Eukaryotic Cells
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
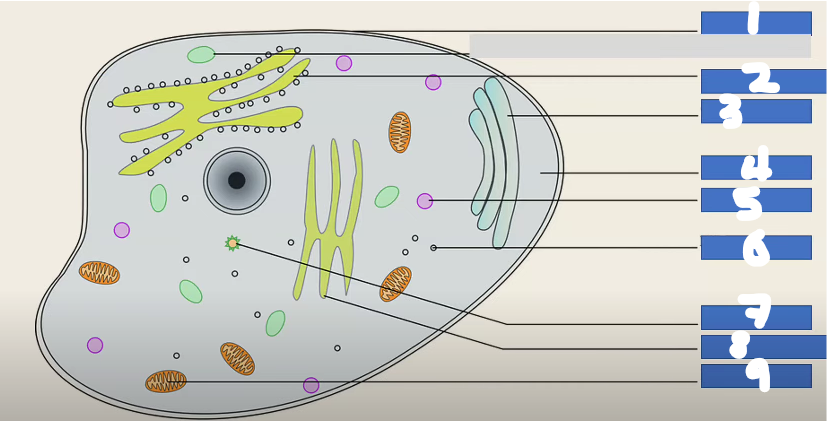
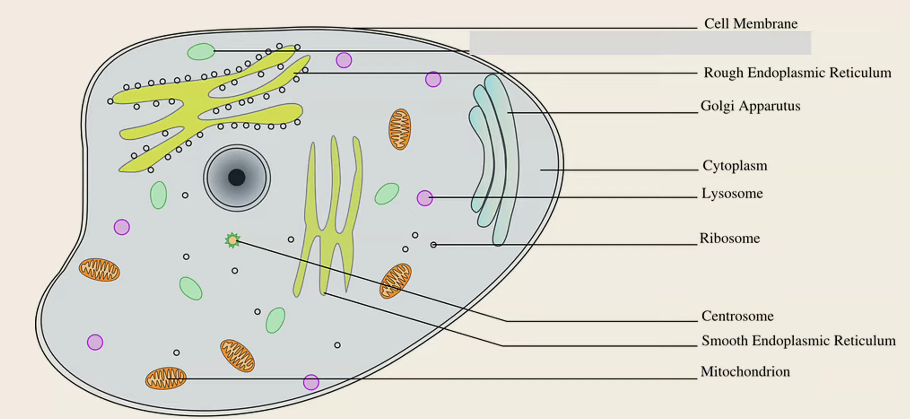
Label this diagram of an animal cell
Cell Membrane
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Cytoplasm
Lysosome
Ribosome
Centrosome
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mitochondrion
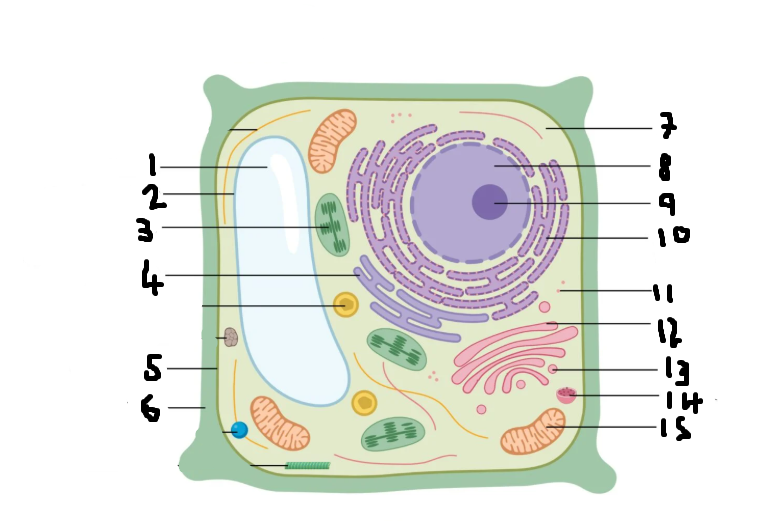
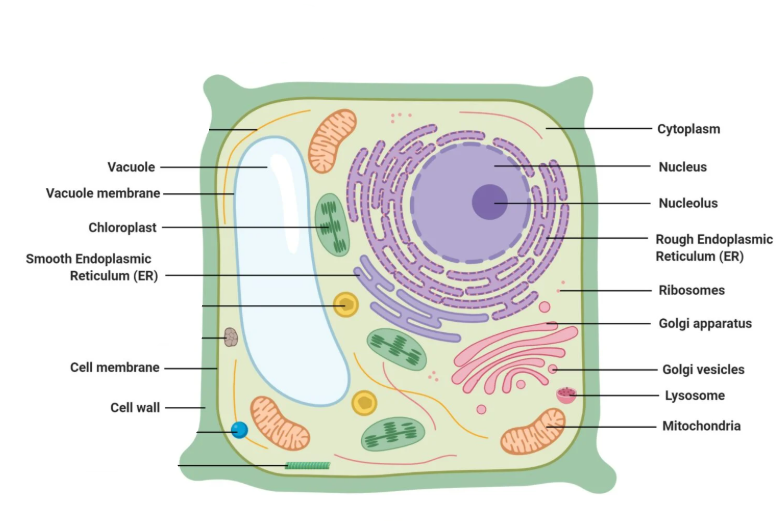
Label this diagram of a plant cell
Vacuole
Vacuole membrane
Chloroplast
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
Golgi vesicles
Lysosme
Mitochondria
What are the two main functions of the nucleus?
