BIO25 Ch.16 : Sensory and Receptors Flashcards
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the senses (vision, hearing, smell, taste).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is the general function of sensory receptors?
To provide information about external and internal environments by responding to stimuli and converting it into electrical energy.
What is the role of transducers in sensory reception?
To convert stimulus energy (e.g., light or sound) into electrical energy.
What is a receptive field in the context of sensory neurons?
The distribution area of the endings of a sensory neuron.
What is sensation in the context of sensory information?
A stimulus we are consciously aware of.
What is modality in the context of sensory receptors?
The type of stimulus based on a "labeled line."
Define exteroceptors.
Receptors that detect stimuli from the external environment, such as skin and mucous membranes.
Define interoceptors.
Receptors that detect stimuli from internal organs.
Define proprioceptors.
Receptors that detect body and limb movements. (muscle, tendons, and joints)
Name the five types of receptors categorized by modality of stimulus.
Chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors.
What do chemoreceptors detect?
Chemicals dissolved in fluid. smell of food, oxygen lvl in blood
What do thermoreceptors detect?
Changes in temperature.
What do photoreceptors detect?
Changes in light intensity, color, and movement.
What do mechanoreceptors detect?
Distortion of the cell membrane.
What do nociceptors detect?
Painful stimuli.
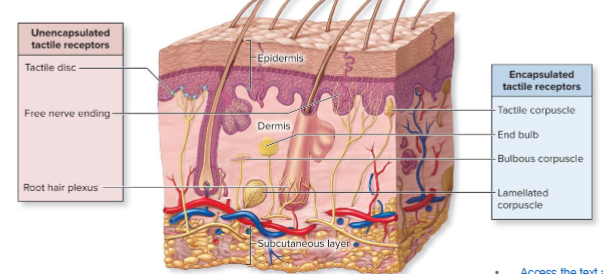
What is the function of tactile receptors?
Mechanoreceptors of skin and mucous membranes that detect hair displacement, pressure, and vibration.
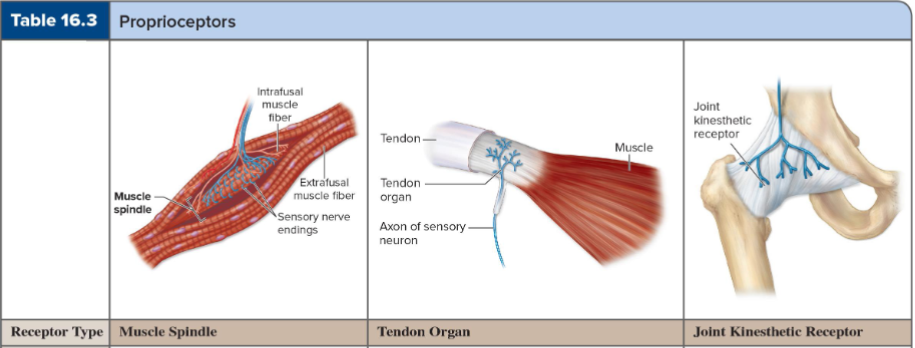
What is the role of proprioceptors in muscles, tendons, and joints?
To relay sensory information regarding body position and movement.
What is the 'sixth sense' also known as?
Proprioception, the sense of body position and movement.
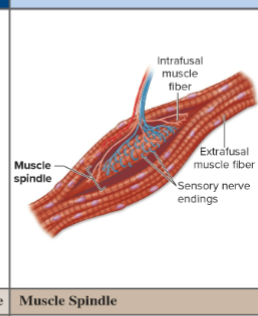
What do muscle spindles detect?
Stretch in skeletal muscle.
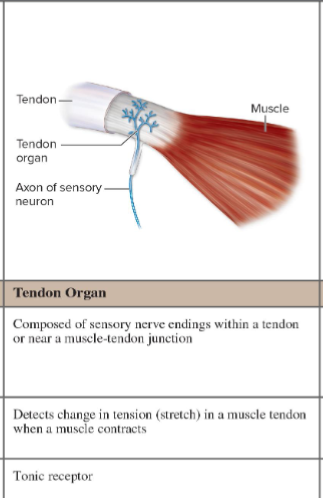
What do Golgi tendon organs detect?
Stretch in tendon.
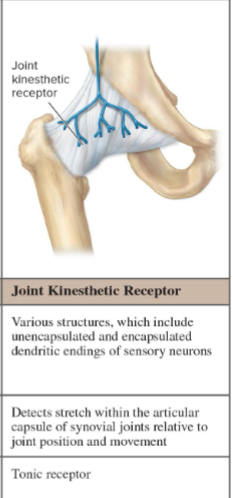
What do joint kinesthetic receptors detect?
Stretch in the articular capsule.
What is referred pain?
Inaccurate localization of sensory signals, where signals from viscera are perceived as originating from skin or muscle.
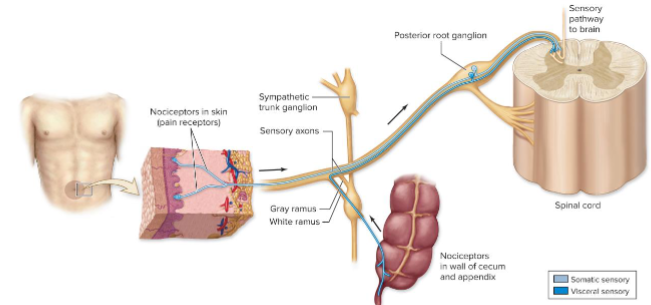
Where might heart attack pain be referred to?
Pectoral region and medial arm.
Where might kidney and ureter pain be referred to?
Inferior abdomen.
What is phantom pain?
Sensation associated with a removed body part.
