Chapter 39: The Respiratory System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
simple organisms, like cnidarians, exchange gas via ___
simple diffusion
what system do insects have that contain epithelial tubes that function as a respiratory organ?
tracheal system
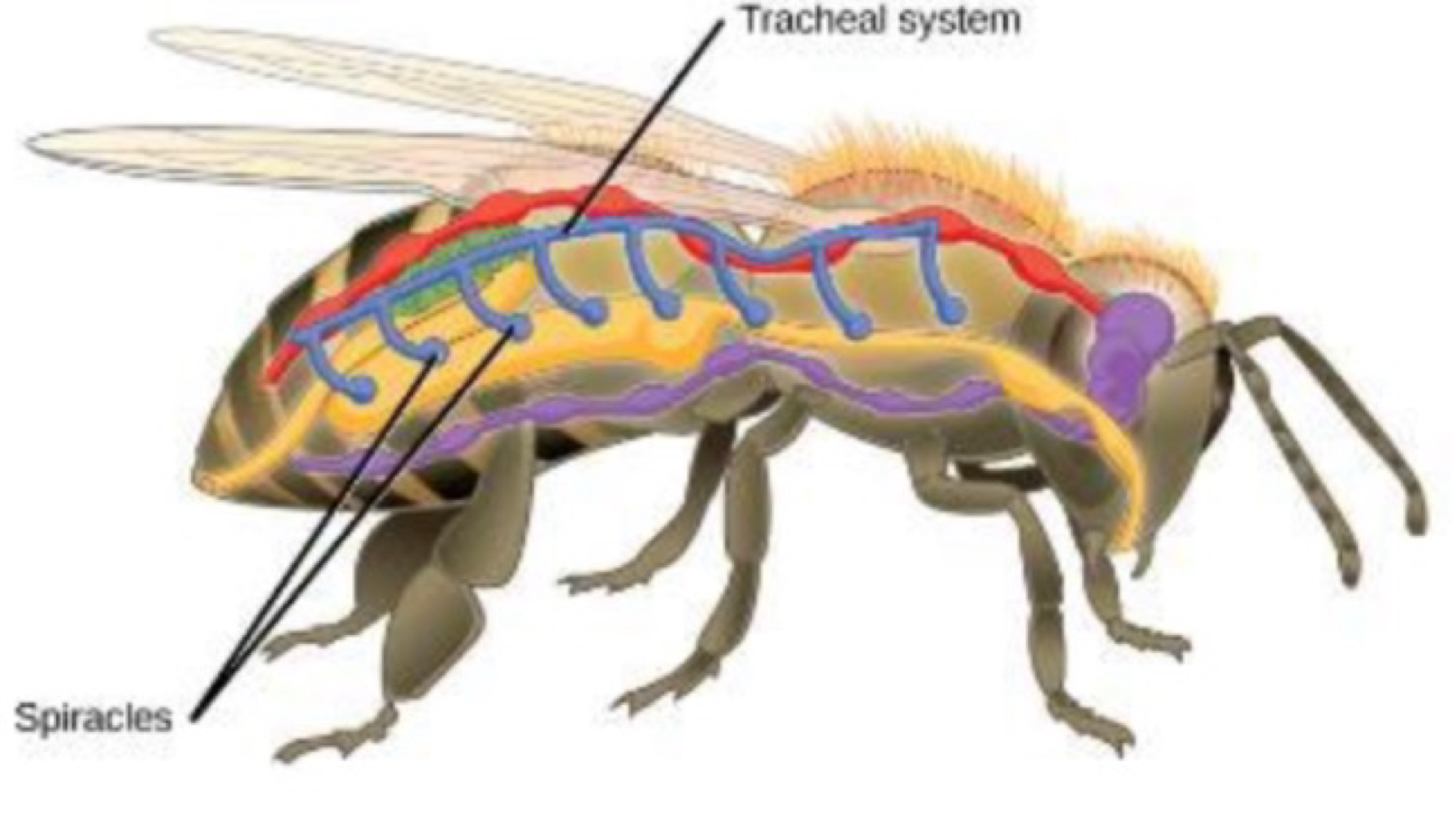
insects have this hole structure that pulls gas from the environment into the trachea
spiracles
“trachea → air sacs → tracheoles” describes ___
how insects respire
respiration through the skin is done via ___
cutaneous gas exchange
what kind of vertebrates have cutaneous respiration and functional lungs?
