Lecture 5: Antibody Structure
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
antibodies
produced when naïve B cells with surface Ig bind Ag causing activation to proliferate and differentiate into Ab secreting plasma cells
features of antibodies
secreted Ig
responds to extracellular pathogens and toxins
binds pathogen to disable it or make it more susceptible to immune system
circulates in blood plasma, lymph and stays at mucosal surfaces
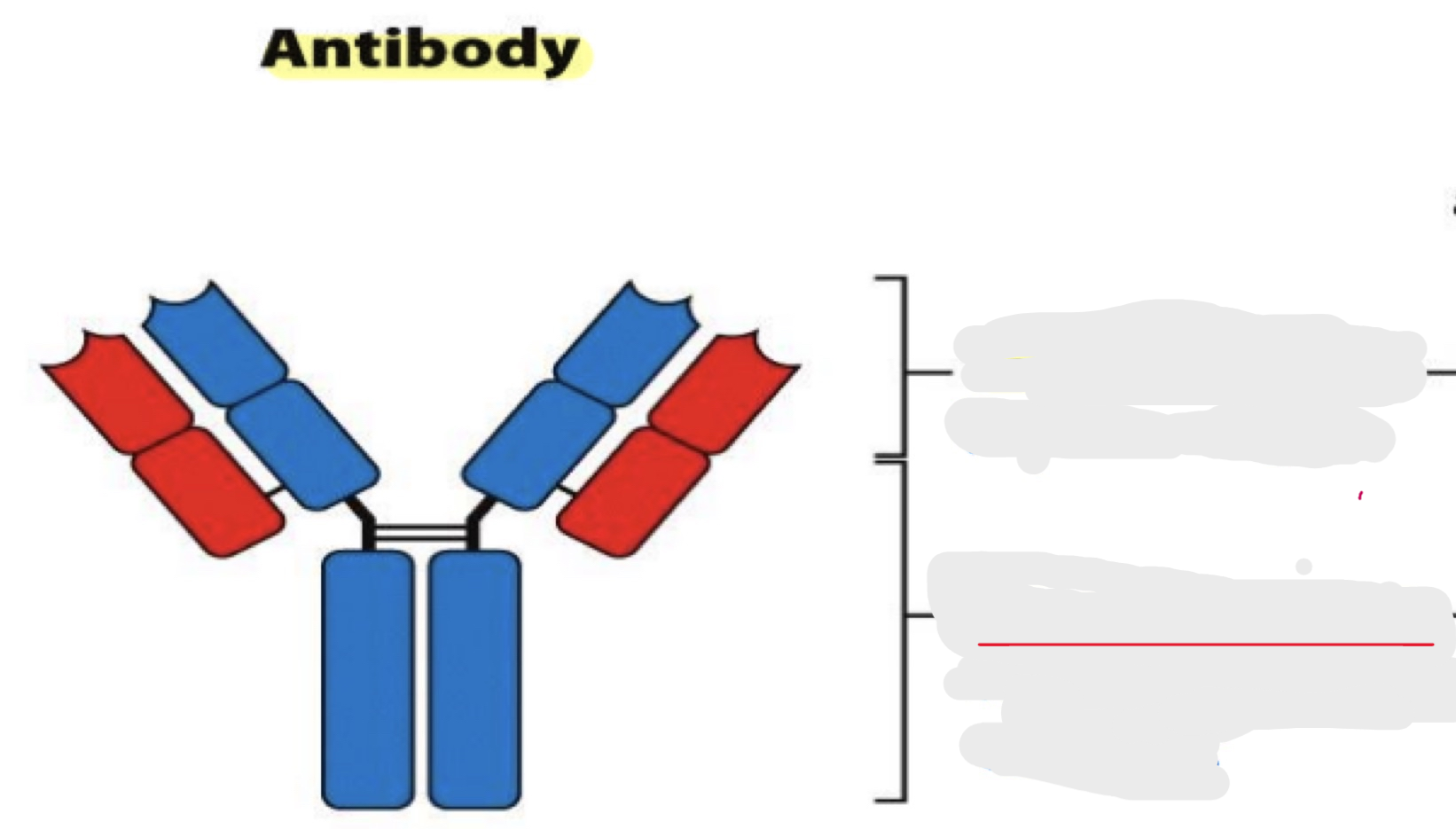
structure of antibodies
glycoprotein
disulfide bonds
hinge region: G, D, A
benefit of hinge region
makes more shapes possible to improve binding
classes/isotypes of Ab
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgG
IgM
immunological domain
folded peptides that protect the antibody from degradation
hypervariable regions / complementarity determining regions