What is olfaction?
Detection of odorants dissolved in the air.
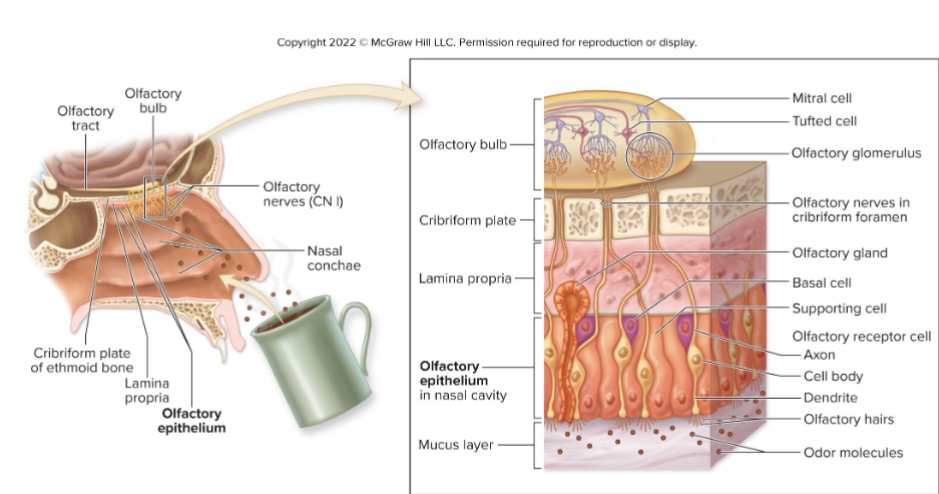
What is the olfactory epithelium?
The sensory receptor organ for smell, located in the superior region of the nasal cavity.
What is the role of olfactory receptor cells?
To detect odorants.
What is the role of supporting cells in the olfactory epithelium?
To sustain receptors.
What is the role of basal cells in the olfactory epithelium?
To continually replace olfactory receptor cells.
What is gustation?
The sense of taste; detection of tastants.
What are gustatory cells?
Chemoreceptors within taste buds. Receptor cells detect tastants
What is the function of filiform papillae?
Help manipulate food but have no role in gustation. (Located on Anterior two-thirds of tongue surface)
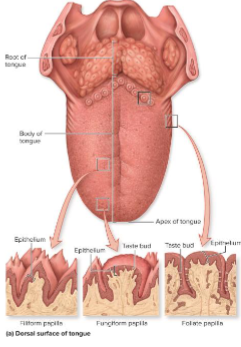
What is the function of fungiform papillae?
Each contains a few taste buds and are located on the tip and sides of the tongue.
What is the function of gustatory cells?
Receptor cells that detect tastants.
What is the function of supporting cells in taste buds?
To sustain gustatory cells.
What is the function of basal cells in taste buds?
Neural stem cells that replace gustatory cells.
Which cranial nerve carries sensory information from the anterior part of the tongue?
Facial nerve (CN VII).
Which cranial nerve carries sensory information from the posterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
Name the five basic taste sensations.
Sweet, salt, sour, bitter, and umami.
What causes the sweet taste sensation?
Organic compounds like sugar or artificial sweeteners.
What causes the salt taste sensation?
Metal ions like Na+ and K+.
What causes the sour taste sensation?
Acids, like vinegar.
What causes the bitter taste sensation?
Alkaloids, like unsweetened chocolate.
What causes the umami taste sensation?
Amino acids producing savory or meaty flavor.
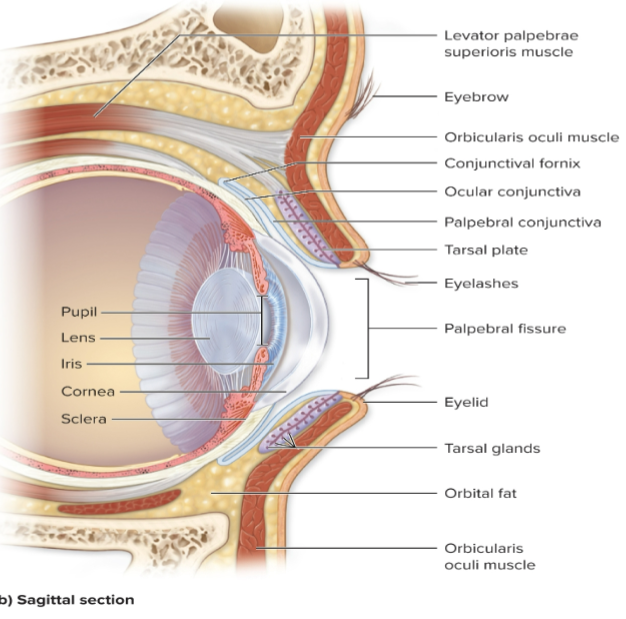
Name the accessory structures of the eye.
Six extrinsic eye muscles, eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, lacrimal glands.
What are the functions of eyebrows?
Aid in nonverbal communication and prevent sweat from dripping into eyes.
What are the functions of eyelashes?
Prevent objects coming into contact with eye and can initiate blink reflex.
What is the conjunctiva?
Transparent lining of eye and lid surfaces.
