Anatomy test 1
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
what is anatomy?
the study of structure
what isn’t anatomy?
the study of function
cytology
the study of cells
histology
the study of tissue
anatomical position
upright, facing forward, feet apart, palms facing forward
anatomical quadrants
patients right and left
right lob of liver
right upper quadrant
gallbladder
right upper quadrant
right kidney
right upper quadrant
portions of stomach
right upper quadrant
small and large intestine
right upper quadrant
cecum
right lower quadrant
appendix
right lower quadrant
portions of small intestine
right lower quadrant
reproductive organs (right ovary in female and right spermatic cord in male)
right lower quadrant
right ureter
right lower quadrant
left lobe of liver
left upper quadrant
stomach
left upper quadrant
pancreas
left upper quadrant
left kidney
left upper kidney
spleen
left upper quadrant
portions of large intestine
left upper quadrant
most of small intestine portions of large intestine
left lower quadrant
left ureter
left lower quadrant
reproductive organs (left ovary in female and left spermatic cord in male)
left lower quadrant
proximal
toward an attached base
distal
away from an attached base
medial
towards the midline
lateral
away from the midline
cranial/cephalic
toward the head
caudal
toward the tail
posterior or dorsal
towards the back
anterior
towards the front
superficial
surface level
lower middle region
hypogastric region
lower right region
right inguinal region
lower left region
left inguinal region
middle right region
right lumbar region
middle left region
left lumbar region
center middle region
umbilical region
upper right region
right hypochondriac region
upper left region
left hypochondriac region
upper middle region
epigastric region
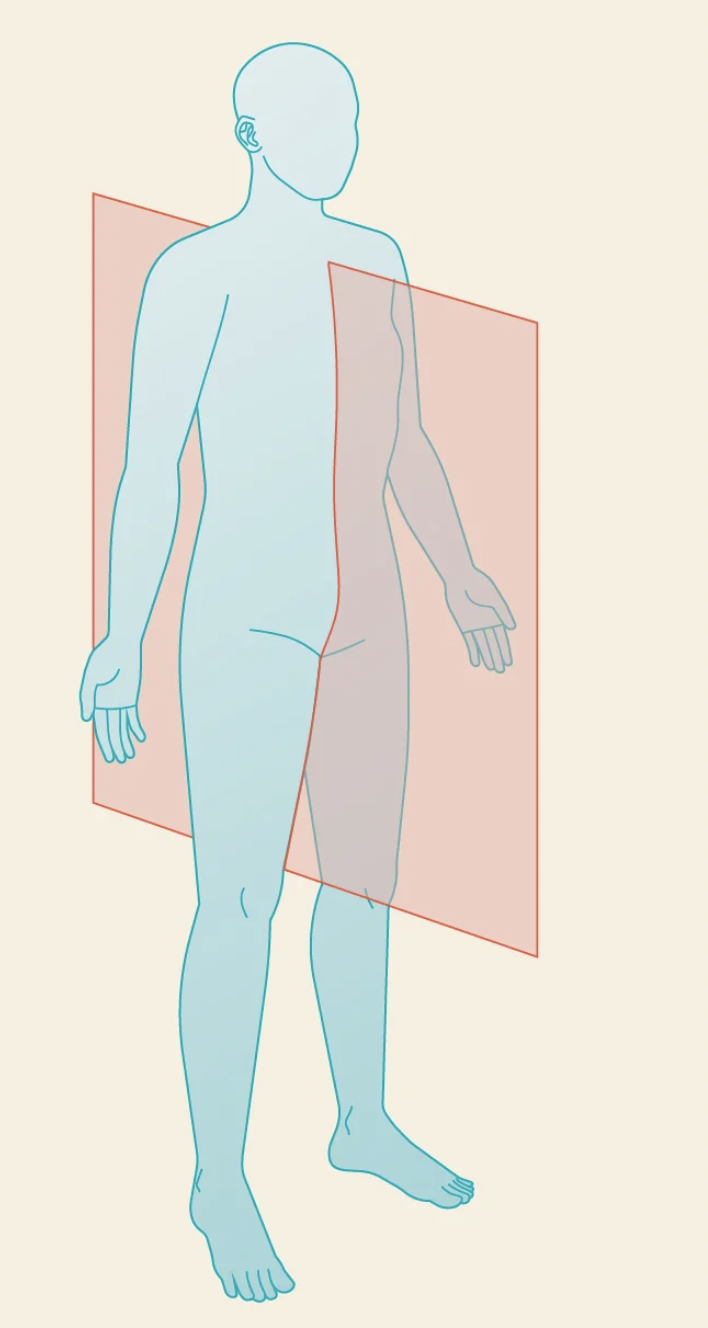
this plane is called
frontal/coronal plane
what does the frontal plane do?
