EKG rhythms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
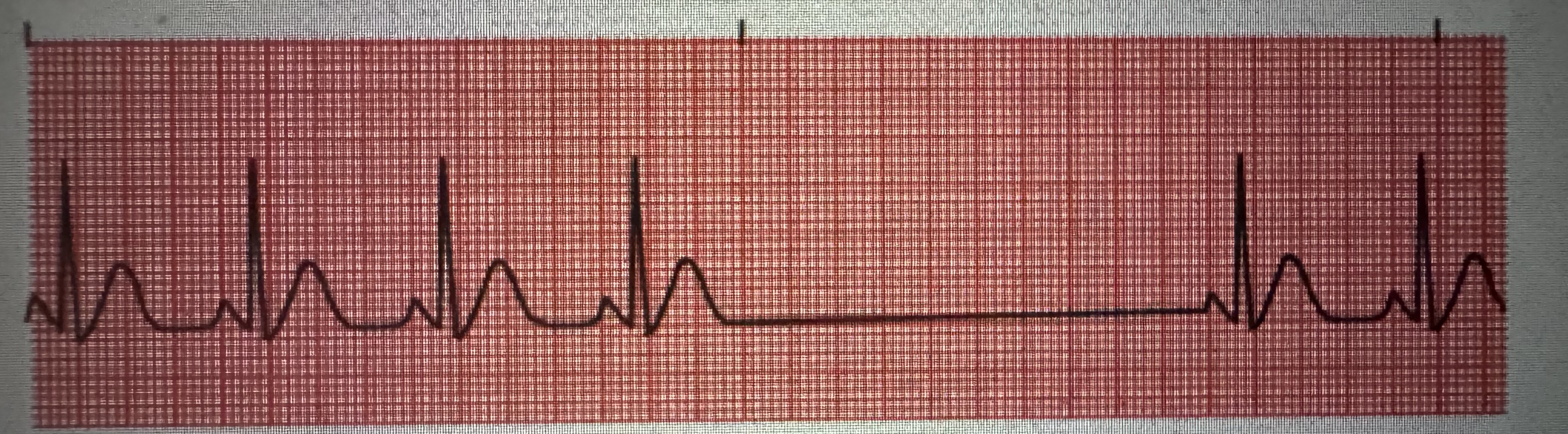
Sinus Arrest
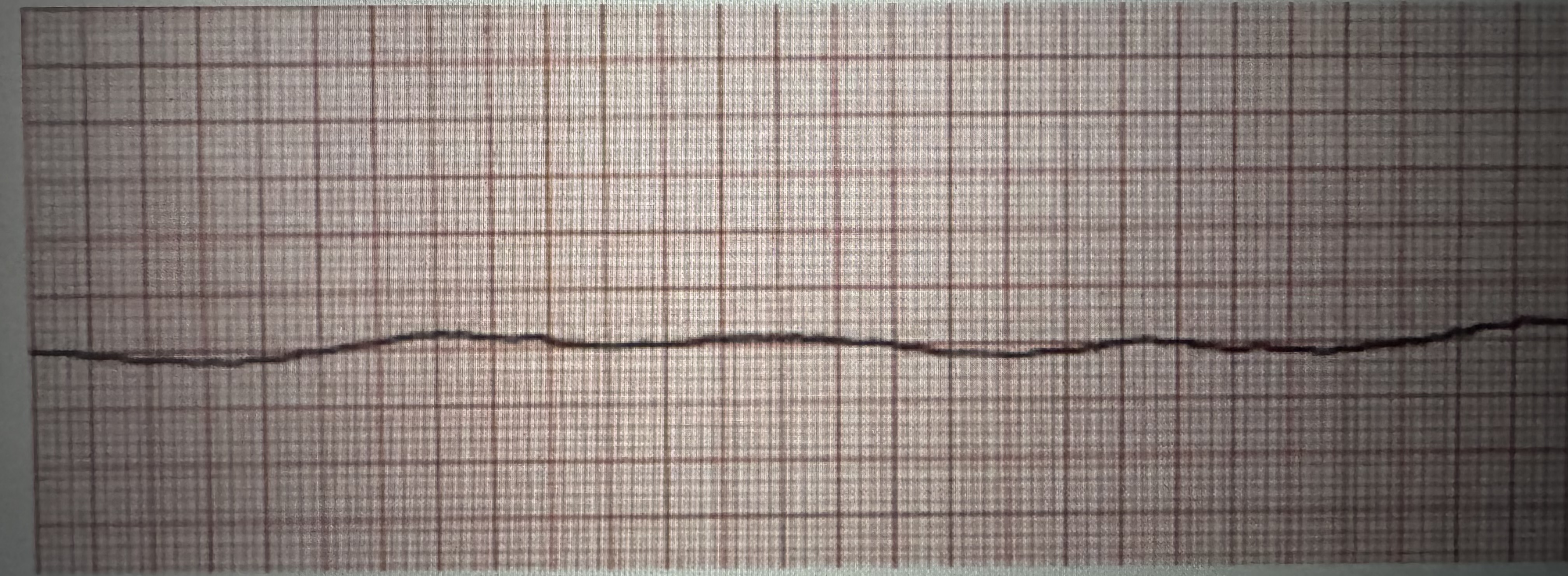
Asystole
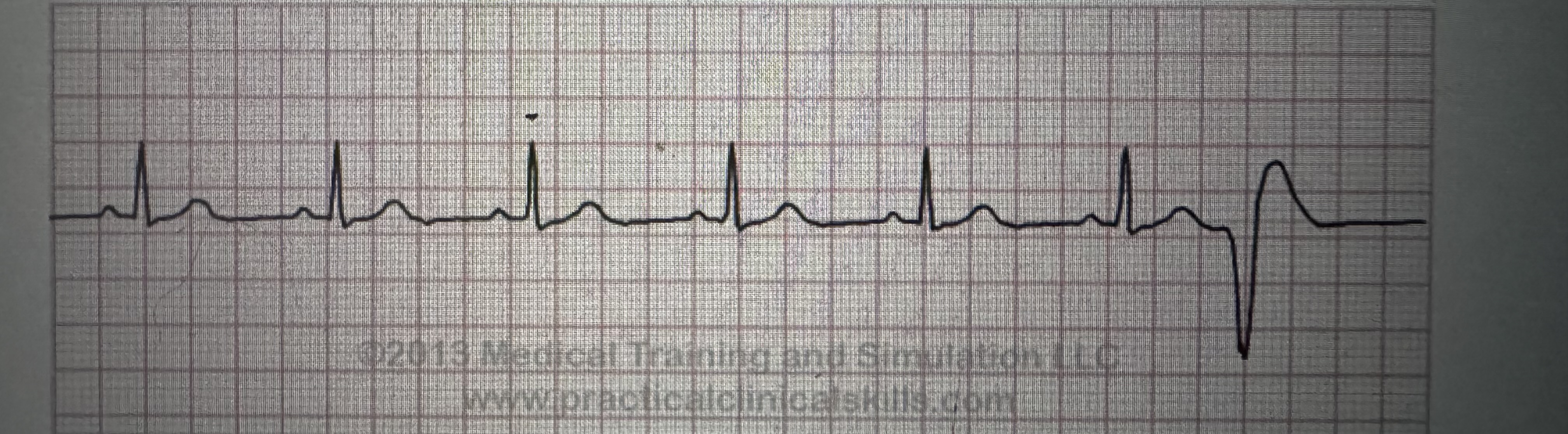
