Hearing problems and testing quiz
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
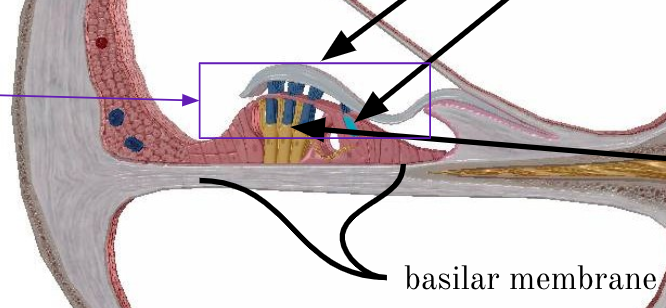
Basilar membrane
separates scala media from scala tympani
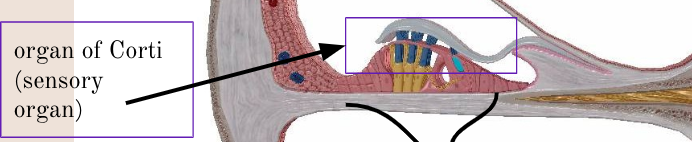
organ of Corti
rests on the basilar membrane
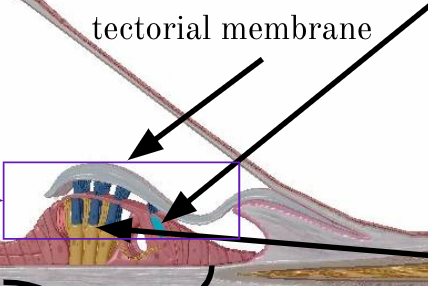
tectorial membrane
located above the outer hair cells
outer hair cells
sits on the basilar membrane in three rows
inner hair cells
single row of hair cells that rest on basilar membrane
stereocilia
sensory hairs at the top of the IHCs and OHCs
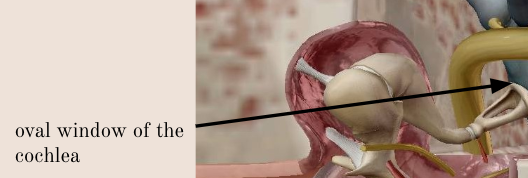
oval window
beyond the stapes footplate
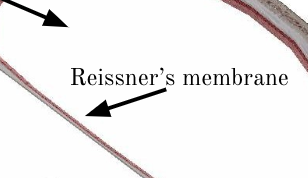
Reissner’s membrane
Separates the cochlear duct from scala vestibuli
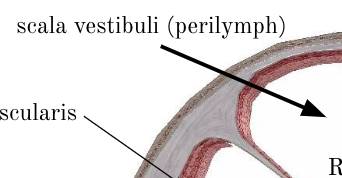
scala vestibuli
uppermost chamber filled with perilymph, which is high in sodium; found beyond the oval window
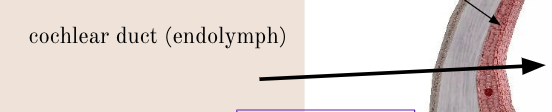
cochlear duct (scala media)
middle chamber filled with endolymph, which has high potassium
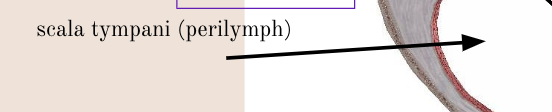
scala tympani
lowest chamber filled with perilymph that ends at round window
round window
opening, covered by a membrane between middle ear and scala tympani

stria vascularis
found in lateral wall of cochlea
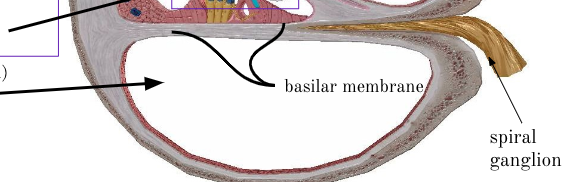
spiral ganglia
cell bodies along the modiolus
modiolus
bony structure in center of cochlea
Basilar membrane base
high frequency, thin, stiff
Basilar membrane apex
low frequency, wide, lax
The sensory organ of hearing is the organ of
Corti
This is a cross section of the
cochlea
Endolymph fills this canal in the cochlea
scale media
Three rows are ______, are responsible for generating autoacoustic emissions
outer hair cells
The top of OHCs in the cochlea are known as the _______, which are below the “roof” known as_______
sterocilia, tectorial membrane
The outer hair cells are part of the_____ system
efferent
The inner hair cells are part of the _____ system
afferent
Afferent means sensory information travels
to the brain and spinal cord
The efferent auditory system sends sensory information from the brainstem to the
outer hair cells
Otoacoustic emissions are generated from the
outer hair cells
From the inner hair cells, afferent signals are sent to _____ before the auditory nerve
spiral ganglia
The ____ is the beginning of the central auditory nervous system
cochlear nuclei
Auditory processing and decoding occurs in
Herscl’s gyrus in the temporal lobe
What are otoacoustic emissions (OAEs)?
sounds generated in the cochlea that can be measured in the ear canal and arise from activity of the outer hair cells
How are OAEs generated?
When sound is presented to the ear canal via a probe, the basilar membrane moves and reaches a peak.
Outer hair cells have motility
lengthen and shorten, controlled by a protein in the cochlea
voltage changes (because of ion current flow) produced by a traveling wave