bio unit 3
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
land plants were the first organisums that could survive with their
tissues exposed to air
before plants could evolve, terrestrial life was limited to
bacteria, archea, single celled protists
building soil provides
food for decomposers
holding soil prevents
nutrients from being lost to wind or water erosion
water and hold soil
plants provide services such as
producing oxygen, build & hold soil, moderates climate
how do plants moderate climate
provides shade, reduces impact of wind on landscapes
artificial selections
changes traits of domesticated species
non vascular plants
lack vascular tissue, mosses, use spores not seeds for reproduction
seed plants
have vascular tissue, make seeds
cuticle
keeps plant from drying out
what 3 adaptations solved the drying problem in early plants
preventing water loss
protection from UV rays
moving water to tissues from direct to no acces to water
first plants had
cuticle, UV absorbing compounds (sunscreen)
stoma
waxy cuticle cover that allows gas exchange and minimizes water loss
three adaptations that were instrumental for efficient plant reproduction in dry environment
spores, gametes , embryos
spores resisted
drying due to coat of spropollenin
gametes are
produced in complex multicellular structures
embryos are
retained and nourished by parent plant
all land plants undergo alternation of generations which in which indivauls have
multicellular haploid phase, multicellular diploid phase
multicellular haploid phase
gametoppyte
multicellular diploid phase
sporophyte
dipold soprophytes produce
haploid spores by meosis