PVC
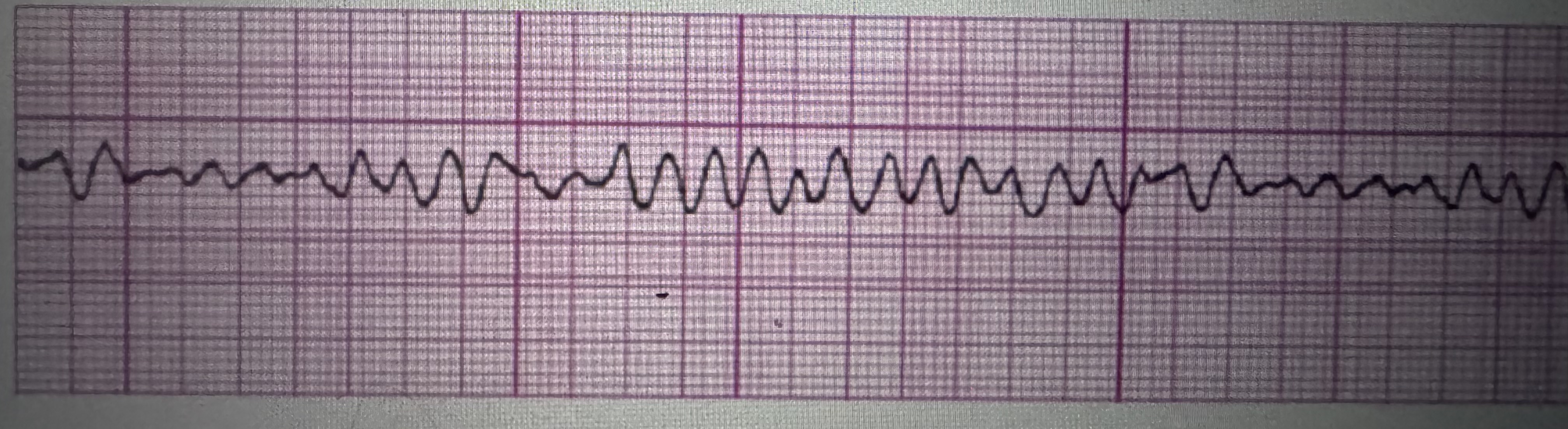
V. Fib
Sinus tachycardia
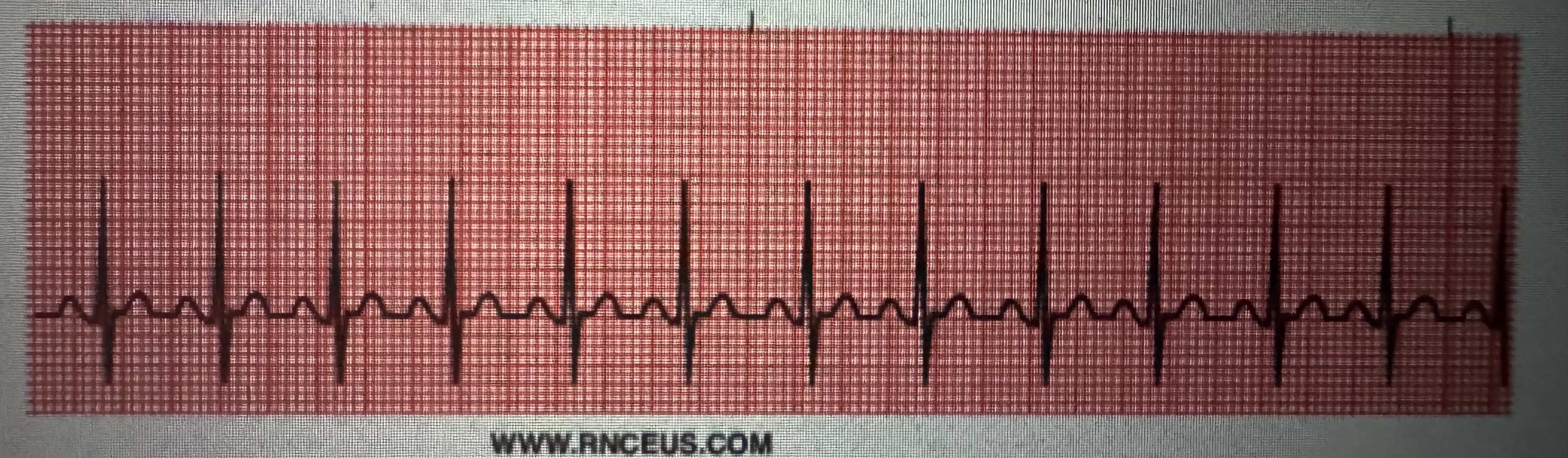
PAC
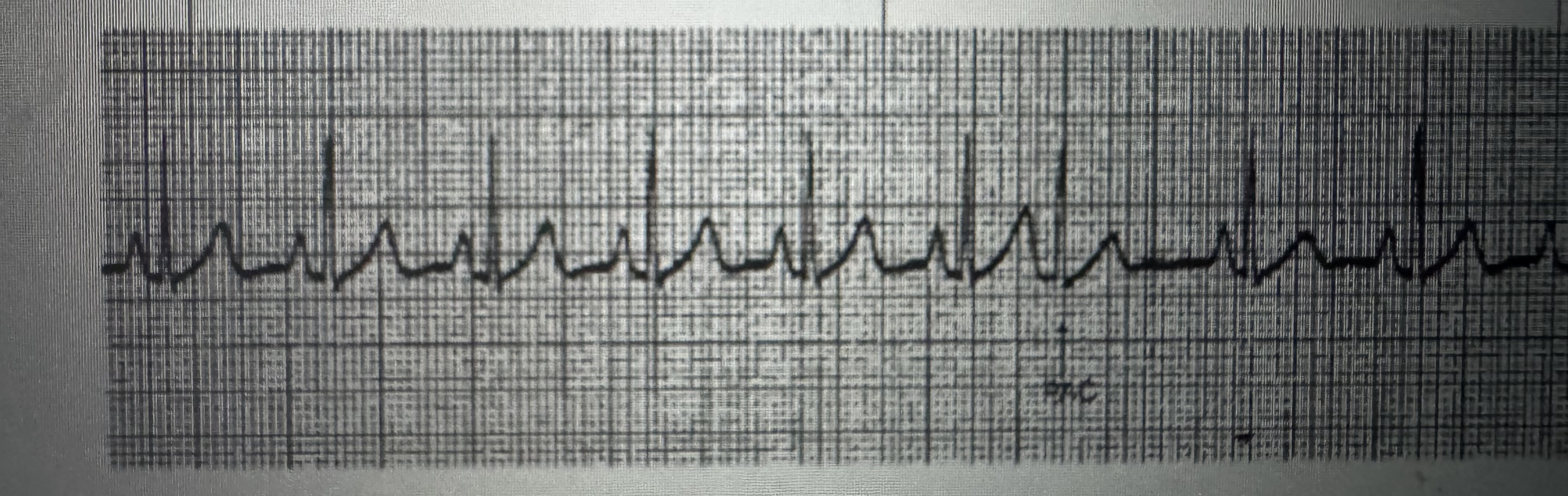
Sinus bradycardia
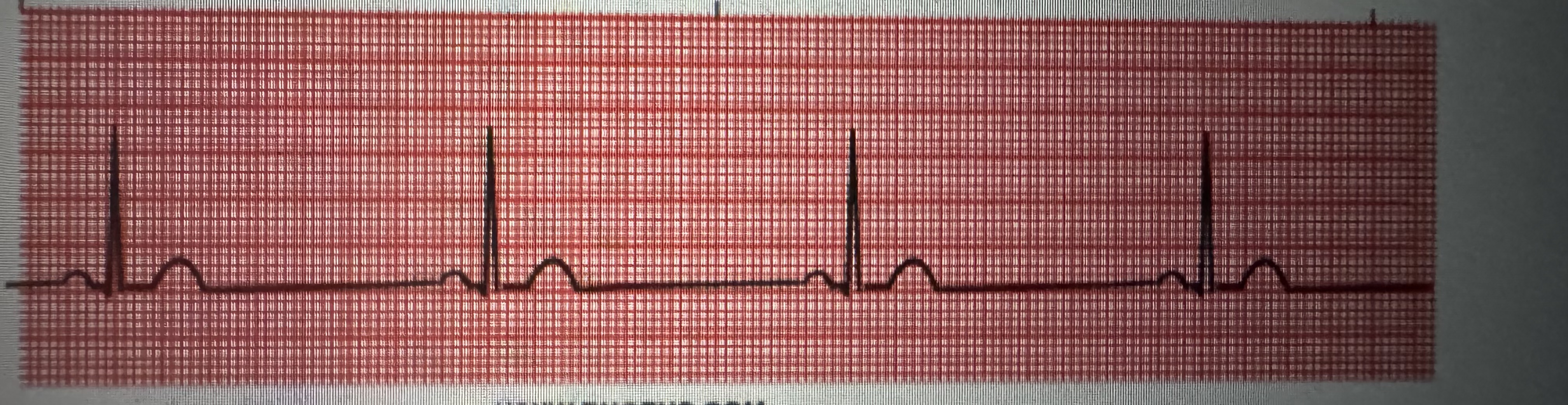
