Chapter 12 (cont.) - cell cycle regulation and cancer
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What does the G1 checkpoint look for?
Cell size adequate (large enough)
nutrients are sufficient
social signals are present
DNA is undamaged
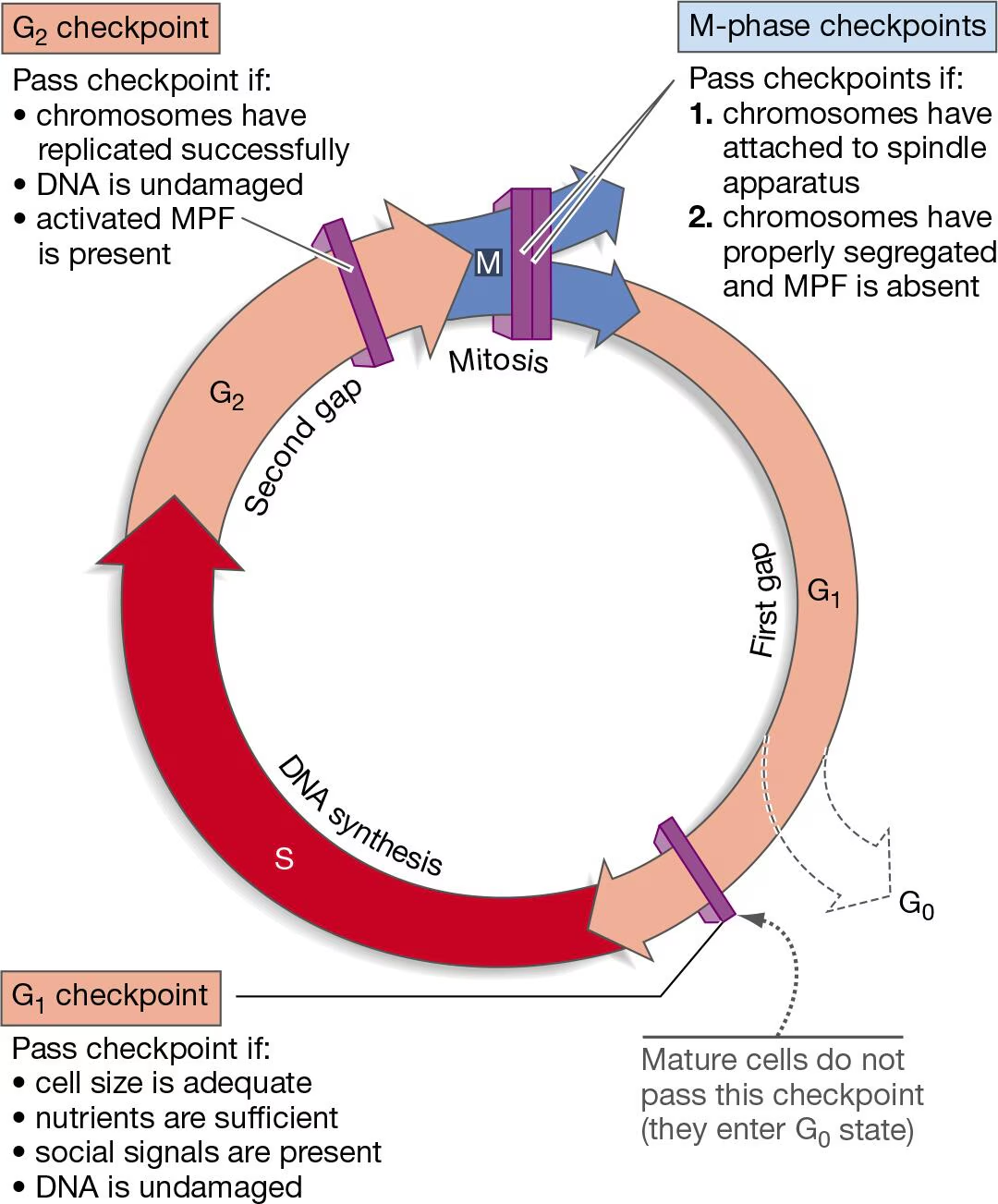
If a cell does not pass the G1 checkpoint where does it go?
G0 - “sent into retirement”
No more cell division
How do cells enter G0
Do not pass G1 checkpoint
Once cell has gone through “max” cell divisions in lifetime will retire
What does the G2 checkpoint look for?
