AP World Notebook 14, 15, 16, and 17 Quiz
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
facilitation of trade
The Spanish Silver Trade, The Atlantic System, The Columbian Exchange, Mercantile System
royal patronage
the support and endorsement of an organization by a member of a royal family, which helps raise its profile, attract publicity, and potentially secure funding
England
attempted to settle territories in North America and the Caribbean; established the seeds of the American colonies that eventually became the United States with the founding of the Virginia Colony in 1607, and several surrounding colonies over the new 150 years
compass
An addition to the ancient method of navigation based on sightings of the sun/stars. Used for navigation in China by 11th century & adopted by Arab traders in Indian Ocean. Spread to Europe by late 12th/early 13th century. Use for navigation in Indian Ocean was 1st mentioned in 1232. The first mention of use in Europe was in 1180. The Europeans used a "dry" compass, with a needle on a pivot.
Vasco de Gama
A Portuguese sailor who was the first European to sail around southern Africa to the Indian Ocean, establishing a sea route to India in 1498.
gunpowder
allowed military advantage over the ships and cities of non-Europeans: advanced gunpowder weapons—most-notably the cannon
Portugal
Iberian/Hispanic maritime empire; Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) = got Brazil/access to most of Old World; a trade-post empire, controlling coastal cities, ports, trade in Africa/Asia; had mandatory trade certificate (cartaz), non-Portuguese traders in Africa/Asia required to purchase, providing Portugal w/ revenue; solidified trade relations w/ West Africa slave economies; slave trade grew end of 17th century as demand for labor in New World grew
cartaz
Portuguese mandatory trade certificate non-Portuguese traders in Africa and Asia were required to purchase, providing Portugal with a stream of revenue
riches
Great treasure or wealth. Europeans in the EME believed there was a 'fixed wealth' or certain amount of wealth (gold & silver) in the world, and the goal was to control most of it. Ex: The Spanish Silver Trade
joint stock
Whatever percentage of financing investors put into an expedition, they received in profit on the return of a successful voyage or mission; to keep their investments safe, they spread their funds across many missions rather than lumping it all into one
Germany
The Hanseatic League, a confederation of merchant guilds and their towns in northern Germany along the North Sea and Baltic Sea, was instrumental in commercial development of the region. In the 12th century the region of Flanders, Hainault and Braband produced the finest quality textiles in northern Europe, which encouraged merchants from Genoa and Venice to sail there directly.
