chapter 2: cells
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Last updated 3:13 AM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
cells
the basic unit of all organisms
2
New cards
two basic type of cells
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
3
New cards
what are the four common traits of eukaroytes and prokaryotes cells
1. surrounded by a plasma membrane
2. contain a semifluid substance called cytoplasm
3. contain structure called chromosomes DNA
4. contain ribosomes
4
New cards
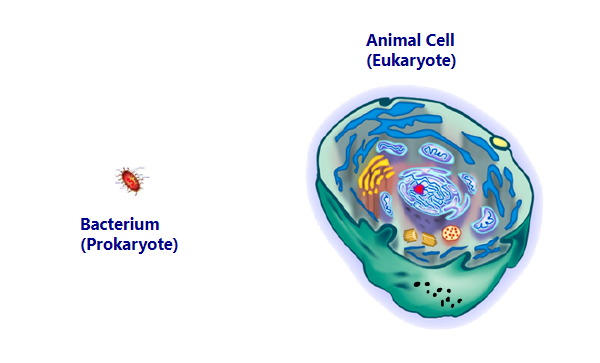
what is the difference between a eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell in terms of **size**
eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells
5
New cards
what is the difference between a eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell in terms of **organelles**
eukaryotic cells contain **organelles** inside of them; prokaryote cells do not
\
**this includes the nucleus**
\
**this includes the nucleus**
6
New cards
what is the difference between a eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell in terms of how **quantity of** **cells** contained in the organism
eukaryotes are multi-cellular organisms while prokaryotes are single cellular organisms
7
New cards
what is the difference between a eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell in terms of **chromosomes**
Eukaryote chromosomes are contained **within the nucleus** prokaryote chromosomes do not
8
New cards
what is the difference between a eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell in terms of **the number of chromosomes**
eukaryote chromosomes vary in number from organism to organism while prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome
9
New cards
surface area
determines the amount of substances the cell can take in and the amount of waste it can release
10
New cards
volume
determines the amount of chemical activity it can carry out
11
New cards
what is the ratio of surface area to volume and why?
surface area is **larger** than volume
\
allows more materials to move in/out of the cell so chemical reactions can occur
\
allows more materials to move in/out of the cell so chemical reactions can occur
12
New cards
organelles
specialized internal cell structures that carry out specific cell functions
13
New cards
what type of cell processes do organelles carry out?
essential cell processes like protein synthesis, energy transformation, digestion of food, excretion of wastes, and cell division
14
New cards
protists
first eukaryotic cells
single-celled eukaryotes
they can range from protozoans to algae
single-celled eukaryotes
they can range from protozoans to algae
15
New cards
what eukaryotes are multicellular
fungi, plants, animals
16
New cards
what does the nucleus contain
contains the DNA
17
New cards
what does DNA do
stores information used to make proteins for cell growth, function and reproduction
\
the manager
\
the manager
18
New cards
ribosomes
organelles that help manufacture proteins
19
New cards
what are ribosomes made of
RNA and protein
\
(not bound by a membrane)
\
(not bound by a membrane)
20
New cards
where is the site of ribosome production
nucleolus
21
New cards
what leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores?
ribosomes
22
New cards
what structure is DNA packed into
chromosomes
23
New cards
how do cells become specialized
turning on, or expressing certain genes in DNA
24
New cards
endomembrane system
made up of organelles that make protein, process them, and ship them to where they are needed, inside or outside of the cell
25
New cards
what organelles are included in the endomembrane system
nucleus
rough/smooth ER
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
rough/smooth ER
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
26
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a membrane of folded sacs and interconnected channels that serves as the site of protein and lipid synthesis
27
New cards
rough ER
ribosomes are attached to it’s membrane
\
the attached ribosomes will synthesize proteins
\
the attached ribosomes will synthesize proteins
28
New cards
smooth ER
does not have ribosomes on its surface
\
makes lipids, detoxifies the cells, and stores calcium ions
\
makes lipids, detoxifies the cells, and stores calcium ions
29
New cards
how does the golgi apparatus and the ER work together?
the golgi receives the transported vesicles that bud off from the ER and contains proteins
30
New cards
golgi apparatus
takes the substance from the ER (proteins) and modifies them chemically in order to mark them and sort them into different batches depending on their destination
\
the finished product will either move to the lysosomes, inserted into the plasma membrane, or dumped out of the cell
\
the finished product will either move to the lysosomes, inserted into the plasma membrane, or dumped out of the cell
31
New cards
lysosomes
contain hydrolytic enzymes used to breakdown other substances
\
used to digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulf viruses or bacteria
\
used to digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulf viruses or bacteria
32
New cards
peroxisomes
special type of lysosomes
\
contains an enzyme which produces hydrogen peroxide and breaks it down
\
contains an enzyme which produces hydrogen peroxide and breaks it down
33
New cards
plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer with proteins and other molecules interspersed throughout
34
New cards
three main functions of the plasma membrane
selective permeability
protection
structural support
protection
structural support
35
New cards
phospholipid
amphiphilic having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
contains a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (fatty acid)
contains a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (fatty acid)
36
New cards
why do phospholipids form a bilayer when placed in water?