If chromosomes have replicated successfully
If DNA is damaged
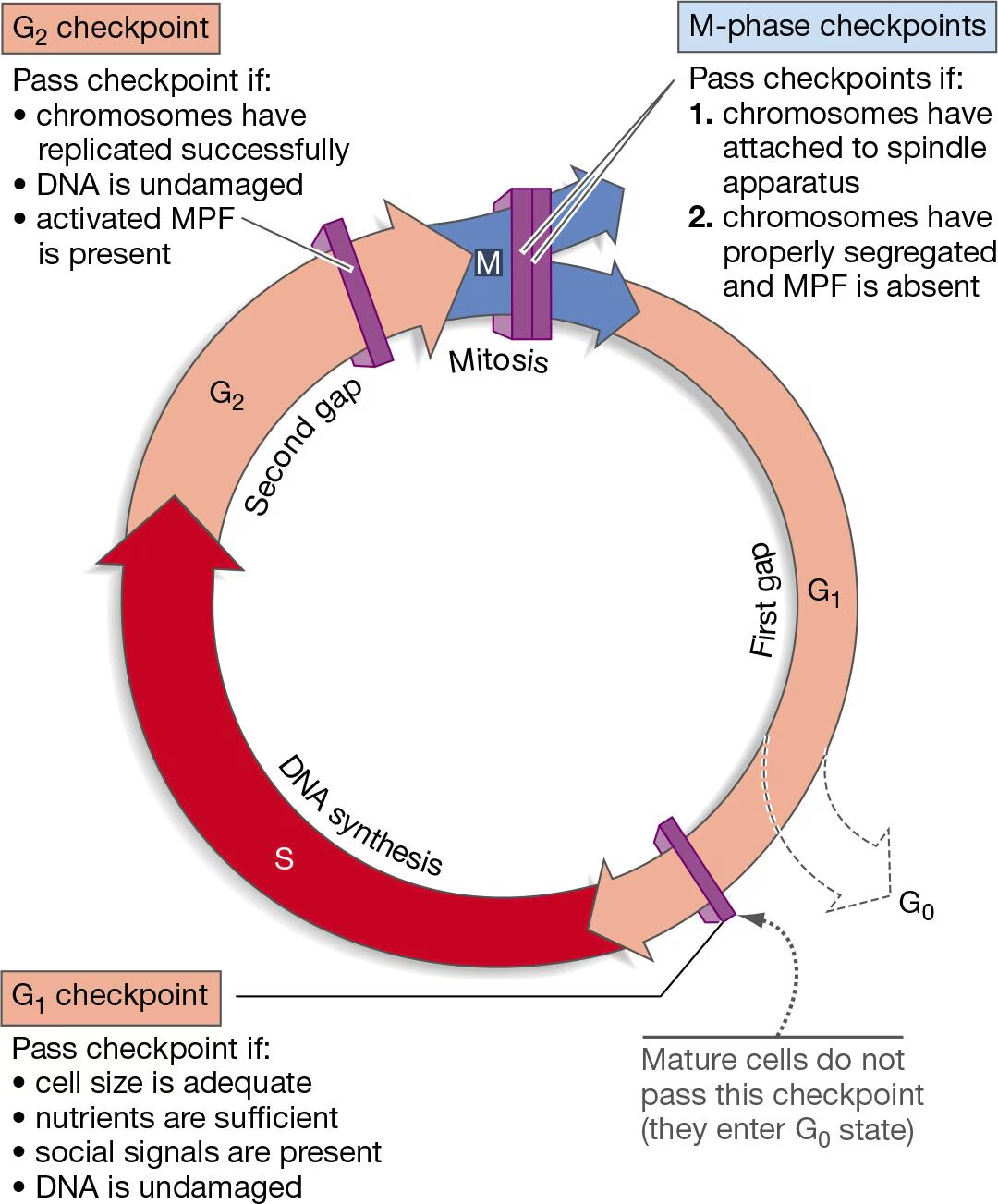
What does M-phase checkpoints look for?