amphibians and reptiles
true or false: permeable skin may result in dehydration or toxic absorption
true
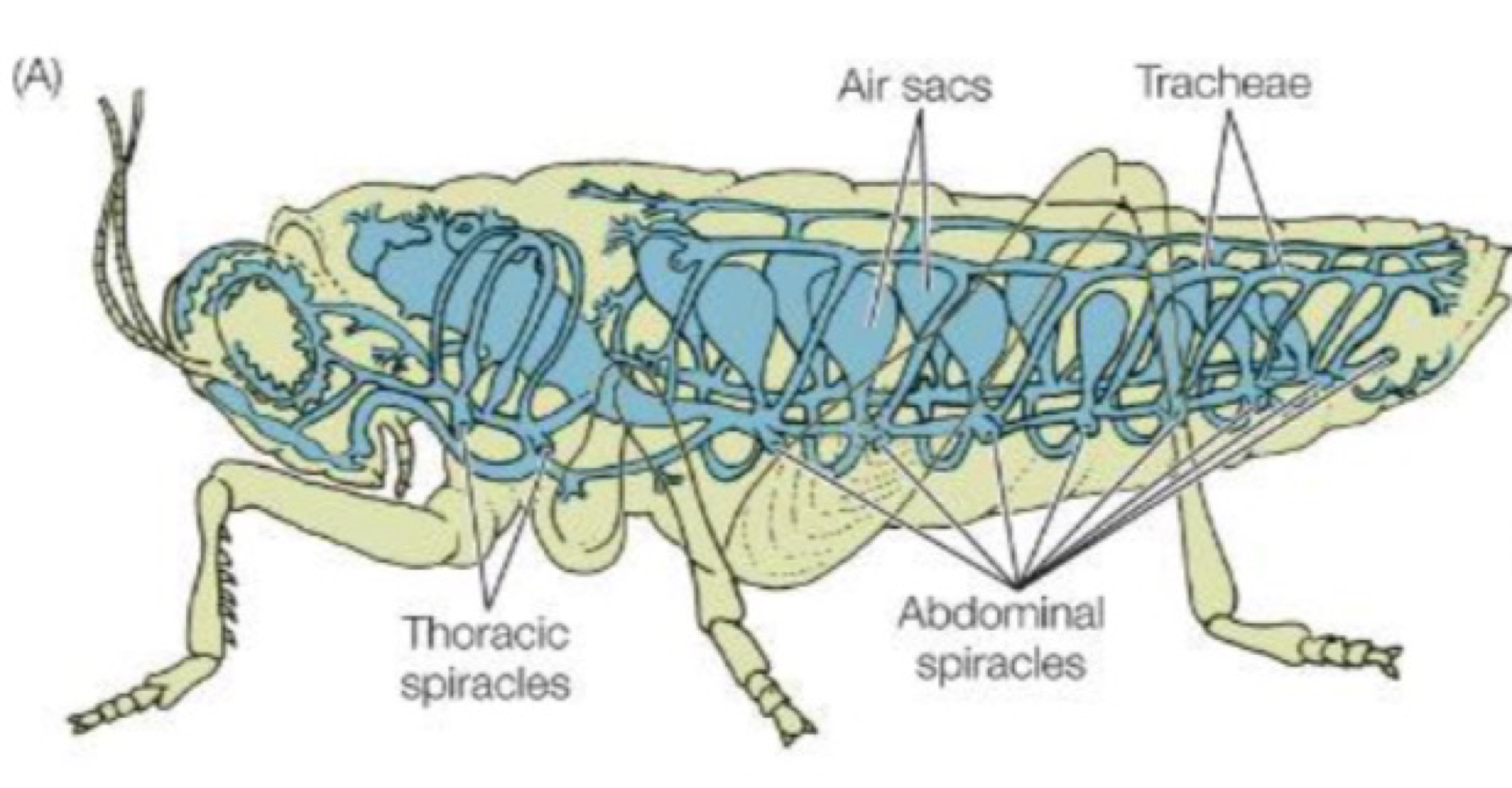
these thin tissue filaments are highly branched and folded with many capillaries