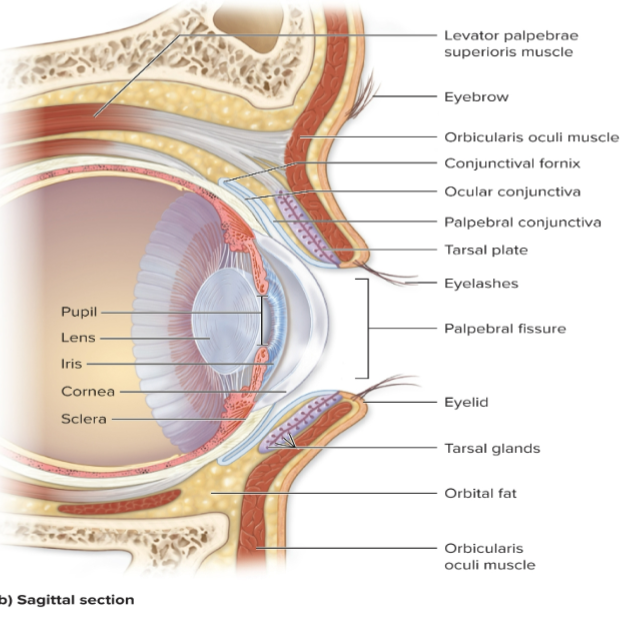
What is the ocular conjunctiva?
Covers the anterior sclera (white of eye).
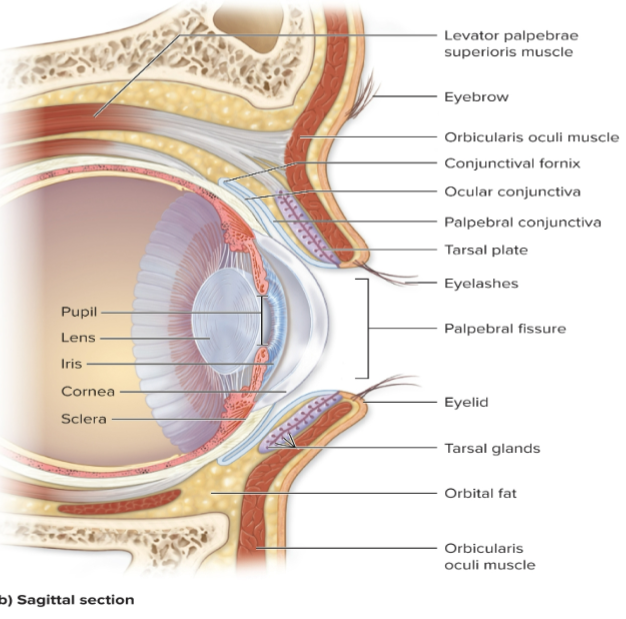
What is the palpebral conjunctiva?
Covers the internal surface of eyelid.
What is conjunctivitis?
Inflammation of the conjunctiva. (Pink eye)
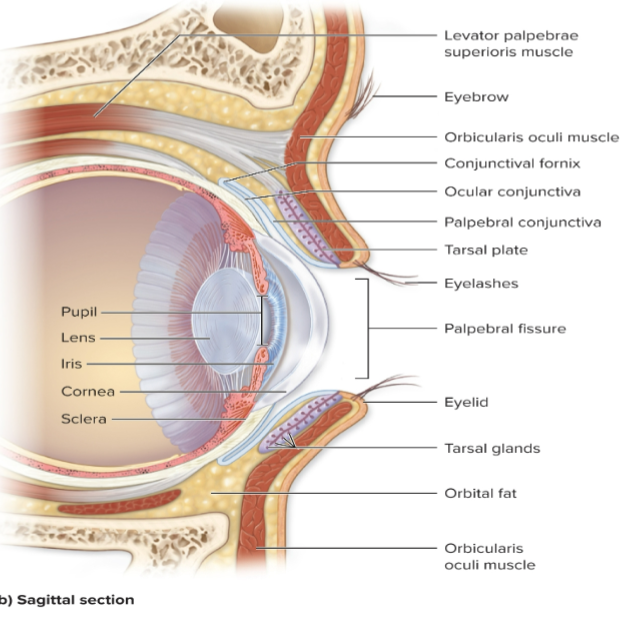
What is the sclera?
White of the eye, composed of dense irregular CT.
What is the function of the sclera?
Provides eye shape, protects internal components, and is an attachment site for extrinsic eye muscles.
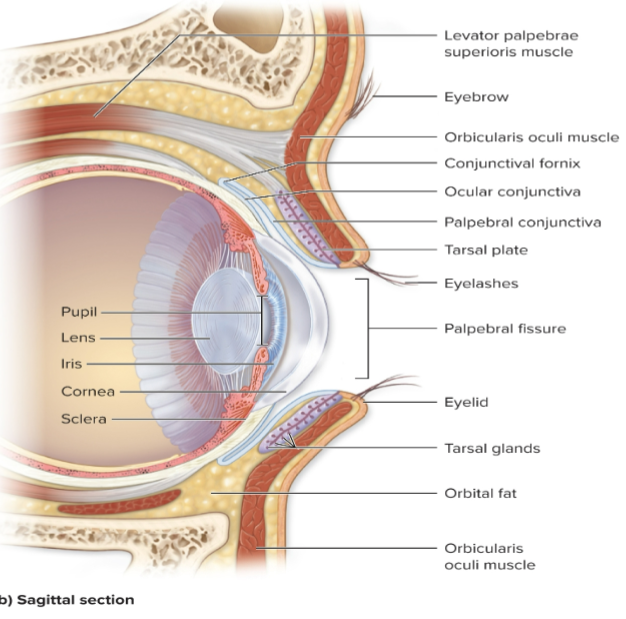
What is the cornea?
Anterior convex transparent "window" of the eye.
What is the iris?
Gives eye color and controls pupil diameter.
What is the pupil?
Opening in center of iris connecting the two chambers.
What does the retina contain?
Photoreceptor cell, Rods and cones.
What is the function of the lacrimal apparatus?
Produces, collects, and drains lacrimal fluid.
What is lacrimal fluid composed of?
Water, Na+, antibodies, lysozyme.
What are the functions of lacrimal fluid?
