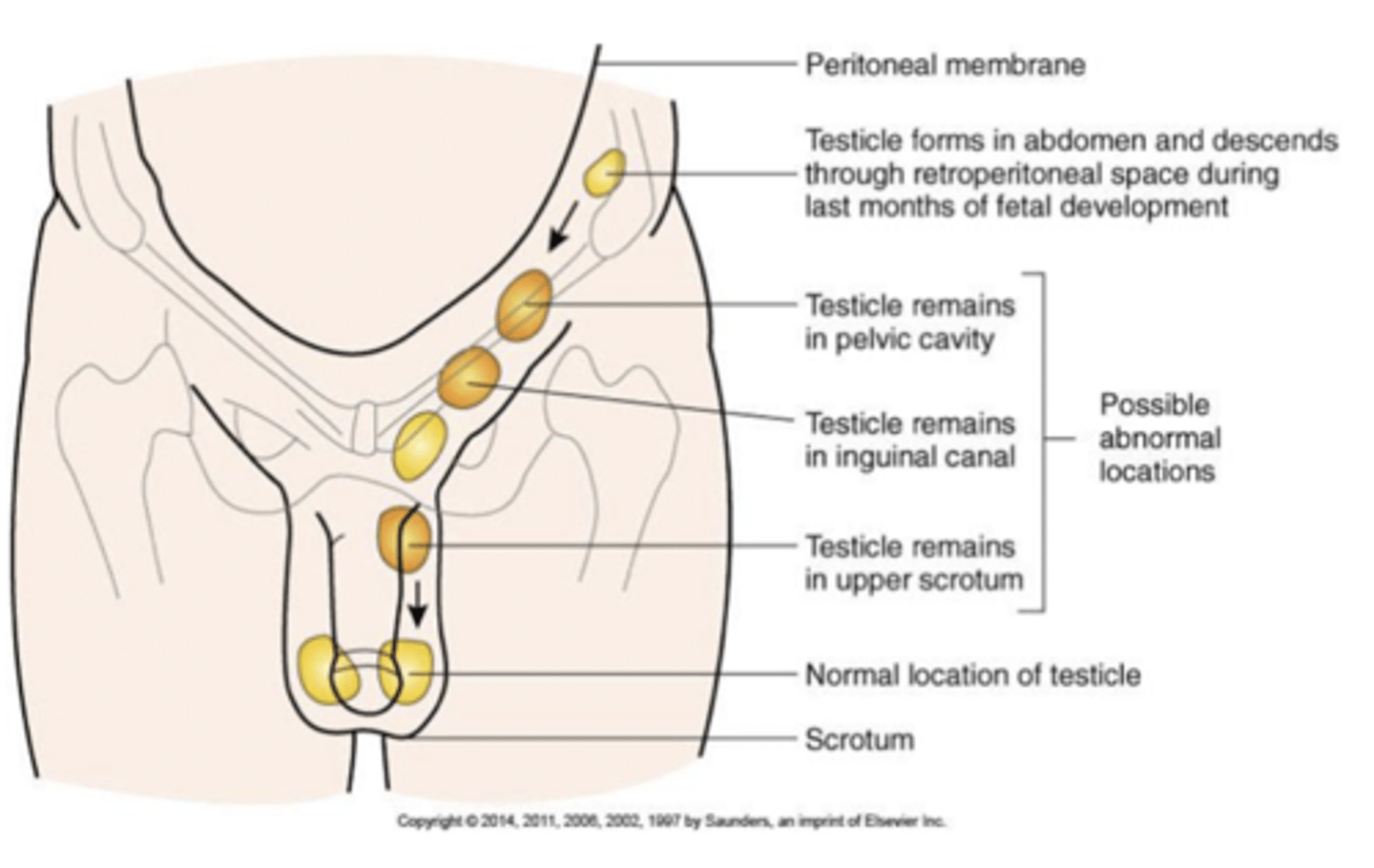
cryptorchidism
the testes fail to descend into the scrotum properly
ectopic testis - the testis are positioned outside of the scrotum that can cause degeneration of seminiferous tubules and impair spermatogenesis. testicular cancer risk is increased
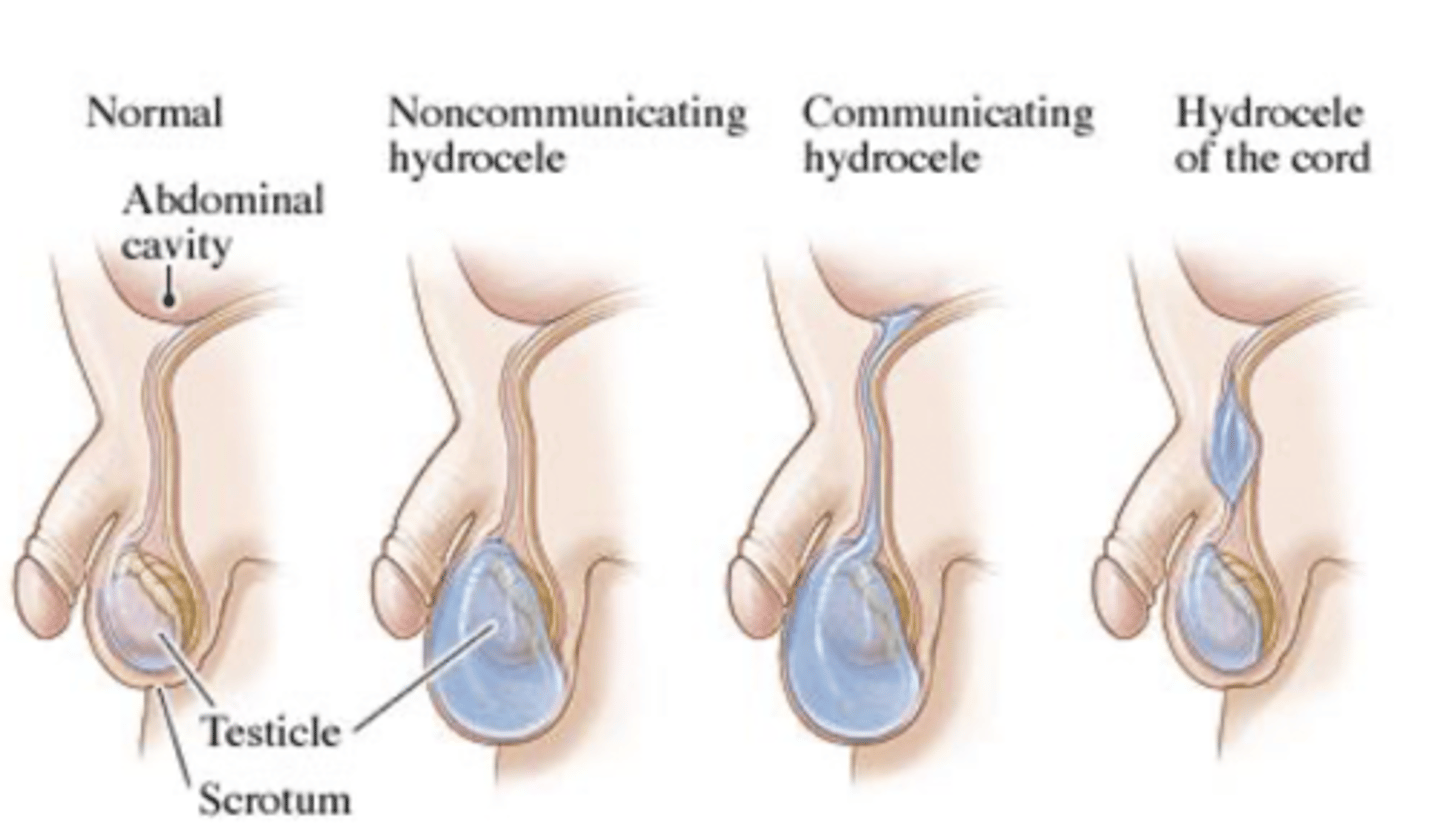
