Faraday’s Law/Induction/EM Oscillation and Waves/AC Circuits - Science UIL
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Faraday's Laws
describes the magnitude of the electromotive force (emf), or voltage, induced (generated) in a conductor due to electromagnetic induction (changing magnetic fields)
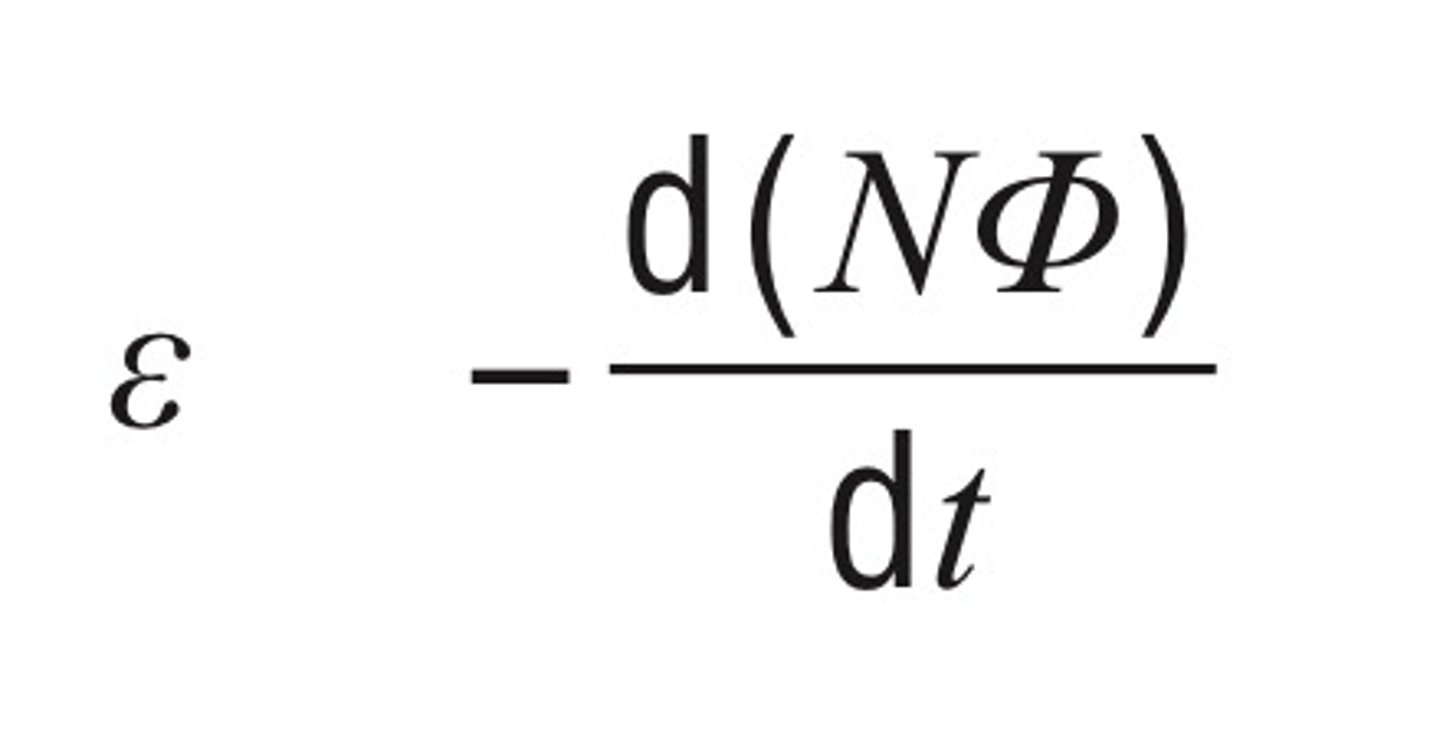
Lanz' Law
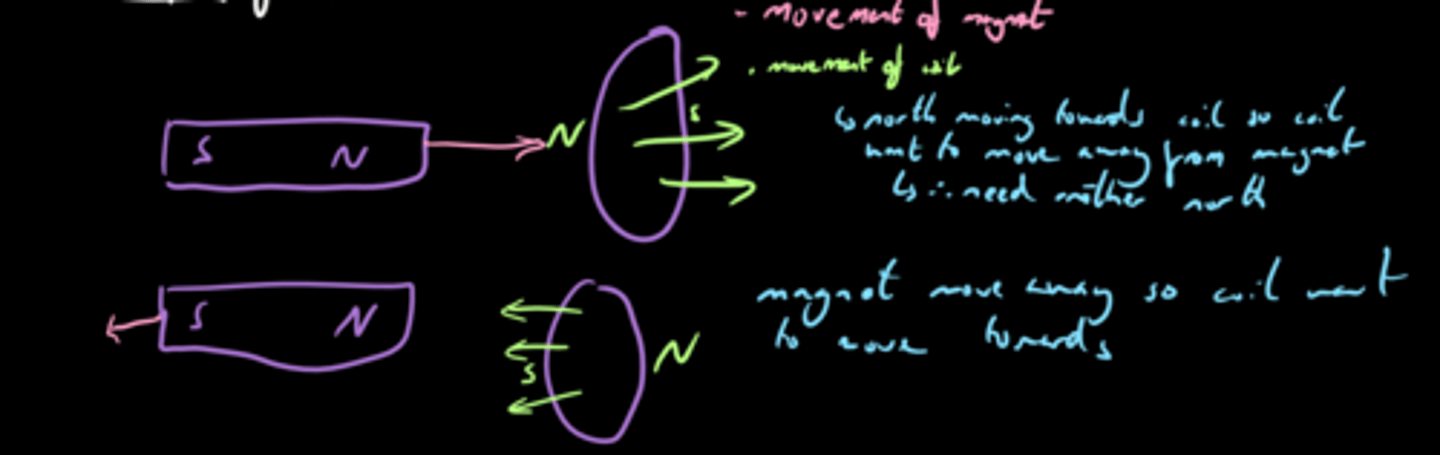
the direction of the induced current will oppose the change in flux that created it
Electromagnetic Waves
a form of radiation that travel though the universe