Lubricates, cleanses, moistens eye, reduces eyelid friction, defends against microbes, oxygenates and nourishes cornea.
Where is the lacrimal gland located?
Superolateral orbit.
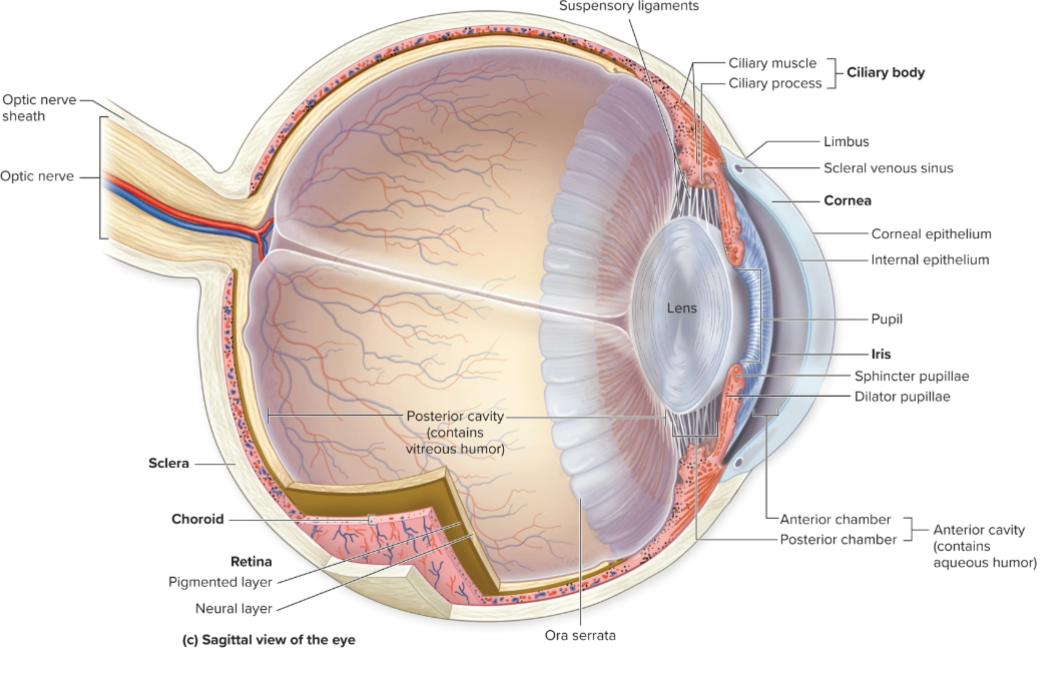
What is the posterior cavity of the eye filled with?
Vitreous humor.
What is the anterior cavity of the eye filled with?
Aqueous humor.
What is glaucoma?
A condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure.
What is a detached retina?
Occurs when outer pigmented and inner neural layers of the retina separate.
What is emmetropia?
Normal vision where parallel light rays are focused on the retina.
What is hyperopia?
Farsightedness, trouble seeing up close; eyeball too short.
What type of lens corrects hyperopia?
Convex lens.
What is myopia?
Nearsightedness, trouble seeing faraway objects; eyeball too long.
What type of lens corrects myopia?
Concave lens.
What is astigmatism?
Unequal focusing due to unequal curvatures in refractive surfaces.
What is presbyopia?
Age-related change in vision where lens is less able to become spherical.
What causes color blindness?
Absence or deficit in one type of cone cell.
What does the ear detect?
Sound and head movement.
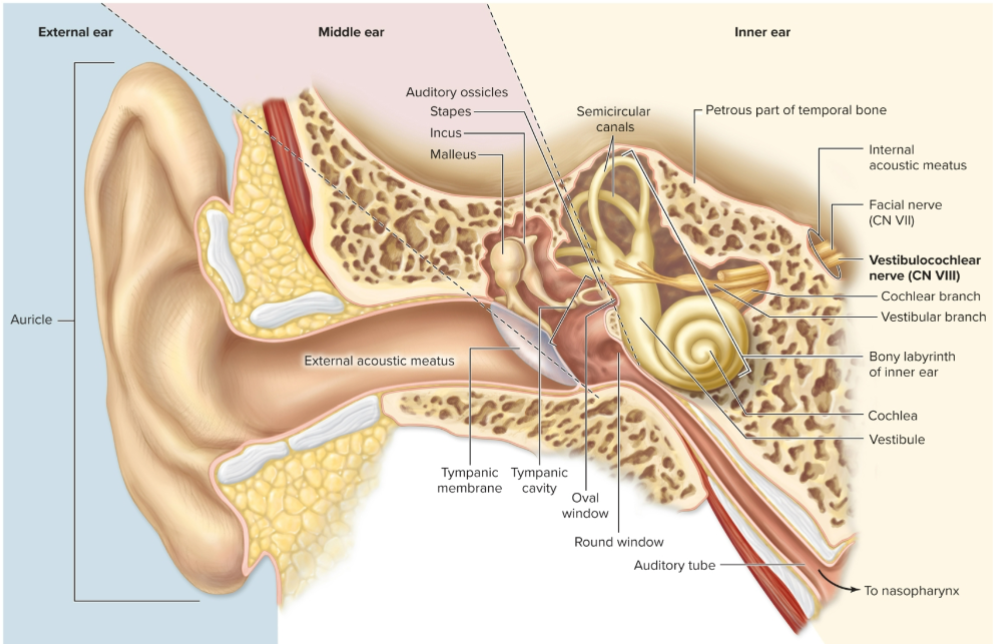
Which cranial nerve transmits signals from the ear?