A. Flutter
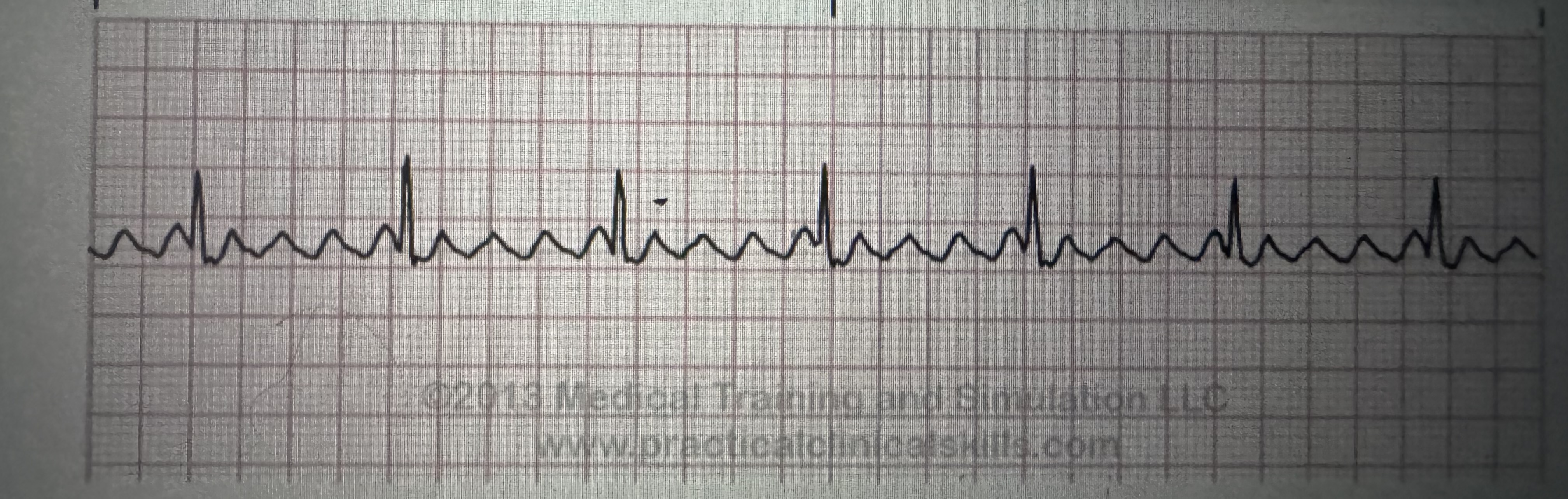
V tach
normal sinus
A. fib
PR interval
measure from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS
normal is 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS
Ventricular depolarization and contraction
normal 0/06 to 0.10 seconds
What does it mean if the PR interval is greater than 0.20 seconds
delay
blockage
What does it mean if the QRS is longer than 0.10 seconds?
problems with ventricular conduction
ST segment
beginning of ventricular repolarization
T waves
represent ventricular repolarization
What causes abnormalities in the T waves?
