The Multi-store model
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Short term memory, long term memory, sensory memory, The multistore model
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the coding of short term memory + research/findings?
Acoustic - storing information based on how it sounds. It is the reason why people might confuse words that are similar when recalling them from STM.
Baddeley 1996 - Gave participants a list of acoustically similar and dissimilar words and asked them to recall immediately. Acoustically similar words were harder to recall suggesting STM relies of acoustic coding.
What is the capacity of Short term memory + research/findings?
7± 2 items
Miller 1956 - Reviewed previous research on memory capacity including Jacob’s 1887 research on digit span and found that people could typically remember about 7± 2 items and suggested that people could remember more information by chunking.
What is the Duration of Short term memory + research/findings?
18 -30 Seconds
Peterson and Peterson (1959) - 24 Participants were given a trigram, after seeing the trigram they were asked to countdown in threes from a given number to prevent rehearsal, after different time intervals they were asked to recall. After 3 seconds recall was about 80% correct and after 18 seconds recall dropped to less that 10%. So short term memory is very short, unless rehearsed.
What is the coding of Long term memory + research/findings?
Semantic, storing information based on its meaning.
Baddeley (1996) - Participants were given a list of semantically similar and dissimilar words and asked to recall after 20 minutes to test LTM. LTM was worse for Semantically similar words suggesting that LTM relies on semantic coding.
Short term memory - capacity, coding and duration + researcher
Capacity = 7± 2 Miller 1956
Coding = Acoustic - Baddeley
Duration = 18-30 seconds - Peterson and Peterson
What is the duration of LTM + + research/findings?
Potentially unlimited
Bahrick et al. (1975) - 392 American participants aged 17 -74, tested their memories using photo and free recall tests.
After 15 years - after 48 years : Photo recognition: 90% - 70% Free recall: 60% - 30%
Found that LTM can last a lifetime especially meaningful memories. Recognition is better than free recall suggesting that retrieval failure is the reason for forgetting.
What is the capacity of LTM + + research/findings?
Unlimited
Bahrick et al. (1975) - 392 American participants aged 17 -74, tested their memories using photo and free recall tests.
After 15 years - after 48 years : Photo recognition: 90% - 70% Free recall: 60% - 30%
Found that LTM has a very large capacity since memories can last decades.
What is the coding on sensory memory + researcher?
Modality specific - information is stored in the same form it was received. Sub stores for each sense. (Visual info → iconic store, auditory info → echoic store, touch info → haptic store, taste info → gustatory store, smell info → olfactory info.)
Sperling (1960) - participants were shown a grid of 12 letters for 0.5 seconds and asked to recall as many as possible. One of the conditions → tone was used to recall a specific line. Recall was higher when a tone was used.
Suggests that auditory and visual information is stored seperately.
What is the duration of the sensory register + researcher?
50 ms / 0.5 sec
Sperling (1960) - participants were shown a grid of 12 letters for 0.5 seconds and asked to recall as many as possible. One of the conditions → tone was used to recall a specific line. Recall was higher when a tone was used.
They would quickly forget the letters suggesting that duration was incredibly short
What is the capacity of sensory memory + research/findings?
Very large
Sperling (1960) - participants were shown a grid of 12 letters for 0.5 seconds and asked to recall as many as possible. One of the conditions → tone was used to recall a specific line. Recall was higher when a tone was used.
Lots of information can be stored, it just decays quickly.
Long term memory coding, capacity, duration + researcher:
Coding - semantic - Baddeley
Capacity → unlimited - Bahrick et al
Duration → unlimited - Bahrick et al
Evaluate Baddeley’s research on the capacity of LTM and STM - strength
Supports MSM
Supports the distinction between LTM and STM.
Baddeley found that LTM is stored semantically and STM is stored acoustically
Supports the MSM which states that they are separate stores.
Therefore, the study provides empirical evidence for how memory is structured.
Evaluate Baddeley’s research on the capacity of LTM and STM - strength
Highly controlled
Study was highly controlled
Lab setting → minimised extraneous variables.
Increases internal validity so we can be more confident in encoding difference are due to stm and LTM process and not other factors.
Makes the study reliable and replicable.
Evaluate Baddeley’s research on the capacity of LTM and STM - limitation
Low ecological validity
Study used artificial tasks
Remembering lists of words - doesn’t reflect real life memory/situations.
Lacks ecological validity as memory may differ in an everyday context
Findings may not generalise
Evaluate Millers findings the capacity of STM - strength
Real life application
Research has useful real life application
Concept of chunking is used in phone numbers, number plates ect.