haploid gametoppyte produce
gametes by mitosis
gametophyte (n) have ____ (n) which fuse to ____ (2n)and undergoes ____ to turn in _____
____(2n) undergo ___ to turn to ____(n)
____ (n)undergo ____ to turn to gametophyte(n)
gametes , zygotes, mitosis, sporpphyte
sporophyte, meiosis, spores
spores, mitosis
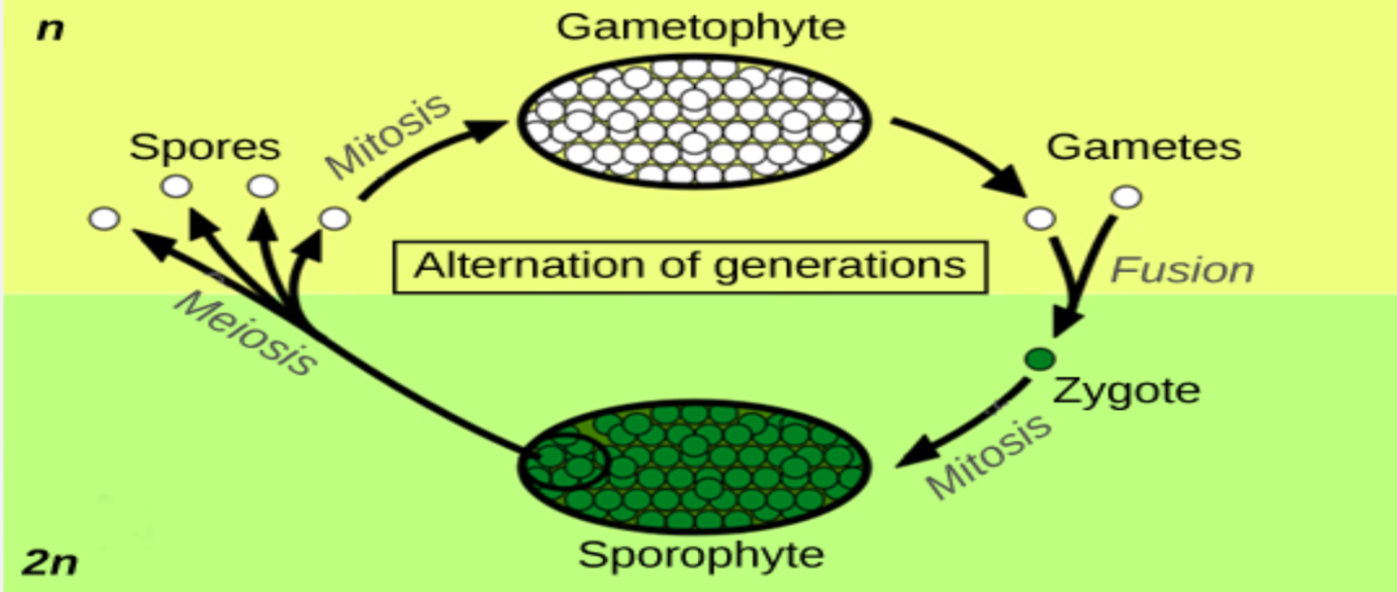
gametophyte-dominat life cycle found in
non vascular plants
depends on gametophyte for nutrition while sporophyte is small and short lived
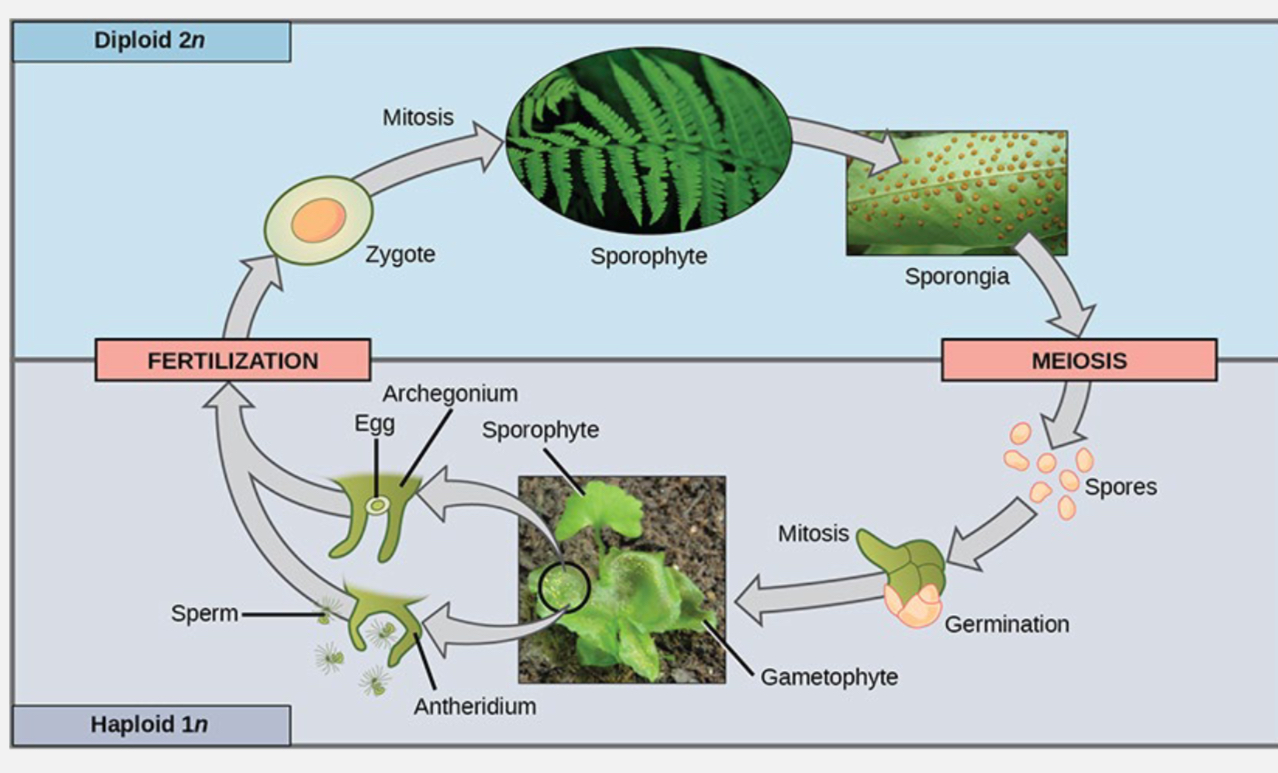
sporophyte-dominat life cycle found in
ferns and other vascular plant
sporophyte is larger and longer lives than gametophyte
sporophyte-dominat life cycle is more advantageous due to
sporophyte having 2n
means diploid can respond to varying enviromental condition better
in a dominat sporophyte life cyle
gametophytes grow from sporophytes
pollen grains in land plants allow
plants living in dry habitats to reproduce effiecenly
pollen grains are
tiny male gametophytes surround by coat of sporpollenin
also carried to female gametophyte by wind or animals
in ferns or horsetails sporophytes live in same place as
thier parent gametophyte
seeds contain
embryo and nutrients provided by mother
stamen
conatins anther, where microsporangia develop
carpel
contains ovary, ovules are found containing megosporangia
angiosperm fertaliztion
one fuses with egg to form diploid (2n) zygote
one fuses with two nuclei in female gametophyte which forms triploid (3n) nutritive tissue (endosperm)
flower life cycle of double fertilization
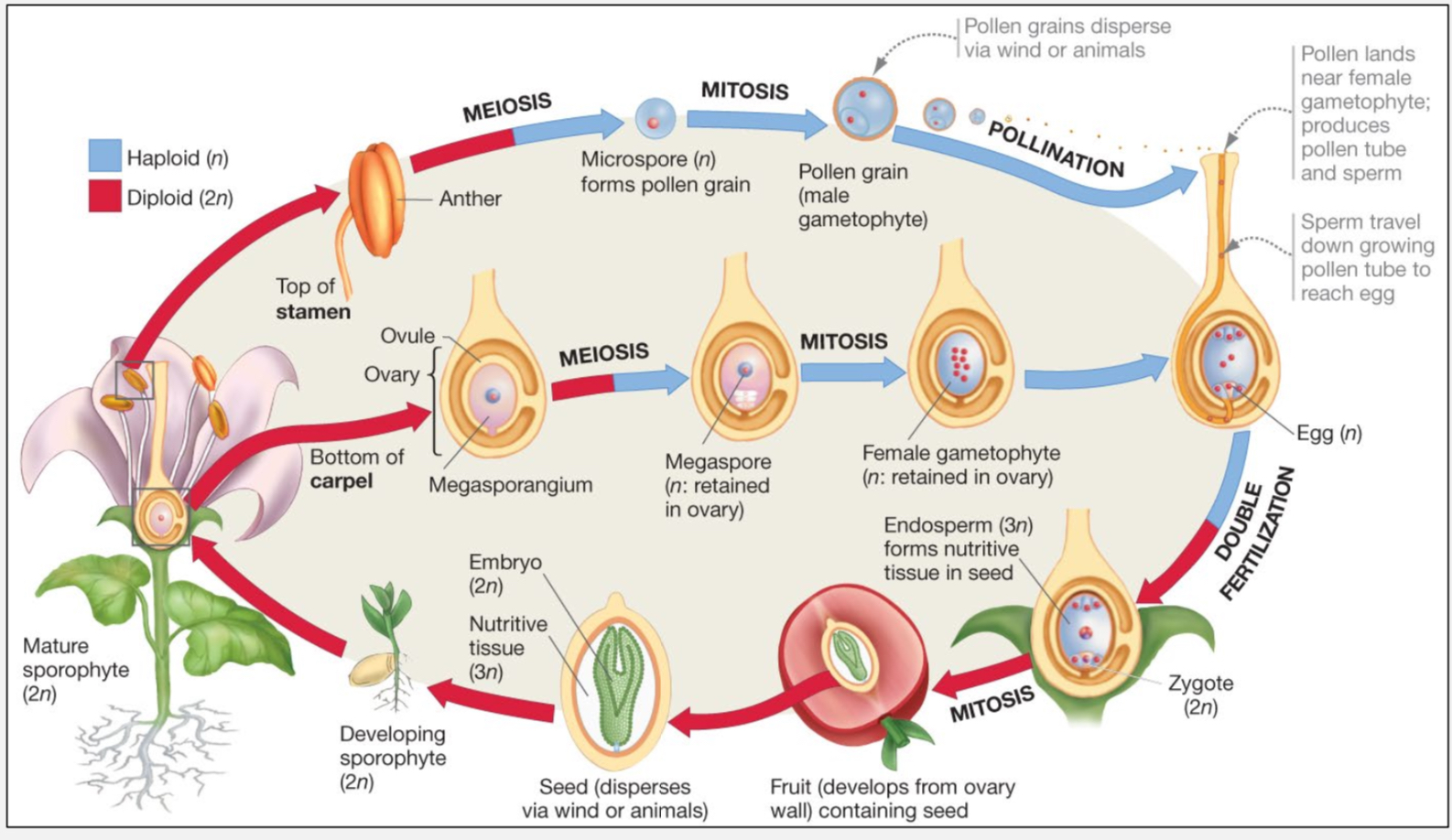
fruits are structures
