Bio Chem Exam 2
1/510
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
511 Terms
Amino Acid Sequence of Bovine Insulin
Side chain A and B. Has a shared amount of six S groups. Occasionally, disulfide bonds are shown as a part of B as it is a covalent bond.

Alanine
Ala
Arginine
Arg
Asparagine
Asn
Aspartic acid (Aspartate)
Asp
Cysteine
Cys
Glutamic acid (Glutamate)
Glu
Glutamine
Gln
Glycine
Gly
Histidine
His
Isoleucine
Ile
Leucine
Leu
Lysine
Lys
Methionine
Met
Phenylalanine
Phe
Proline
Pro
Serine
Ser
Threonine
Thr
Tryptophan
Trp
Tyrosine
Tyr
Valine
Val
What is the amino terminus of the tripeptide Gly-Ala-Asp?
In any peptide the amino terminus (N-terminus) is the free –NH₂ group at the first amino acid in the sequence.
The carboxyl terminus (C-terminus) is the free –COOH group at the last amino acid in the sequence.
So the answer is Glycine (Gly)
What is the approximate molecular weight of a protein composed of 300 amino acids?
On average, one amino acid ≈ 110 daltons (Da) in a protein chain.
So: 300 amino acids x 110 Da/amino acid = 33,000 Da
Number of amino acids for a protein with a molecular weight of 110,000
110,000 Da/110 Da (amino acid) = 1,000 amino acids.
Where is rotation permitted in polypeptide chains?
The N-Ca bond and the Ca carbonyl bond
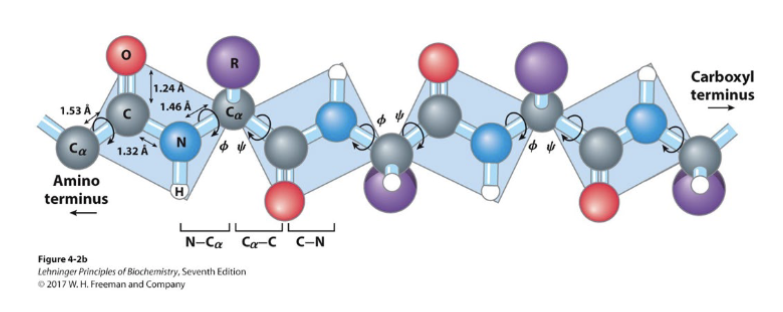
What determines the path of the polypeptide chain?
The rotation of the Φ and ψ bonds, called the torsion angles
Torsion angles of the polypeptide lie between…
-180 and +180 degrees.
Torsion angles are sometimes called…
Dihedral angles
Torsional angles describe the angle between…
Two planes formed by four atoms in a molecule
The bond angle defines the angle between the three atoms connected to…
one central common atom
The dihedral angle defines the angle between…
The groups attached to adjacent (C1 and C2) carbon atoms
Conformational change
A change in structure that arises solely from rotation about the covalent bonds.
No bonds are broken or reformed.
The +180° and –180° represent the same
physical conformation: just…
Two ways of describing a full half-turn
The range is centered around 0°, which
corresponds to the…
Eclipsed conformation also called “syn”
A dihedral angle of +180 is called…
“anti”
___________ mean rotation in one direction (clockwise), and ___________ mean rotation in the opposite direction (counter clockwise)
Positive and negative angles
A range of _ and _ is not used as -180 and +180 is better for specificity
0 and 360 degrees
Occurs when the bonds on adjacent atoms are directly aligned with each other. This causes a steric clash and is a high-energy, unstable state
Eclipsed conformation
Occurs when the bonds on adjacent atoms are staggered, or twisted, relative to each other. This minimizes steric hindrance and is a low-energy, stable state
Staggered conformation
The polypeptide chain is made up of a series of planes linked at _________. In the backbone of a polypeptide chain, the two most important single bonds for rotational freedom are those around the __.
α carbons
Dihedral/Torsion angles are also called______
Ramachandran angles
Torsion angles control __________. Freedom of rotation about two bonds of each amino acids allows the protein to fold in several ways.
protein folding
Some φ and ψ combinations are very unfavorable because of ______________ of backbone atoms with other atoms in the backbone or side chains.
steric crowding
Some φ and ψ combinations are more favorable because of chance to form favorable ________ along the backbone.
H--bonding interactions
A __________ shows the distribution of φ and ψ dihedral angles that are found in a
protein.
