Electrical Sem 1 - Unit 3 Electical machines
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are the 3 types of conventional rotary machine.
DC Machines
Synchronous Machines
Asynchronous Machines
What are the 2 types of DC machine?
Brushed DC motor
Brushless DC motor
What is the difference between them?
Brushed motor:
Electromagnetic field or permanent field
Physical carbon brushes
Brushless DC motor:
Eletrical commutator
Hall effect sensors
Permanent and electromagnetic field
Why are the brushes needed in a brushed DC motor?
The brushes are required to switch which fields are active as the rotor rotates to ensure the torque is always being produces in the correct direction. With out switching the field, the rotor poles will just align to the field direction.
What is hall effect sensors Permanent for?
For detecting the presence and strength of a magnetic field.
What is an electrical commutator for?
The commutator is a complex switching circuit that switches which coils are active and producing the field as the rotor rotates to produce smooth and consistent torque based on the output of the hall effect sensors.
What is described by the machine constant?
It desiprubes how effective an electrical machine is at generating emf from being driven or vide versus. If the the field current is kept constant, the machine constant tells you how much emf was generated for a certain rotor speed.
How is electromagnetic torque calcualted?
Defined as armature power over angular speed and is calculated using the machine constant.

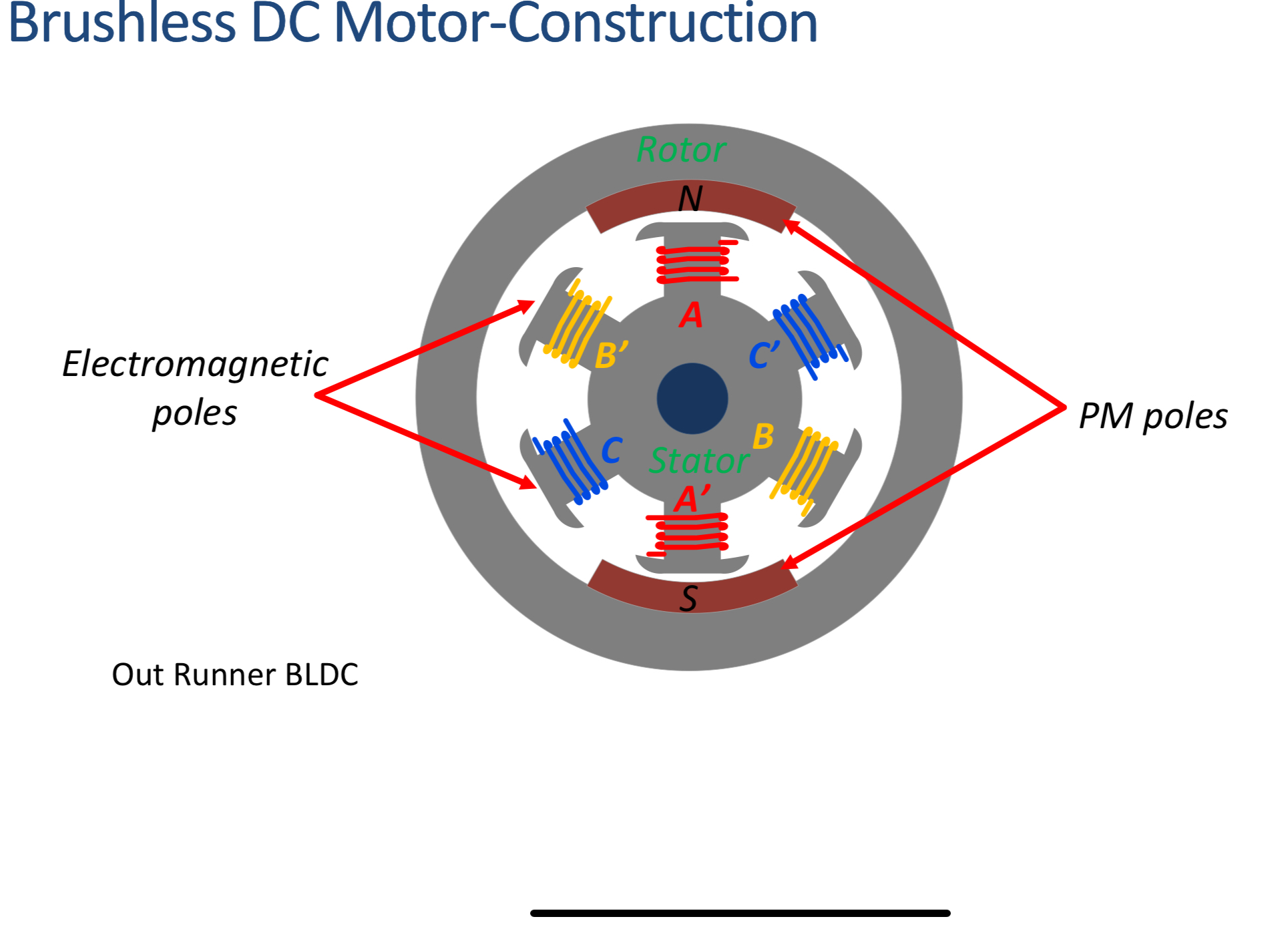
How is a brushless DC motor constructed?
Central stator and a surrounding rotor.