caravel
(made in mid-15th century) a small, maneuverable ship with lateen sails that was able to sail windward more than any other in Europe at the time. Evolved from fishing ships designs, they were the first that could leave the coastal cabotage navigation and sail safely on the open Atlantic.
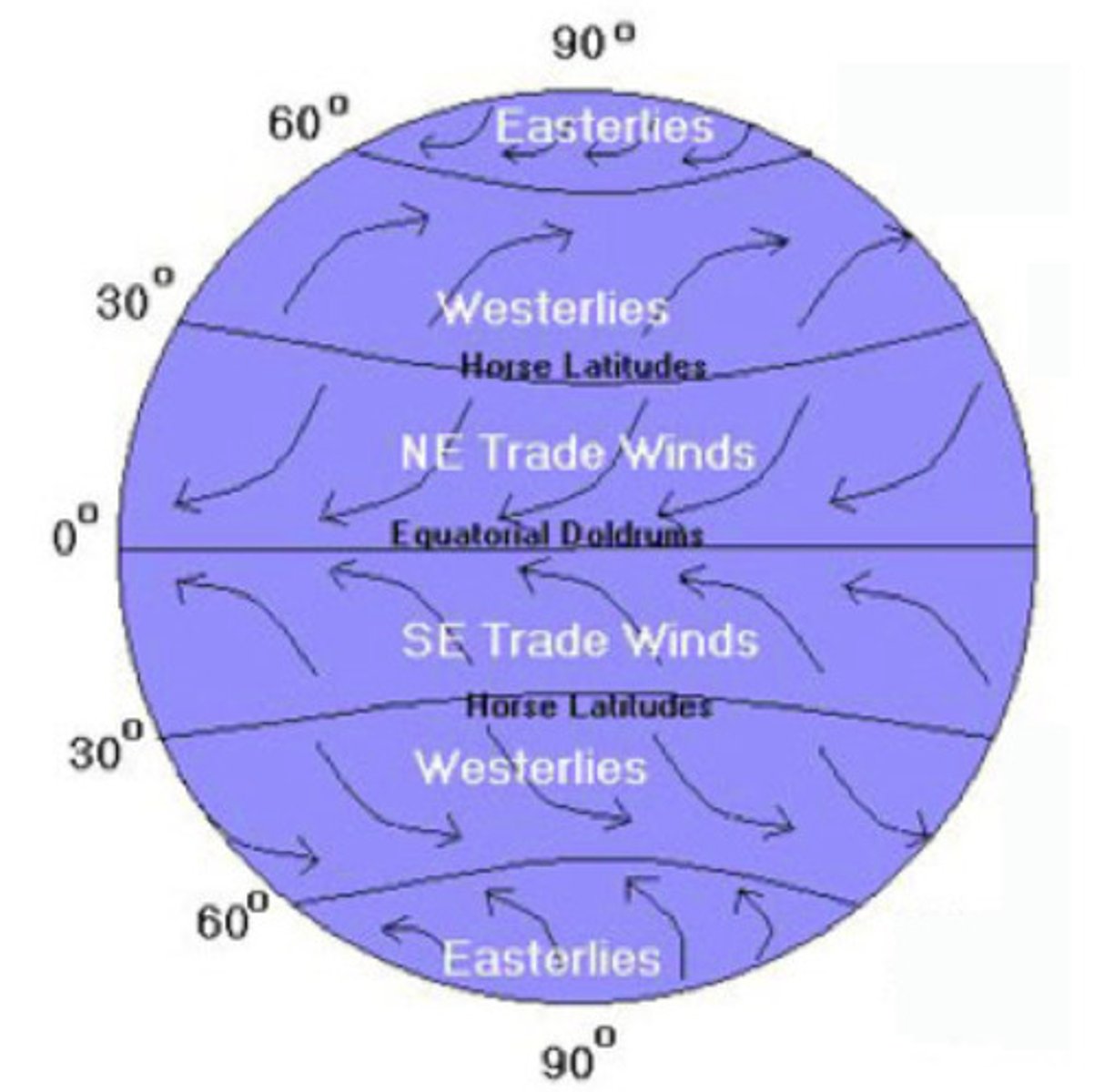
Westerlies
prevailing winds that blow from west to east between 30 degrees and 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres
astrolabes
an ancient astronomical instrument that acts as a star chart and physical model of the sky, capable of performing various calculations
Renaissance
Europe experienced a 'rebirth', old ideas returned and new ideas/innovations emerged once the cycle of theological thinking were broken. Most important impacts of the European Renaissance was the impact of Greco-Roman skepticism on knowledge—one that questioned and rejected traditional answers. Big things that happened: Scientific Revolution (1543-1687), Johannes Gutenberg's printing press published works of Copernicus, Galileo, Descartes, and Newton. English/Spanish formed by writers/playwrights: William Shakespeare & Miguel de Cervantes
feudal ranks and grants
Encomienda System in Spain = large feudal land grants given to Spanish conquerors and settlers who oversaw/organized labor of settlers/American Indians, as well as were given the task of Christianizing the populations (both peacefully and by force). Devolved racial caste system, gave specific social/political advantages to Peninsulares (Spanish born in Spain), with Criollos (Spanish born in the Americas) one stratum below. Below were racial mixes, with a highly-racist hierarchy that demoted/promoted an individual or family based on the pigment of their skin, with darker colors positioned lower on the hierarchy
France
attempted to settle territories in North America and the Caribbean; the French settled the colony of New France in the Great Lakes region and St. Lawrence River starting in 1524, establishing missionaries and trade posts with local tribes, such as the Huron and Algonquian
Netherlands
attempted to settle territories in North America and the Caribbean; established colonial trade posts and small colonies in places like New Amsterdam on Manhattan Island in 1624 (known today as New York [city])
Henry the Navigator
This Portuguese prince who lead an extensive effort to promote seafaring expertise in the 14th century to trade with West Africa, find allies in legendary Christian lands, try to find sea route to India for spice trade. Sent many expedition to the coast of West Africa in the 15th century, leading Portugal to discover a route around Africa, ultimately to India and the Atlantic islands of Maderia and Azores.