derived from ovary and encloses one or more seeds
trees grown in shade have
larger leaves
plant cells are surrounded by
cellulose-rich primary cell wall
some plants have rigid secondary cell wall
cytoplasm of
adjacent plant cells are connected by plasmodesmata
allows for communication between cells
epiphytic plants
non parasitic, grow in absence of soil, leaves or branches of trees
parasitic plants
live on or in a host
most parasitic plants are photosynetic and use
haustroia to extract water and ions from the xylem of host plant
some parasitic plants are heterotroph producing structures called
haustroia that can penetrate host vascular system to obtain water and neutrients
heterotrophy
obtain energy and organic molecules by ingesting other organisums
Cambrian period
most rapid period of animals evolution
542-488 mya
choanoflagellates and sponges comparison
benthic (live at bottom of aquatic enviroments)
sessile (adults live permanently attached to substrates instead of moving freely)
feeding occurs at cellular level
diploblats
animals whos embryos have two types of tissues
radiata diploblats
two germ layers: entoderm and endoderm
group of radially symmetrical animals that are diploblastic,
body parts are arranged around a central axis
bilaterata triploblasts
three germ layers
entoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
acelomates
lack body cavity
mesoderm is filled with tissue
flatworms
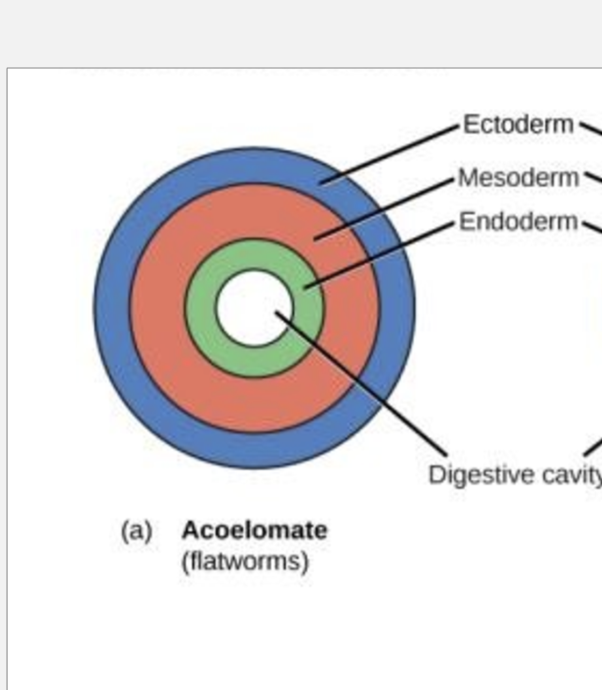
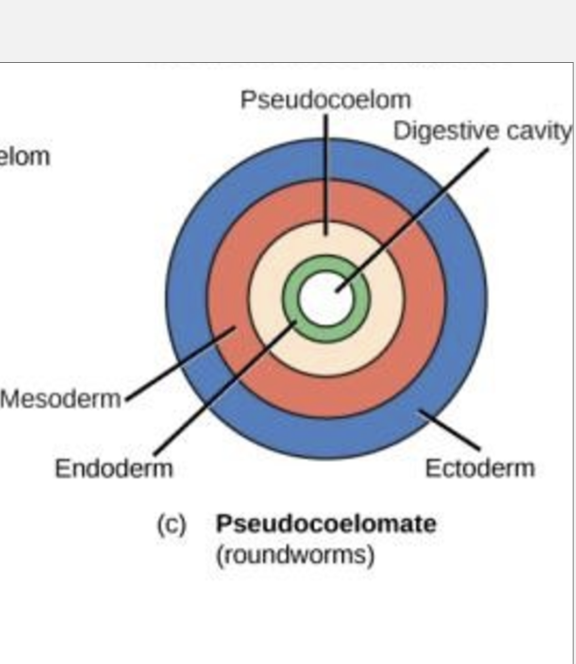
pseudocoelomates
false body cavity
made from endoderm and mesoderm
hydrostatic skeleton
roundoworms
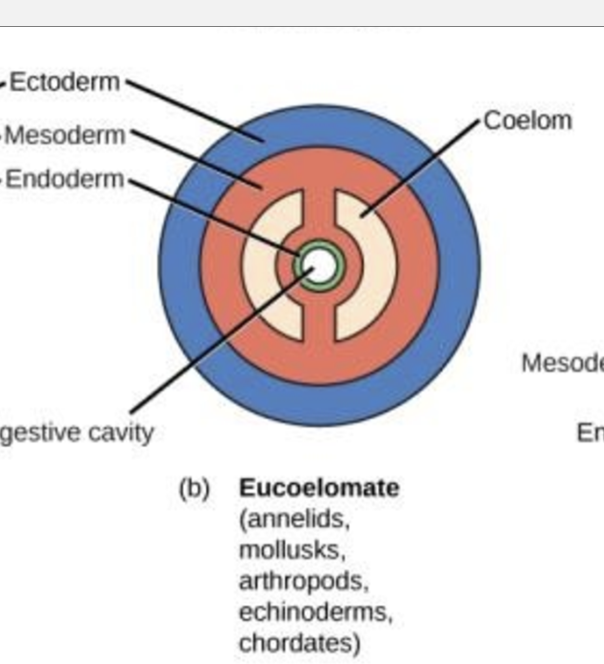