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
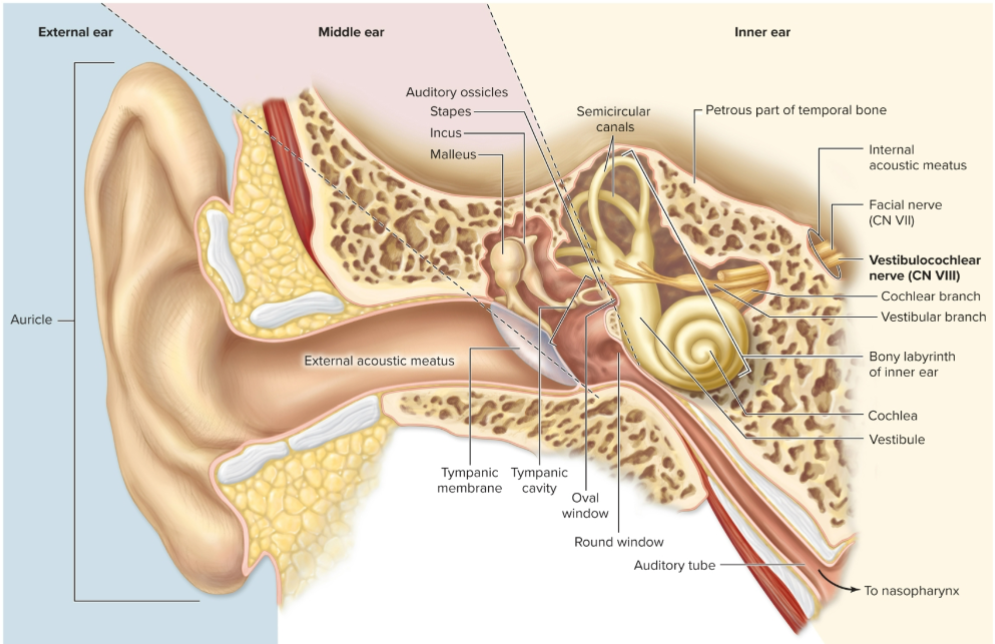
What is the auricle?
Funnel-shaped visible part of ear with elastic cartilage.
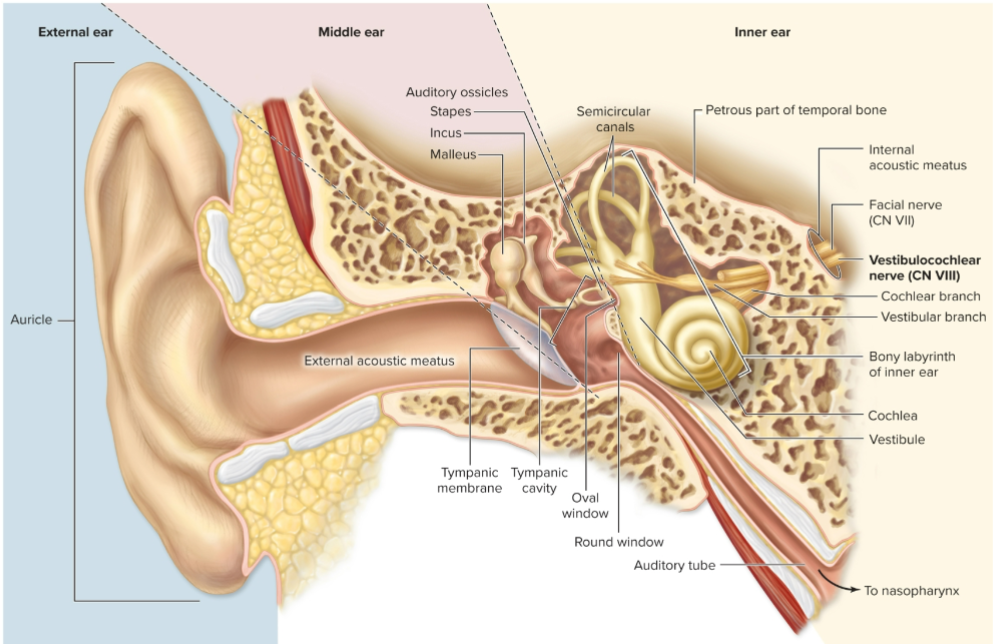
What is the external acoustic meatus?
Ear canal.
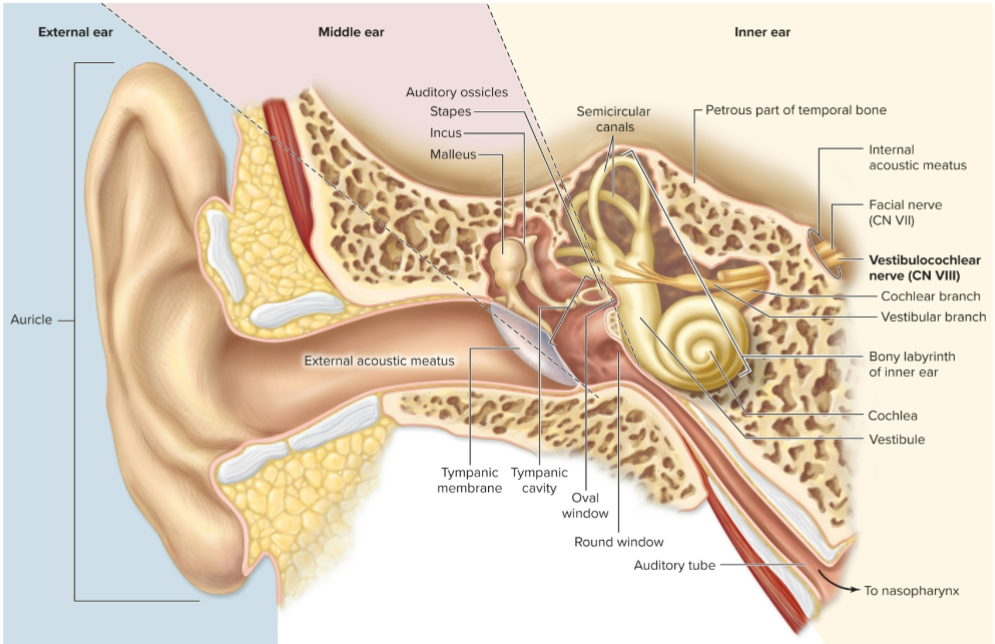
What is the tympanic membrane?