splits body into anterior and posterior
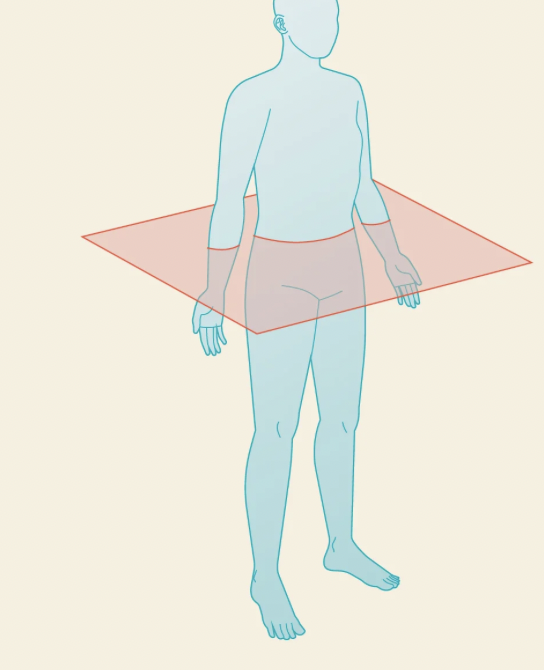
this plane is called
transverse/horizontal plane
what does the transverse plane do?
split the body into cephalic and caudal
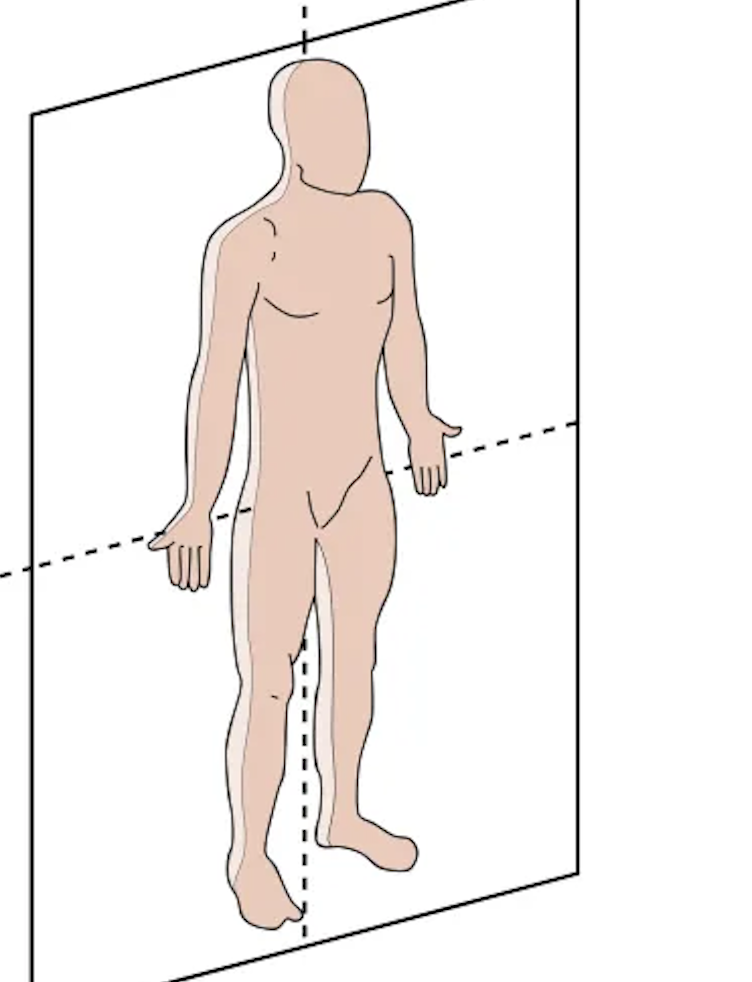
this plane is called
sagittal
what does the sagittal plane do?
split the body into left and right halves
which type of sagittal plane splits the body into equal planes?
midsagittal
which type of sagittal plane splits the body into unequal planes?
parasagittal
what are the two dorsal cavities?
cranial cavity ans spinal cavity
What are the two ventral cavities?
