Femur and Hip
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the angle of the femur slant and which way does it lie?
The femur slants 5-10 degrees medially
How can the leg rotation effect the femur?
Femoral neck visualisation
Trochanter visualisation
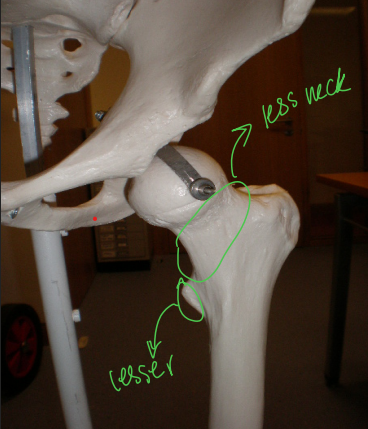
External rotation of the leg allows for ___?
Better visibility of the lesser trochanter
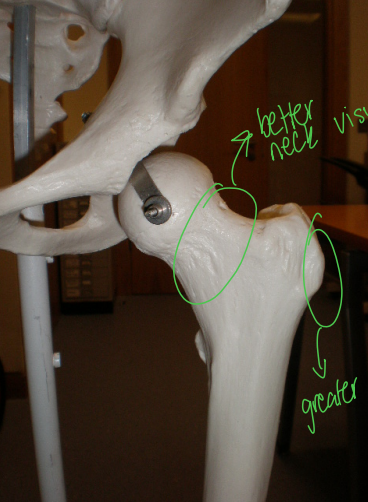
Internal rotation of the leg allows for ___?
Better visibility of the greater trochanter and femoral neck
What’re the most common reasons for imaging the femur?
Trauma
Bone pain
Femoral plates
Joint replacements
Soft tissue calcifications (bone spurs)
Osteosarcoma (bone cancer)
Metastases
Imaging pathway for hip trauma
Plain radiographs —> CT —> MRI/Bone scan
What is the most common imaging modality for arthritis?
Plain radiographs
What is avascular necrosis/osteonecrosis?
Failed blood supply to the bone, this can lead to cell death and bone collapse (bone dies) if left untreated
How would you adjust if the patient has metal prosthetics in their leg?
Do manual exposures, don’t use automatic settings
What is the imaging view series for femur trauma?
Pelvis
AP femur (proximal and distal)
HBL femur ((proximal and distal)
What is the imaging view series for femur non-trauma?
AP femur with 15 degree internal rotation (proximal and distal)
Mediolateral femur (proximal and distal)
AP Proximal Femur
Collimation:
Centering point:
Leg rotation
Collimation:
Top of image should be 2cm above the ASIS
Include hip joint
Skin margins
Centering point: Mid femur
Leg rotation: 15 degrees internally (non-trauma)
AP Distal Femur
Collimation:
Centering point:
Leg rotation
Collimation:
Include 5cm below knee joint
Overlap with previous proximal image
Skin margins
Centering point: Mid femur
Leg rotation: 15 degrees internally (non-trauma)
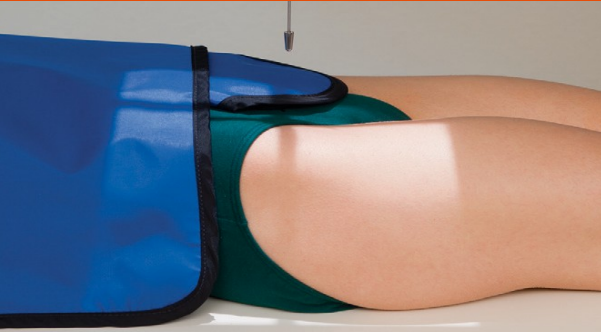
Name this view
AP hip
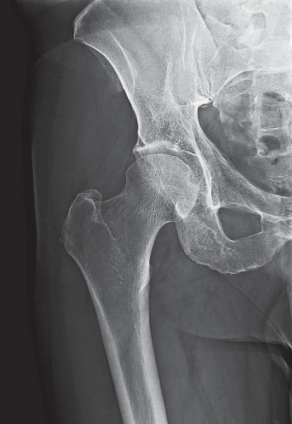
Name this view
AP proximal femur
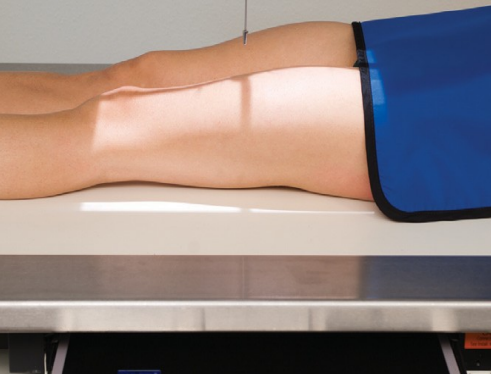
Name this view
AP distal femur
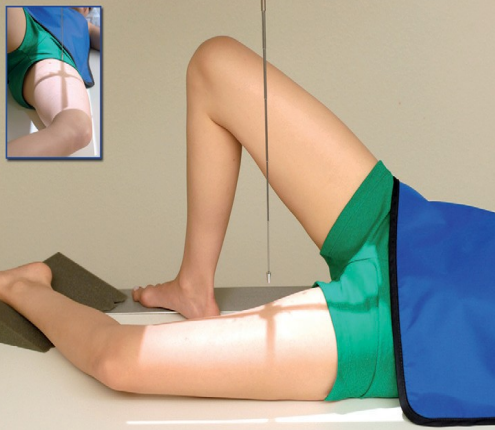
Name this view
Mediolateral proximal femur
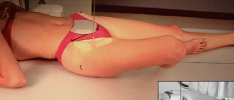
Name this view
Lateral hip
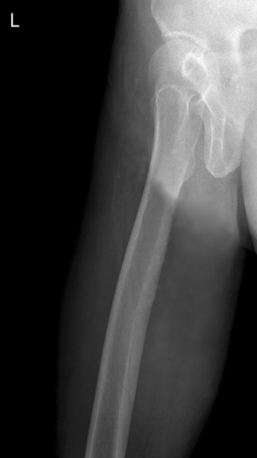
Name this view
Mediolateral proximal femur
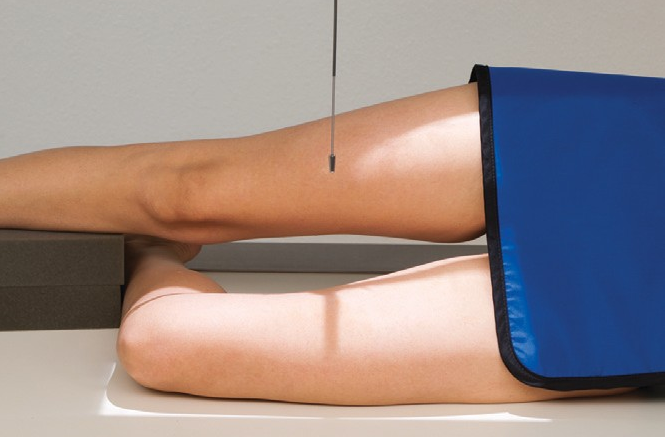
Name this view
Mediolateral distal femur
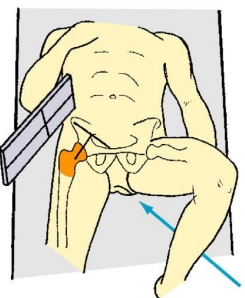
Name this view
HBL hip/proximal femur (axiolateral)
What angle should the detector and tube be for a HBL?
45 degrees
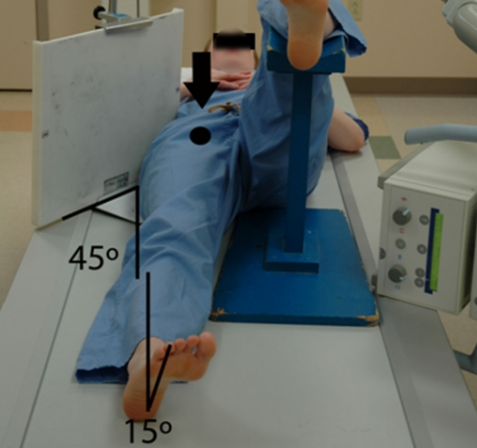
HBL Proximal Femur/Hip
Collimation:
Centering point:
Leg rotation:
Collimation: Include ASIS at the hop of image
Collimation: Perpendicular to the femoral neck
Leg rotation: 15 degrees (ONLY IF THEY CAN)
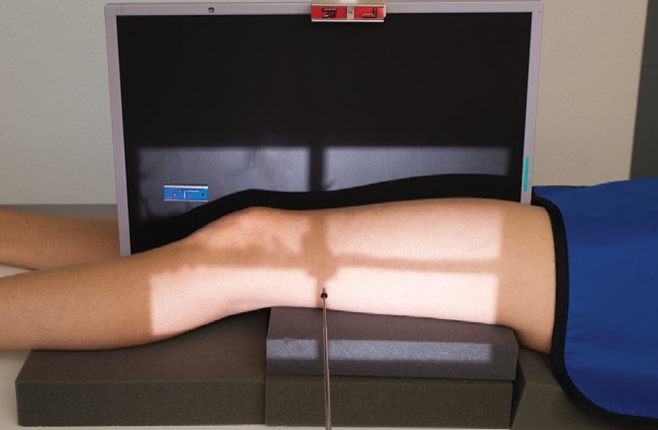
Name this view
HBL distal femur
What is osteosarcoma?
Bone cancer caused by malignant tumor due to transformed cells in the bone