Site of DNA replication and transcription (making mRNA)
Contains the genetic code for each cell
What are the 5 key structural components of the nucleus?
Nuclear envelope (inner and outer membrane)
Nuclear pores
Nucleoplasm
Nucleolus (site of RNA production and makes ribosomes)
Chromatin
What are the two main functions of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth ER → Synthesis and store of lipids and carbohydrates
Rough ER → Protein synthesis
What are the 2 key structural components of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Cisternae (folded membranes)
Rough have ribosomes on the cisternae
What is the main function of the golgi apparatus?
Modifying and packaging lipids and proteins
What is the main function of vesicles?
Transporting and storing molecules
What is the golgi body made up from?
Folded membrane (cisternae)
What is a vesicle?
A small, membrane bound sac
What is the role of lysosomes?
Break down and recycle cellular waste and unwanted material
What is a lysosome?
Membrane bound sac of digestive, hydrolytic enzymes
What is the function of mitochondria?
Site of aerobic respiration and ATP production
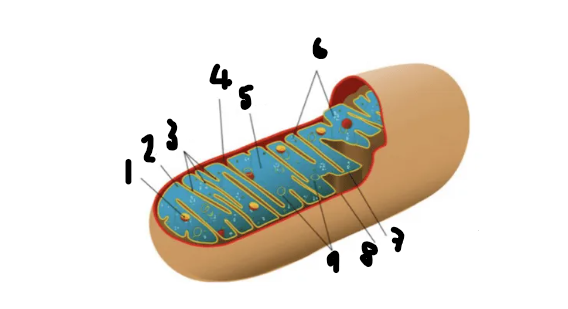
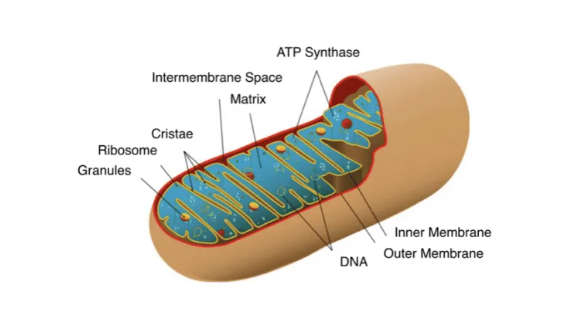
Label this diagram
Granules
Ribosomes
Cristae
Intermembrane space
Matrix
ATP Synthase
Inner Membrane
Outer Membrane
DNA
What is the function of ribosomes?
The site of protein synthesis
What are the two ribosomal subunits made up from?
rRNA and proteins
What are the 2 types of ribosomes and their relative sizes?
80s= larger ribosome (found in eukaryotic cells)
70s= smaller ribosome (found in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts)
What is the function of the vacuole?