Eardrum, an epithelial sheet separating external and middle ear.
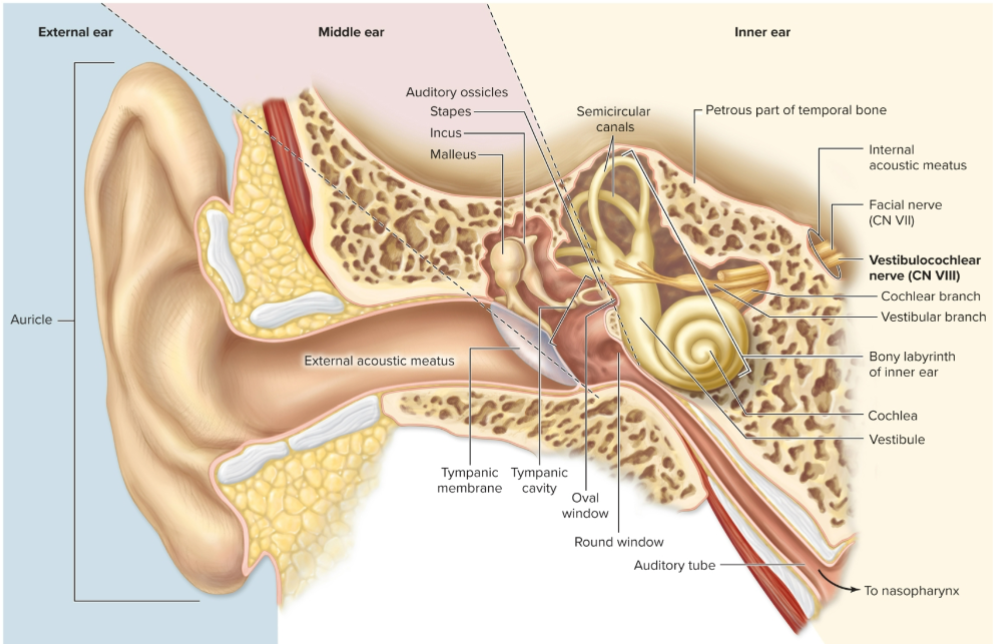
What is the auditory tube?
Passage extending from middle ear to nasopharynx (upper throat).
Name the auditory ossicles.
Malleus, incus, and stapes.
What is the malleus?
Auditory ossicle attached to medial surface of tympanic membrane; resembles a hammer.
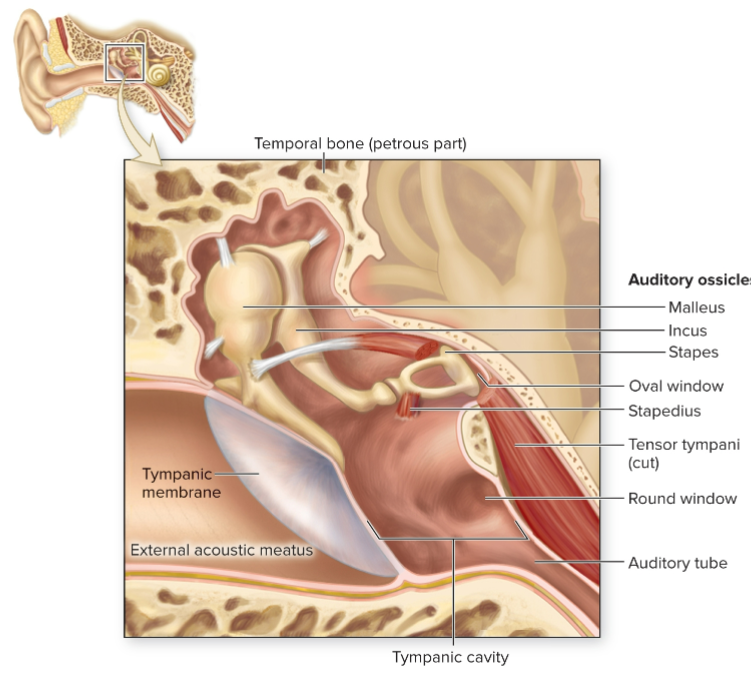
What is the incus?
Auditory ossicle resembling an anvil.
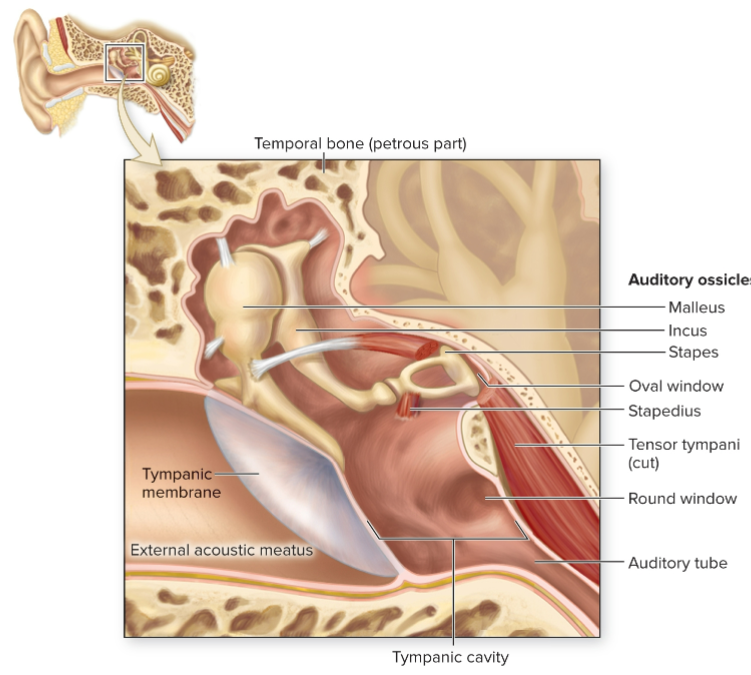
What is the stapes?
