b1.1 carbs and lipids
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Covalent Bonds
Carbon forms four covalent bonds with other atoms.
carbon
- forms 4 covalent bonds
- combinations of single and double bonds
- carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids (carbon compounds)
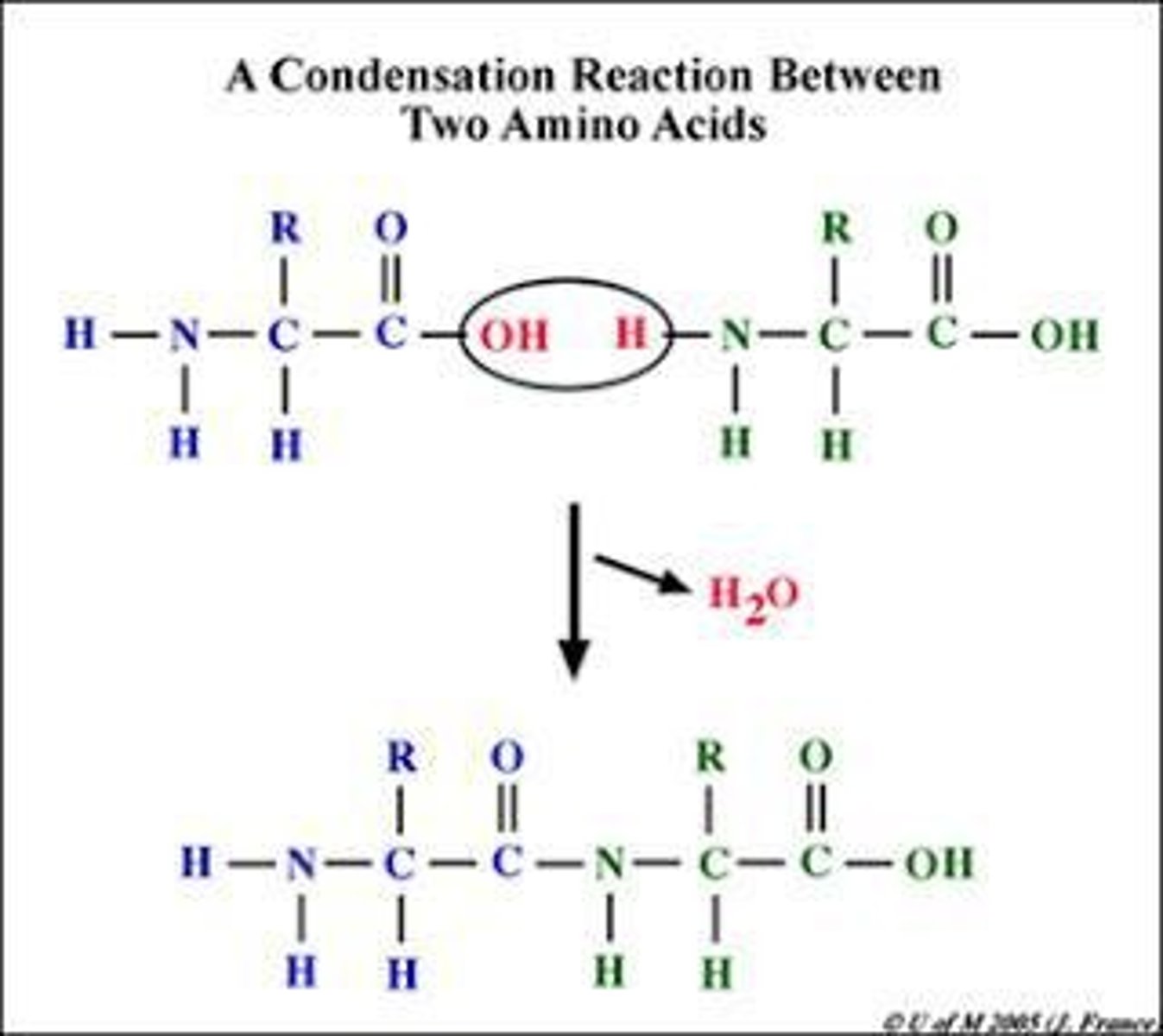
Condensation Reaction
hydroxyl of one molecule and the hydrogen break off to form water and join the two smaller molecules or monomers together.
- polymerization
- protein synthesis
- polysaccharides from monosaccharides
- DNA replication
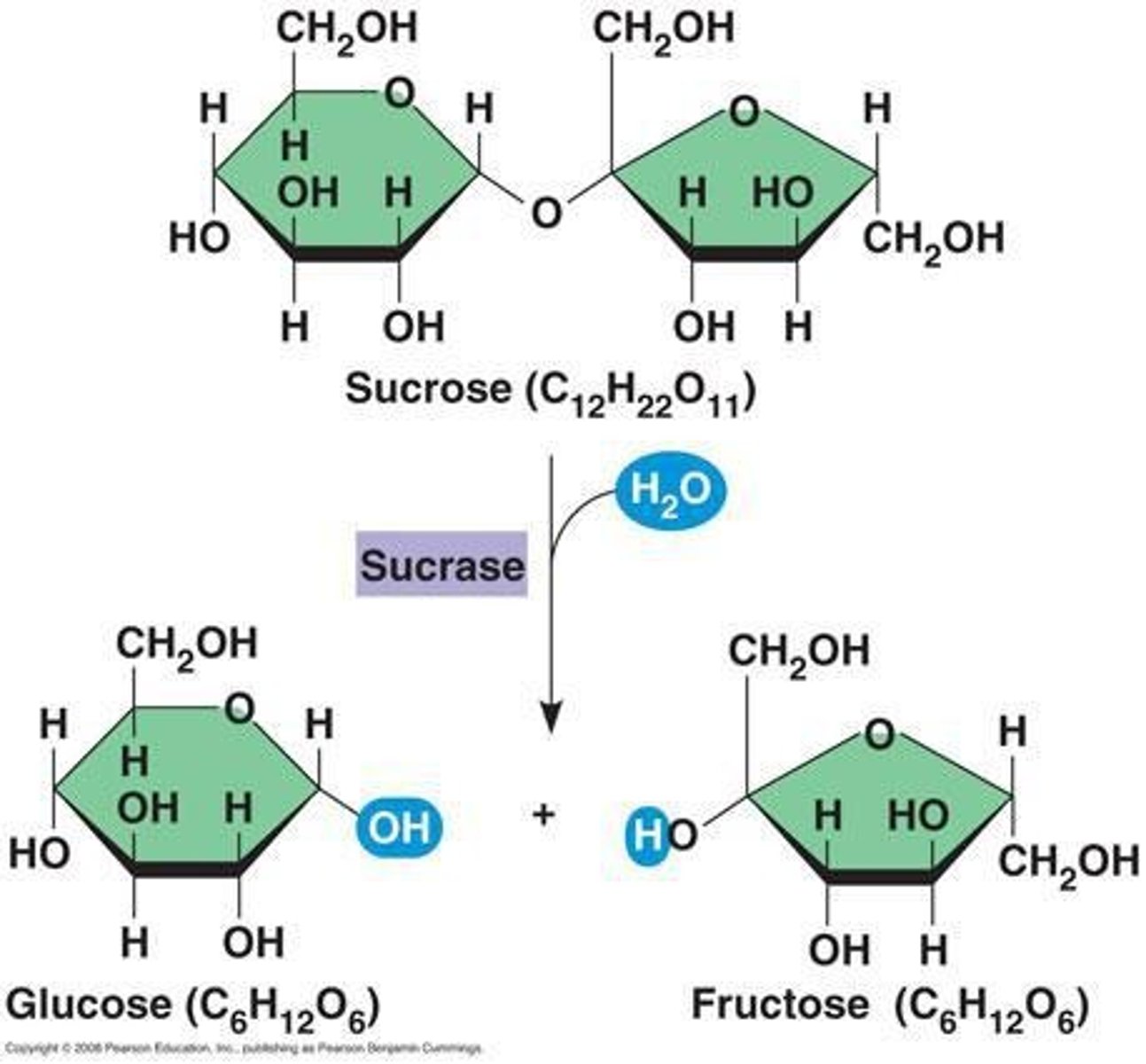
Hydrolysis
water molecule is added and broken down into a hydroxyl and a hydrogen
- separates macromolecules into smaller molecules (monomers)
- digestion
- cell respiration
Monosaccharides
glucose and ribose
- glucose= hexose sugar (6 sides)
- ribose= pentose sugar (5 sides)
functions of monosaccharides
soluble in water- glucose= polar, dissolves in plasma+ easy transport
- can be oxidized= source of energy when covalent bonds are broken in an oxidation reaction during cellular respiration
- molecular stability= covalent bonds within glucose do not break easily
starch
- (polysaccharide) how glucose is stored in plants
- alpha glucose
- amylose= not branched
- amylopectin= branched
glycogen
- (polysaccharide) how glucose is stored in animals
- alpha glucose
- branched, but more frequently than amylopectin
α-glucose
Glucose with downward bond orientation, (spiral)
- more compact, better storage
- branching helps w storage as well
- add or remove glucose molecules to build and use energy stores
β-glucose
Glucose with alternating bond orientation, structural role.
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides for energy storage.
conjugated carbon molecules
macromolecules join to become a single structure w specific functions
- lipid+ protein= lipoprotein
- lipid+ carbohydrates= glycolipid
- carbohydrate+ protein= glycoprotein
glycoprotein
cell id tags in cell to cell recognition for:
- cell to cell communication/signaling
- cell to cell adhesion
- recognition of self vs non self cells (antigens)
blood cells and glycoproteins
glycoprotein present on red blood cells determines compatibility for donating and receiving blood
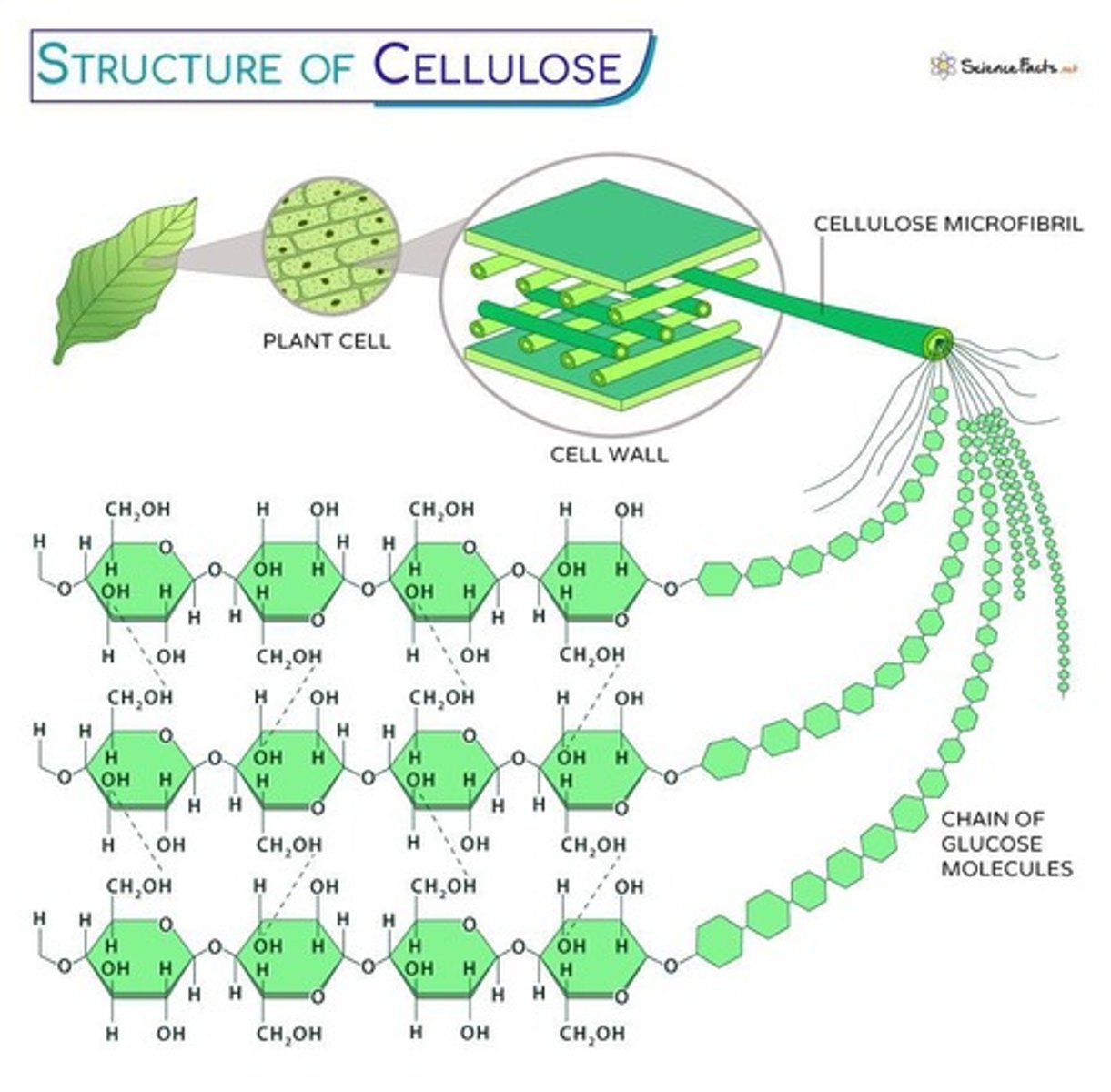
Cellulose
Plant cell wall component, made of β-glucose.
- alternating pattern= linear structure, tensile strength
- insoluable in water
Lipids
- fats, oils, waxes, steroids
- carbon and hydrogen are non polar covalent bonds
- insoluable in polar solutions (water)
Triglycerides
Fats made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
- makes 3 water molecules in the process
- high source of energy storage
- long term energy storage (limitations in transport and breakdown)
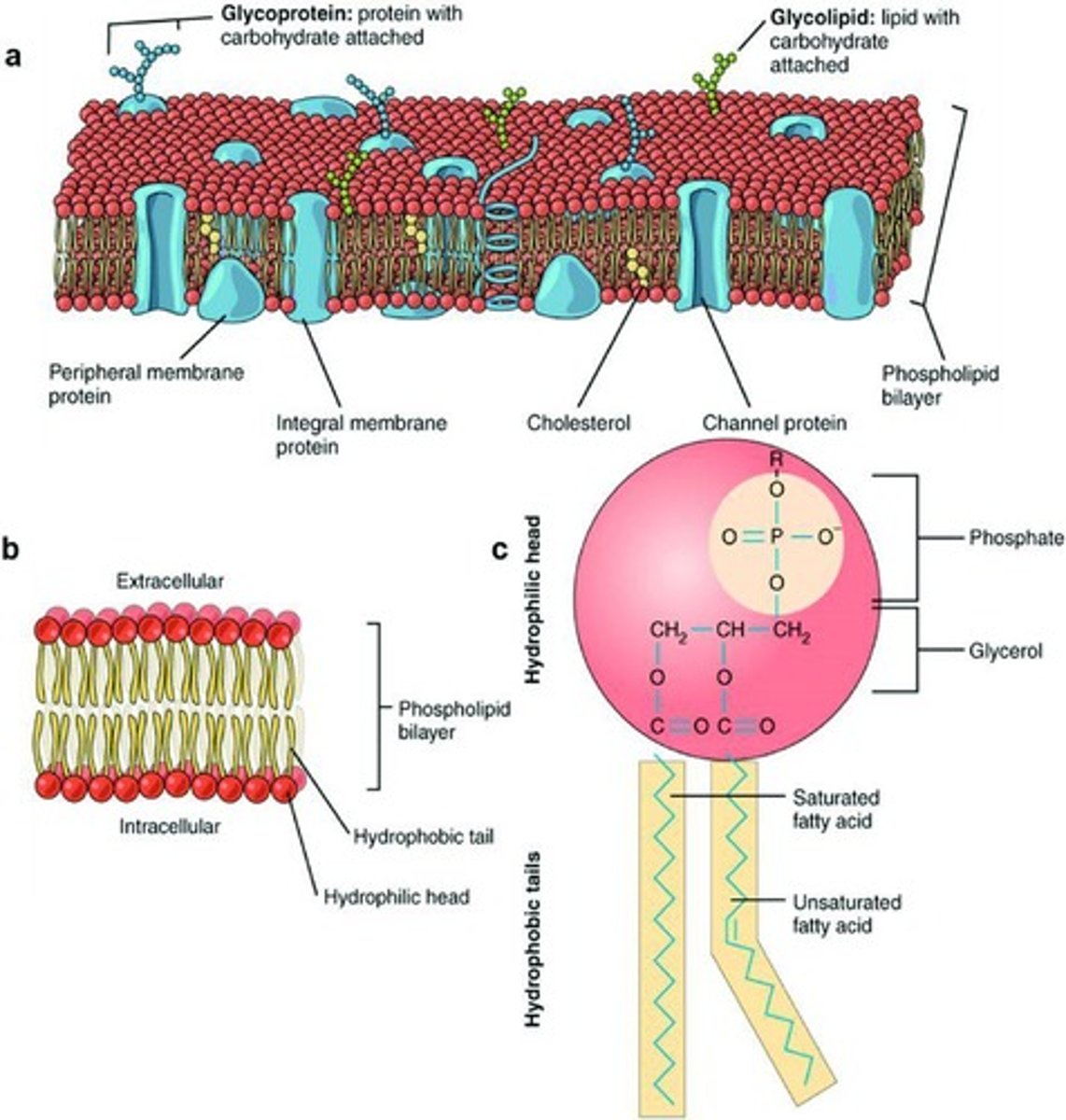
Phospholipids
- make up majority of cell membrane
- amphipathic
- 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group joined in a condensation reaction, making 3 water molecules
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds, solid at room temperature.
- animal fat
Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
One double bond between carbons
- lower melting point
- liquid at room temperature.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Multiple double bonds, liquid at room temperature.
Adipose Tissue
- how triglycerides are stored in animals
- fat storage determined by food intake vs energy expenditure
- excellent thermal insulator (animals in cold environments maintain body temp and have a greater amount of adipose tissue)
phospholipid bilayers
phospholipids= amphipathic
- phosphate heads face out (hydrophillic)
- fatty acid tails face away on the inside (hydrophobic)
- forms bilayer
- selectively permeable
- large/polar molecules cannot pass through
Steroid Hormones
- hormones= chemical messengers made up of glands
- steroids= hormone that contains cholesterol, can pass through bilayers easily. affect gene expression
- cholesterol= lipid, hydrophobic
Oestradiol
A steroid hormone involved in female reproduction.
Testosterone
A steroid hormone involved in male reproduction.