for gas exchange among gnathostomes
gills
true or false: gills can only be external
false. gills can be internal (protection) or external
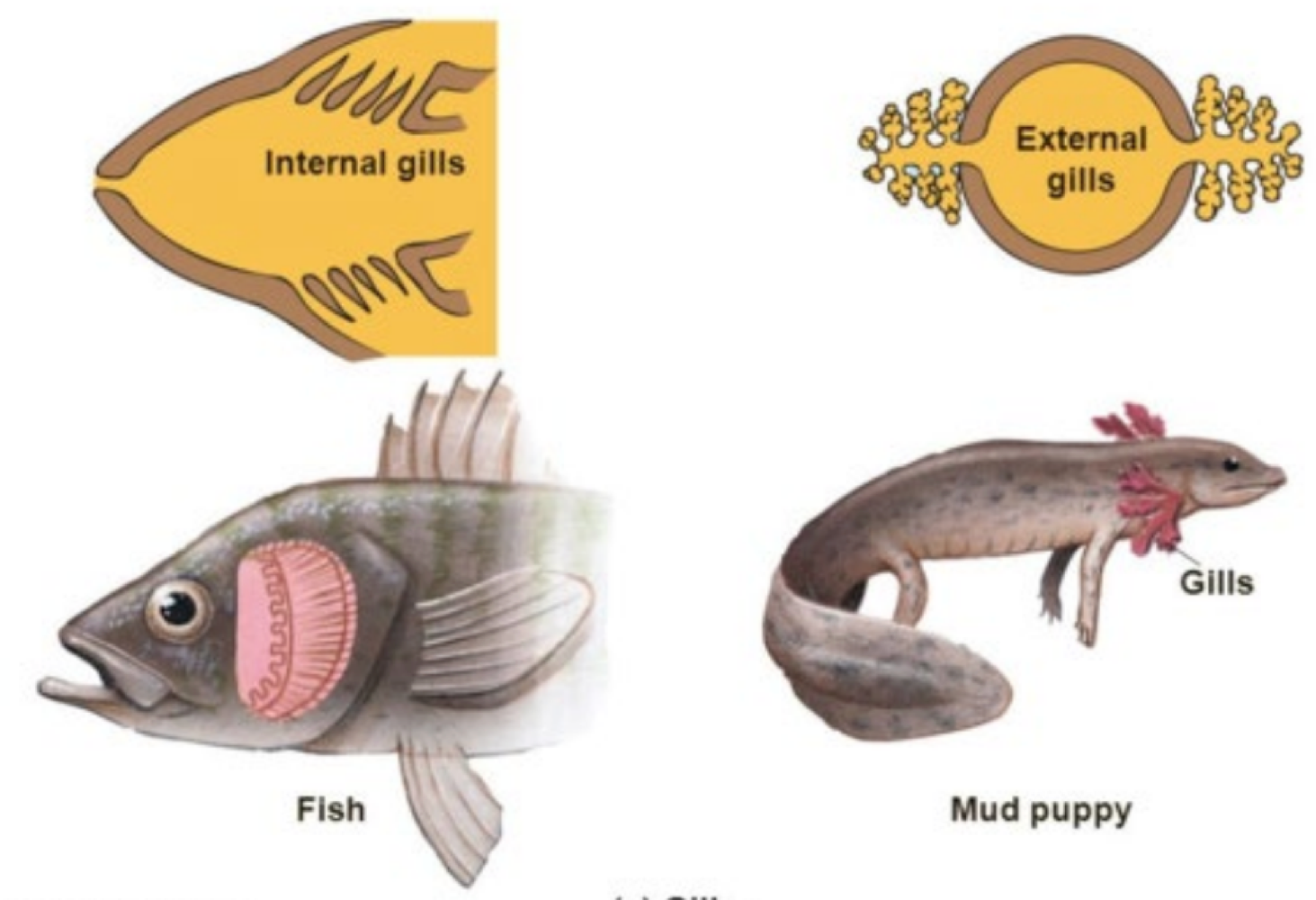
why are gills needed for gas exchange?
