Principles of Management: Planning and Decision-Making (CH5)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Planning
Choosing a goal and developing a strategy to achieve that goal.
Benefits of Planning
Intensifies efforts, leads to persistence, provides direction, encourages the development of task strategies, and works for both companies and individuals.
Pitfalls of Planning
Impede change, prevent or slow needed adaptation, create a false sense of certainty, and lead to detachment of planners.
S.M.A.R.T. goals
Goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely.
Goal commitment
The determination to achieve a goal.
Action plan
A plan that lists the specific steps, people, resources, and time period needed to attain a goal.
Proximal goals
Short-term goals or subgoals.
Distal goals
Long-term or primary goals.
Options-based planning
Maintaining planning flexibility by making small, simultaneous investments in many alternative plans.
Slack resources
A cushion of extra resources that can be used with options-based planning to adapt to unanticipated changes, problems, or opportunities.
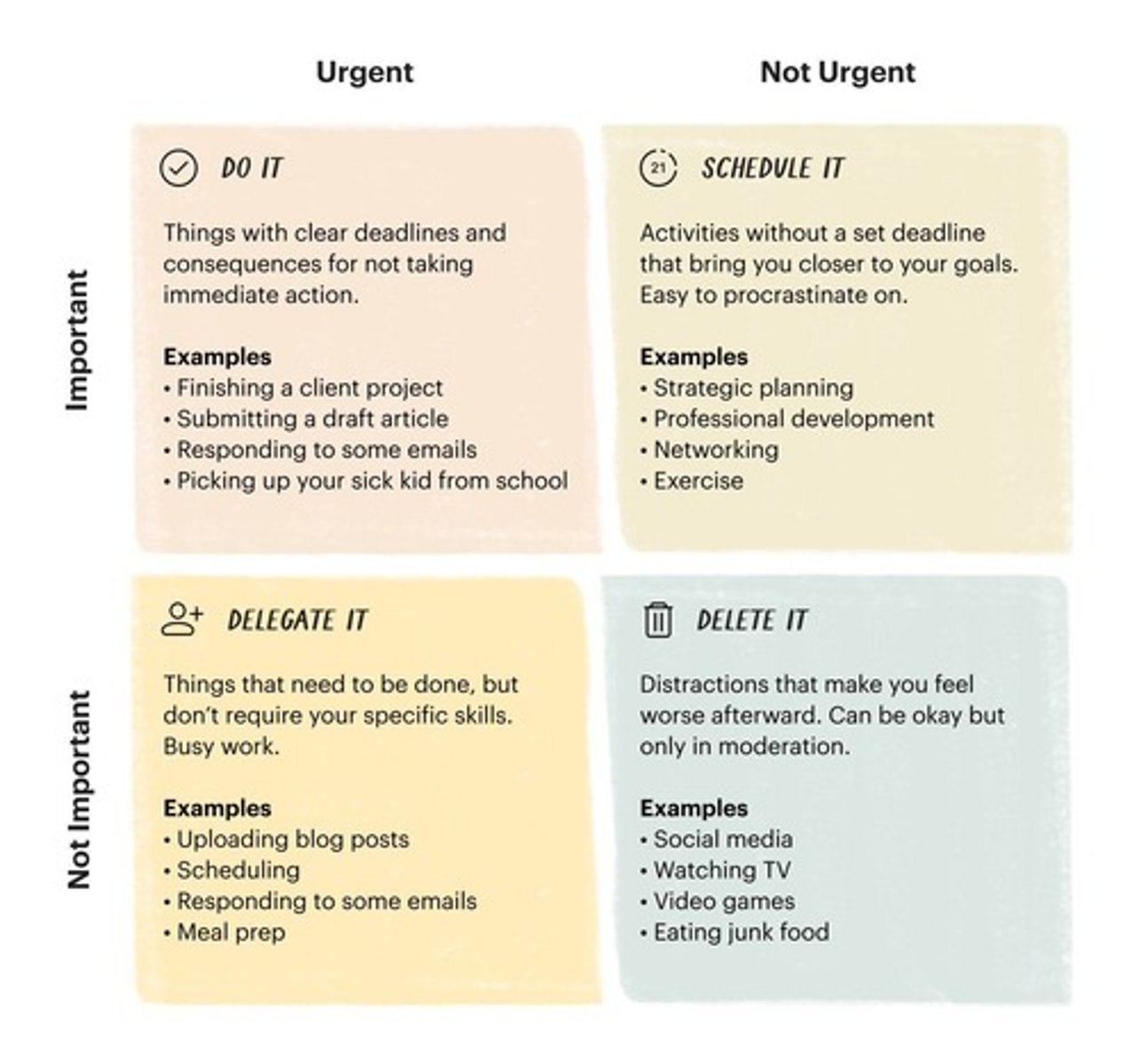
Urgent Important Matrix
A tool used to provide direction in planning.