If chromosomes have attached to spindle apparatus (pro-metaphase → metaphase)
If chromosomes have properly segregated
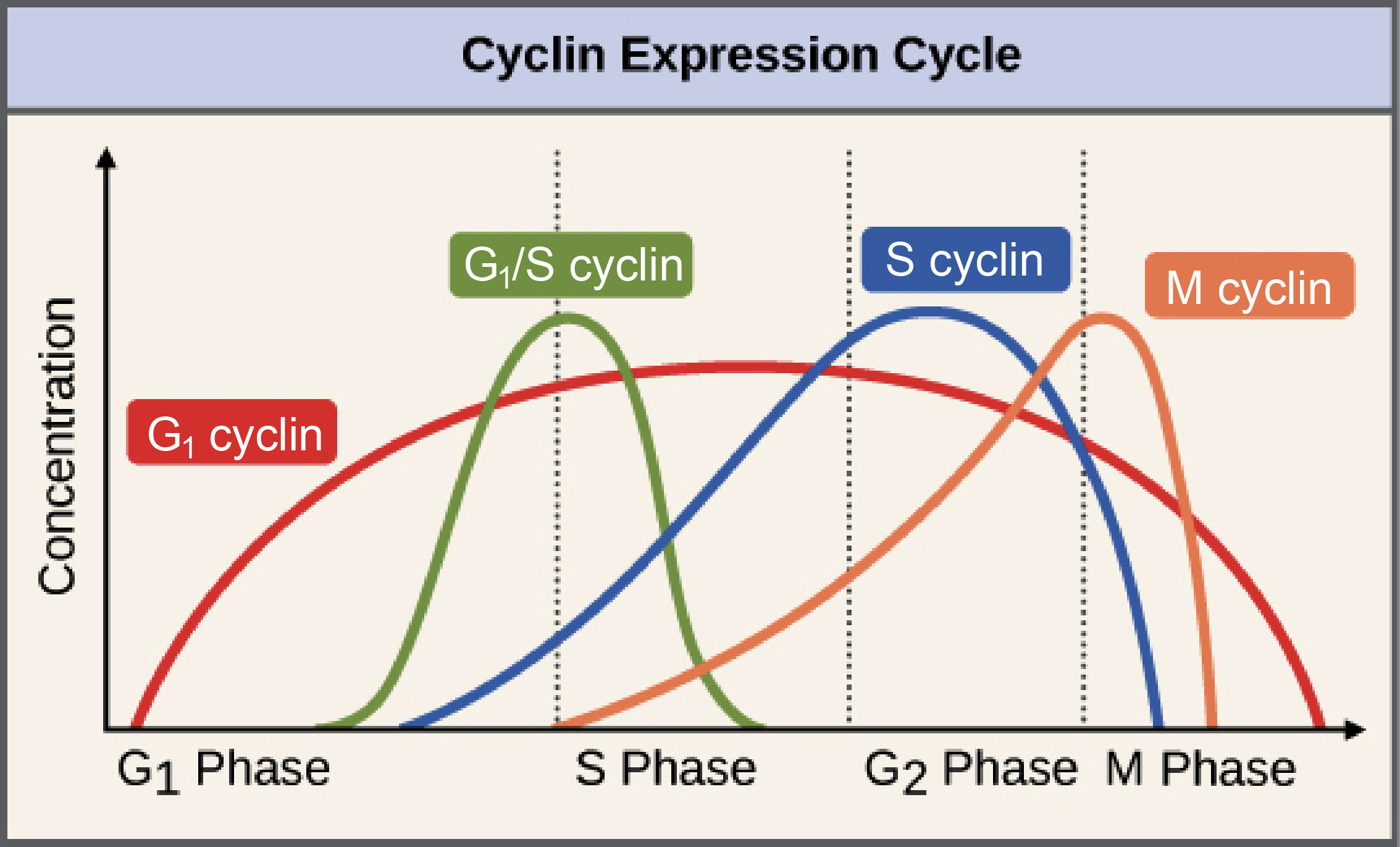
Cyclins
Only produced when needed
Different types for different phase transitions
G1, G1/S, S, and M
Cdks
an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins
Cyclin dependent kinases
