Bio PPQs got wrong topic 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
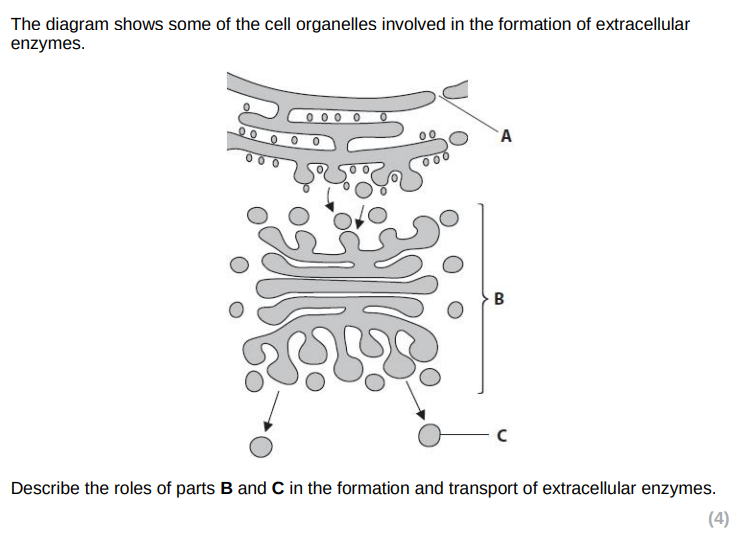
vesicles fuse with/protein enters golgi apparatus
modification of protein inside golgi apparatus
protein enzyme packaged into secretory vesicles
vesicles fuse with cell surface membrane
eukaryotic organisms have membrane - bound organelles
eukaryotic organisms contain a named membrance - bound organelle
size of ribosomes larger than in prokaryotes
eukarotic organisms do not contain plasmids (in cytoplasm)
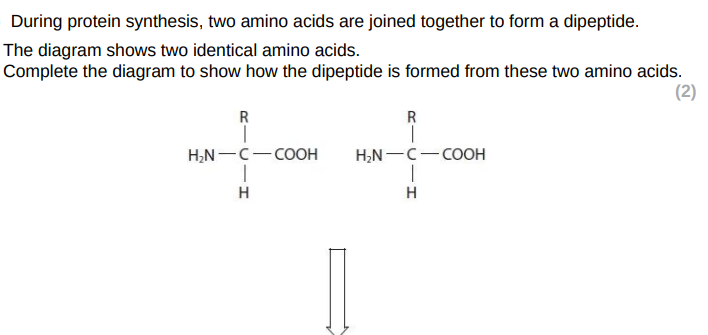

+ water

Ignore (i)
presence of a cell wall
circular DNA/plasmids
small/70s robosomes
pili/flagellum
capsule/mesosome
Explain why the nucleus cannot be observed at the end of prophase in a eukaryotic cell.
because the nuclear membrane is broken down
because DNA is coiled/condensed into individual chromosomes

ignore (i)
phase 1 - to make sure the phospholipase inhibitor is not harmful
phase 2 to see if it is effective in treating the condition/preventing allergic reactions to wasp venom
phase 3 to gather much data for statistical tests / to look for rare side effects
Some fish live in very cold parts of the sea where ice can form. Many of these fish produce anti-freeze proteins, which help to stop ice forming inside the fish. Anti-freeze glycoprotein (AFGP) is one type of anti-freeze protein. Messenger RNA coding for AFGP is translated at a ribosome to produce a polypeptide. Describe how this polypeptide is then processed to make AFGP. (4)
the polypeptide chain moves through the ER then the golgi apparatus
in the rER the polypeptide is folded
in the golgi apparatus/ER carbohydrate is added
the polypeptide/protein is transported around the cell in a vesicle