Research has practical benefits for improving memory recall
Study isn’t just theoretical
Evaluate Millers findings the capacity of STM - Limitation
Other research
Miller may have overestimated
Cowan (2001) found that STM is close to 4 chunks
Suggests his finding are too high and STM may be more limited that he claimed
Lacks accuracy
Evaluate Bahrick et al’s research on the duration and capacity of LTM - strength
Ecological validity
High ecological validity
Baddeley utilised real life memories
Meaning finding are more applicable
Study can be generalised
Evaluate Bahrick et al’s research on the duration and capacity of LTM - limitation
Lacks control over extraneous variables
Lacks control over extraneous variables
Participants may have looked over their yearbooks over the years, so memory was rehearsed. Some people may have better memories
Decreases internal validity and doesn’t account for individual differences
May have overestimated, and be an inaccurate representation
Evaluate Bahrick et al’s research on the duration and capacity of LTM - Limitation
Sample bias
Sample bias
Only studied Americans
Findings may not apply to people of different cultures. Lacks population validity
Not universal
Evaluate Peterson and Peterson’s findings on the duration of STM - strength
Controlled
High validity
Took place in a lab where participants were asked to recall letters from a trigram
No extraneous variables present, increasing the internal validity
Meaning the study is reliable and replicable
Evaluate Peterson and Peterson’s findings on the duration of STM - limitation
Artificial stimuli
Artificial stimuli
Trigrams were used which don’t replicate real life scenarios
No meaningful information So it may not apply to real life
Lacks ecological validity
Evaluate Peterson and Peterson’s findings on the duration of STM - Limitation
Other reasons for forgetting
Forgetting could have been due to interference rather than decay
Counting backwards could have meant that retroactive interference took place
Therefore challenging the conclusion that STM fades due to the short duration
Findings may not be accurate
Evaluate Sperlings findings on sensory memory - strength
High internal validity
Lab experiment → controlled conditions
Few extraneous/confounding variables
Replicable and reliable findings.
Evaluate Sperlings findings on sensory memory - Limitation
Ecological validity
Low ecological validity
artificial tasks - grid of 12 letters
Non meaningful information - memory may work differently in real life
Therefore findings may not generalise
Evaluate Sperlings findings on sensory memory - limitation
Demand characteristics
Demand characteristics
People just guessing the letters and getting them correct
Decreases the accuracy of the findings
Limits generalisability and external validity
Memory store model diagram
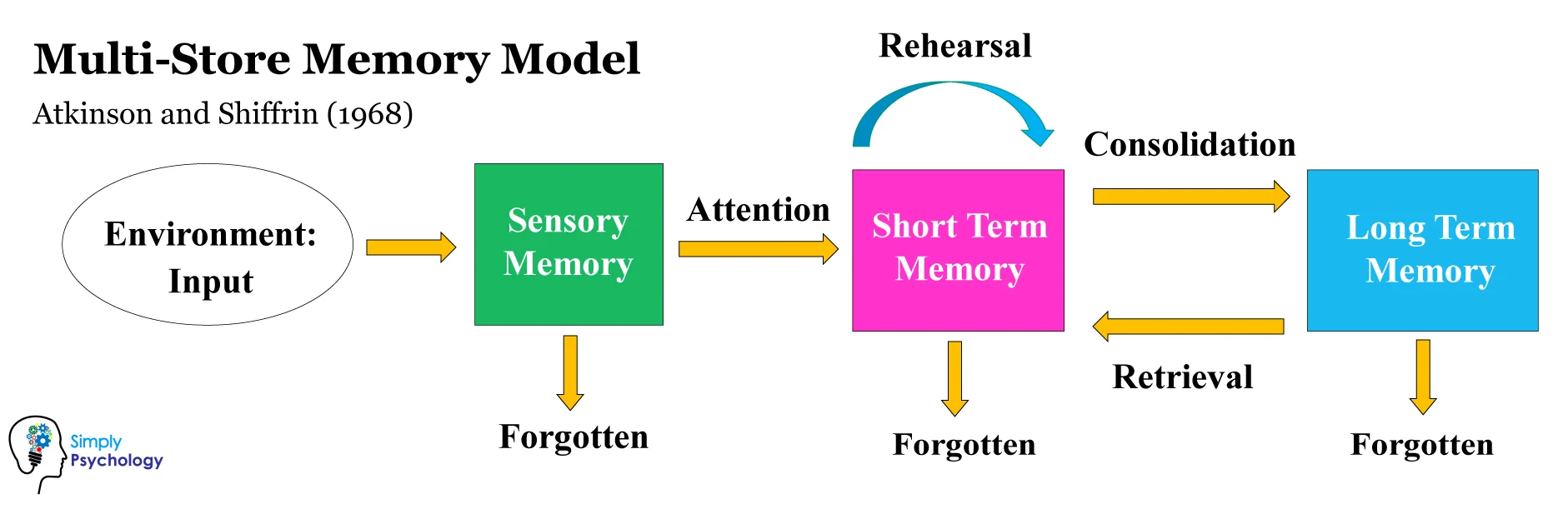
What is meant by attention?
Moving information from sensory to stm, if information doesn’t receive attention it will decay due to the short duration of STM
What are the 2 types of rehearsal?
Maintenance rehearsal - repeating information to try and remember it (doesn’t guarantee info will move to LTM)
Elaborative rehearsal - linking new info to old info. - more effective in transferring info to LTM
Without rehearsal, information will decay or be displaced to to limited capacity.
What are the 2 types of retrieval?
Recall - information is retrieved without specific cues
Recognition - information is retrieved when prompted by a cue.
Who came up with the multi-store model?
Richard Atkinson
Evaluate the multi store model as a whole - strength
Qualitative differences
Acknowledges the qualitative differences in coding
These are proven by Baddeley
Meaning they are an accurate representation.
However Baddeley lacks ecological validity
Evaluate the multi store model as a whole - limitations
Oversimplified stm
May be oversimplified
Suggests that STM is unitary - shallice and Warrington KF case study → intact visual memory but impaired verbal memory.
STM may have separate subsections
So the multi store model is a limited explanation
Evaluate the multi store model as a whole -limitation
Oversimplified LTM
Oversimplified LTM
Suggests that LTM is unitary → Tulving → 3 separate LTM store supported by HM (impaired episodic.)
Doesn’t account for different LTM stores
Limited explanation