Trade Winds
East-to-west winds in the tropics, found in both the Northern Hemisphere (blowing from the northeast) and the Southern Hemisphere (blowing from the southeast).
printing
Knowledge was either duplicated or catalogued, and disseminated with unparalleled speed and cost efficiency after the invention of Johannes Gutenberg's printing press in the 15th century
Christian missionary work
Catholic Spanish/Portuguese missionaries aggressively evangelized in China, Japan, and Philippine. While initially tolerated, China and Japan, would soon oppose presence of Western peoples, religion, and ideals, deeming them barbaric or too individualistic
portolan maps
(essentially marking distance based on time traveled in a single direction) which made it far easier to accurately chart and navigate new areas
Spain
Had the Spanish Silver Trade; had land in the Americas, focused on conquest, extraction & exportation of natural resources (gold, silver, cash crops). New Spain, Spanish Empire from tip of South America to California. Disease exposure and conquistadors eliminating major American Indian civilizations. Developed a feudal system: encomienda system. Devolved into a racial caste system, gave specific social/political advantages to Peninsulares (Spanish born in Spain), with Criollos (Spanish born in the Americas) below, racial mixes below that. Highly-racist hierarchy that demoted/promoted an individual/family based on pigment of their skin, with darker colors positioned lower on the hierarchy
Omani
a powerful maritime force and a historical trading community with a strong presence across the Indian Ocean, known for their seafaring skills, extensive trade networks, and the influence of the Omani Empire
mercantilism
state control of trade in the hopes of enhancing national power at the expense of rival countries
imports
goods and services that one country purchases from another country
Pizarro
Spanish conquistador who led the conquest of the Inca Empire in what is now Peru. He is known for capturing and executing the Inca emperor, Atahualpa, after ambushing and defeating his forces in 1532. Pizarro's actions led to the fall of the Inca Empire, the establishment of Spanish colonial rule in the region, and the founding of Lima, the capital of Peru
Shimabara
uprising in Shimabara Domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate in Japan from December 17, 1637 to April 15, 1638. Matsukura Katsuie, the daimyō of Shimabara Domain, enforced policies that raised taxes and violently prohibited Christianity. In December 1637, an alliance led by Amakusa Shirō rebelled against the Tokugawa shogunate. The Tokugawa Shogunate sent a force of over 125,000 troops supported by the Dutch to suppress rebels. Rebellion was the largest civil conflict in Japan during Edo period and a direct trigger of Sakoku isolation.
national isolation
a foreign policy approach where a country deliberately limits its involvement in international affairs, such as avoiding political or military alliances and restricting trade. Japan did this
wheat
From the Old World to the New World crop
Malay
traders from the indigenous Malay people and various ethnic groups of Southeast Asia who historically dominated regional maritime trade, particularly through the Straits of Malacca
Cortez
Hernán Cortés was a Spanish conquistador who led the conquest of the Aztec Empire, resulting in its fall in 1521 and the establishment of Mexico as a Spanish colony known as New Spain. He achieved this by forming alliances with native tribes who resented Aztec rule, using superior weaponry, and capitalizing on a smallpox epidemic that devastated the native population.
tariffs
taxes that governments impose on imported goods
national monetary surplus
when a government's total revenue (primarily from taxes) exceeds its total spending in a given fiscal year. A surplus can lead to a government having more flexibility to pay down debt, fund new programs, or cut taxes.