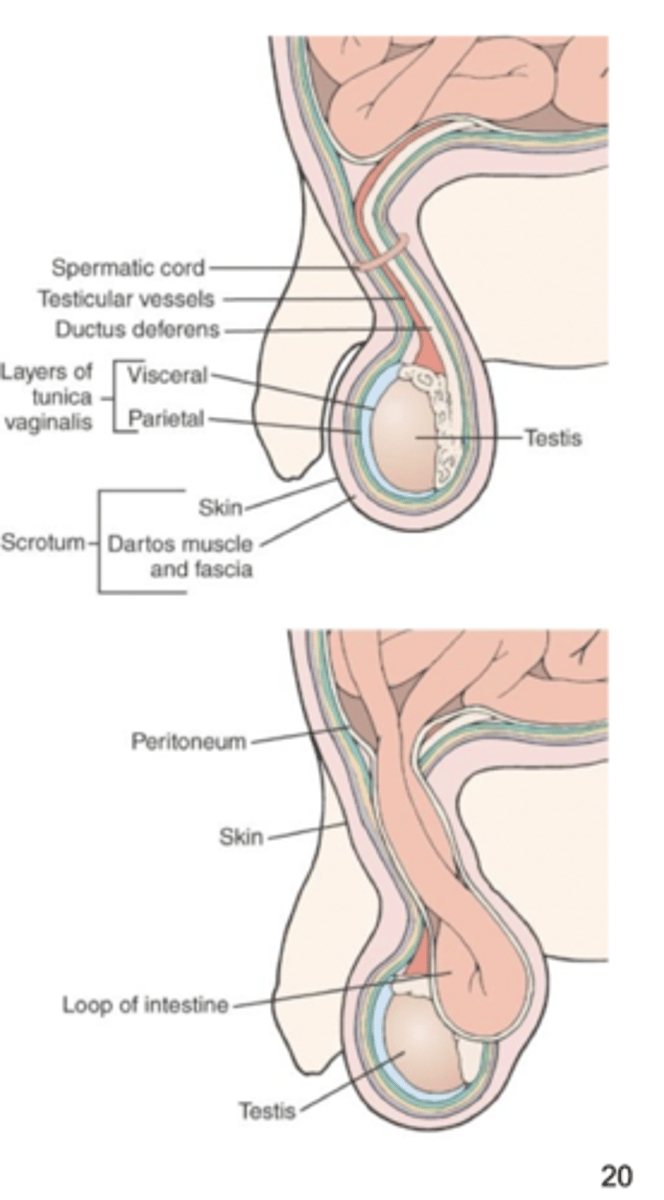
hydrocele
occurs when excessive fluid collects in the space between the layers of the tunica vaginalis of the scrotum
varicocele
dilated vein in the spermatic cord - lack of valves allows backflow in the veins which causes pressure and dilation. blood flow to testes is impaired along with spermatogenesis - causes decreased