Makes cell turgid, therefore providing support
Describe two structural features of the vacuole
Filled with fluid
Surrounded by a single membrane (tonoplast)
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis
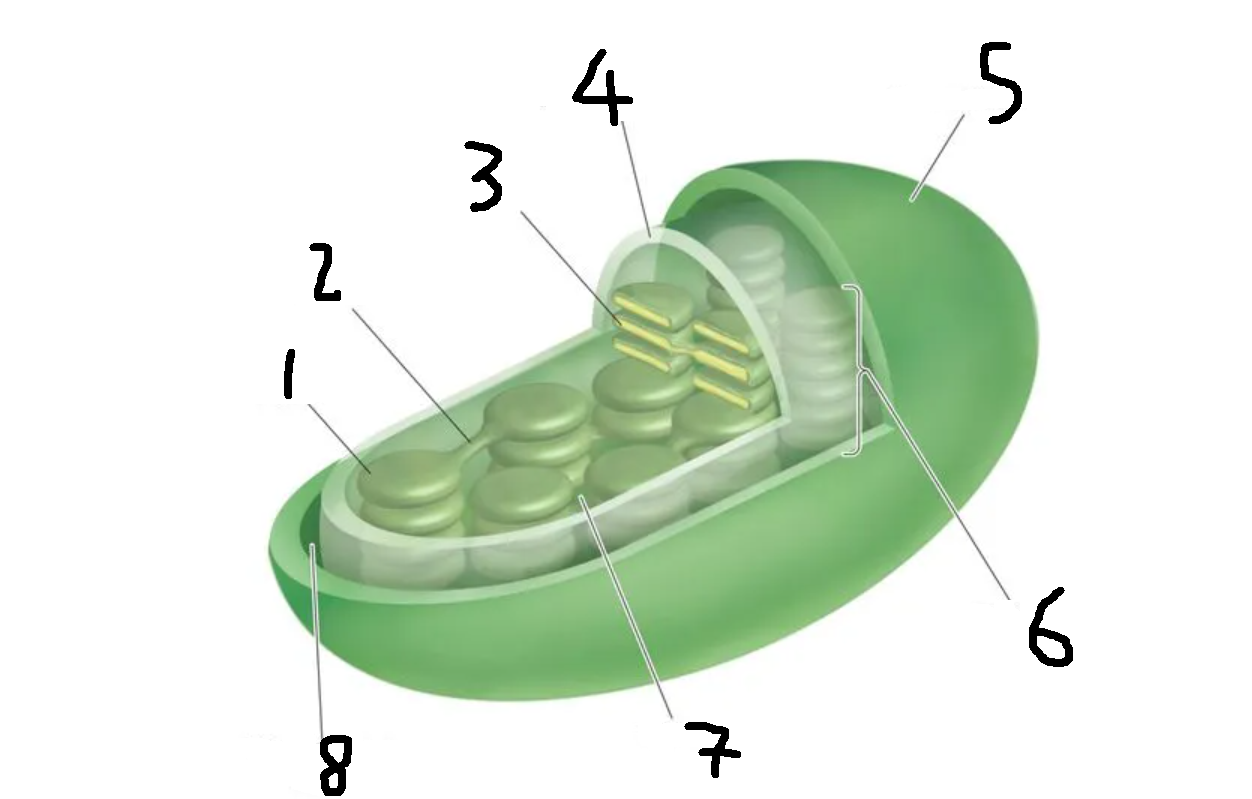
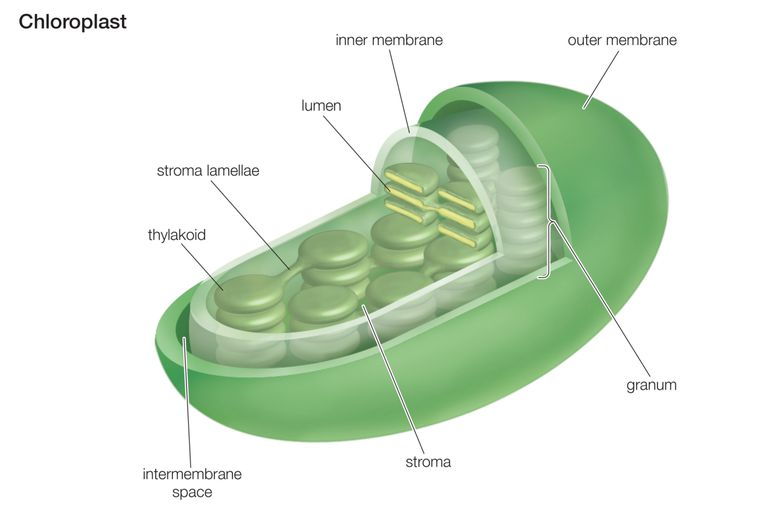
Label this diagram
Thylakoid
Stroma lamellae
Lumen
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Granum
Stroma
Intermembrane space
What is a thylakoid and what is its function?
Folded membranes embedded with pigment
Site of light dependent reactions on photosynthesis
What is the stroma?
Fluid containing enzymes required for photosynthesis in light independent reactions
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provides structural strength to the cell
What is the cell wall made from (in plants and fungi)
Plants= cellulose microfibrils
Fungi= chitin
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Controls entrance and exit of molecules into and out of the cell
What is the plasma membrane made up from?
Phospholipid bilayer