because oxygen dissolves less than 1% in water
true or false: water and blood move bidirectionally in the gills and their blood vessels, respectively
false. water and blood move in one direction in the gills and their blood vessels, respectively
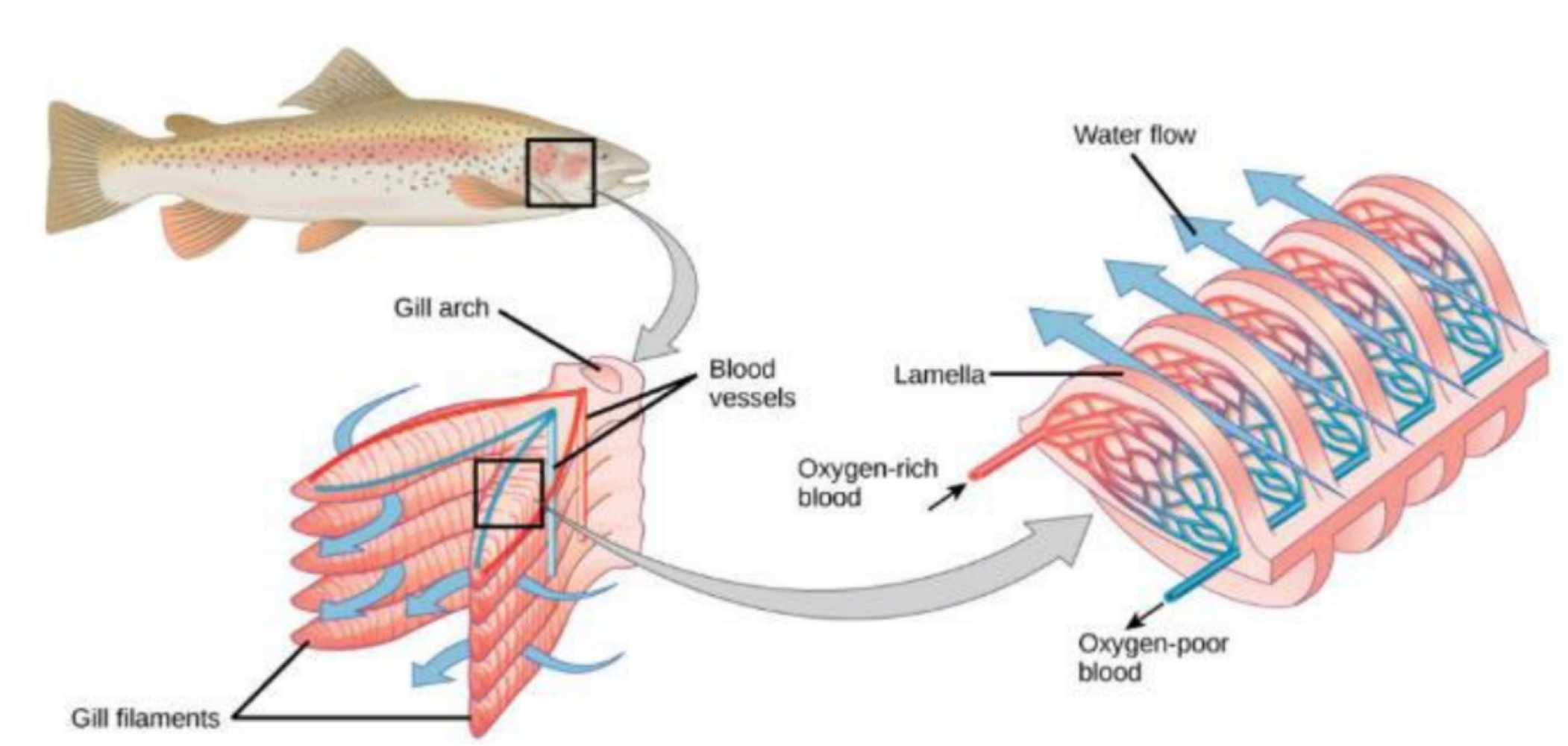
this form of gas exchange allows oxygen to move from water into the blood
countercurrent gas exchange
true or false: in countercurrent gas exchange, oxygen concentration is higher in water
true
true or false: countercurrent gas exchange allows for max oxygen extraction and carbon dioxide secretion
true
this form of gas exchange prevents more oxygen from entering the blood after a certain point
cocurrent gas exchange
true or false: in concurrent gas exchange, oxygen concentration is different in water and blood
false. in concurrent gas exchange, oxygen concentration is the same in water and blood
this type of respiration brings oxygen in and removes it from the body
inhalation
this type of respiration exchanges gases between air and blood in the lungs
external respiration
this type of respiration exchanges gases between blood and body tissues
internal respiration
this type of respiration exchanges gases between cells to make energy
cellular respiration
this component of the upper respiratory system contains the nose, nasal passage, and sinuses
nasal cavity
“passageway for respiration composed of ciliated cells and resonating chambers for voice” describes the ___
function of the nasal cavity
this component of the upper respiratory system connects the nose and mouth to the esophagus
pharynx
this component of the upper respiratory system is known as the voice box
larynx
“flexible cartilage flap that routes air and food” describes what structure of the larynx?
epiglottis
“vibrates for sound production” describes what structure of the larynx?
vocal cords
this component of the upper respiratory system transports air to and from lungs
trachea (windpipe)
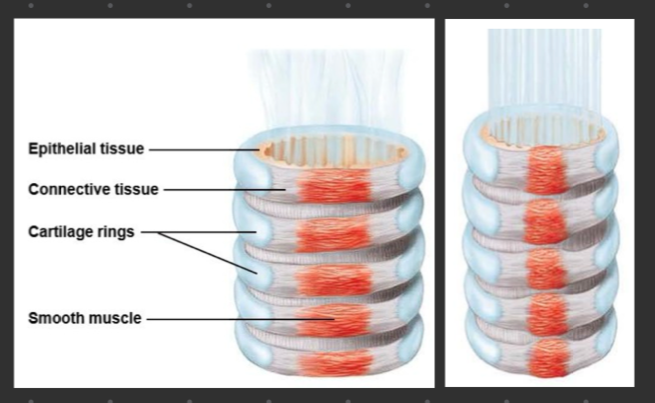
