Organic Chemistry - Values
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
~50
What is the pka of this molecule (methane)
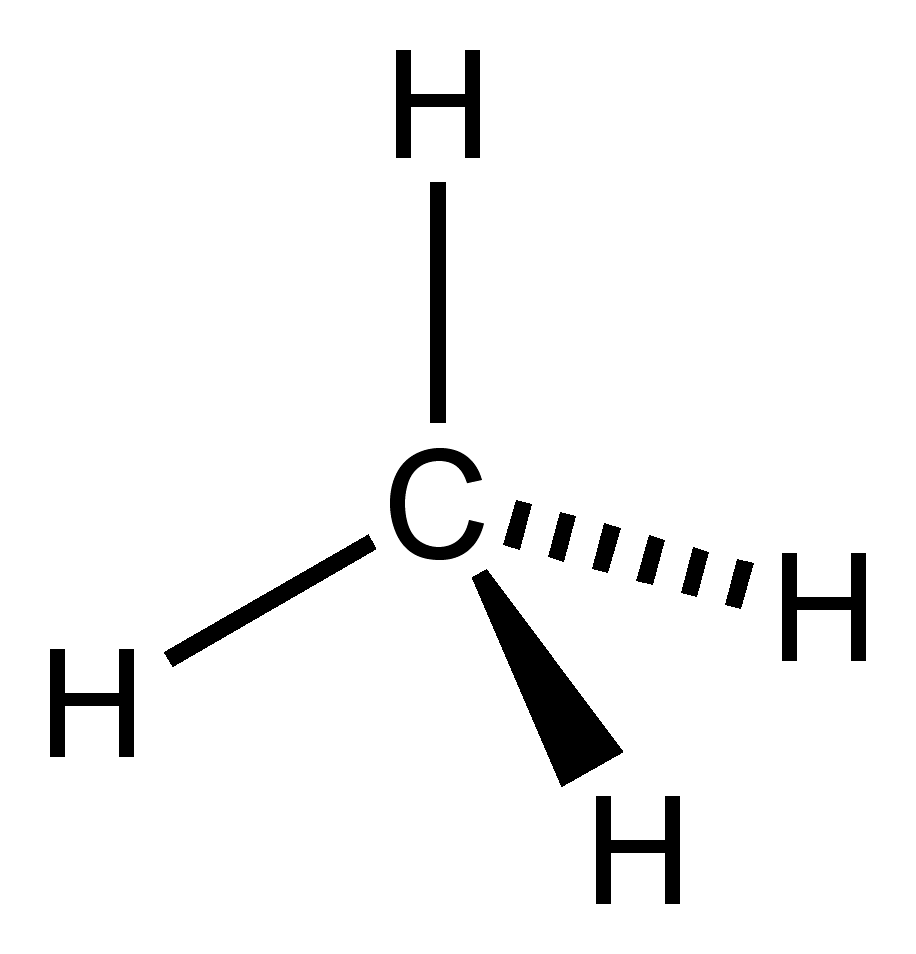
2
New cards
~15
What is the pka of this molecule (water)
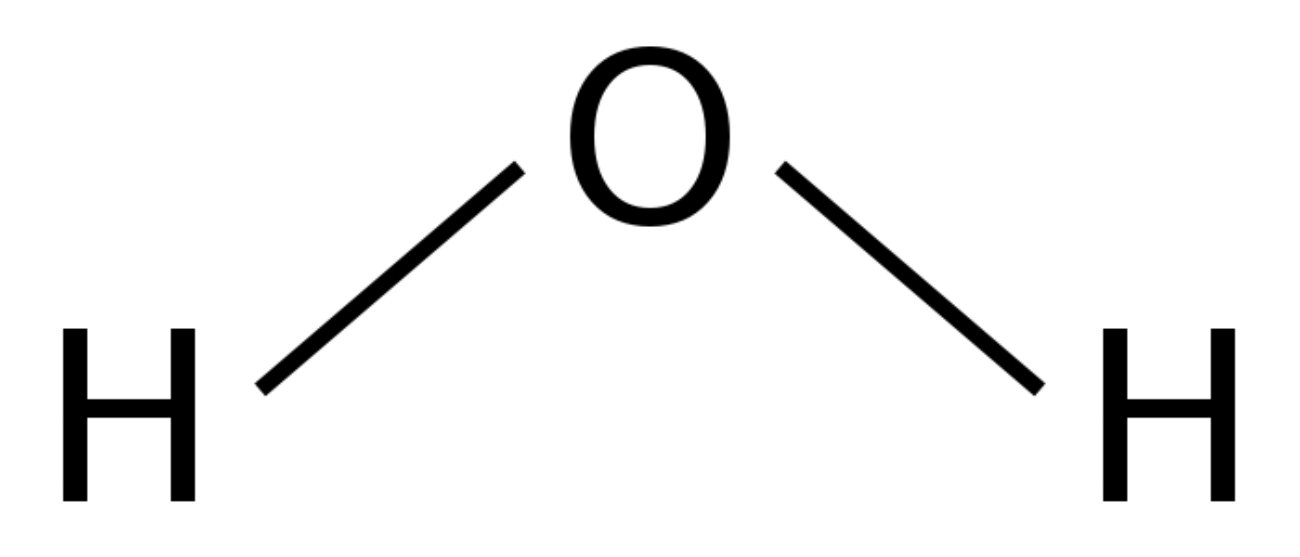
3
New cards
~35
What is the pka of this molecule (ammonia)
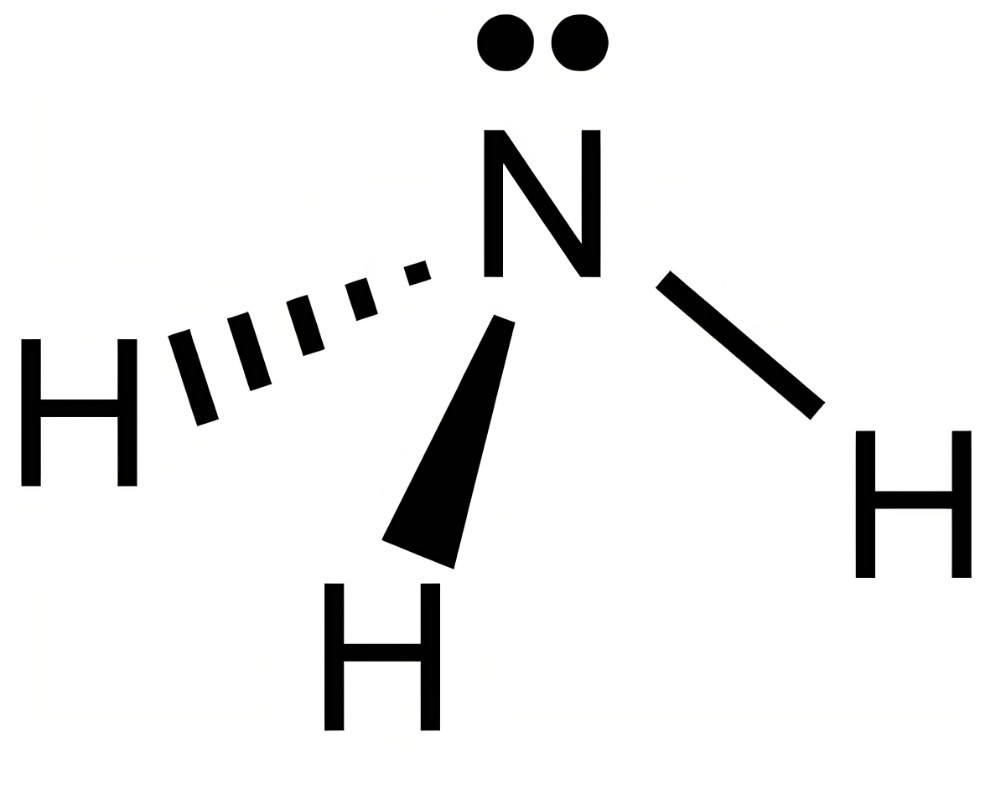
4
New cards
~4
What is the pka of this molecule (hydrofluoric acid)
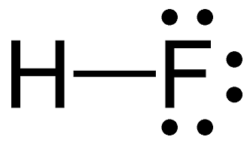
5
New cards
~5
What is the pka of this molecule (carboxylic acids)
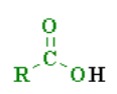
6
New cards
~10
What is the pka of this molecule (phenols)
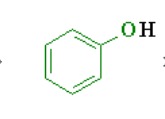
7
New cards
~16
What is the pka of this molecule (alcohols)
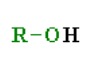
8
New cards
~35
What is the pka of this molecule (amines)
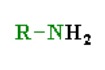
9
New cards
44
What is the pka of this molecule (alkene)
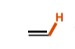
10
New cards
25
What is the pka of this molecule (alkyne)
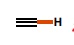
11
New cards
~35
What is the pka of this molecule (hydrogen)
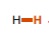
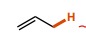
12
New cards
~43 (note how close this value is to that of C2H4, another alkene, but with the bond next to the double bond)
What is the pka of this molecule
13
New cards
~20
What is the pka of this molecule (ketone)
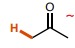
14
New cards
~25
What is the pka of this molecule (ester)
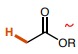
15
New cards
~30 (unless R=H, which would make the N-H bond the most acidic pka= 10-15)
What is the pka of this molecule (amides)
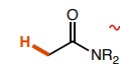
16
New cards
~10
What is the pka of this molecule (thiols)

17
New cards
~15 for the alcohol, ~10 for the thiol (polarizability due to the size of the sulfur atom plays a big role here)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?