when paired together with a cyclin, ativate other proteins to progress the cell cycle
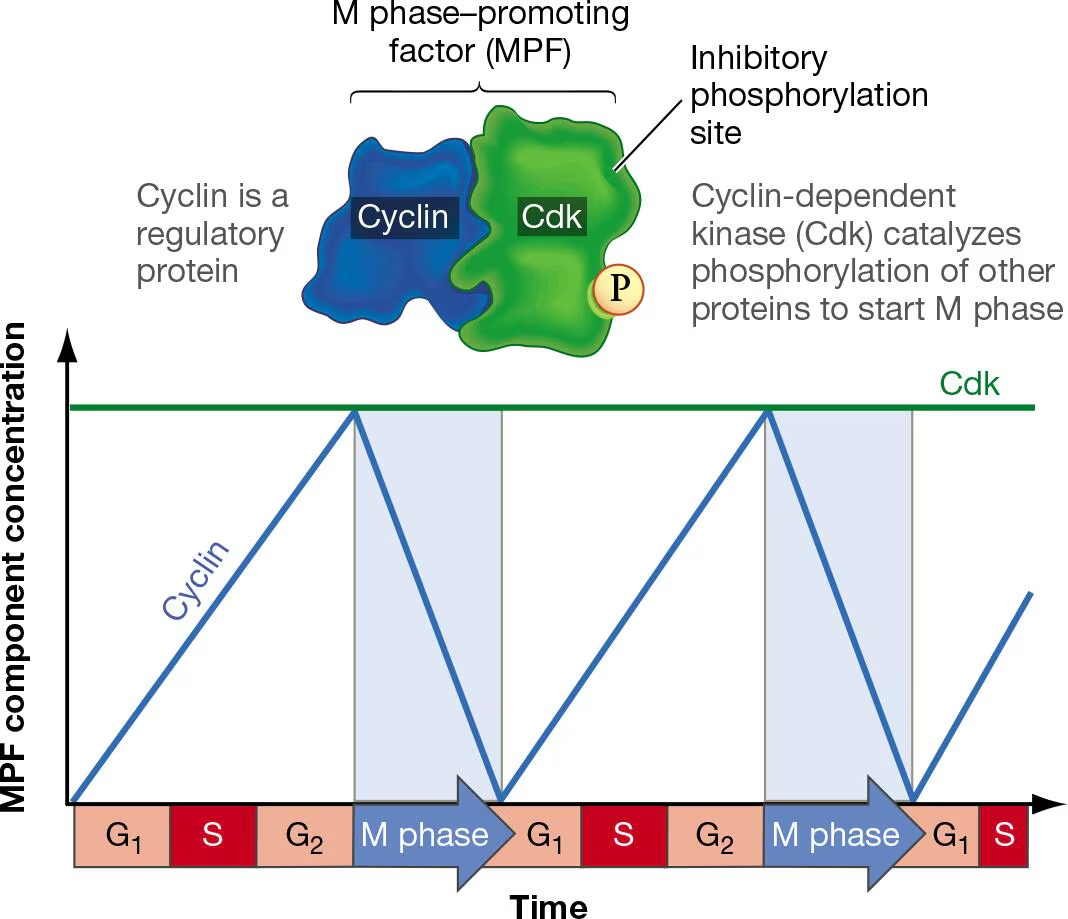
M-phase-promoting factor (MPF)
Cycle cycle protein that tells a cell to go into M phase (in cytoplasm)
Made up of Cyclin B + CDK1
Steps:
Interphase
G2 checkpoint
M-phase checkpoint
What stops Cdk from being prematurely active?