fertility and is seen most commonly on the left side in men 15-35
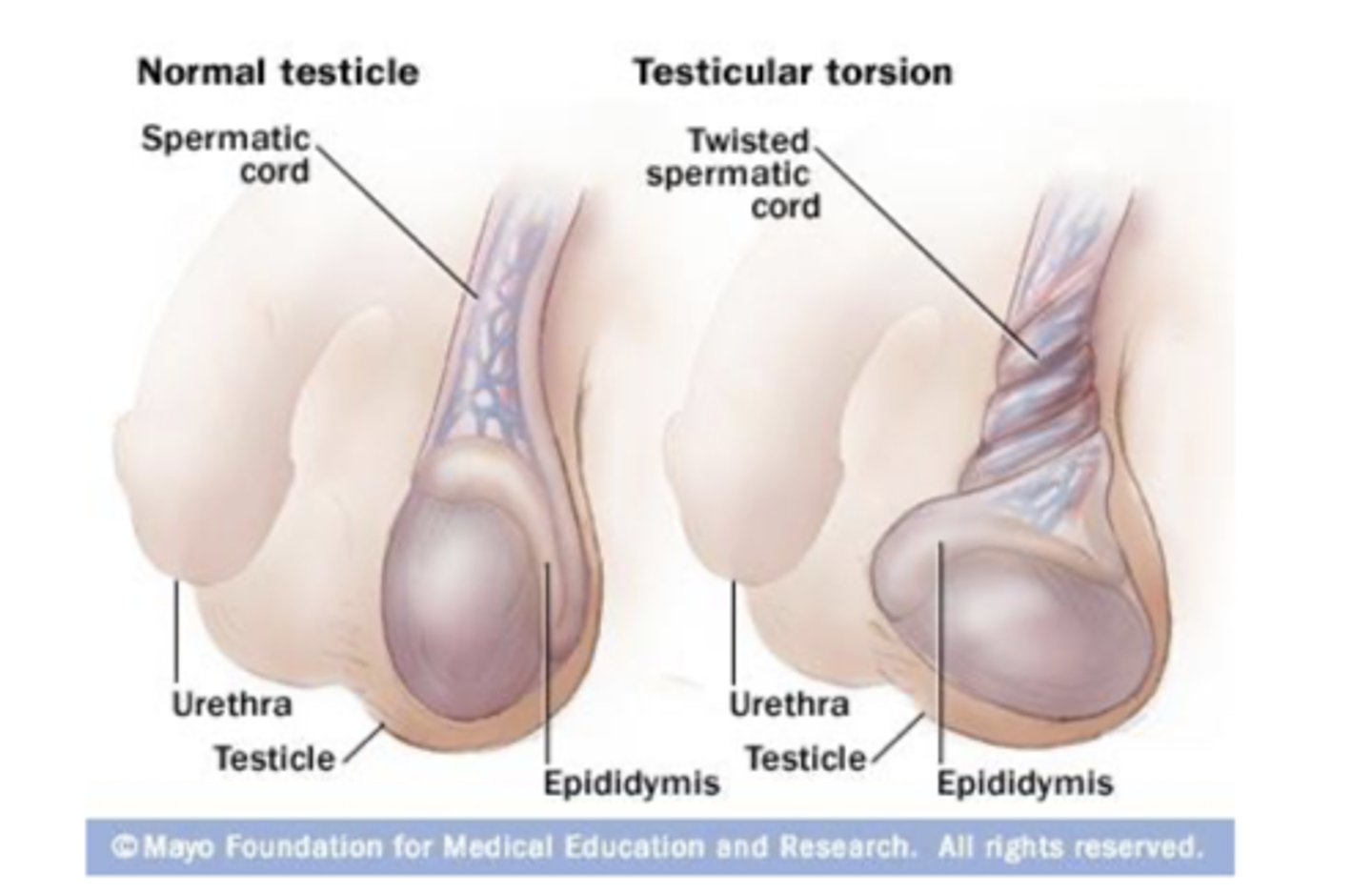
torsion of the testes
testes rotate on the spermatic cord, compressing arteries and veins - causes ischemia or infarction. most cases occur in adolescence and must be treated like an emergency. can be spontaneous or due to injury
epididypitis
inflammation of the epididymis from a bacteria infection... STIs associated with urethritis and non-STIs are associated with UTIs and prostatitis
orchitis
infection of the testes that can be precipitated by a primary infection in GU and can spread to testes through bloodstream or lymphatics such as with the mumps virus.
how is epididymitis diagnosed?