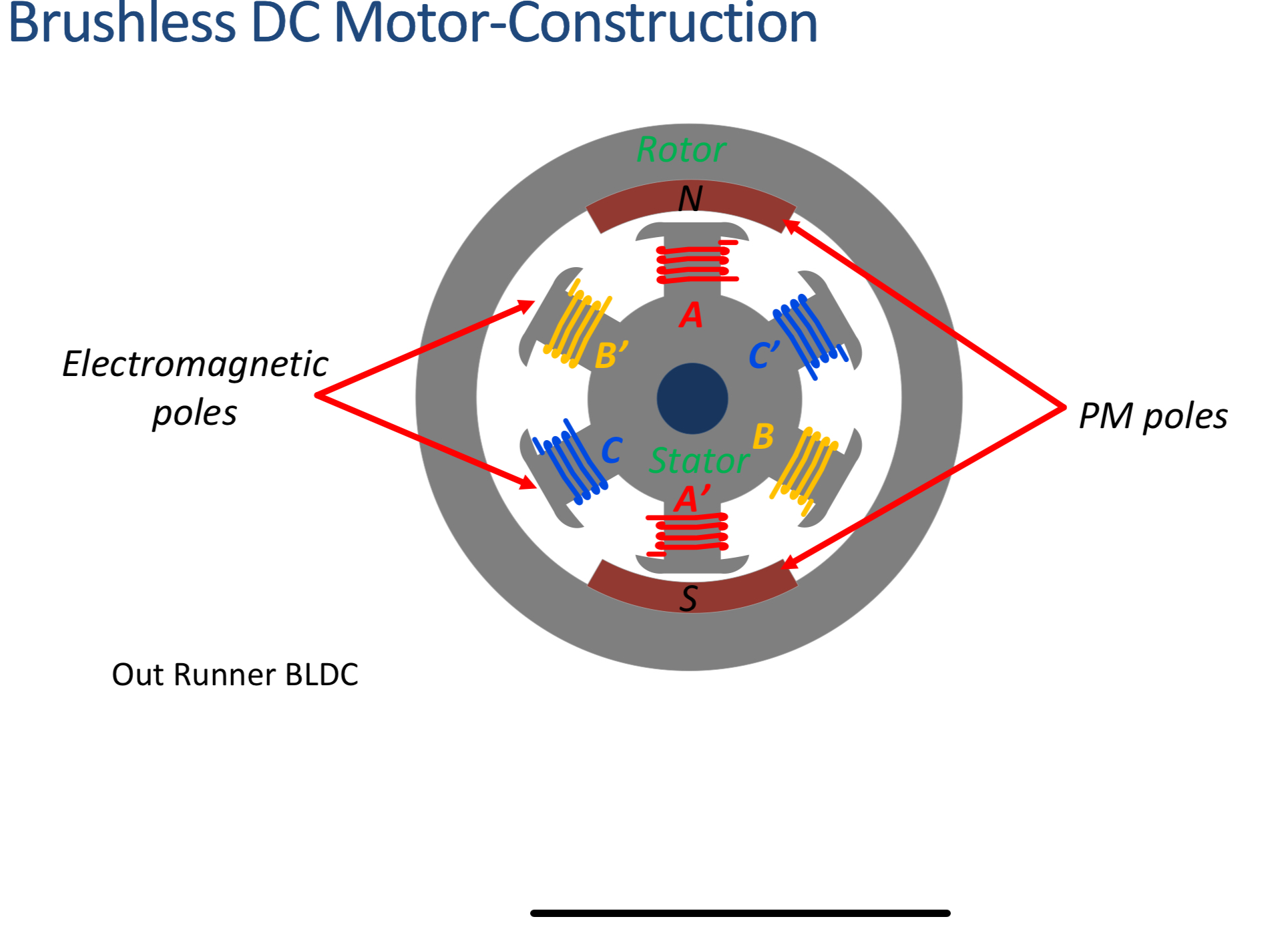
Where are the permanent magnets and electro magnets located?
Permanent magnets on the rotor and electromagnets on the stator.
What is a stepper motor and what is it used for?
They are highly accurate motors that change the angle of the rotor per pulse. Steps per revolution can vary from a few up to 400. Used for precise control applications where incremental motion is needed.
What is the fundamental type of the motor?
Variable relucatance machine.
What is the principle of operation?
Coils on the stator are switched on and generate a magnetic field. The rotor is made of a high permeability, low reluctance material and aligns itself to the field to minimise the reluctance of the system giving a certain angle of movement per coil switch.
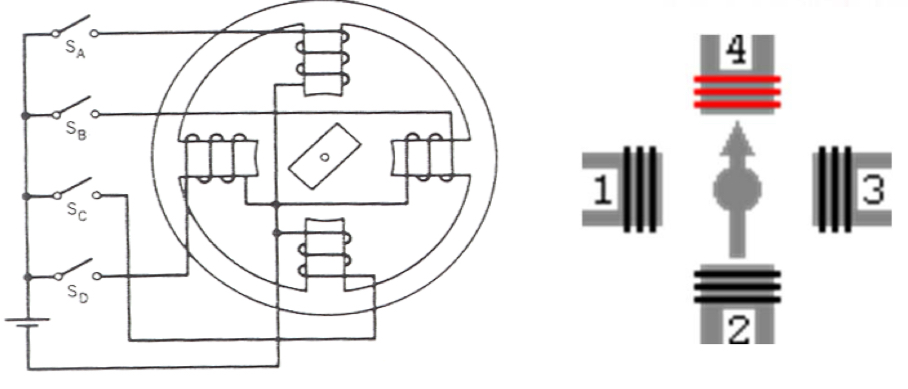
What is meant by pull over torque?
The driving torque of the motor to move one step.