Key Terms- Prehistory
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Geography
Four Main Islands of Japan: Honshū (lit., “main land”), Kyūshū, Shikoku, Hokkaidō Bodies of Water: Tsushima Strait, Inland Sea, Sea of Japan (N.B., controversial name) Regions: Kantō, Kansai, Yamato Plain
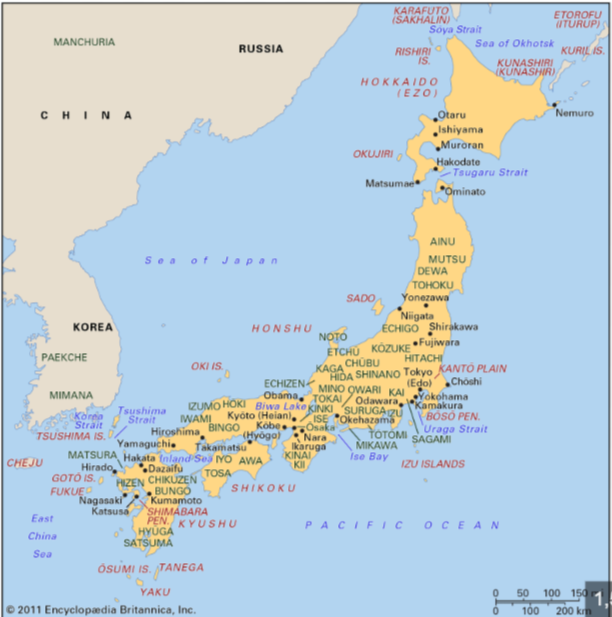
Chronology
Jōmon Period, 14,000 BCE – 300 BCE (global warming around 10,000 BCE, peaks ca. 2500 BCE, cooling from ca. 1500 BCE)
Yayoi Period, 300 BCE – 300 AD Iron Age
Kofun Period, ca. 3rd – 7th centuries
Asuka Period, ca. 6th c. – 710 CE.
Yamato Clan and Polity, ca. 5th c. to present
Jōmon Culture
Lack of metalworking
Sedentary (not H/G)
Hunted fish and game
Cultivated Plants
Managed trees
Used lacquer
Perhaps cultivated rice
Ceramics: coil-built, open pit (up to 900 C) Appliqué Stamps Ropework Wooden tools


Dogū
(Clay figurines)
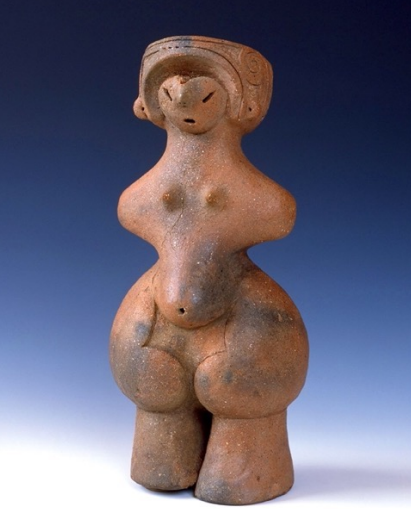

“Jōmon Venus”
Middle Jōmon
National Treasure excavated from the Tanabatake Archaeological Site in Nagano Prefecture.

Yayoi Civilization
7yrs after Jōmon, in Yayoi site (1884) Also in Tokyo
Wet rice cultivation
Silk weaving
Metalworking: BRONZE
Swords
Moats around settlements
Raised storehouse architecture
Rise of political polities
E.g., Queen Himiko of Yamatai

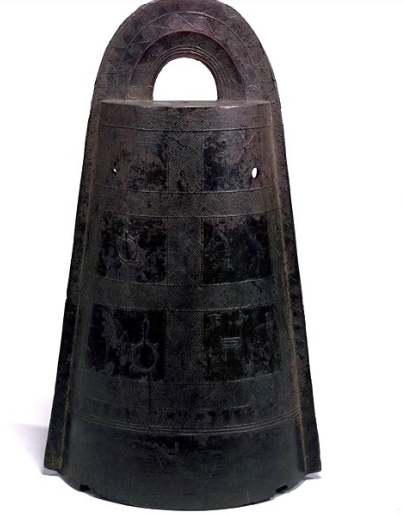
Dotaku
Bells

Kofun period, late 4th–early 5th century
TOMB OF EMPEROR NINTOKU.
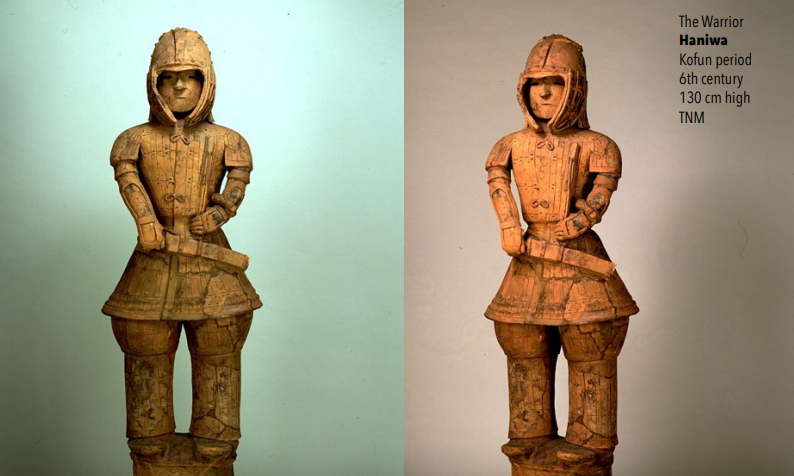

Haniwa
(Funerary figurines)
Magatama
(Comma-shaped stones)

Anagama kilns (lit., “cave kilns”)
allows for stoneware and firing

Sueki ware
Kofun (Tumulus) period, ca. 550-600
Stoneware clay with natural ash glaze 52.7 x 46.4 x 46.4 cm