lab findings reveal elevated WBC count.. urinalysis and urine culture, urethral specimen, midstream specimen, gram-staining, doppler ultrasound to reveal blood flow patterns to testes
prostatitis
infection of inflammation of the prostate gland
acute bacterial prostatitis
gland is tender and swollen, urine and secretions contain bacteria
nonbacterial prostatitis
urine and secretions contain large numbers of leukocytes
chronic bacterial prostatitis
gland only slightly enlarged, dysuria, frequency, urgency
asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
painless inflammation of the prostate gland where there is no evidence of infection
etiology of prostatitis
acute bacterial by E. coli, Pseudomonas proteus, Strep faecalis.. chronic is associated with many E. coli infections. occurs in young men with UTIs, old men with hypertrophy, STDs, catheterization, bacteremia
signs and symptoms of prostatitis
acute and chronic forms both manifested by dysuria, urinary frequency and urgency. decreased stream, acute fever and chills, lower back pain, leukocytosis, abdomen discomfort, systemic signs, anorexia, muscle aches
treatment of postatitis
antibacterial drugs like ciprofloxacin or antiinflammatory drugs and prophylactic antibacterial agents
hernia
some males still have an opening were testes descended from the abdominal cavity, which makes these males more prone to inguinal hernias
benign prostatic hypertrophy
occurs in half of older men.. compression of urethra and urinary obstruction.. estrogen-testosterone imbalance. no coma. typically a nonmalignant enlargement that is characterized by the formation of large, discrete lesions in periurethral region