It has an additional phosphate group on it that keeps it from doing its job
How is the Cdk affected by the G2 checkpoint (regulation of MPF)
Phosphatase removes inhibitory phosphate
Cdk is active
How is M-phase checkpoint affect Cdk/cyclin? (Regulation of MPF)
Cyclin is degraded
This causes Cdk1 to inactivate
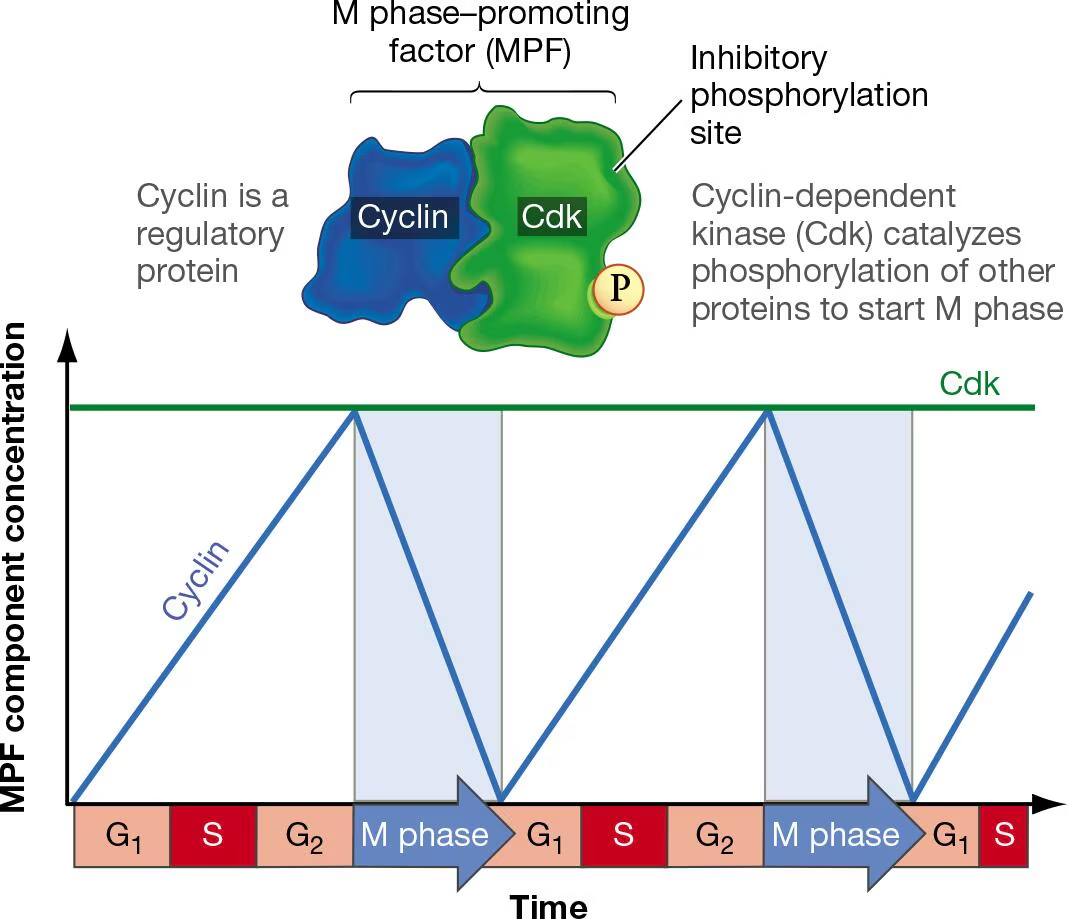
What is the G1 checkpoint controlled by?
1) Growth factors
2) Tumor suppressors
p53 - DNA repair
RB (pRB) - blocks transition from G1 to S-phase
Growth factors
Hormones (polypeptides or small proteins) that stimulate cell division
“gas” of the cell cycle (when they’re around the cell cycle moves forward/progresses)
Tumor suppressors
proteins that restrict cell division
“brakes” of the cell cycle
What is the activator of S-phase?
E2F
must be sequestered until cell is ready
Cancer
A collection of diseases caused by cells that:
Divide in an uncontrollable fashion
Invade nearby tissues
spreads to other sites in the body
Tumor
Mass of cells
even a single cell can begin to divide uncontrollably and form a tumor
Benign tumor
noninvasive and thus noncancerous
Malignant tumors
invasive and cancerous
Metastasis
spreading from a primary tumor site to establish secondary sites
Proto-oncogenes
Promote cell growth and division (ex. growth factors)
when mutated become oncogenes
Oncogenes
an allele that promotes cancer development
too much or “broken” proto-oncogene = cancer
Tumor suppressors
Restrict cell growth and division
removal of tumor suppressors = cancer
Mutations in Cancer?