encomienda
large feudal land grants were given to Spanish conquerors and settlers who oversaw and organized the labor of settlers and American Indians, as well as were given the task of Christianizing the populations (both peacefully and by force). Like FEUDALISM
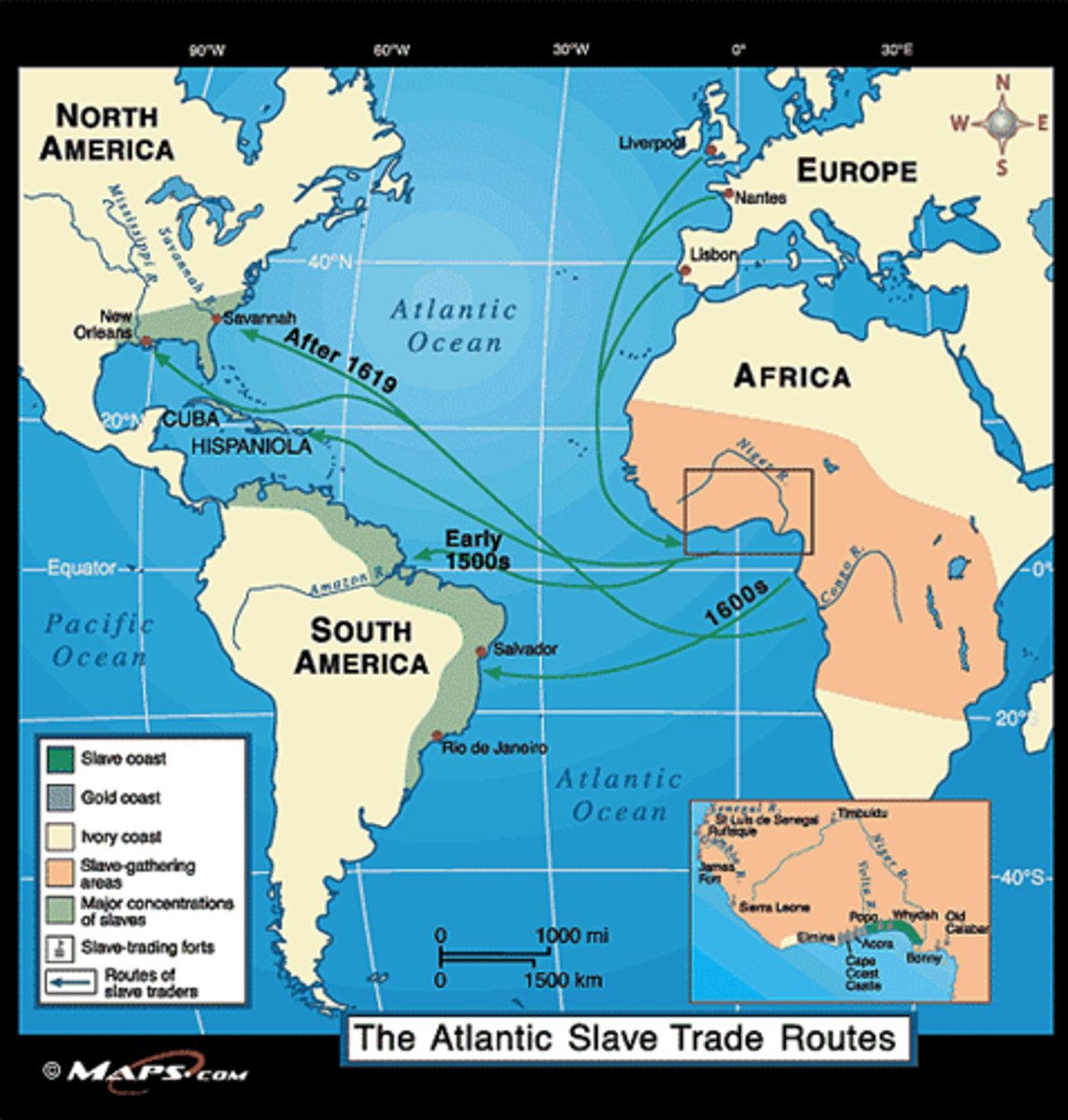
Atlantic system
a triangular system of trade in which increase profits from colonial holding returned to Europe and fueled the purchasing of more African slaves evolving Economic Practices
Catholicism
The faith, practice, and church order of the Roman Catholic Church. Spanish laborers in the encomienda system's principal benefit was the Catholic religion. Spain had Christian conquests. Catholic Spanish and Portuguese missionaries aggressively evangelized in China, Japan, and the Philippines. In Shimabara Rebellion, anti-Catholic policies (among other things) in the region, so Japanese peasants and Catholic converts rebelled against the shogunate
Tokugawa
military/political leader, Tokugawa Ieysau unified Japan in 1615. Tokugawa Shogunate, the shogun ruled from Edo capital, maintaining a ceremonial relationship w/ Japanese emperor. Ruled as a centralized feudal kingdom. Shogunate responsible for foreign relations, national security, coinage, standardization of coinage and weight, transportation. Shogun maintained own bureaucracy from Edo. Tokugawa Shogunate = Edo Period (1603-1867); prosperous period in Japanese history. Relative stability, peace, and prosperity, rises in literacy rates, population, & production. Anti-foreign sentiments overtook the Tokugawa govt. Shimabara Rebellion caused edicts of Sakoku. Disintegration of the samurai fighting class
Columbian Exchange
a wide transfer of plants, animals, food, human populations (including slaves), communicable diseases and culture between the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Encomienderas
The encomiendas were a Spanish colonial system that compelled Indigenous people to provide labor and tribute to Spanish settlers in the Americas and the Philippines. Originating from a medieval Spanish practice, the system was implemented in the colonies during the 16th century following the expeditions of Christopher Columbus.
corn
new crop; from the New World came staple and lucrative crops