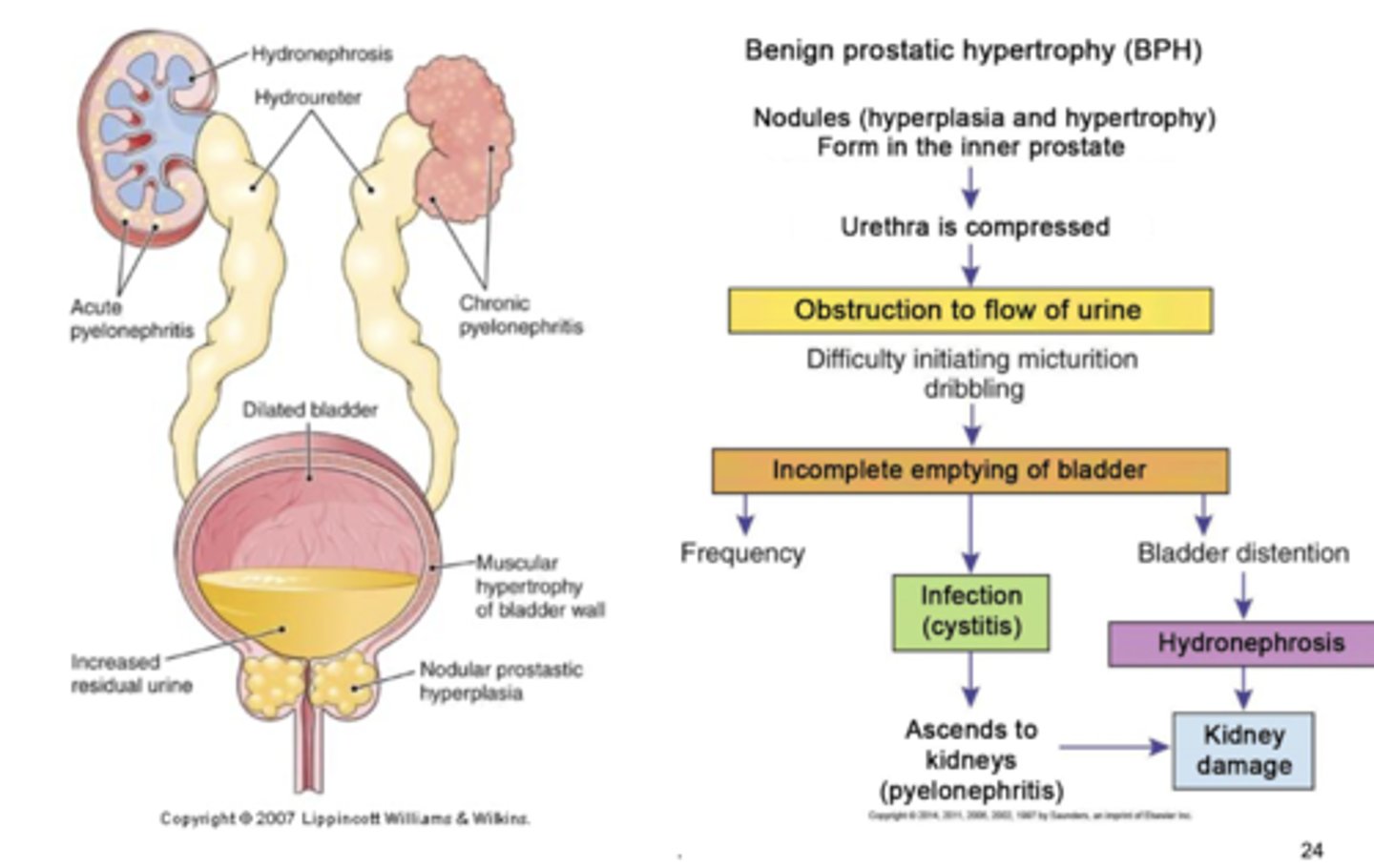
other notes on benign prostatic hypertrophy
enlarged gland palpated on digital rectal exam, leads to frequent infections, continued obstruction will cause distended bladder, dilated ureters, hydronephrosis, renal failure.
signs and symptoms of BPH
obstructed flow, hesitancy in flow starting, dribbling, decreased flow strength, increased frequency and urgency, nocturia, dysuria w infection
treatment of BPH signs and symptoms
drugs like dutasteride to slow enlargement, smooth muscle relaxers like tamsulosin, surgery, combination of finasteride and doxazosin to reduce progression of hypertrophy
prostate cancer
most common cancer in older men.. third leading cause in death and 1/6 are affected. most are adenocarcinomas arising near surface of the gland. many are androgen-dependent
risk factors for prostate cancer
>40 in black men... frequency increased in black men. family history.. fatal prostate cancer linked with smoking and higher BMI
prostate cancer is both invasive and metastatic
some forms are highly aggressive and some aren't. 5-10% are caused by inherited mutations. other causes are high androgen levels, increased insulin-like growth factor, history of recurrent prostatitis.
signs and symptoms of prostate cancer
hard nodule felt on periphery of gland, hesitancy in urination, decreased urine stream, frequent urination, recurrent UTI
grading of prostate tumor
T1: asymptomatic and discovered in histologic exam
T2: tumors are palpable on digital exam but confined to prostate gland
T3: tumors extend beyond prostate
T4: tumors pushed beyond prostate to involve adjacent structures
Dx of prostate cancer