Auditory ossicle resembling a stirrup; has a footplate fitting into oval window.
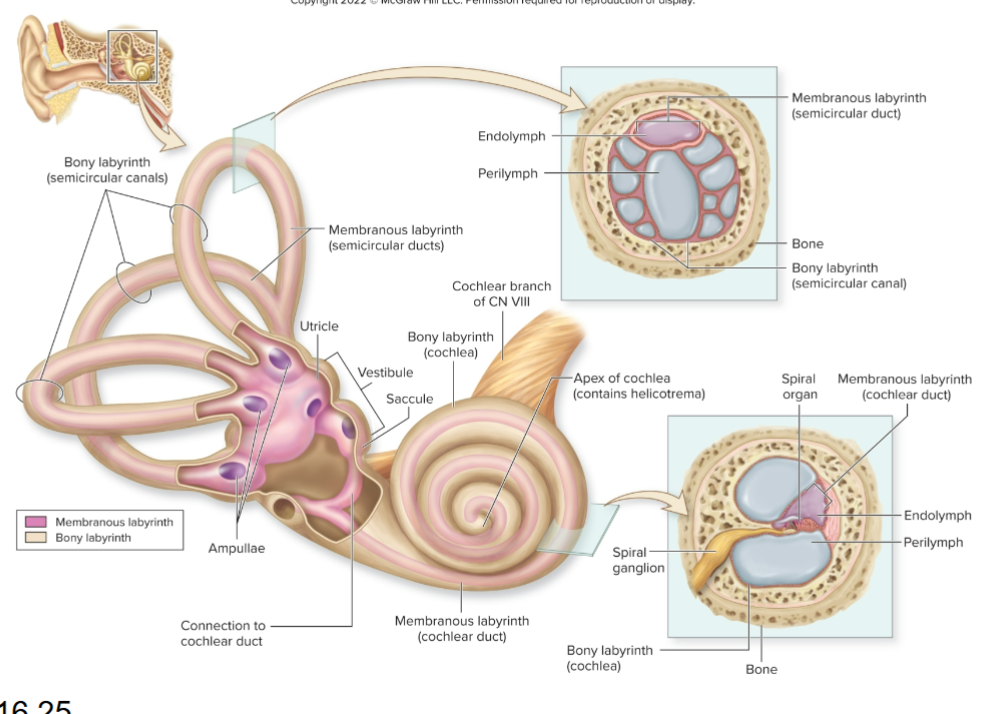
Name the three main regions of the inner ear?
Cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
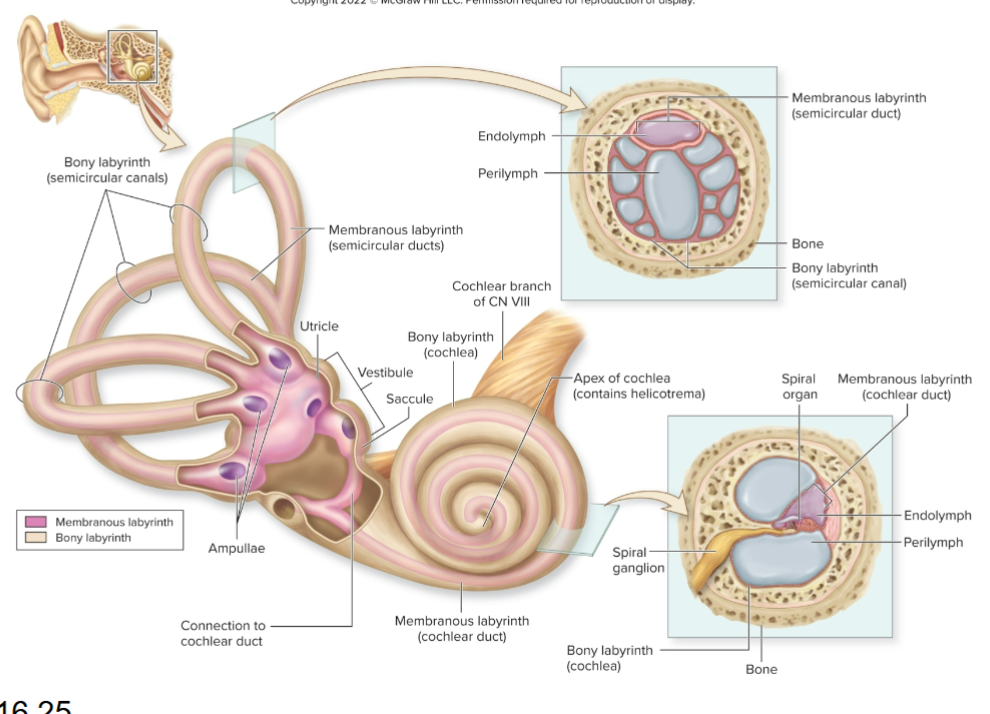
What does the cochlea house?
Membranous cochlear duct.