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
what is included in the thoracic cavity?
right and left pleural cavities, mediastinum and pericardial cavity
what is the mediastinum?
the space between the left and right pleural cavities
what does the pericardial cavity contain?
heart
what are the three parts of the abdominopelvic cavity?
abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity, peritoneal cavity
what is the peritoneal cavity?
the peritoneal cavity is the space within the abdominal cavity lined with peritoneum
what is the abdominal cavity?
a large space that houses organs that are both within and outside of the peritoneum
what is the pelvic cavity?
located at bottom of abdominopelvic cavity, included reproductive organs, rectum, urinary bladder, and pelvic floor muscles
what are ventral cavities surrounded by?
serous membrane
what are the two layers of serous membrane?
parietal and visceral
what does the parietal layer of serous membrane do?
lines cavity walls
what does the visceral layer of serous membrane do?
surrounds each organ
what are the functions of the integumentary system?
protection, thermoregulation, waste excretion, liquid synthesis/storage, metabolic functions, cutaneous sensation
what are the 3 ways the integumentary system protects?
protects from physical, chemical and biological
what is one example of thermoregulation?
sweating
what are NOT examples of thermoregulating?
shivering and goosebumps
what is the lowest layer of the epidermis?
stratum basale (burnt)
with layer of the epidermis is attached to the basal lamina?
stratum basale
nemonic for remembering layers of epidermis?
“Come, let’s get sun burnt”
what is the second lowest layer of epidermis?
stratum spinosum (sun)
which layer of the epidermis has several layers of keratinocytes connected by desmosomes?
stratum spinosum
what is the job of keratinocytes?
to make keratin
what is the middle layer of the epidermis?
stratum granulosum (get)
which layer of the epidermis had 3-5 layers where keratinization begins?
stratum granulosum
what is keratinization?
cells become so full of keratin they die
which layer of the epidermis is under the stratum corneum?
stratum lucidum (let’s)
which layer of the skin is only then in thick skin such as the palms of hands or areas with calluses?
stratum lucidum
which layer of skin is the topmost layer of the epidermis?
stratum corneum (come)
what layer of the skin has 15-30 layers of dead keratinocytes known as cornfield cells?
stratum corneum
what are basal cells?
large stem cells that divide to replace lost superficial cells
what is the function of melanocytes?
produce melanin
cells found in the epidermis that are sensitive to touch
merkel cells
primarily filled with loose connective tissue with fibroblasts and leukocytes
dermis
which layer of the dermis has areolar CT with collagen and elastic fibers, and contains dermal papillae?
papillary layer
which layer of the dermis is dense irregular CT with adipose cells and many thick collagen fibers?
reticular layer
which layer is deeper, dermis or hypodermis?
hypodermis
what is another name for the hypodermis?
subcutaneous layer
which layer has superficial fascia composed mostly of adipose?
hypodermis
which layer loosely anchors skin to underlying structures and is not technically part of the skin?
hypodermis
is the hypodermis or dermis more richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels?
dermis
hair
flexible strands of mostly dead keratinized cells
hair papilla
carries blood vessels and nerves into the bulb
where does mitosis occur in a hair follicle
mitosis occurs just above papilla in hair matrixin the hair matrix
bands of smooth muscle that cause hair to raise ex. goosebumps
arrestor pili
everything from the papilla to the skin
hair follicle
fine, short, soft hair that is often unpigmented and typically covers most of the body.
vellus hair
Thicker, longer hair that is usually pigmented and found on the scalp, face, and body after puberty.
terminal hair
A common type of hair loss in men that typically results in a receding hairline and thinning at the crown of the head, often associated with genetic factors and hormonal changes.
male pattern baldness