prostate specific antigen, prostatic acid phosphatase, ultrasonography, biopsy, bone scans
treatment of prostate cancer
surgery, radiation, orchiectomy and antitestosterone drugs, chemotherapy
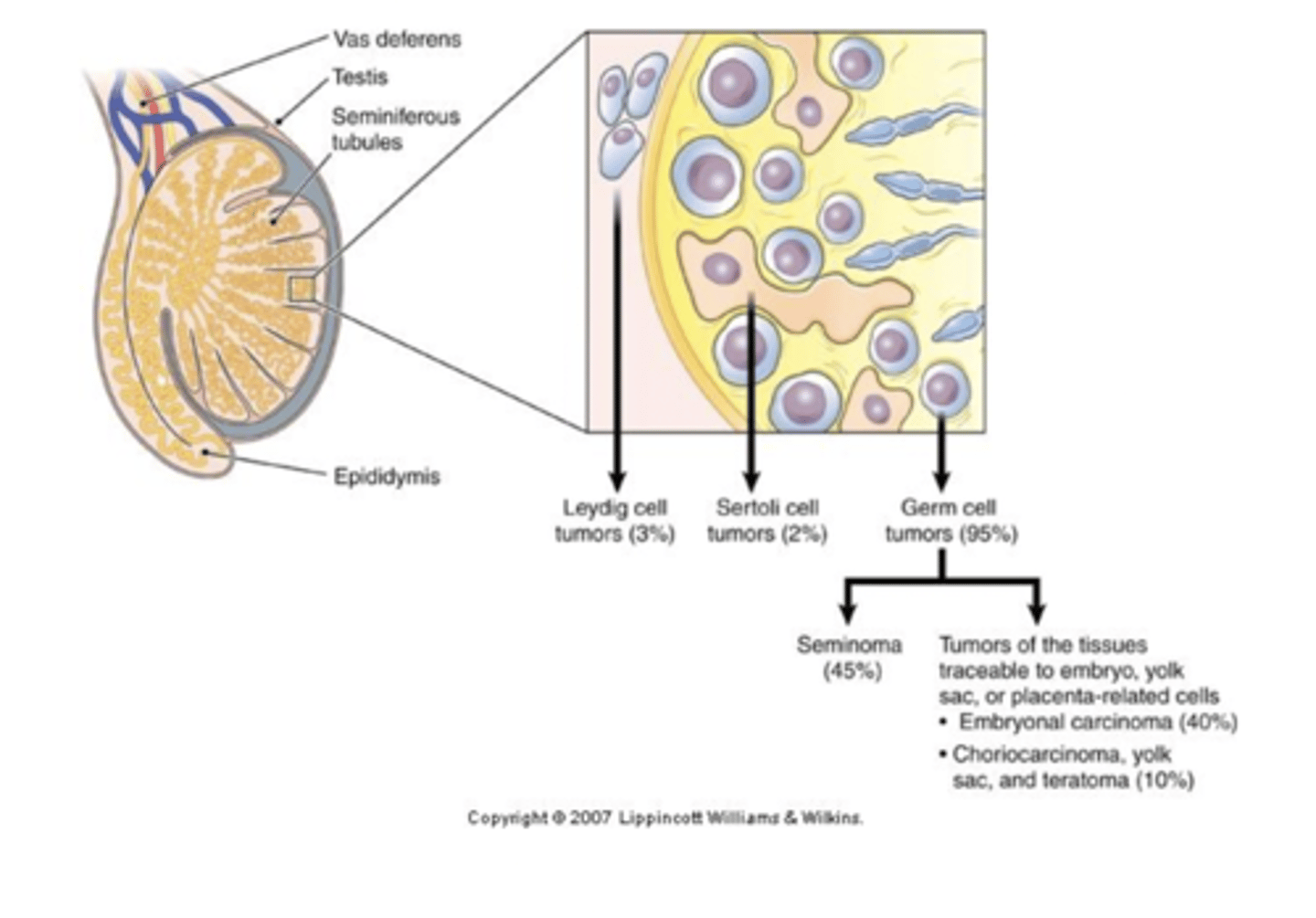
testes cancer
most cancers of the testes are malignent... most common solid tumor cancer in young men with increasing cases. testicular self-exam is needed for detection early
origination of testicular cancer
originate from one type of cell or mixed cells from various sources. teratoma has a mixture of different germ cells, some malignant tumors secrete hCG or AFP which are markers for diagnosis
spreading pattern of testicular cancer
appear in common iliac and paraaortic lymph nodes, then to the mediastinal and supraclavicular lymph nodes, then through the blood the lungs, liver, bone and brain
TNM classification
stage 1: tumor confined to testes, epididymis or spermatic cord
stage 2: tumor spreads to retroperitoneal lymph nodes below the diaphragm
stage 3: metastases outside the retroperitoneal nodes or above the diaphragm
risk factors of testicular cancer
heredity (Chromosome 12), cryptorchidism, exposure to herbicides and other environmental agents
signs and symptoms of testicular cancer
tumors are hard, painless, and usually unilateral. testes may feel enlarged or heavy, scrotum and pelvis may have dull pain, hydrocele and epididymitis can develop.. if tumor secretes hormones then gynecomastia occurs
diagnosis of testicular cancer
usually no biopsy.. tumor markers of hCG and AFP, ultrasound, computed tomography, lymphangiography
treatment of testicular cancer
surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.. client may donate sperm to ensure future fertility