true or false: the trachea is composed of U-shaped cartilage rings held together by epithelia tissue and skeletal muscle
false. the trachea is composed of C-shaped cartilage rings held together by connective tissue and smooth muscle
true or false: the trachea is lined with mucus-secreting ciliated epithelium to trap foreign particles and move them up and out of lungs
true
bronchi
branches of the trachea containing ciliated epithelia, smooth muscle, and cartilage
bronchioles
smallest branches lacking cartilage and cilia
true or false: bronchioles deliver air to tiny sacs called bronchi
false. bronchioles deliver air to tiny sacs called alveoli (alveolus)
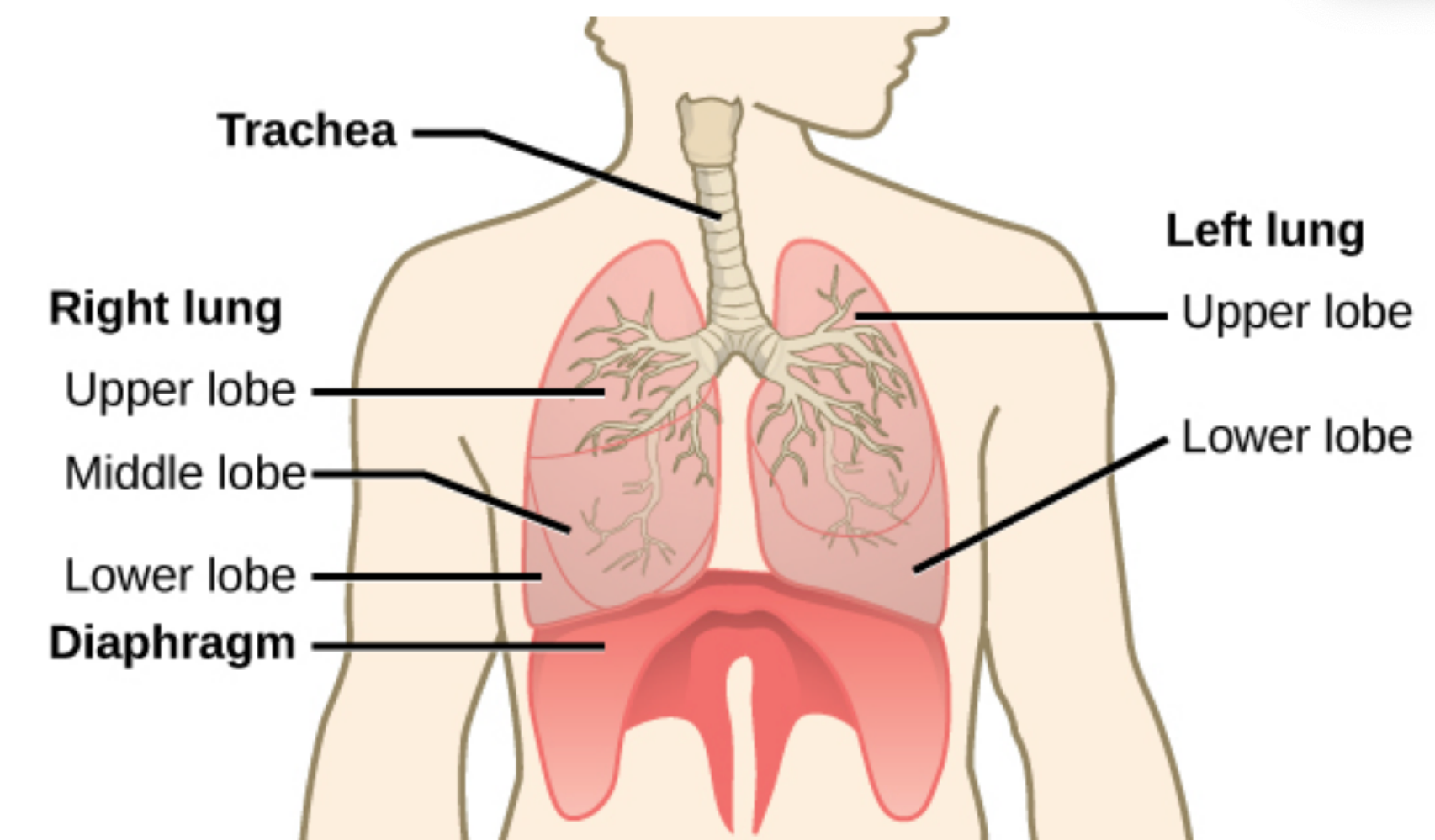
lungs
supportive tissue enclosing bronchi, bronchioles, blood vessels, and alveoli
true or false: lungs are enclosed in two layers of pleural membranes
true
why does the pleural cavity contain fluid?
to reduce friction during breathing
how many lobes does each lung have?