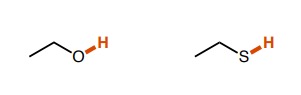
18
New cards
~15 for the alcohol, ~10 for the phenol (resonance hybridization plays a big role here)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?

19
New cards
~50 for the alkane, ~44 for the alkene, ~25 for the alkyne (hybridization plays a big role here)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?
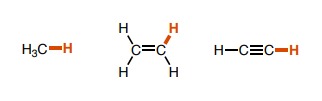
20
New cards
~35 for ammonia, ~31 for the alkene, -10 for the alkyne (charge is the cause of the unexpectedly low pka value)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?
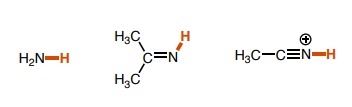
21
New cards
~5
What is the pka of this molecule?
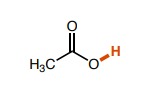
22
New cards
Left: ~2.5 Right: ~3 (Fluorine is more electronegative than Chlorine which results in a stronger inductive effect)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?
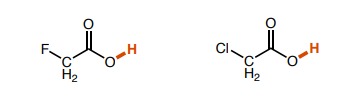
23
New cards
Left: ~5, Middle: ~3, Right: ~4. (the inductive effects of chlorine were affected by the distance from the H bond of intrest)
How do the pka values of these molecules differ?
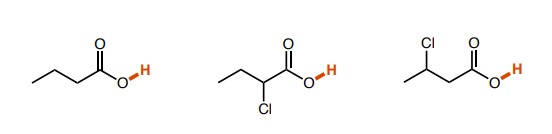
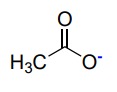
24
New cards
Carboxylate / Acetate Ion
Name a base with a pka of 5
25
New cards
Amines
Name a base with a pka of 10
26
New cards
Hydroxide or Methoxide
Name a base with a pka of 15
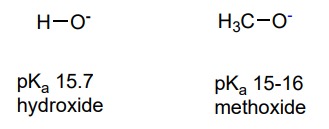
27
New cards
Amide Ions (R2N-) and Hydrides (H-)
Name a base with a pka of 35
28
New cards
Methenium (methyl cation)
Name a base with a pka of over 60
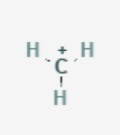
29
New cards
17 (this applies only to the H directly attached to the C=O. Protons further from the aldehyde have very high pka values, similar to amides)
What is the pka of this molecule (aldehyde)
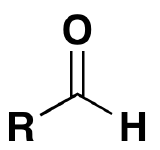
30
New cards
~9 (9.25)
What is the pka of this molecule (ammonium)
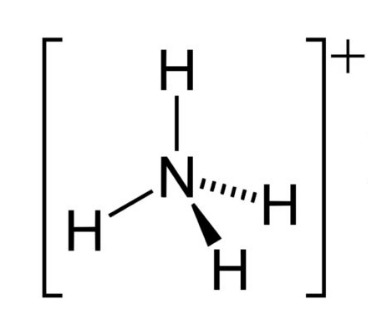
31
New cards
~9 (closest H to nitro group)
What is the pka of this molecule (nitro)