Techniques for Effective Planning
Setting goals participatively, making the goal public, and obtaining top management's support.
Methods for tracking progress
Setting proximal goals and distal goals, and gathering and providing performance feedback.
Steve Jobs Quote
You can't connect the dots looking forward, you can only connect them looking backward. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in your future.
Ray Kroc Quote
Nothing in the world can take the place of persistence.
Polling Activity
Which of the following pitfalls to planning do you believe managers need to work most diligently to avoid?
Top management
Responsible for developing long-term strategic plans.
Strategic plans
Overall company plans that clarify how the company will serve customers and position itself against competitors over the next two to five years.
Purpose statement
A statement of a company's purpose or reason for existing.
Strategic objective
A more specific goal that unifies company-wide efforts, stretches and challenges the organization, possesses a finish line and a time frame.
Middle management
Develops and carries out tactical plans to accomplish strategic objectives.
Tactical plans
Plans created and implemented by middle managers that direct behavior, efforts, and attention over the next six months to two years.
Management by objectives
A four-step process in which managers and employees discuss possible goals, collectively select goals, develop tactical plans, and meet regularly to review progress toward goal accomplishment.
Lower-level managers
Develop and carry out operational plans.
Operational plans
Day-to-day plans, developed and implemented by lower-level managers, for producing or delivering the organization's products and services over a 30-day to six-month period.
Single-use plans
Plans that cover unique, one-time-only events.
Standing plans
Plans used repeatedly to handle frequently recurring events.
Policies
Standing plans that indicate the general course of action that should be taken in response to a particular event or situation.
Procedures
Standing plans that indicate the specific steps that should be taken in response to a particular event.
Rules and regulations
Standing plans that describe how a particular action should be performed or what must happen or not happen in response to a particular event.
Budgeting
Quantitative planning through which managers decide how to allocate available money to best accomplish company goals.
Decision-making
The process of choosing a solution from available alternatives.
Rational decision-making
A systematic process of defining problems, evaluating alternatives, and choosing optimal solutions.
Define the problem
A gap between a desired state and an existing state.
Decision criteria
The standards used to guide judgments and decisions.
Absolute comparisons
A process in which each decision criterion is compared to a standard or ranked on its own merits.
Relative comparisons
A process in which each decision criterion is compared directly with every other criterion.
Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria
A scale where 5=critically important, 4=important, 3=somewhat important, 2=not very important, 1=completely unimportant.
Predicted reliability
Rated as 5 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Owner satisfaction
Rated as 2 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Predicted depreciation
Rated as 1 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Avoiding accidents
Rated as 4 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Fuel economy
Rated as 5 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Crash protection
Rated as 4 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Acceleration
Rated as 1 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Ride
Rated as 3 in the Absolute Weighting of Decision Criteria.
Front seat comfort
5
Daily commute (L)
+1, -1, -1, -1, 0
School system quality (SSQ)
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1
In-ground pool (IP)
+1, +1, 0, 0, +1
Sun room (SR)
+1, +1, 0, 0, 0
Quiet street (QS)
+1, +1, 0, 0, 0
Newly built house (NBH)
0, +1, -1, 0, 0
Total weight
+2, +5, -3, -2, -2, 0
Step 4: Generate alternative courses of action
A step in Rational Decision-Making
Step 5: Evaluate each alternative against each criterion systematically
A step in Rational Decision-Making
Step 6: Compute the optimal decision
Involves multiplying the rating for each criterion by the weight for that criterion and then summing the generated scores
Bounded rationality
Limits to Rational Decision-Making due to real-world constraints faced by managers
Maximize
Choosing the best alternative
Satisficing
Choosing a 'good-enough' alternative
Advantages of Group Decision-Making
Groups perform better than individuals in defining the problem and in generating alternative solutions
Pitfalls of Group Decision-Making
Groupthink, takes considerable time, individuals can dominate group discussions, equality bias
Groupthink
A barrier to good decision-making caused by pressure within the group for members to agree with each other
Conditions for Groupthink
The group is insulated from others with different perspectives, the group leader expresses a strong preference for a particular decision, no established procedure for systematically defining problems and exploring alternatives, group members have similar backgrounds and experiences
C-type conflict
Disagreement that focuses on problem- and issue-related differences of opinion.
A-type conflict
Disagreement that focuses on individuals or personal issues, resulting in hostility, anger, resentment, distrust, cynicism, and apathy.