Some fish live in very cold parts of the sea where ice can form. Many of these fish produce anti-freeze proteins, which help to stop ice forming inside the fish. Anti-freeze glycoprotein (AFGP) is one type of anti-freeze protein. Messenger RNA coding for AFGP is translated at a ribosome to produce a polypeptide. Describe how this polypeptide is then processed to make AFGP. (4)
the polypeptide chain moves through the endoplasmic reticulum then the golgi apparatus
in the rER the polypeptide is folded
in the golgi apparatus/ER carbohydrate is added
the polypeptide/protein is transported around the cell in a vesicle
Many of the proteins synthesised become extracellular enzymes. Describe what happens to these proteins following the process of translation until they are released from the cell. (3)
the proteins are folded in the RER
the proteins are packaged into/ transported in vesicles
the protein is modified in the golgi apparatus
exocytosis
Cells in people with these diseases produce incorrectly folded enzyme molecules. Explain why enzymes that are incorrectly folded cannot carry out their function. (3)
if the protein is not folded correctly the tertiary structure/3D shape would be different
therefore the active site of the enzyme would not fit/bind with the substrate/it would not be able to form an enzyme substrate complex
therefore it would not be able to catalyse the reaction
bacteria fo not possess rER/golgi apparatus
polypeptide chain is not processed/modified properly
therefore the protein is incorrectly folded/carbhydrate is not added
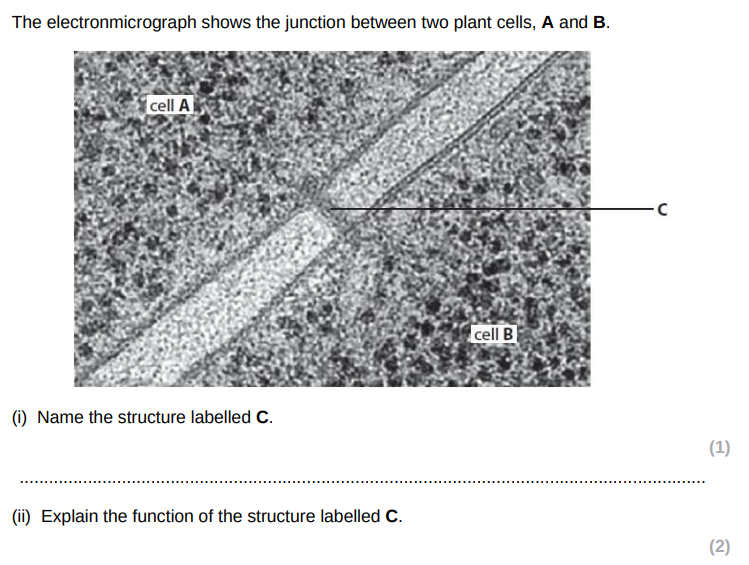
cytoplasmic connection between cells
which allows transport/communication between cells
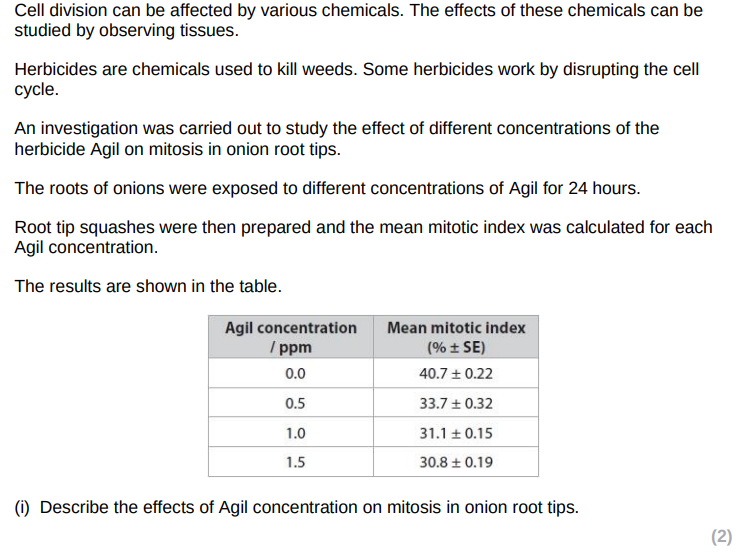
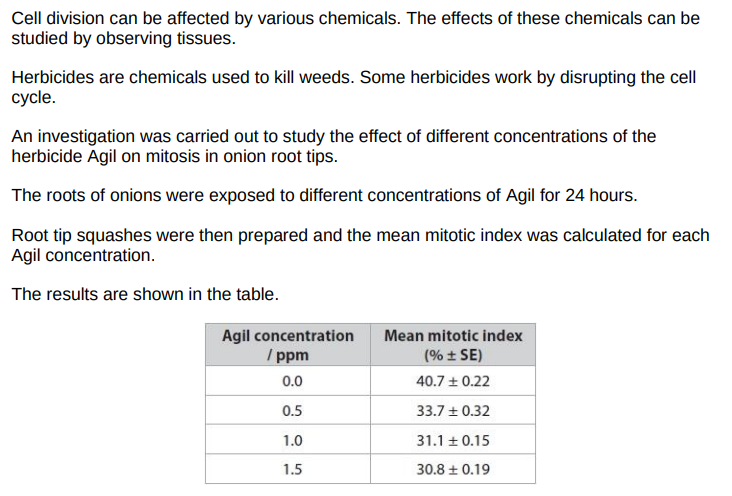
negative correlation between Agil concnetration and number of cell undergoing mitosis/ mitotic index
no significant difference between 1.0 and 1.5ppm Agil
Devise an investigation to determine the effect of exposure time to Agil on the rate of mitosis in onion root tips.