left = 2, right = 3
these structures are the sites of gas exchange
alveoli
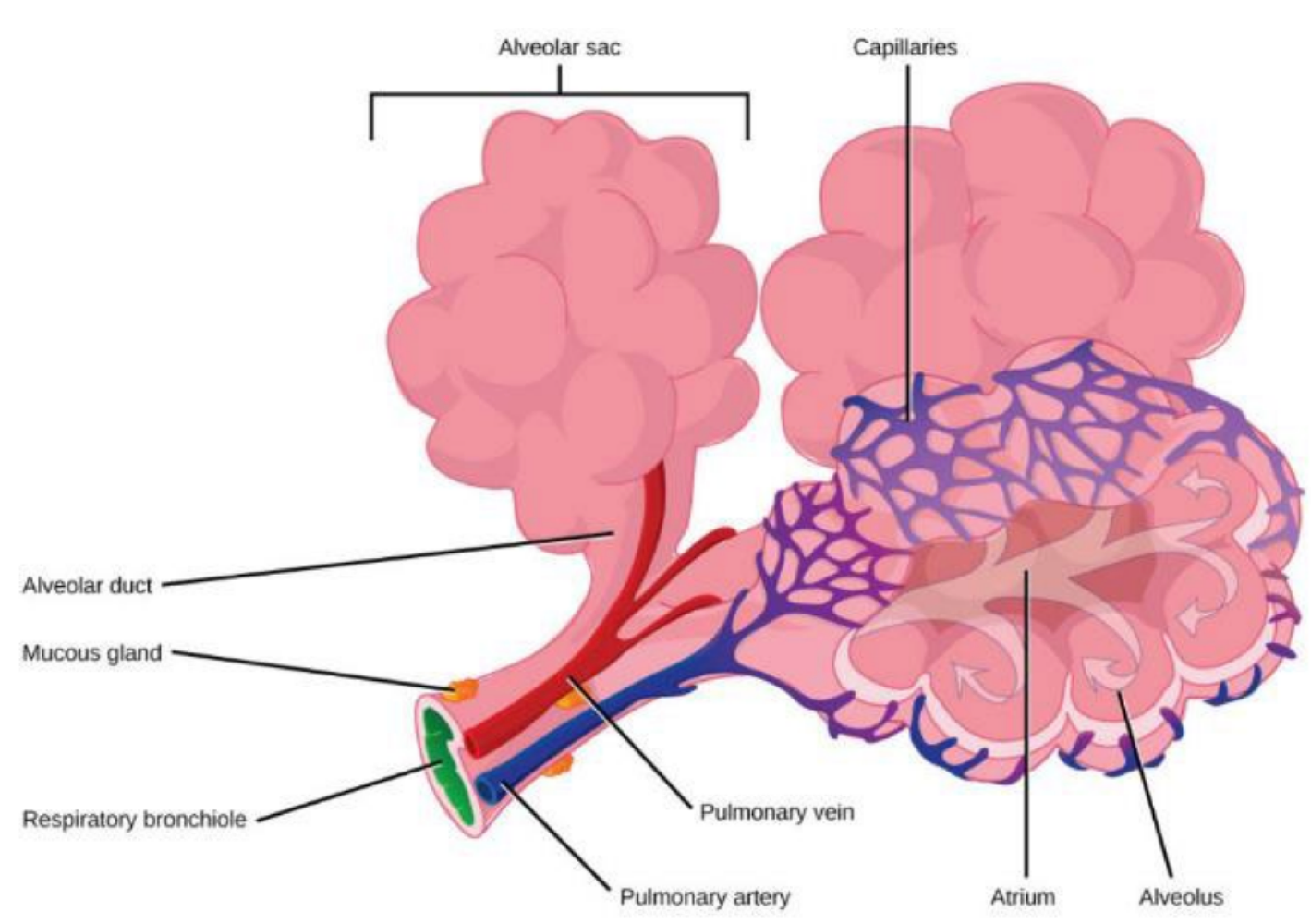
what do lungs receive from the heart via pulmonary arteries?
deoxygenated blood
what structures allow blood to come into close proximity with air in alveoli?
pulmonary capillaries
veins collect oxygenated blood from alveolar capillaries, sending it to which side of the heart?
the left side of the heart
breathing involves a pressure gradient and what type of effort?
muscle effort
true or false: lungs have skeletal muscles
false. lungs don’t have skeletal muscles
“diaphragm contracts → muscle pulls down → thoracic cavity volume expands” describes ___
inspiration (step 1 of breathing)
“diaphragm relaxes → thoracic cavity volume decreases” describes ___
expiration (step 2 of breathing)