to protect the hydrophobic tails from the water and then the hydrophillic heads can interact with the water on the inside and outside of the cell
37
New cards
passive transport
movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the requirement an energy input
38
New cards
active transport
the movement of substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration and requires an input of energy
39
New cards
exocytosis
used to excrete a large molecule from the cell
the vesicle that encloses the proteins fuse with the plasma membrane and the vesicle then opens up and spills their contents outside of the cell
the vesicle that encloses the proteins fuse with the plasma membrane and the vesicle then opens up and spills their contents outside of the cell
40
New cards
endocytosis
the cell takes in macromolecules or other particles by forming vesicle or vacuoles from its plasma membrane
41
New cards
chloroplasts
reside in plant cells and some protists and convert solar radiation into energy stored through **photosynthesis**
42
New cards
mitochondria
resides in all eukaryotic cells and converts chemical energy from glucose into ATP through **cellular respiration**
43
New cards
what makes mitochondria and chloroplast different from other eukaryotic organelles
they have their own DNA, their own ribosomes, and have a double cell membrane
44
New cards
Endosymbiotic Theory
the mitochondria and chloroplast were once prokaryotes that got engulfed by another prokaryote
\
they were both considered *bacterias*
\
when they got eaten by another prokaryote they got dragged by one prokaryote’s cell membrane around theirs making the **double membrane** and allowed the new eukaryote to make their own ATP/be able to do photosynthesis to make its own food
\
evolution of eukaryotes
\
they were both considered *bacterias*
\
when they got eaten by another prokaryote they got dragged by one prokaryote’s cell membrane around theirs making the **double membrane** and allowed the new eukaryote to make their own ATP/be able to do photosynthesis to make its own food
\
evolution of eukaryotes
45
New cards
what is the evidence of endosymbiotic theory
the mitochondria and chloroplasts can arise only from preexisting mitochondria and chloroplasts and cannot be formed in a cell that lacks them
\
they both have their own DNA and resembles the DNA of bacteria or prokaryotes (single circular DNA)
\
mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which closely resembles bacteria ribosomes than eukaryote’s ribosomes
\
they both have their own DNA and resembles the DNA of bacteria or prokaryotes (single circular DNA)
\
mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which closely resembles bacteria ribosomes than eukaryote’s ribosomes
46
New cards
Mitochondrial Eve
DNA is passed through from mother to child and you **inherit** your mitochondria from your mother only
\
the egg contains our mothers organelles and only dad’s sperm contains the chromosomes
\
mitochondrial DNA is a way to trace maternal heritage through a family or through a species and we can **trace all humans back to her** (eve) through mitochondrial DNA
\
the egg contains our mothers organelles and only dad’s sperm contains the chromosomes
\
mitochondrial DNA is a way to trace maternal heritage through a family or through a species and we can **trace all humans back to her** (eve) through mitochondrial DNA
47
New cards
chloroplasts
organelles convert solar energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis
48
New cards
three major compartments of chloroplasts
thylakoids
stroma
intermembrane space
stroma
intermembrane space
49
New cards
two major compartments of the mitocondria
matrix
intermembrane space
intermembrane space
50
New cards
vacuoles
membranous sacs which come in different shapes/sizes and have a variety of functions
51
New cards
central vacules
in plants store water which gives their strength and rigidity
stores vital chemicals, pigments, and waste products
stores vital chemicals, pigments, and waste products
52
New cards
full central vaculoes
take over the cytoplasm and push the organelles to the side
53
New cards
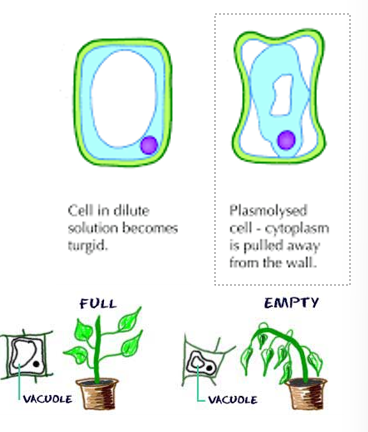
what happens when plants do not get enough water
the vacuoles are not full and the cytoplasm is pulled away from the wall, the plant wilts, limps, and droops
54
New cards
contractile vacuoles
found in certain single-celled protists
\
acts as **pumps to expel excess water** from the cell and keeps the cell from exploding
\
acts as **pumps to expel excess water** from the cell and keeps the cell from exploding
55
New cards
cytoskeleton
a network of fibers within the cytoplasm
\
provides structural support and are involved in various types of cell movement and motility
\
provides structural support and are involved in various types of cell movement and motility
56
New cards
cell wall
an outer layer besides the plasma membrane
57
New cards
what are cell walls made out of
cellulose
fungal: chitin
fungal: chitin
58
New cards
cell junctions
allows cells to communicate and pass substances to one another
59
New cards
how do plant cell junctions connect
plasmodesmata
plasmodesmata (plural)
plasmodesmata (plural)
60
New cards
tight junctions
bind cells together into leakproof sheets
61
New cards
adhering junctions (desmosomes)
fasten cells together into strong sheets and are somewhat leakproof
62
New cards
gap junctions
allow substances to flow from cell to cell
63
New cards
what do plant cells have that animal cells do not have
cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuoles