Chapter 18 Practice Quiz
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
(Q001) Which of the following correctly matches the phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle with an event that takes place in that phase?
M phase—cytokinesis
(Q002) Which is NOT a transition point where the cell cycle control system regulates progression through the cell cycle?
S/G2 transition
(Q003) The expression levels of different ___________ fluctuate throughout the cell cycle.
cyclins
(Q004) The slow rise of S cyclin levels throughout G1 phase is due to ___________, and the abrupt decrease is caused by ___________.
transcription; proteolysis
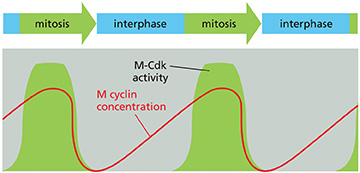
(Q005) What accounts for the difference in the curve shapes depicting concentration of M-cyclin versus M-Cdk activity during the cell cycle?
The M-Cdk complex is not activated until M-cyclin is bound and M-Cdk is dephosphorylated.
(Q006) At the end of M phase, cells shut down Cdk activity through which of the following mechanisms?
deployment of Cdk inhibitors
(Q007) Rb is an important protein for controlling cell proliferation by blocking entry into S phase. How does it exert its effect?
In its unphosphorylated state, Rb is active and blocks transcriptional regulators.
(Q008) In response to DNA damage, the ___________ protein is phosphorylated and activates the transcription of a Cdk inhibitor to halt cell cycle progression.
p53
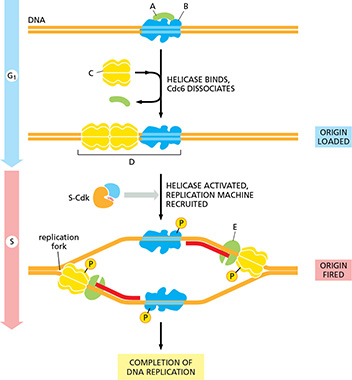
(Q009) The figure below shows some steps involved in the initiation of DNA replication. What is the identity of the complex labeled "B"?
ORC
(Q010) How does S-Cdk prevent re-replication?
phosphorylation of ORC and Cdc6
(Q011) M-Cdk is suddenly activated at the end of G2 by
dephosphorylation by Cdc25.
(Q012) What is the function of condensins?
to coil sister chromatids into a compact form
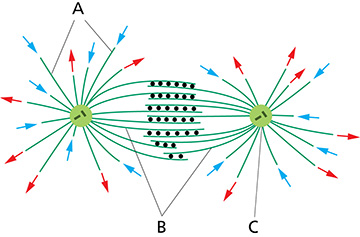
(Q013) Shown below is the structure of a bipolar mitotic spindle. Which element(s) is/are the interpolar microtubules?
b
(Q014) In which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down?
prometaphase
(Q015) How are spindle microtubules attached to chromosomes?
The microtubules bind to the kinetochore complexes through a connecting protein.
(Q016) If a chromosome is attached to two microtubules from opposite poles and one of the microtubules is experimentally severed, what occurs?
The chromosome migrates quickly to the pole to which it is still attached.
(Q017) Cohesin is cleaved by the enzyme ___________, which is held in an inactive state by ___________ until it is degraded by the APC/C complex.
separase; securin
(Q018) What drives the reassembly of the nuclear envelope?
dephosphorylation of lamins
(Q019) What determines the position of the cleavage furrow of the dividing cell?
The interpolar microtubules send signals to form a cleavage furrow between the poles.
(Q020) The contractile ring is composed of
actin and myosin.
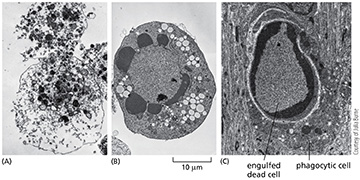
(Q021) Which of the following cells died by apoptosis?
b
(Q022) In response to an apoptotic stimulus, initiator caspases
cleave and activate executioner caspases.