myocardial ischemia
myocardial injury
electrolyte imbalances
Medications that can prolong QT
antiarrhythics/antidysrthmics
Amidarone
Norpace
Tikosyn
Procainamide
Quinidine
Sotalol
antimicrobials/antifungals
Azithromycin
Clarithromycin
Erythomycin
Itraconazole
psychotropics
Haldol
Thorazine
Tricyclics
Droperidol
U wave
not typically seen
thought to be repolarization of the terminal purkinje fibers
most commonly seen in hypokalemia
Rate: 60-100 bpm
P QRS: 1 to 1
PR interval: 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: regular
Treatment: none
normal sinus rhythm
Rate: 101 to 151 bpm
P QRS: 1 to 1
PR interval: 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: regular
Treatment: treat cause
sinus tachycardia
Rate: less than 60 bpm
P QRS: 1 to 1
PR interval: 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: regular
Treatment: if symptomatic treat cause (atropine, pacing)
sinus bradycardia
Rate: 60 to 100 bpm
P QRS: 1 to 1
PR interval: 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: irregular
Treatment: none
sinus arrhythmia
Rate: Variable
P QRS: 1 to 1
PR interval: 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: irregular
Treatment: none
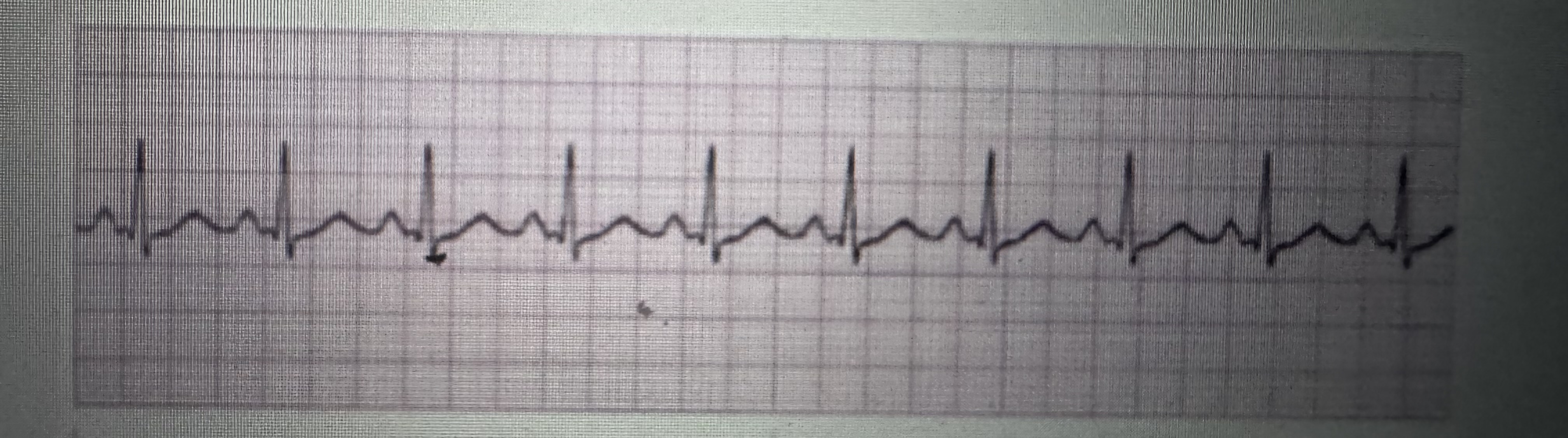
PAC’s (premature atrial contractions) and underlying rhythm
Rate: atrial 300 to 600 bpm
Rate: ventricular 100 to 18 bpm