small regions of high amino acid sequence diversity within the V (variable) regions off Ig and TCR, which correspond with the antigen binding site on the light chain
benefit of hypervariable regions / complementarity determining regions
increases antigen binding diversity
affinity
strength of the antibody for its epitope
avidity
accumulated strength of multiple affinities summed by many binding interactions
multivalent antigen
antigen with >1 epitope that can be bound by Ab
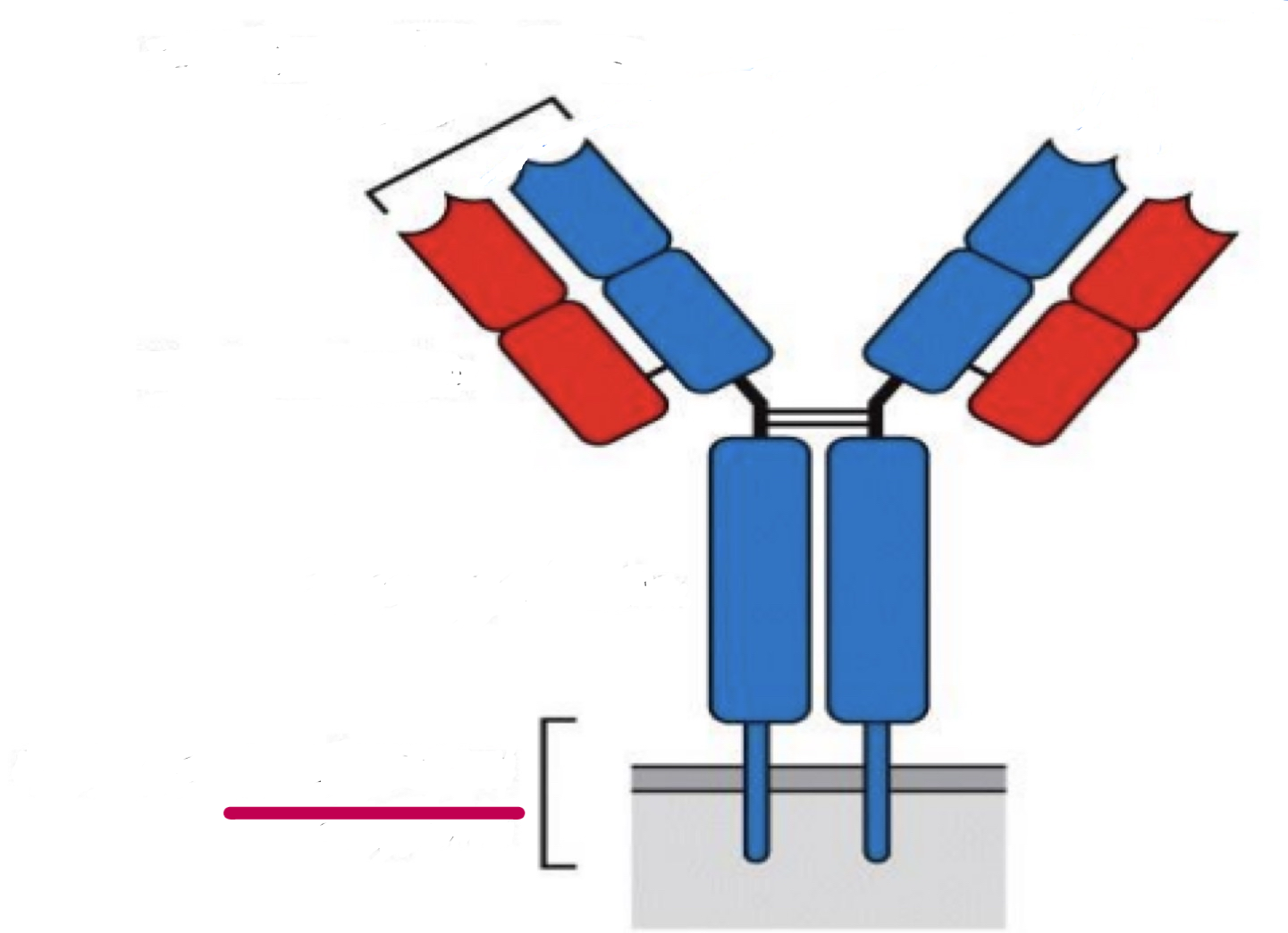
transmembrane region
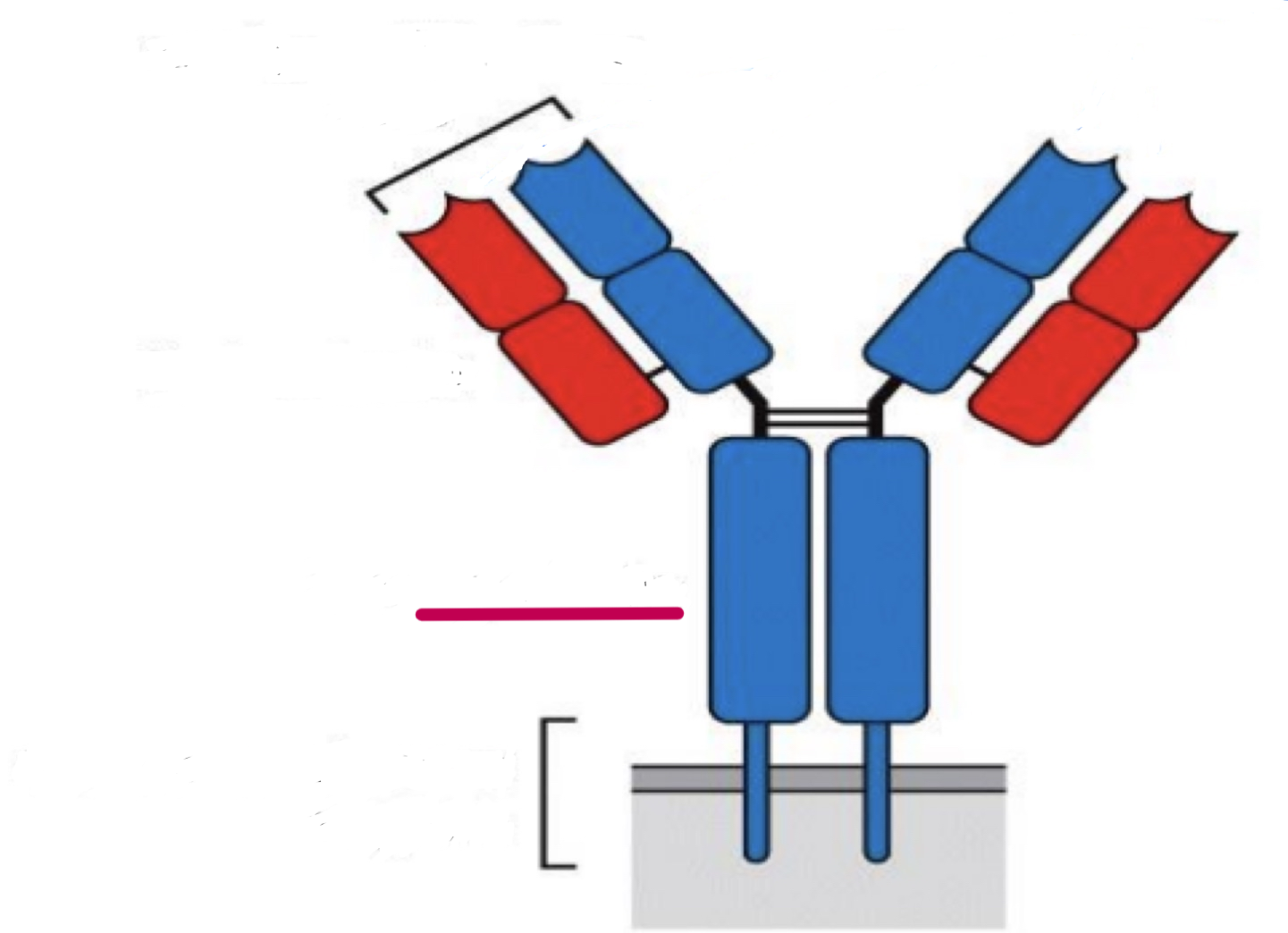
heavy chain
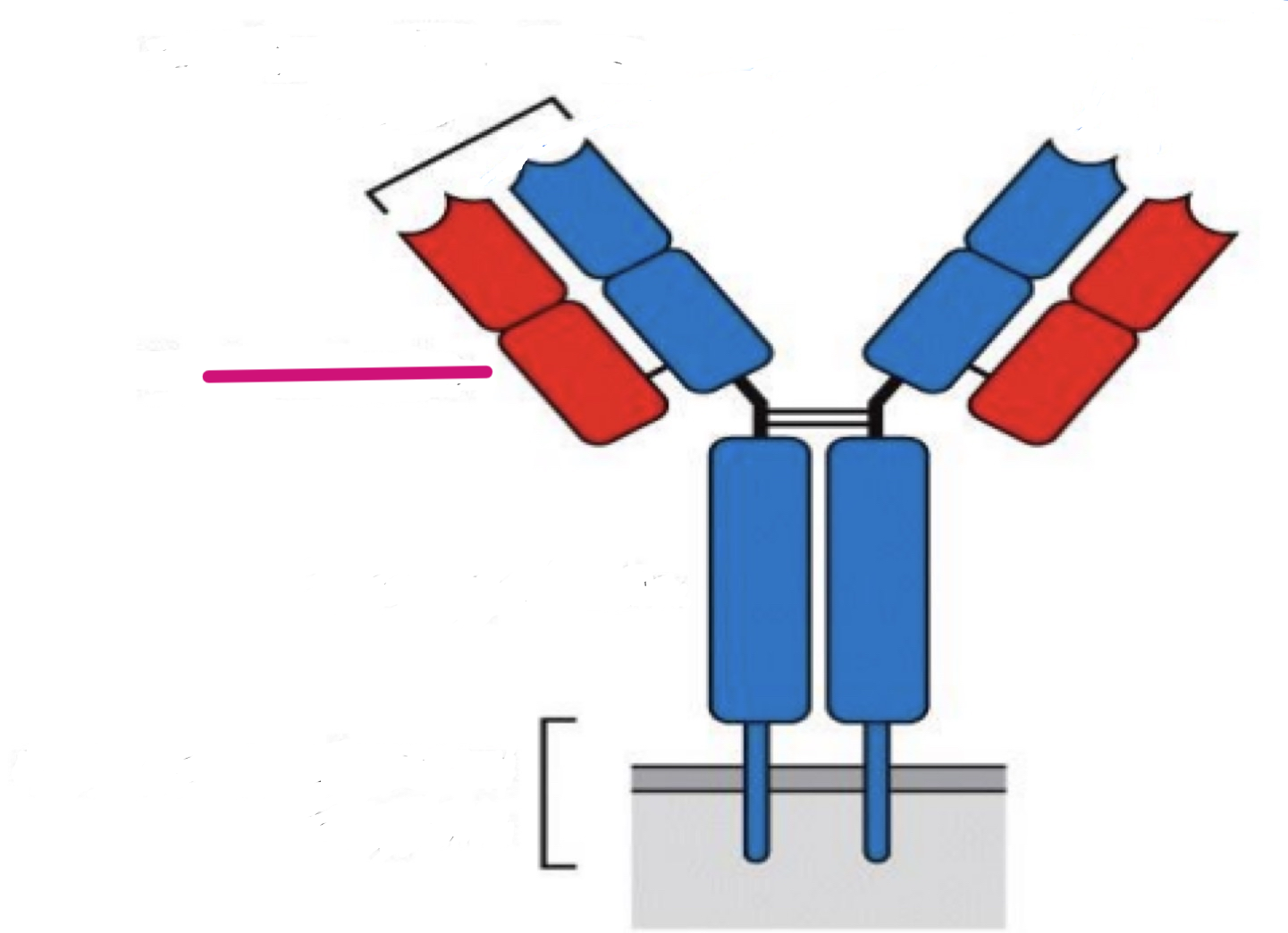
light chain
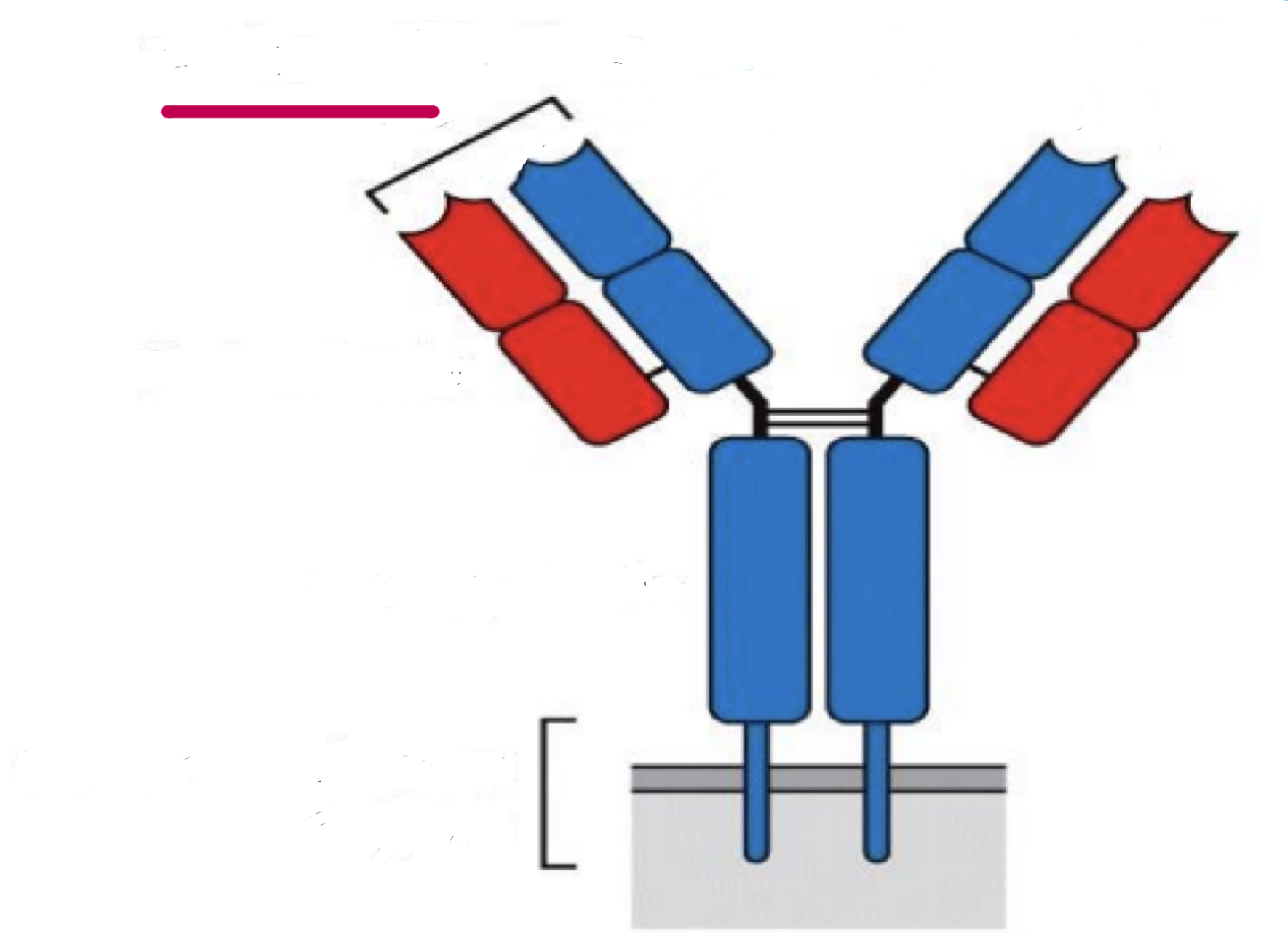
antigen binding site
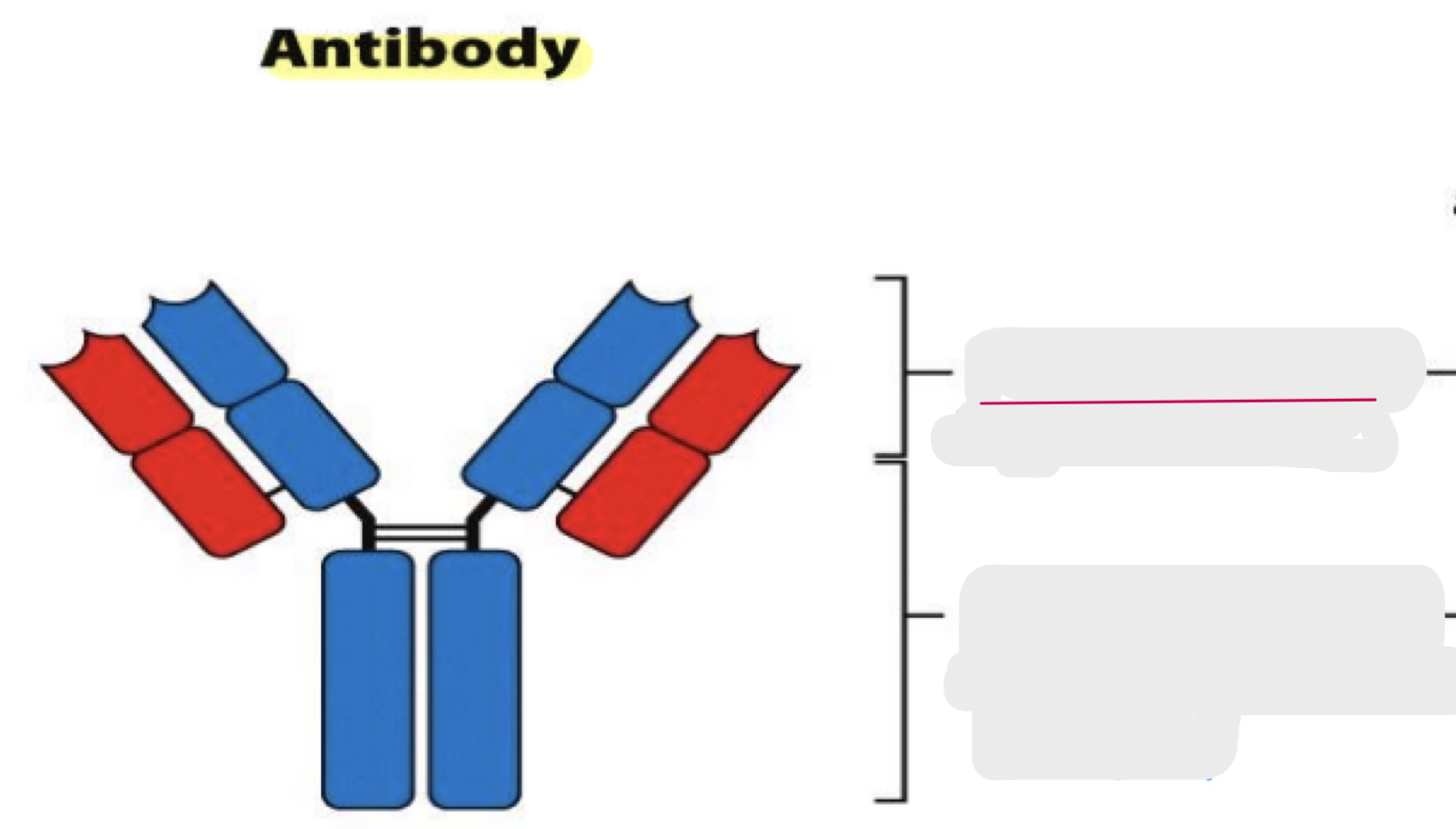
variable region
linear epitope
binding sites are continuous on the epitope/protein amino acid sequence
discontinuous epitope
binding sites are separated on the epitope/protein amino acid sequence
benefit of B cell diversity
allows protection from a wide variety of pathogens
processes that contribute to B cell diversity
VDJ/somatic hypermutation
junctional diversity
somatic hypermutation
processes that occur before antigen exposure
VDJ/somatic hypermutation
junctional diversity
alternative mRNA splicing (to co-express IgD and IgM)
allelic exclusion
processes that occur after antigen exposure
producing secreted antibodies
somatic hypermutation and isotype switching
effector function
recombination signal sequence (RSS)
a site for enzymes to identify to ensure correct directionality
structure of RSS
1 heptamer (7bp) + 12 bb spacer + nonamer (9bp)
1 heptamer (7bp) + 23 bb spacer + nonamer (9bp)
12/23 rule
only segments with opposite RSS will combine (12 + 23). this rule ensures that no D (diversity) regions are lost.