controlled concentration of Agil
one other variable contorlled - e.g. temp. same type onion, source
roots exposed to agil for a range of time intervals
details of root tip squash procedure
an appropiate named stain - toludine blue
counting number of cells undergoing mitosis (to calculate mitotic index
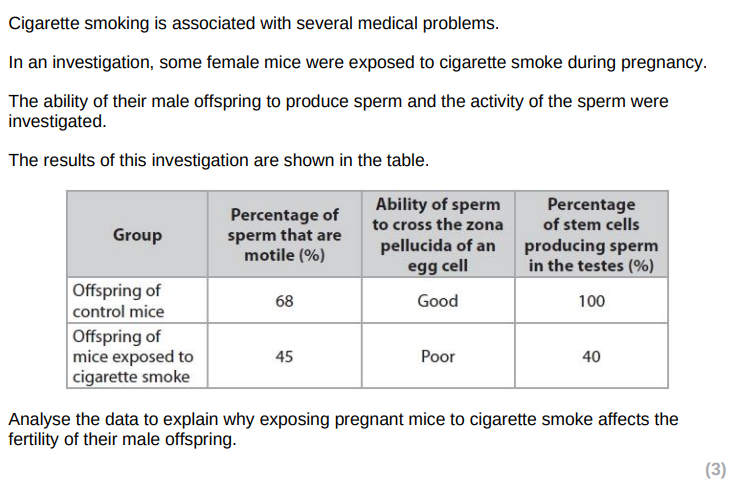
fewer stem cells producing sperm (therefore fewer sperm cells produced)
fewer motile sperm therefore fewer sperm will reach the egg
poor ability to cross zona pellucida/acrosome reaction inhibited therfore sperm will not reach egg cell membrane
therefore reducing chance of fertilisation
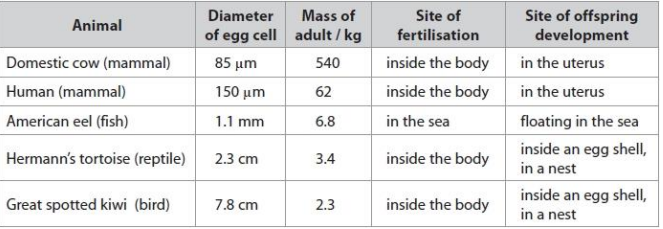
Deduce the relationship between egg cell diameter and the mass of the adult animal shown by the data (1)
as adult mass increases, egg diameter decreases OR negative correlation between adult mass and egg diameter
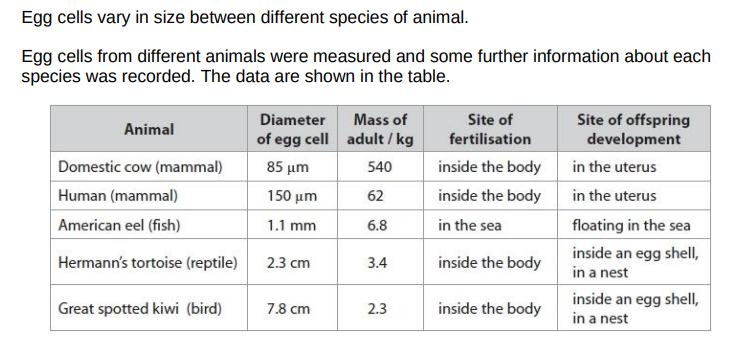
Criticise this data set as evidence for a relationship between egg cell diameter and the mass of the adult.(4)
this data set includes only a few species/animals
the species in the data are from different taxonomic groups
there is no evidence of repeats/data for these individuals may not be representative
the reproductive strategy of the species is likely to influence egg size/ should be controlled
there are other factors that may affect the egg cell/may affect adult mass/should be controlled
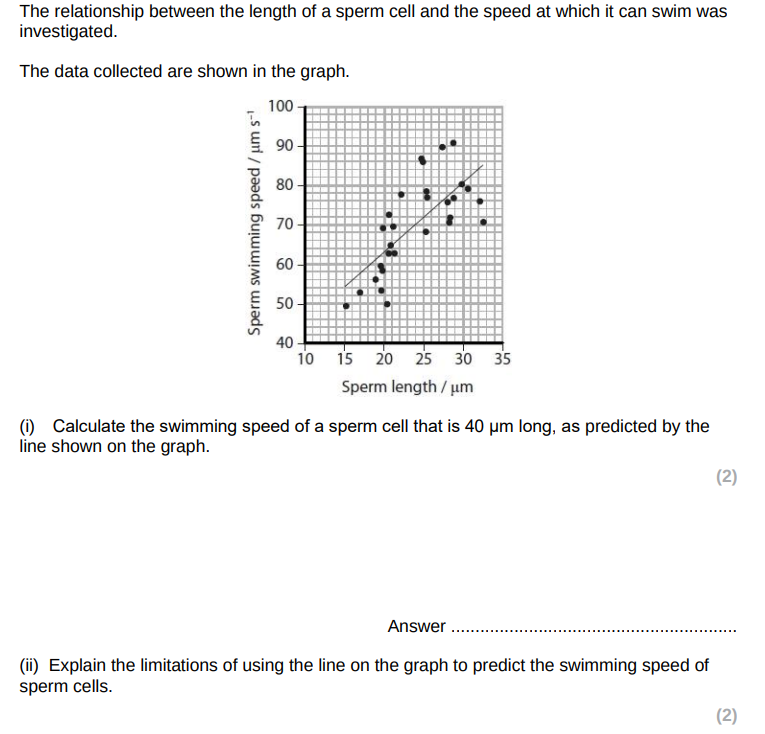
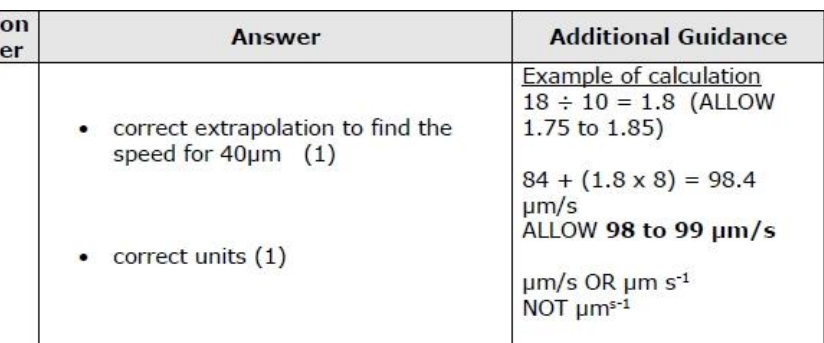
there is variation about the line/few data points lie exactly on the line therefore the prediction will not be exact
the gradient of the line may not remain the same
What does autosomal mean?
not on sex chromosomes
what is a complementary gene?
when two or more genes that
Cell division in a plant such as an onion can be observed using a light microscope. Explain why the following techniques are used when producing a root tip squash to observe cell division. (4) Adding hydrochloric acid to the root tip
Adding a stain to the root tip
adding hydrochloric acid
breaks down middle lamella
allowing cells to be separated produce a thin layer of cells
to allow light
Adding stain
makes chromosome visible
so that the stages of mitosis can be identified
Cell division can be affected by various chemicals. The effects of these chemicals can be studied by observing tissues. Chemotherapy is used to treat cancer. Cancer involves uncontrolled cell division. Some chemotherapy treatments have an effect on mitosis. Paclitaxel is a chemical used in chemotherapy to treat various types of cancer. It works by preventing the shortening of spindle fibres. Explain how preventing the shortening of spindle fibres affects mitosis. (2)
sister chromatid cannot be separated/centromere cannot be split
mitosis stops at metaphase/anaphase cannot occur/ chromosomes remain at equator
daughter cells produced with incorrect numbers of chromosomes
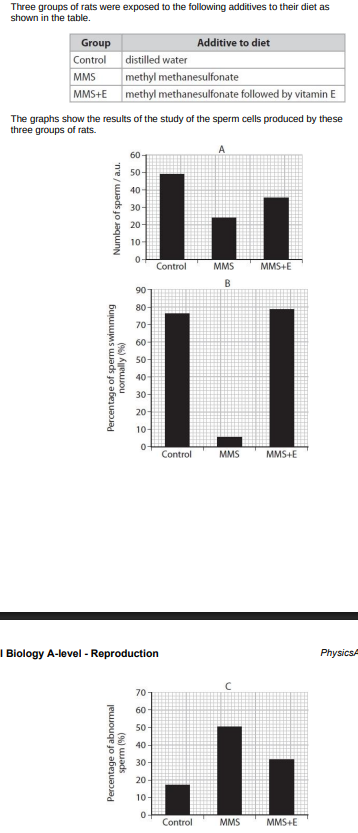
Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) can be used as a cancer treatment. One side effect associated with MMS is teratozoospermia. Three groups of rats were exposed to the following additives to their diet as shown in the table.
Deduce the effects of MMS on the production of sperm cells in rats. (3)
MMS reduces sperm count/number of sperm cells
MMS increases percentage of sperm cells with abnormalities
as the greatest effect is on percentage of sperm swimming normally MMS is likely to affect production of flagella/mitochondria
Give the meaning of the term polygenic (2)
a characteristic showing continuous variation
caused by multiple genes at different loci
What is heterochromatin?
tightly packed chromatin
What is euchromatin?
loosely packed chromatin
Fertilisation in humans involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. Factors such as the diet of the mother during pregnancy can cause epigenetic changes in the embryo. Explain how epigenetic changes affect the development of tissues in the embryo. (3)
DNA in a chromosome is wrapped around histones
acetylation/modification of the histone affects binding of RNA polymerase/chromosome unwinding
methylation of DNA affects transcription of gene/production of mRNA
therefore gene expression is altered
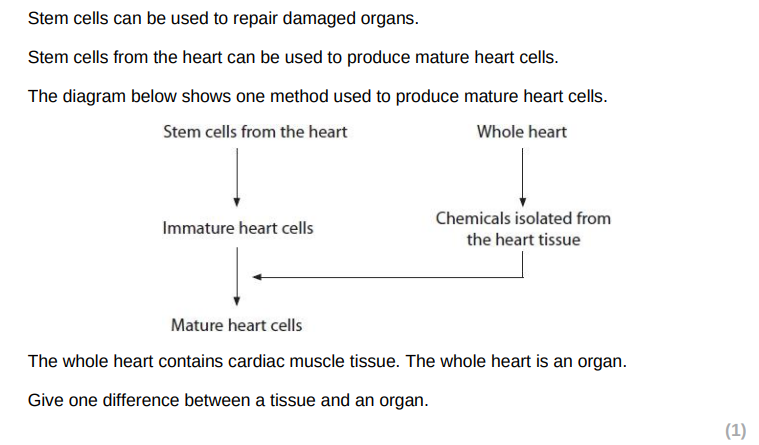
a tissue is made of one type of cell and an organ is made of different tissues
Stem cells can be used to repair damaged organs. Human embryos are another source of stem cells used in medical therapies. Describe the decisions that society has to make about the use of these embryonic stem cells. (3)
embryonic stem cells are totipotent and can be used in a wider range of therapies
source of embryonic stem cells has to be considered/regulated
moral/ethical issues as the use of embryonic stem cells destroys embryos
need for research establishments to be regulated/licensed
Fertilisation in humans involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. Cell division of the fertilised cell produces a ball of totipotent cells. (i) Give the meaning of the term totipotent cell. (2)
a cell that has the ability to differentiate into all cell types
This ball of cells continues to divide to form the embryo. The cells of the embryo become specialised to form tissues and organs. Describe how cells become specialised. (3)
chemical signals cause some genes to be activated/switched on
only activated genes are transcribed/produce mRNA
mRNA leads to synthesis of specific proteins which cause cell modification
Stem cells can be used to repair damaged organs. Part of the eye contains stem cells. These cells can be used to repair damaged corneas in the eye. (i) Explain why stem cells from the heart cannot be used to grow cells to repair the cornea. (3)
cells are not totipotent
therefore some genes have already been activated and deactivated
therefore they will not be able to specialise into cornea cells
Explain why chemicals from the eye are needed to produce corneal cells from a suitable source of stem cells. (4)
chemicals cause some genes (related to the cornea) to be activated/switched on
these genes are transcribed producing specific mRNA
specific mRNA is translated into specific proteins
these proteins cause the cell to develop into a corneal cell
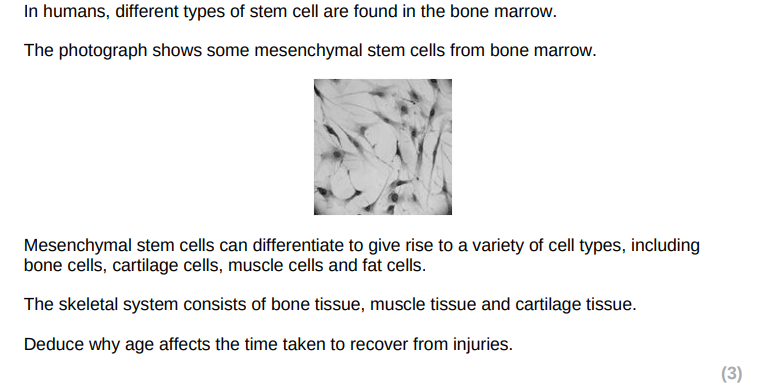
time will increase with age
due to fewer (mesenchymal) stem cells in bone marrow) with age
(fewer mesenchymal stem cells) to replace cells in bone/muscle/cartilage tissues
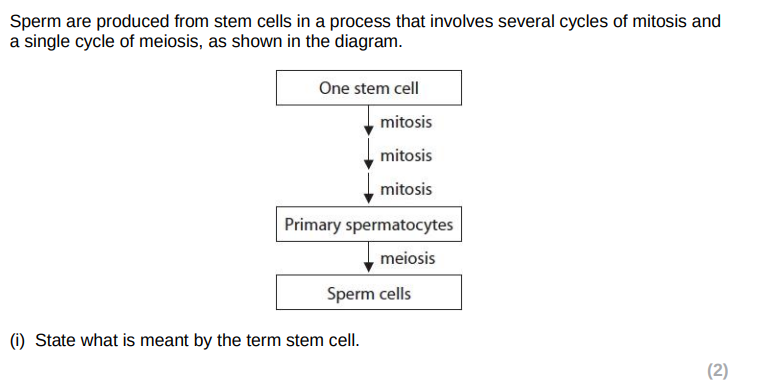
an cell that is undifferentiated
that can give rise to specialised cells
that can divide to produce more stem cells
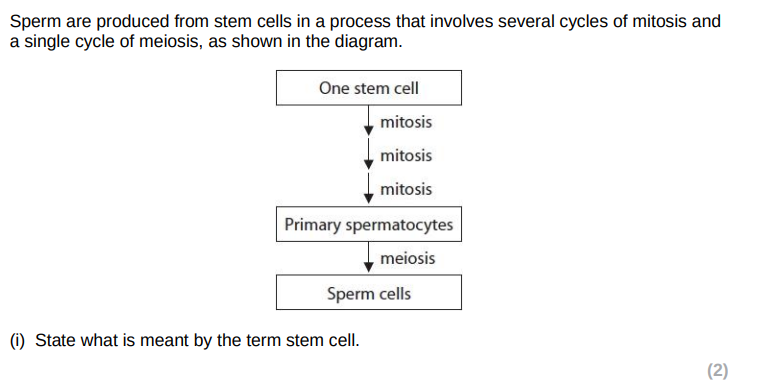
(ii) Compare and contrast the results of mitosis and meiosis in the production of sperm cells from stem cells (4) (ignore i)
similarity
both increase the number of cells
differences
mitosis produces cells that are genetically different to each other whereas mitosis produces genetically identical cells
meiosis produces cells that are genetically different to each other whereas mitosis produces genetically identical cells
mitosis results in 8 spermatocytes from each stem cell whereas meiosis results in 4 sperm cells from each spermatocyte
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a sex-linked disorder. (i) Explain what is meant by the term sex-linked disorder. (2)
a disorder caused by a mutated faulty gene
located on the X/Y chromosome
therefore the disorder is more likely in one gender than another
Dystrophin is a protein needed to maintain the structure of muscle cells. In DMD the affected allele prevents the production of this protein, leading to symptoms that include a progressive effect on muscle tissue. Stem cells are a potential treatment for DMD. Explain why stem cells from a healthy donor may provide a treatment for this disorder. (3)
stem cells can differentiate into muscle cells
these cells will not have the affected allele
the protein/dystrophin will be produced
Epigenetic changes can cause monozygotic twins to have different body masses. Explain how epigenetic changes can cause differences in a characteristic. (3)
histone modification/DNA methylation
affects activation of/ activates/deactivates genes
affecting enzyme production/metabolism
As pluripotent stem cells divide, epigenetic changes are passed on. Explain how epigenetic changes affect the activation of genes in daughter cells. (3)
genes are activated/deactivated in stem cells
because of methylation of DNA/ histone binding
therefore the same genes will be activated in the daughter cells
Explain why an individual may have a greater adult height than their biological parents. (4)
height is affected by the environment as well as teh genotype
height is an example of polygenic inheritance
therefore offspring can inherit a mixture of alleles from both parents that increase height
description of a names environmental factor that increases height e/g higher protein diet
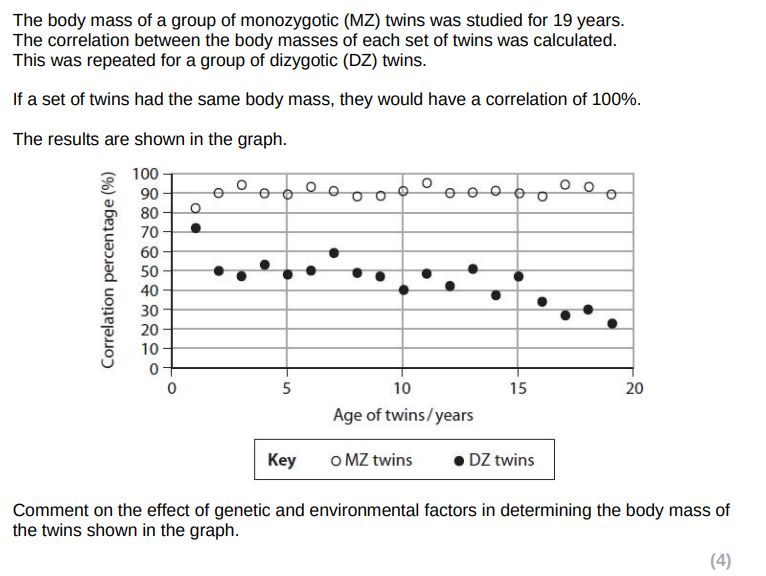
monozygotic twins show higher correlation than dizygotic twins at all ages
therefore genetic factors have a greater effect
because monozygotic twins have identical alleles for body mass
monozygotic twins show less than 100% correlation
therefore environmental factors affect body mass
What is meant by the term molecular phylogeny?
the idea of molecular differences/ similarities
in DNA /RNA
in proteins / proteonmics
Idea of evolutionary relationships between organisms
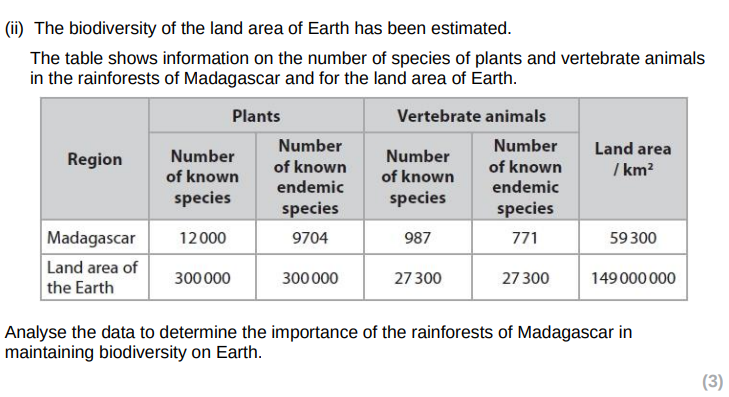
(3)
appropriate calculation e.g:4% of plants, 3.6% of vertebrates or 4% of combined total, 80.9 plants 78.1% of vertebrates endemic, 3.2% of plants, 2.8% of vertebrates or 3.2% of combined total, density of plants/ vertebrates/ total on Madagascar/ earth
the species density of animals / plants in Madagascar is higher than for the earth
many of the species are found in Madagascar are not found anywhere else
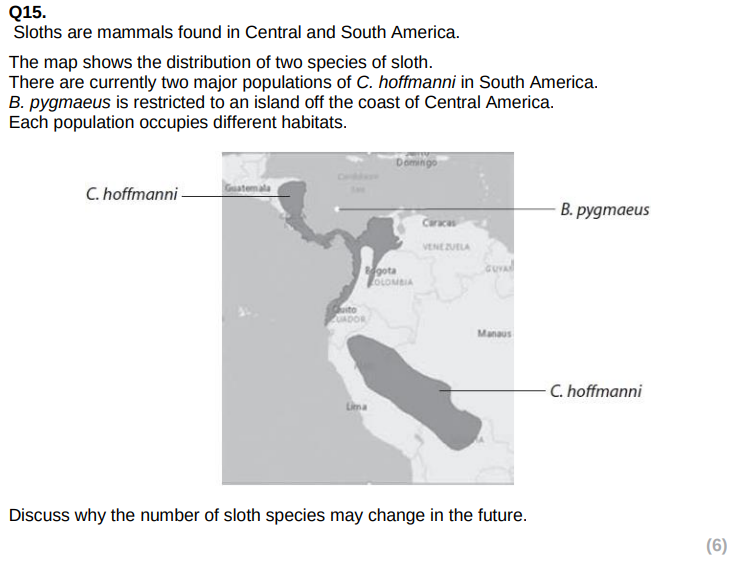
Species number may increase due to
Fragmentation of habitat / geographical isolation
Different selection pressures on populations of C. hoffmanni
Different allele frequencies within separate populations
Evolution leading to formation of new species
Species number may decrease due to
B. pygmaeus is currently critically endangered
Only one population
Therefore could be vunerable to inbreeding depression
At risk of natural disaster, disease, predation etc
Therefore may become extinct
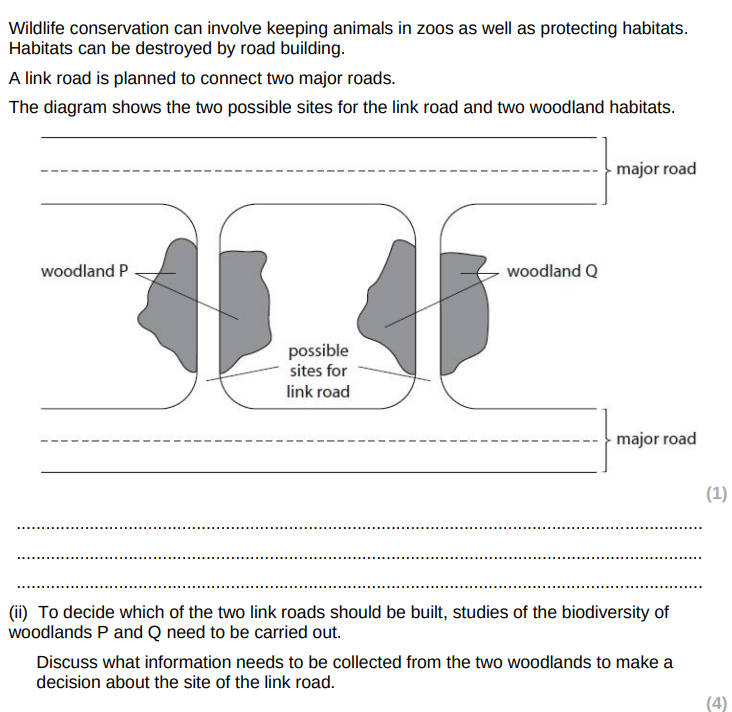
biodiversity measured / compared using a diversity index
species richness assessed
genetic diversity of populations / species
presence of any endemic / rare species
Explain how the primary structure of typsin molecules can be used to produce a phylogenetic tree (3)
determine the sequence of amino acids (for trypsin)
determine the number of differences / similarities in sequences (of amino acids) between species
the greater the number of differences the less closely related the species are
H
Mutation leads to variation within a population
natural selection leads to organisms which were better suited for survival
therefore giving rise to 2 populations with differing allele frequency
as a result of natural selection the 2 populations became reproductively isolated
sympatric speciation
Why might organisms be classed as different species? (2)
they are no longer able to interbreed to produce fertile offspring
because populations have become reproductively isolated
Name the process that leads to new species (1)
Natural selection
True or false archaea has prokaryotic cells
True
Describe how the Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to provide evidence for changes in the elephant population in Mozambique (2)
calculate the allele frequencies / number of dominant and recessive alleles in the population in Mozambique
regular sampling over a period of time
Explain how molecular phylogeny can be used to show that two populations are reproductively isolated (3)
Comparing similarities and differences in DNA/proteins
Comparison of nucleotide sequences / amino acid sequences
the greater the number of differences the more likely they are to be reproductively isolated
Describe how mutations may lead to this population becoming separate species (4)
Mutations result in the production of new alleles
Selection pressures cause the alleles / mutations to be advantageous
more individuals with the advantageous alleles survive and reproduce
after time the population would not be able to reproduce with other badger species to produce fertile offspring
Explain why the frequency of an allele may change from one generation to the next (3)
because the allele may undergo mutation
because gene flow may cause alleles to be lost or gained from the population
due to natural selection / changed selection pressure
because people with the condition may not have children
Explain how the Hardy - Weinberg equation can be used to show that natural selection is occurring in a population (2)
Hardy - Weinberg equation shows the allele frequency in the population
if natural selection is occurring there would be a change in allele frequency over time
Explain how molecular phylogeny could be used to determine the relationship between the Scottish wildcat and other subspecies of European wildcat (2)
compare sequence of bases in DNA / amino acids in proteins
the more similarities in common the more closely relation the subspecies
What is a stem cell? (2)
an undifferentiated cell