sugar
Primary driver of the Atlantic System, creating an immense demand for labor that fueled the transatlantic slave trade and a triangle of trade routes connecting Europe, Africa, and the Americas. The sugar plantation economy in Caribbean and Brazil relied on labor of enslaved Africans, producing sugar, rum, and molasses for European markets
charter companies
corporate entities obtained legal charter to settle a colony in the name of England/Netherlands for a set period w/ eventual goal of state administration. Companies allowed to hire/construct own mercenary soldiers/navies to protect colonial assets against native forces, other Europeans, or pirates. Virginia Company, British East India Company, and Dutch East India Company quickly spread influence in Indian Ocean, Caribbean, and North America, giving colonial mother country access to resources/tax revenue. Many companies failed, but successful in spreading the presence of English Dutch colonies, settlements, and trade throughout the New/Old World
tobacco
new crops; from the New World came staple and lucrative crops
Java
merchants from the island of Java in Indonesia who were active in regional and long-distance trade, particularly in the spice trade, for centuries before the colonial era. They acted as intermediaries, transporting goods like spices from their source in the Moluccas and trading with foreign merchants from Europe, India, China, and Arabia. The Javanese were also part of larger networks that connected Southeast Asia with the Indian subcontinent and East Africa.
Spanish Silver Trade
In Peru, Mexico, and Nevada, the Spanish discovered lots of silver. Made Spain insanely rich, but they didn't know how to handle inflation/taxes. Used silver to fund wars in Europe, ex: invasion of Dutch Republic, Thirty Years War, Catholic forces in France and vs. the Ottoman Turks. Spanish silver = 1st desirable European commodities in East Asian markets and used to purchase luxury goods (tea, silk, porcelain, spices).
The silver trade would initially provide Spain with a great amount of economic and military power, mismanagement of taxes, overspending on foreign wars, and silver inflation would lead to their decline in the 17th century.
exports
send (goods or services) to another country for sale.