Ramachandran plot
Ramachandran plots also
• shows the common secondary structure elements
• reveals regions with unusual backbone structure
Example of Ramachandran plot
(guaranteed question on this)
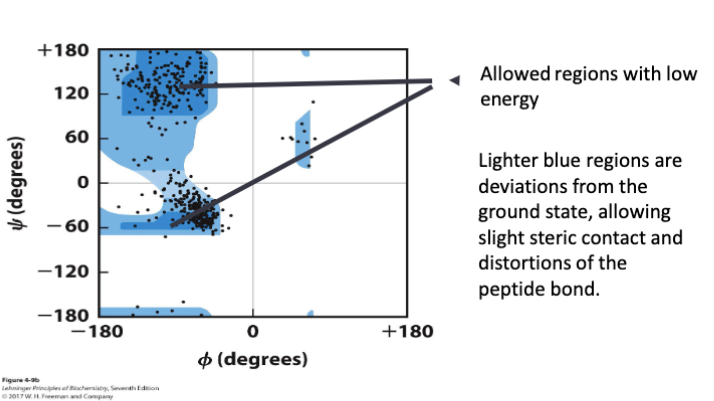
Certain combinations of φ and ψ angles result in ________ conformations where atoms on adjacent residues ______ with each other.
eclipsed-like, clash
These high-energy conformations are ____________________ on the Ramachandran plot
sterically disallowed and appear as empty regions
________ are different conformations of a side
chain, defined by its χ (chi) torsional angles.
Rotamers
Each _______ corresponds to a specific set of
dihedral angles (χ1, χ2, etc.) that describe how the side chain atoms are _____ around their bonds
rotamer, rotated
PTMs like _____________________ introduce new atoms or functional groups, which can shift the preferred rotameric states.
phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation
PTMs are __________________
Post translational modifications
Proteins have irregular 3D structures as they lack _______, designed to ________________, and have functional _____________
symmetry, interact and recognize thousands of molecules, diversity
Despite the irregularity protein structures still have ______________
regular features
________ is a frequent cause for bronchitis in young children
hMPV F glycoprotein
The structures of over _________ proteins are known
137,000
describes the spatial arrangement of the main-chain atoms
in a segment of a polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
Common types
α helix,
β sheets,
β turn, random coils.
α helix and β sheets are the architectural elements of protein structure.
α helix
Simplest arrangement, maximum number of hydrogen bonds.
___________ protrude out from the backbone
R groups
Each helical turn is
3.6 residues, ∼5.4 Å
The average residues in most helices is
∼10
The influenza protein
Hemagglutinin
Approximately how many residues are there per influenza protein
54
________________ R groups protruding away from the helical backbone are the most common
Right handed
_____________ theoretically less stable, not observed in proteins
Extended left-handed
Where are the Interhelical Hydrogen Bonds and what do they add to the structure
• Between the hydrogen atom attached to the electronegative nitrogen atom of residue n and the electronegative carbonyl oxygen atom of residue n + 4.
• Confers significant stability.
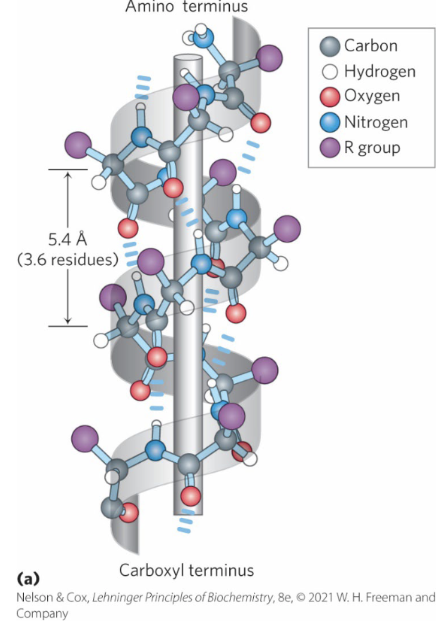
These hydrogen bonds are _________________ meaning they occur within the same polypeptide chain
intrachain/intrahelical
How do intrahelical bonds maintain the helical shape?