P QRS: variable
PR interval: not measurable
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: irregularly irregular
Treatment: IV meds (digoxin, diltiazem, amiodarone), beta blockers, cardioversion, anticoagulants
atrial fibrillation (A. Fib)
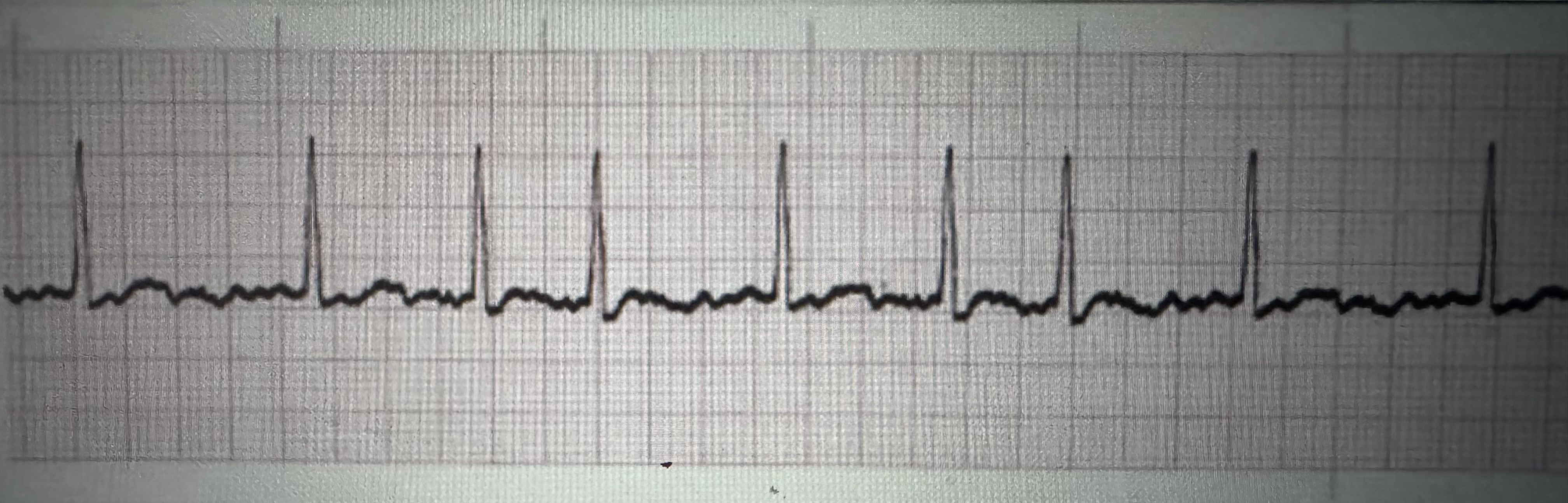
Rate: atrial 240 to 360 bpm
Rate: ventricular <150 bpm
P QRS: 2 to 1, 4 to 1, 6 to 1
PR interval: not measurable
QRS interval: 0.06 to 0.10 seconds
Regularity: atrial regular
Regularity: ventricles usually regular
Treatment: IV meds (digoxin, diltiazem, amiodarone), beta blockers, cardioversion, anticoagulants
Atrial flutter
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
ectopic ventricular beats that occur before the next expected beat of the underlying rhythm
Frequent, recurrent, or multifocal PVCs indicate myocardial irritability and may precipitate?
lethal dysrhythmias
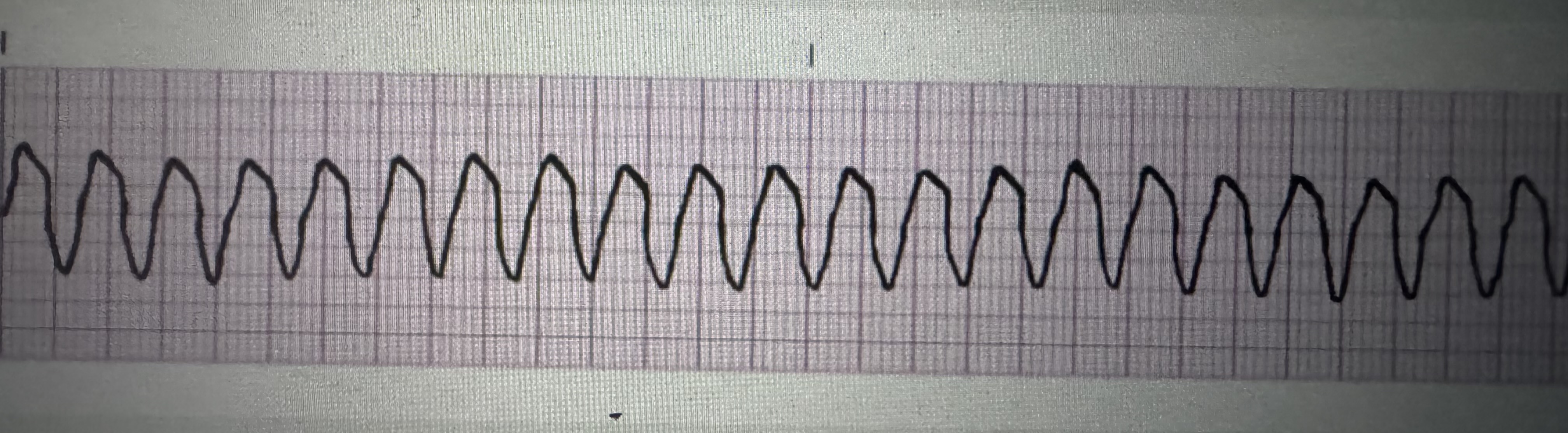
Rate: 100 to 250 bpm
P QRS: no P waves
PR interval: not measurable
QRS interval: >0.12 seconds, bizarre shape
Regularity: regular
Treatment: stable = lidocaine, cardioversion = unstable, defibrillation = no pulse
ventricular tachycardia (VT)
Rate: too fast to count
P QRS: no P waves
PR interval: not measurable
QRS interval: not measurable
Regularity: irregular
Treatment: Defibrillation
ventricular fibrillation (VF, V-Fib)