Typically 2-8 mutations found in tumor DNA
Typically 1+ oncogene and multiple tumor supressors
Genetic predisposition
Increased likelihood of developing a particular disease based on a person’s genetic makeup
Often abnormal (mutant) copy of a tumor-suppressor gene
Carcinogen
Any substance that promotes cancer
Tobacco
Acetaldehyde
UV light
Outdoor air pollution
Why is cancer so difficult to cure
Cancer is not one disease, but many
No singular cure for a group of diverse disorders
Difficult to target only cancerous cells
New and rare cancers are appearing frequently
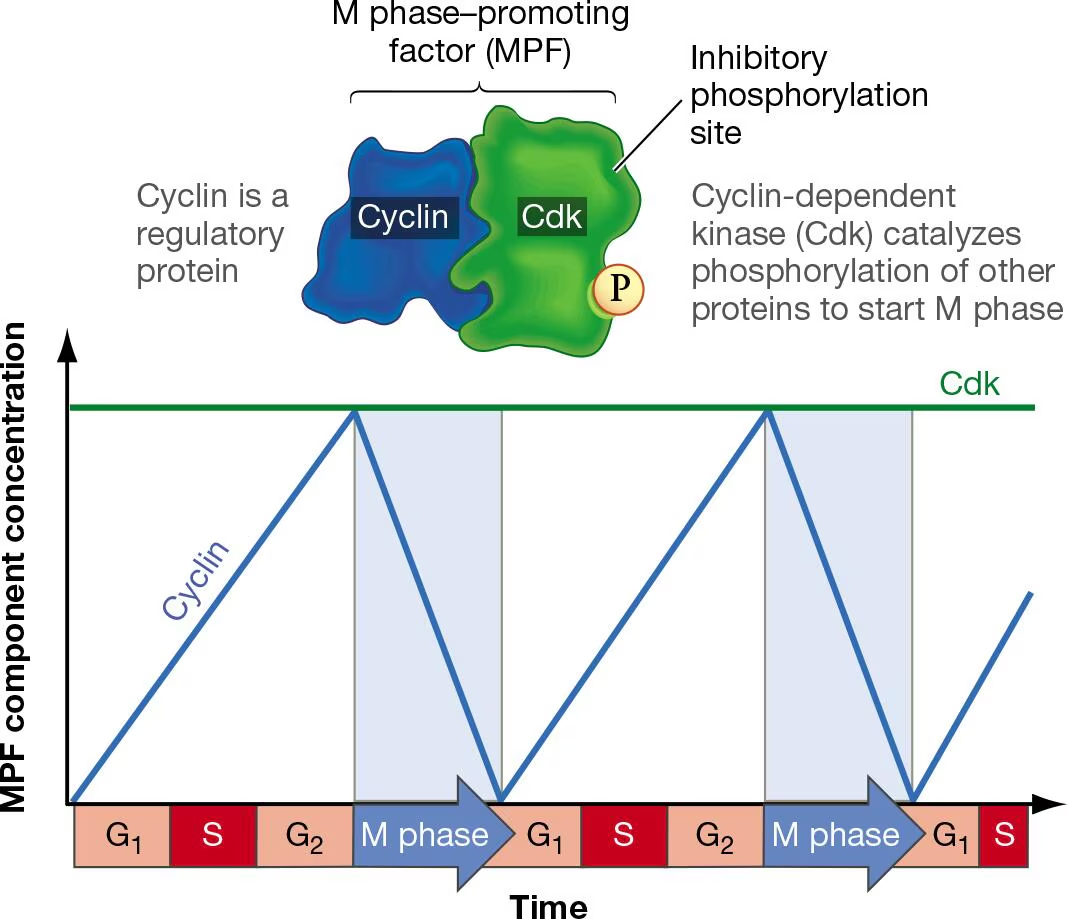
Explain CDK and Cyclin concentrations in this image
CDKS are always around
Constant concentration at all times
Only active when cyclin is attached
What happens with CDK and Cyclin in interphase (Regulation of MPF)
Cyclin B builds up and binds to CDK
CDK inactive due to inhibitory phosphate
Rb role?
Inactivates E2F by binding to it
How its removed:
After idk phosphorylates Rb after inactivating phosphate is removed from cdk/cyclin
Phosphorylated Rb releases E2F
What are some defects that can occur in the control of the G1 checkpoint pathway that can lead to cancer?
Too much growth factor - too much cyclin/E2F
Too much E2F to hold back → unwanted S phase
No Rb
Too much phosphatase- if phosphate removed early -> premature phosphorylating Rb → premature phase
Too much E2F
Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) is…
an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins
A cyclin...
activates a Cdk molecule when it reaches a sufficient concentration