By pulling the backbone into a tight coil
The R side chains (________) of the amino acids project outward from the helix, allowing interactions with the ___________ or _____________
R-groups, environment or other molecules
H-bond donor involving side chains
Residue n-NH
H-bond acceptor involving side chains
Residue n+4-C=O
Amino Acid Sequence Affects Stability of the
α Helix
Amino acid residues have an intrinsic propensity to form
an α helix
Interactions between R chains spaced ________ residues apart can stabilize or destabilize _______
3-4, α helix
Regarding the interactions between R chains the charge, size, and shape of R chains can _________ and the formation of _________ and __________ can stabilize
destabilize, ion pairs and hydrophobic effect can stabilize
Proline and Glycine Occur Infrequently in an
α Helix
Proline
introduces destabilizing kink in helix
Regarding Proline:
nitrogen atom is part of rigid ring - _________
rotation about _________ bond is not possible
This restricts the ____________ of rotation, making it incompatible with the regular geometry of an α-helix
no H-bond donor, N—Cα, φ (phi) angle
Glycine regarding an α Helix
high conformational flexibility, take up coiled structures.
The flexibility of glycine allows it to have many confirmations which destabilizes the regular ____________
geometry of the helix
Helix dipole effect
plays a role in helix stability, protein folding, and molecular interactions.
Small electric dipoles in each peptide bond align the hydrogen bonds. Each peptide bond has a small dipole moment due to the partial
positive charge on the amide hydrogen (–NH) and partial negative charge on the
carbonyl oxygen (C=O)
N-terminus of the α-helix has a ___________ due to the allignment of the dipoles (NH3 +terminus).
Therefore, ______________ (like
Aspartate, Glutamate) are often found near the N-
terminus to stabilize this charge.
partial positive charge, negatively charged amino acids
C-terminus has a _____________
Therefore _________ amino acids (like
Lysine, Arginine) are often found near the ___________ for stabilization.
partial negative charge, positively charged amino acids, C-terminus
A β-sheet consists of multiple β-strands lying side-by-side.
Strands can be: ________ _________
Parallel and Antiparallel
Hydrogen bonds form between the carbonyl oxygen of ____
one
define the rotation around the backbone bonds regarding polypeptide chains
Dihedral angles φ and ψ
In β-sheets:
• φ ≈ ___________
• ψ ≈ ___________
–60° to –150°
+90° to +180°
The β-sheets values allow the backbone to adopt a
highly extended conformation, ideal for sheet confirmation
Adjacent Polypeptide Chains in a β Sheet Can Be
Antiparallel or Parallel
β-Strand
A single extended segment of polypeptide in β-conformation
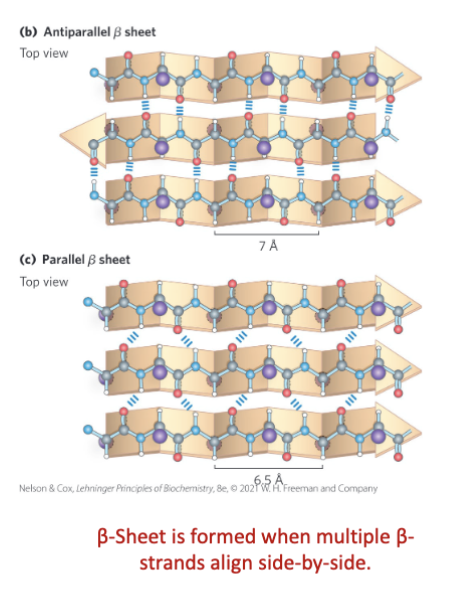
In a B strand the backbone is _______ out in a zigzag pattern
The average length is _______-
The arrows on the plot point from _______
stretched, 6 amino acids, N to C
Antiparallel - opposite orientation ________________
occurs more ___________
More _______ and _________ due to linear to hydrogen bonds
Maybe separated by a minimum of 4 amino acids in a ________. Strands can be _______ or _________ in amino acid sequences.
N to C and C to N, frequent, stable, beta turn, distant, close
Parallel - same orientation. Strands must be __________ in amino acid sequences
Less stable due to __________________
All R groups are _____ or _____ the plane of strands
distant, angled hydrogen bonds, above, below
β turns are common in proteins and connect the ends of two __________________
adjacent antiparallel β-strands in a β-sheet
common names regarding the B turns in proteins
reverse turn, tight turn
regarding reverse turn, tight turn
____° turn
involves _ residues
residue 1: _______
residue 4: _______
Hydrogen bond froms between _______________ reside
180, 4, start of the turn, end of the turn, first and fourth
10 types of turns are found in proteins. The most common is a _________
β turn.