V(D)J recombinase
a set of enzymes that recombine V, D and J segments
structure of V(D)J recombinase
recombination activating gene (RAG)
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
DNA-PKcs and Ku70/80
DNA ligase
DNA Pol
recombination activating gene (RAG)
found only in lymphocytes, made up of 2 proteins (RAG 1 and RAG 2) that cuts DNA @ RSS
enzymes in V(D)J recombinase present in all nucleated cells that repair the DNA after it is cut
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
DNA-PKcs and Ku70/80
DNA ligase
DNA Pol
production of IgM and IgD on the B cell surface with Igb and Iga
BCR is membrane-bound and soluble antibody (IgM and IgD) is secreted
Igb and Iga are required for surface-bound BCR to communicate inside the cell
allelic exclusion
allows only one heavy chain and one light chain per B cell
allelic exclusion benefits/functions
prevents autoimmunity
allows high avidity binding to more effectively clear pathogens
production of secreted IgM
produced by alternative mRNA splicing with IgD
it is often secreted first in humoral immunity
somatic recombination (SRC) / VDJ recombination / gene rearrangement
a single gene segment of each type is brought together to form a DNA sequence encoding the V region of an immunoglobulin chain
enzymes cut & rejoin DNA as directed by RSS
somatic recombination (SRC) / VDJ recombination / gene rearrangement benefit
increases diversity and specificity of antibody response
somatic recombination (SRC) / VDJ recombination / gene rearrangement steps
cut DNA: RAG complex binds two different RSS and cut
DNA repair: enzymes repair DNA forming signal joining and coding joint
somatic recombination (SRC) / VDJ recombination / gene rearrangement order of segment arrangement
D-J segments are joined first, then V joins D-J
coding joint
the DNA sequence formed by the joining of gene segments during V(D)J recombination
junctional diversification
random addition or subtraction of nucleotides at the coding joint
junctional diversification benefit
increases diversity and specificity of antibody response
isotype switching
by altering the heavy chain the isotype of the antibody is changed
isotype switching steps
AID replaces C with U
UNG removes U
APE-1 nicks both DNA strands
two switch regions are ligated together
the result is a new isotype
isotype switching benefit
improves specialization of function and ability to recruit effectors
somatic hypermutation
introduces point mutations by enzyme AID and then selects for antibodies that bind more tightly to the pathogen
somatic hypermutation benefit
improves Ag binding to Ab
affinity maturation
the increase of affinity of Ag binding sites due to SHM and selection of higher affinity BCRs
affinity maturation benefit
increases affinity of Ag binding sites
the only pentameric isotype
IgM
has (2 × 5=) 10 binding sites!
IgA function
neutralization
IgD function
works with IgM
IgE function
sensitization of mast cells (responsible for asthma + allergies)
IgG function
widest range of fucntion
IgM function
activates complement system
framework region
conserved, structurally stable portion of the variable domains of antibody heavy and light chains