Devil's advocacy
A decision-making method in which an individual or a subgroup is assigned the role of critic.
Dialectical inquiry
A decision-making method in which decision makers state the assumptions of a proposed solution (a thesis) and generate a solution that is the opposite (antithesis) of that solution.
Nominal group technique
A decision-making method that begins and ends by having group members quietly write down and evaluate ideas to be shared with the group.
Delphi technique
A decision-making method in which members of a panel of experts respond to questions and to each other until reaching agreement on an issue.
Brainstorming
A decision-making method in which group members build on each others' ideas to generate as many alternative solutions as possible.
Electronic brainstorming
A decision-making method in which group members use computers to build on each others' ideas and generate as many alternative solutions as possible.
Production blocking
A disadvantage of face-to-face brainstorming in which a group member must wait to share an idea because another member is presenting an idea.
Evaluation apprehension
Fear of what others will think of your ideas.
Advantages of electronic brainstorming
Helps overcome production blocking and evaluation apprehension, protects participant anonymity, and is generally more productive than traditional brainstorming.
Disadvantages of electronic brainstorming
Expense of computers, network, and software; challenge of writing rather than speaking ideas.
Conflict management approaches
Methods to find solutions to managing conflict, such as dialectical inquiry, nominal group technique, Delphi technique, and electronic brainstorming.
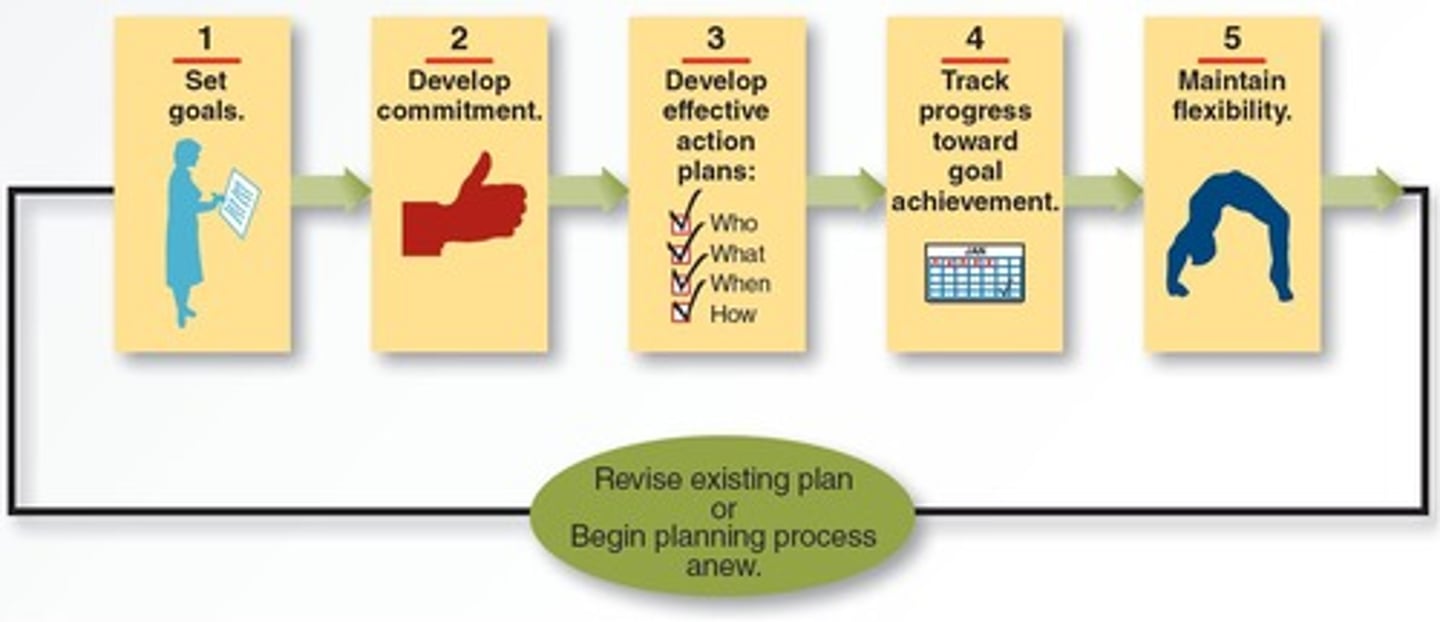
Steps for creating an effective plan
Outline the necessary actions to develop a successful plan.
Use of plans at management levels
Discussion on how companies can implement plans at all management levels, from top to bottom.
Limits to rational decision-making
Identify the steps to avoid limitations in rational decision-making.
Group decision-making techniques
Explain how group decisions and techniques can enhance decision-making.