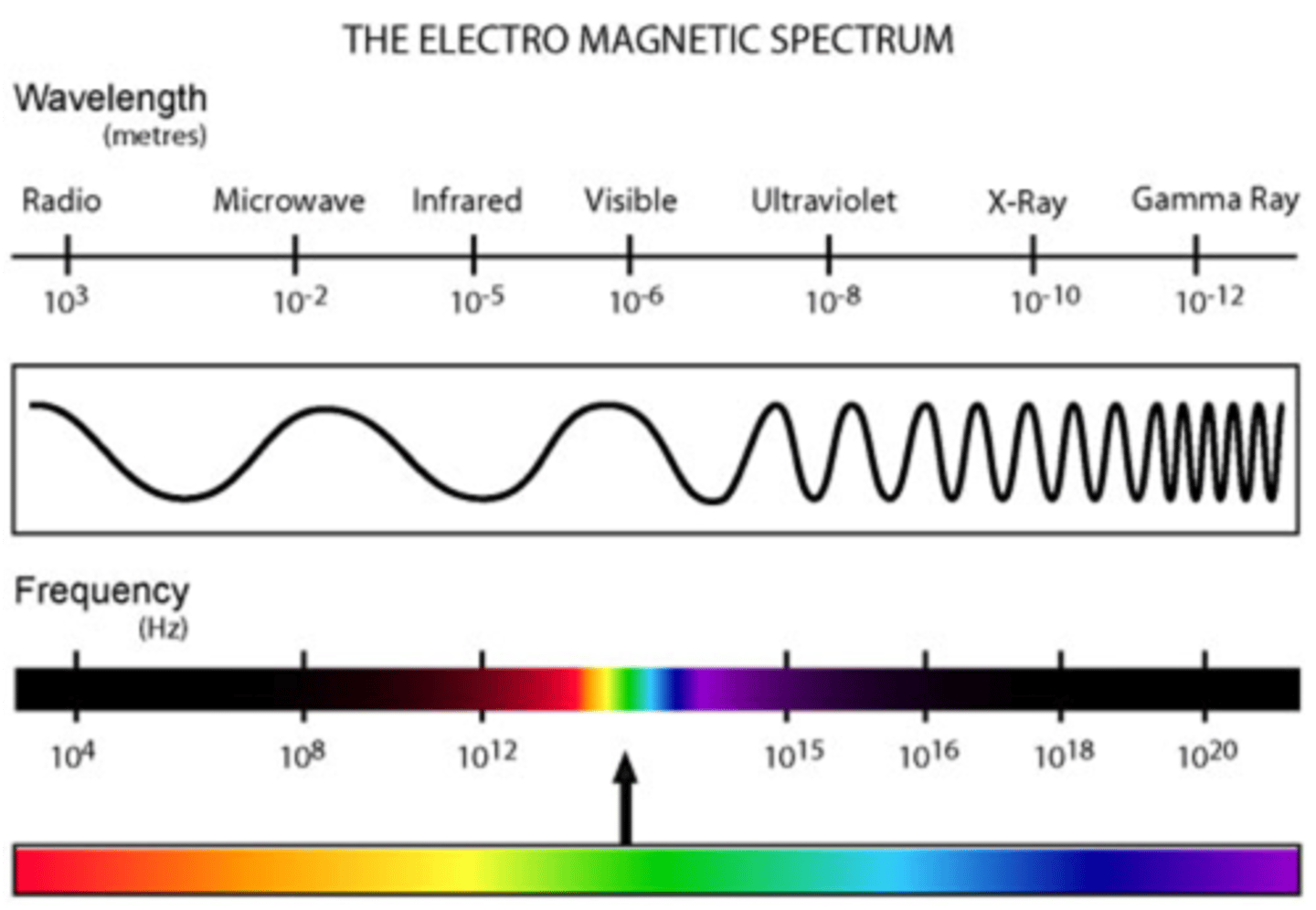
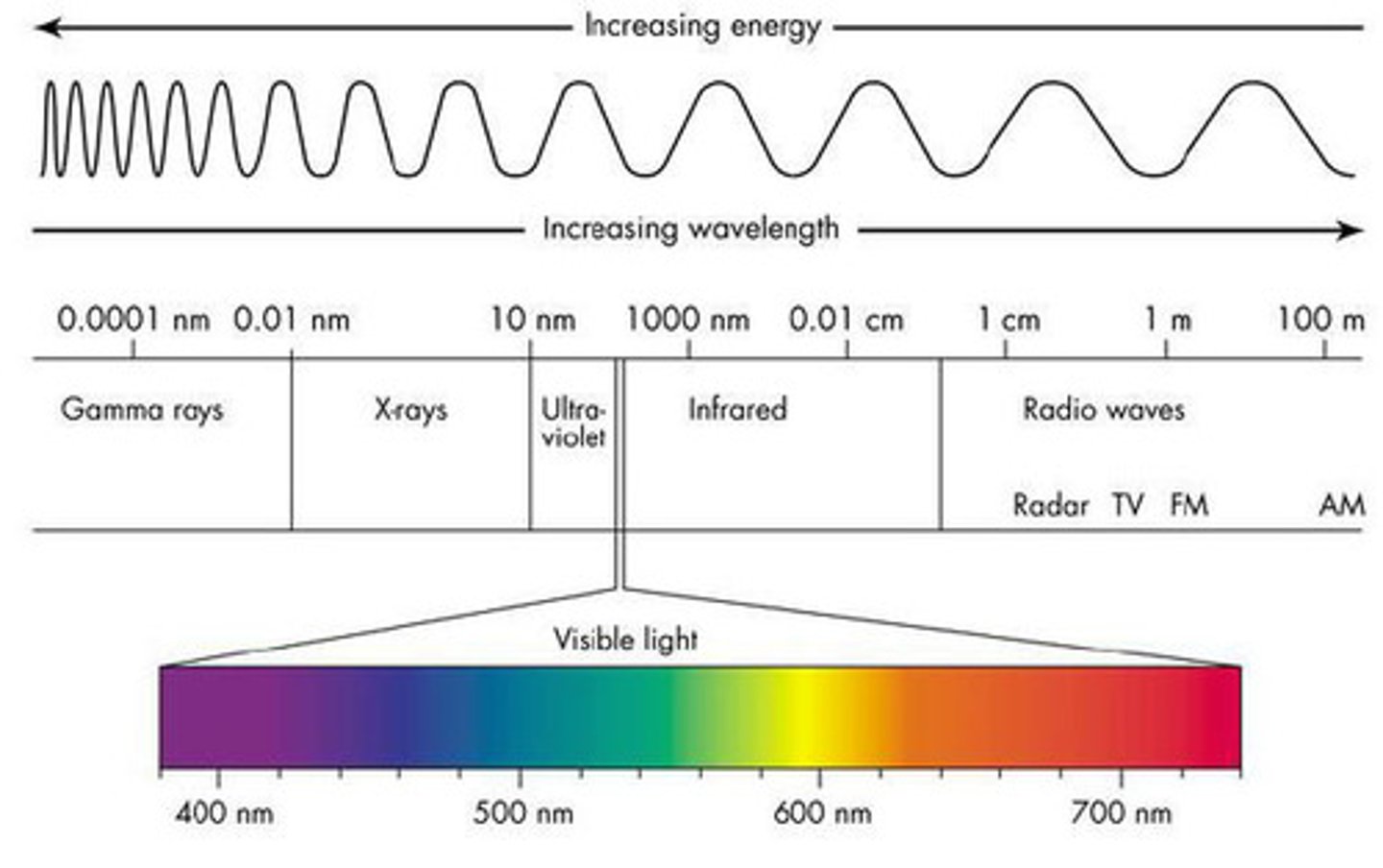
EM Spectrum
the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength
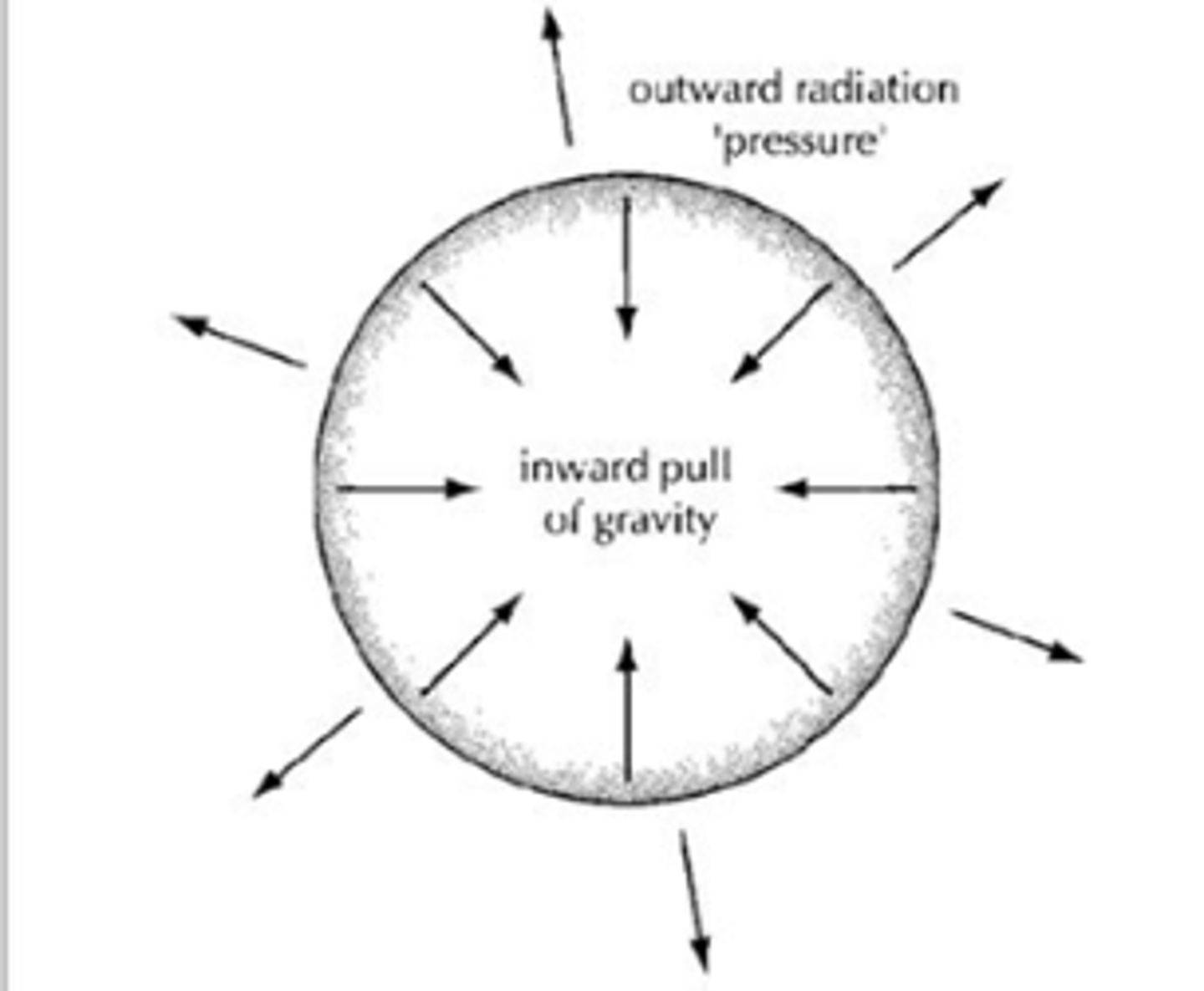
Radiation Pressure
the mechanical pressure that is applied on any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the electromagnetic field and the object
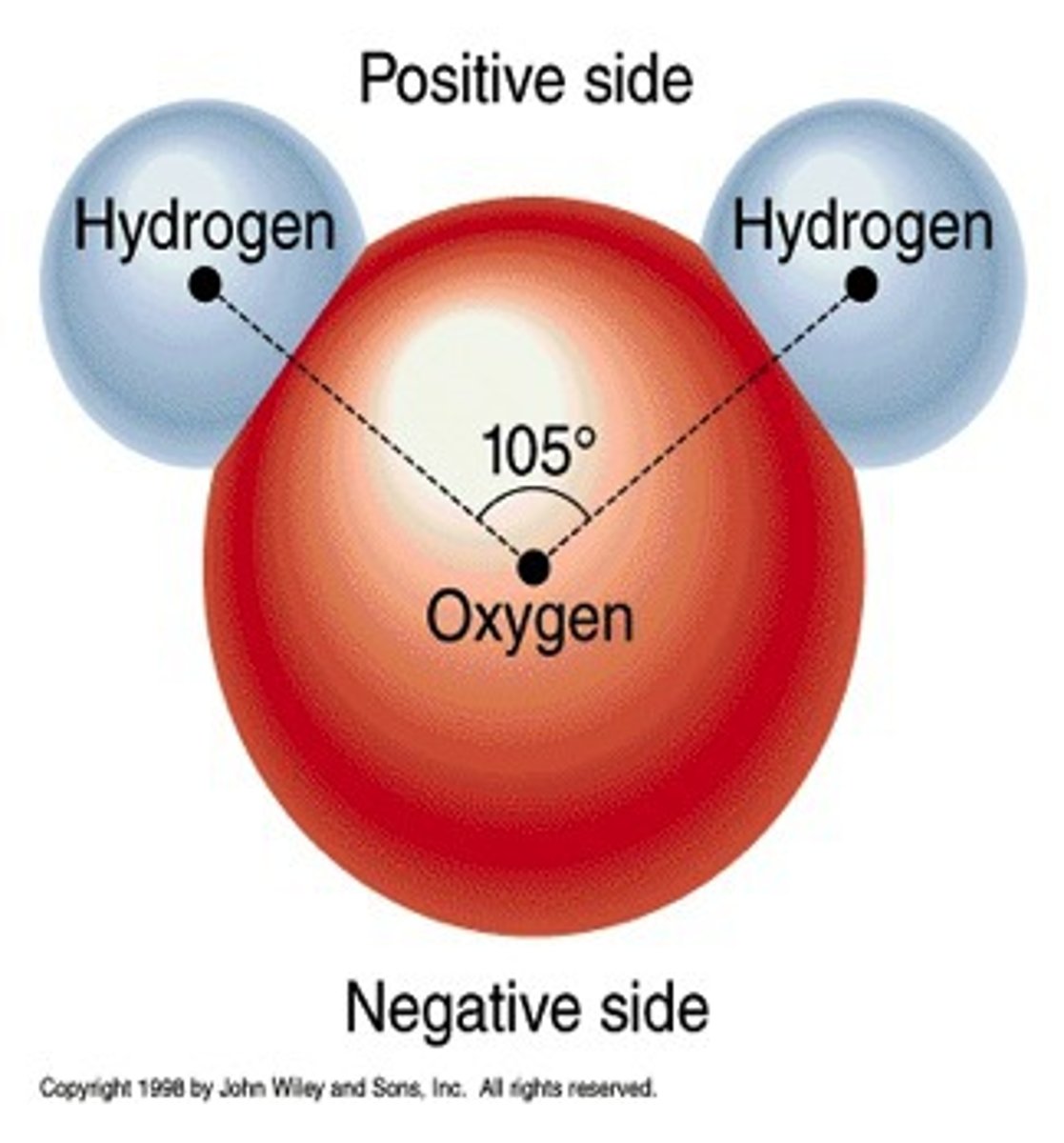
Polarization
a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations
Wave Refraction
the bending of waves as it passes from one material to another
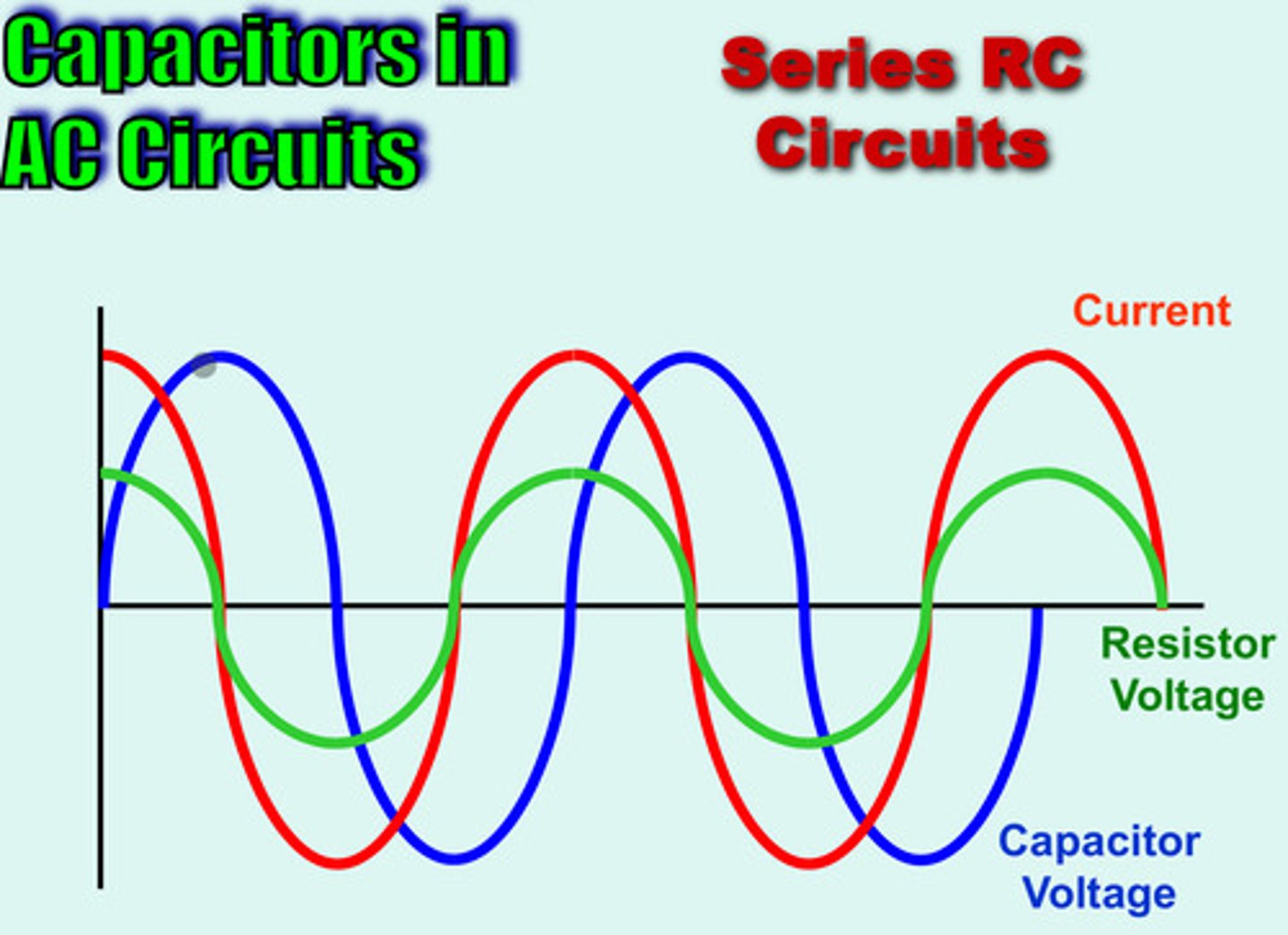
AC Circuits
an electrical current that regularly reverses direction and changes its value constantly with time
LC Oscillations
a circuit that is composed of the capacitor and inductor
RMS
represents the d.c. current/voltage that dissipates the same amount of power as the average power dissipated by the alternating current/voltage
RLC Resonance
occurs when the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude but cancel each other because they are 180 degrees apart in phase
Reactance
a form of opposition generated by components in an electric circuit when alternating current (AC) passes through it
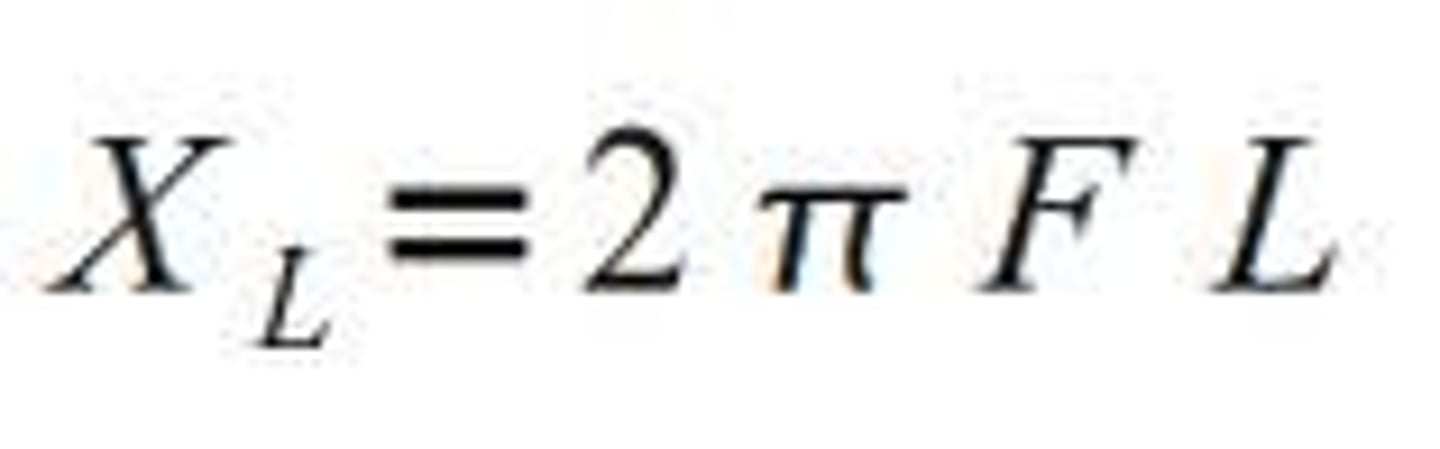
Impendence
measures movement of liquid and air up and down the oesophagus