coelomates
aries from mesoderm
tissues holds organs in place
body tissues holds
segmentation
division of body or part of body in small structures
animal locomotion
finding food
finding mates
escaping from predators
dispersing to new habiatats
hydrostatic skeletion
a type of skeleton supported by fluid pressure within a closed body cavity, common in soft-bodied invertebrates like worms and jellyfish
endoskeleton
support from inside the body
bones
exoskeleton
support from outside the body
external armor
parthanogensis
a form of asexual reproduction where offspring develop from an unfertilized egg
mesoderm
the middle of the three primary germ layers of an embryo that is the source especially of bone, muscle, connective tissue, and dermis
endoderm
the innermost of the three primary germ layers in an embryo, giving rise to the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts, as well as various internal organs and glands.
ectoderm
the outermost layer, forms the outer layer of skin, nervous system, and related structures
earliest vertebrate fossils
are in china and canda
earliest members lived in the ocean
traits of early vertabrates
lived in ocean
streamlined, fish-like bodies, gills, post-anal tail, cranium made of cartilage
first evidence of the jaw and lungs
placoderms had first jaw- from gill arches
lungs(auxiliary source of oxygen for heart)-arose as out pockets of the esophagus
3 major lineages of living tetrapods (4 limnbs)
amphibians
mammals
reptiles
lobe finned fish: the coelacanth have
bone structures in pectoral fins that allow for support
amphibians (both sides living) are