that can give rise to specialised cells
that can divide to produce more stem cells
Describe how pluripotent stem cells become specilaised cells (4)
idea of stimulus e.g. chemical
idea that some genes are active / switched on / expressed
idea of transcription / mRNA produced at active genes
mRNA is translated / used to produce protein
idea that this protein modifies cell OR idea that this protein determines cell structure / function
Explain what is meant by the term sex linked disorder (2)
a disorder caused by a mutated / faulty gene
located on the X / Y chromosome
therefore the disorder is more likely in one gender than another
Explain why the genotype frequency for males with a sex linked ddisorder cannot be calculated using the Hardy - Weinberg equation (2)
males only have 1 allele for this gene
males cannot be heterozygous
the Hardy-Weinberg equation assumes all individuals have 2 alleles for the gene
Dystrophin is a protein needed to maintain the structure of muscle cells. In DMD the affected allele prevents the production of this protein, leading to symptoms that include a progressive effect on muscle tissue. Stem cells are a potential treatment for DMD. Explain why stem cells from a healthy donor may provide a treatment for this disorder. (3)
stem cells can differentiate into muscle cells
these cells will not have the affected allele
the protein / dystrophin will be produced
Explain how vesicles are involved in the successful fertilisation of an egg cell by only one sperm (2)
cortical granules fuse with the egg cell surface membrane (exocytosis)
releasing contents / enzyme that harden / thicken zona pellucida
Explain why some genes show linkage and others show sex linage (3)
there are more genes than there are chromosomes
linkage relates to genes for different characteristics located on the same (non-sex) chromosome
sex linkage relates to genes on the sex / X / Y chromosome
Explain how crossing over and independent assortment can produce gametes with new combinations of the alleles shown in the diagram of the two pairs of chromosomes (4)
Crossing over
chromatids are produced with different combinations of alleles
for example (Ab/aB)
Independent assorment
different combinations of chromosomes (1 and 2) are produced
therefore alleles for A and B could be in the same gamete as C or c
Explain why DNA is replicated before mitosis begins (2)
to ensure that diploid chromosomes / one copy of each chromosome in each daughter cell
to ensure daughter cells are genetically identical
Expain how large number of cells with the same phenotype can be produced in a tissue (2)
phenotype is determined by genotype and effect of environment
mitosis produces cells with the same genotype
Explain why the nucleus cannot be observed at the end of prophase in a eukaryotic cell (2)
because the nuclear membrane is broken down
because DNA is coiled / condensed into individual chromosomes
Describe how each gamete only receives one allele of each gene (2)
in meiosis homologous chromosomes carrying alleles for the same genes are separated from one another
sister chromatids containing copies of the same alleles are also separated form one another
spindle fibres pull the chromosomes / chromatids to opposite poles of the cell
Describe how the acrosome is involved in the digestion of the zona pellucida (2)
the membrane of the acrosome fused with the plasma membrane of the sperm cell
releasing enzymes from the acrosome
by exocytosis
Describe the events that occur during prophase (3)
nuclear envelope breaks down
spindle fibres formed
chromosomes / chromatids condense
centrioles migrate to opposite poles of cell
Explain why genes found on the sex chromosome pair have a pattern of inheritance that is different from genes found on other chromosomes pairs (2)
X chromosome carries genes / loci not present on the Y chromosome
males have only one copy / allele of some genes
if only one allele is inherited it will be expressed
Describe the appearance of the chromosomes in the cells undergoing metaphase (3)
condensed / visible
seen as pairs of chromatids held together by a centromere
joined to the spindle fibres
aligned on the equation of the cell