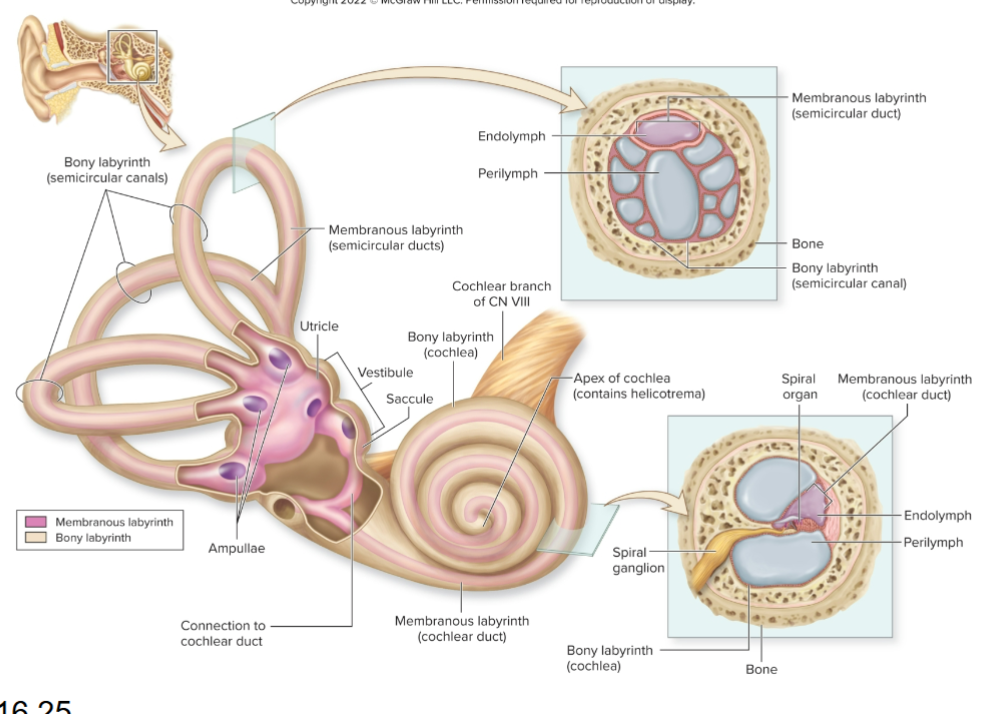
What does the vestibule contain?
Saclike membranous parts interconnected and positioned at right angles.
What do semicircular canals contain?
Membranous semicircular ducts.
What is otitis media?
Infection of the middle ear.
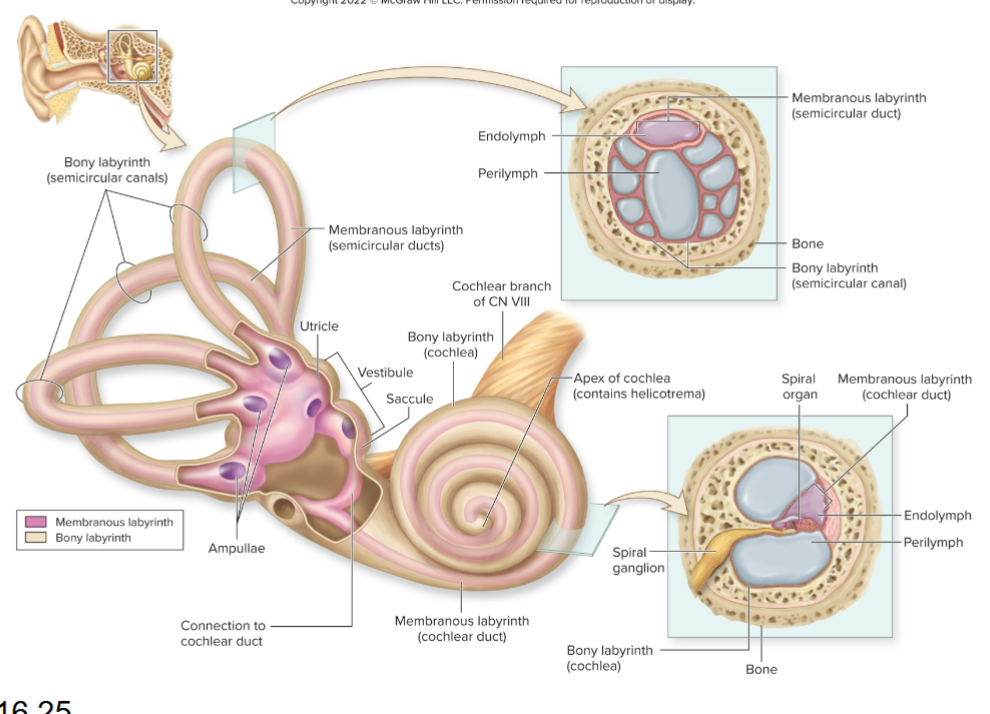
What are hair cells?
Receptors in the cochlea that release neurotransmitter to sensory neurons.
What do cochlear implants consist of?
Microphone, processor, and transmitter.
Define deafness.
Any hearing loss.
What is conductive deafness?
Interference of wave transmission in external or middle ear.
What is sensorineural deafness?
Malfunction in inner ear or cochlear nerve.
What is the macula?
Receptor for static equilibrium and linear acceleration.
What is the role of extrinsic eye muscles?
Control eye movement
What type of tissue forms the inner layer of the cornea?
Simple squamous epithelium
What structure changes shape to focus light on the retina?
Lens
What structures are found in the posterior cavity of the eye?
Vitreous humor
What is the function of ceruminous glands?
Produce ear wax to trap debris
What receptor is responsible for linear acceleration?
hair cells in the macula.