the first tetra pods to live on land (frogs , salamanders,etc)
feed on land, lay eggs in water
gas exchange occurs on moist skin
amniota
lineage that includes other terta pods other than amphibians
the amniotic egg consists of
yolk/yolk sac
chorion
allantois
amnion
albumen
yolk/yolk sac
transports nutrients to circulatory system of embryo
chorion
promotes exchange in of oxygen and carbon dioxide between embryo and the eggs external enviroment
allantois
stores nitrogenous waste produced by embryo and facilitates respiration
amnion
protects embryo from mechanical shock and supports hydration
albumen
provides the embryo with water and protein
reptiles
monophyletic group that represents second mjaor living lineage of amniotes besides mammals
four major lineages
lizards and snakes
turtles
crocodiles and alligators
birds
many reptiles are ectotherms, meaning:
dont use internally generate heat to regulate body temp
for land transition new adaptations in protostomes must allow
exchange of gases
avoid drying out
holding up thier bodies
round and earth worms has high surface area to volume ratio that allow
efficiency in gas exchange
arthropods and mollsucks have
respiratory structures in body
waxy layer drying out resistant eggs
spiracles
small opening in exoskeletons acting as respiratory opens allowing air and water
arthopod taxonomy lineage
myriapods
chelicerates
insects
crustaceans
characteries of chordates
notochord- rod shaped structure that runs along nerve chord
dorsal hollow nerve cord-in vertebrates develops into spinal cord
pharyngeal gill splits - in vertebrate: gill splits
, in tetra pods develop into ear and tonsils
post anal tail