MOD 08 - Gypsum (Type IV & V)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
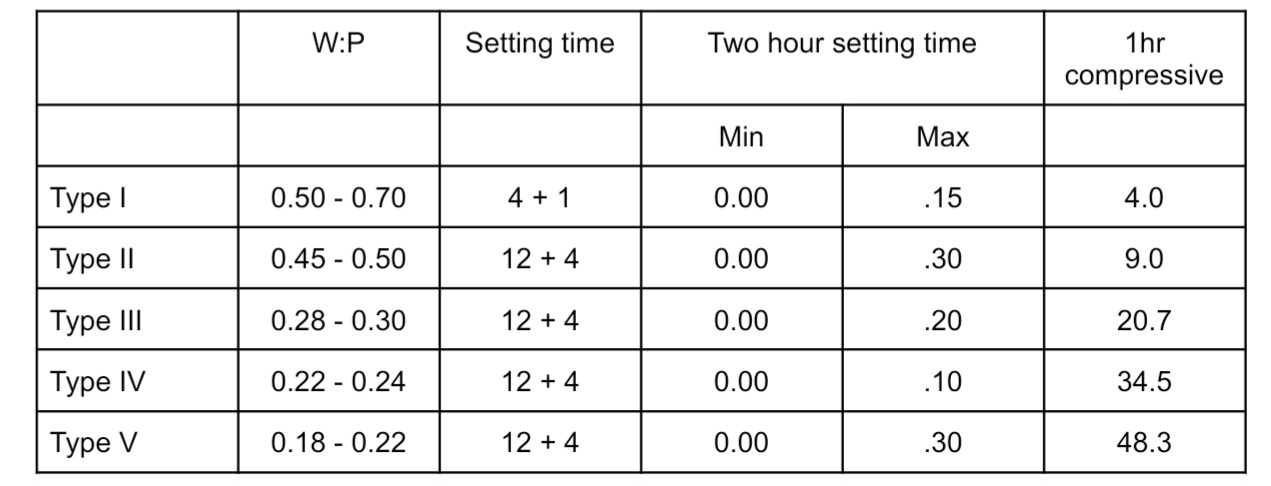
High strength
Type IV, Class II stone, Densite, Improved dental stone, modified alpha hemihydrate, and die stone
Strongest and most expensive
Making cast or dies for crowns, bridge, and inlay fabrication
Principle requisites for high strength
Strength, Abrasion, Resistance, Hardness, Minimal setting expansion
Mnemonics: Strong athletes run hard miles
hard surface is necessary in type iv because
tooth prep is covered with wax and carved flush with margins of die
This instrument is used in Type IV, thus it must be resistant to abrasion
Sharp Instrument
Advantage of type IV
surface resists to abrasion
Average dry surface gypsum hardness solution in type IV
92
Type V
Dental stone, High strength, High expansion
Used for inlays, onlays bcs expansion leads to unnacceptability tightly fit
Strength is achieved by lowering w:p
Higher setting expansion to aid compensationg for alloy solidication shrinkage
Setting expansion is increased, since few base metal alloys have greater tendency of shrinkage
How to make Type V
Calcined by boiling it in 30% CaCl
Washed away or autoclave by sodium succinate 0.5%
Results to more shorter and thicker
Residual CaCl and sodium succinate is removed by washing powder with hot water
fill out the properties of gypsums: