phys 120: lenses, refraction, reflection, and other stuff: equations and concepts
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
index of refraction equation (and the constant)
n=c/v (c is the speed of light in a vacuum and = 3.00×10^8
Snell’s law, which relates the index of refraction and angle of incidence of one medium to another
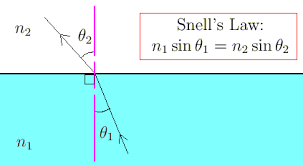
What is the critical angle, and what does it represent?
the critical angle: the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90 degrees. if this angle is exceeded, then there is total internal reflection. Sin@c=n2/n1
NOTE: n1 must be greater than n2, meaning that total internal reflection can only happen when it goes from a more dense medium to a less dense medium
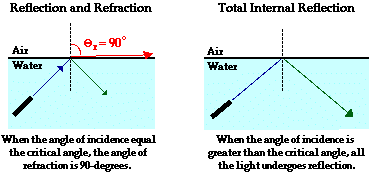
relationship between reflected ray and incident ray on a flat surface
@i=@r
equations for focal length
P = 1/f = 1/di + 1/do
f = 1/2(R) OR f = -1/2(R), for use with a convex mirror
rules for drawing ray: CONCAVE MIRROR
ray 1: leaves parallel to principal axis, reflects off mirror, and passes through focal point
ray 2: passes through foal point, reflects off mirror, and emerges parallel to axis
ray 3: travels along a line that passes through the center of curvature, C
rules for drawing rays: CONVEX MIRRORS
Ray 1: initially parallel to principal axis, reflects, and emerges in a way that seems like it came from the focal point on the other side
ray 2: heads towards the focal point on the other side, and emerges parallel to axis
ray 3: travel towards center of curvature, C, and reflects back on itself
CONVEX mirrors produce a predictable image:
located behind the convex mirror
a virtual image
an upright image
reduced in size (i.e., smaller than the object)
sign conventions for MIRRORS: di, do, f, and m
f is positive for a concave lens (usually) and negative for a convex lens
di is positive if in front of mirror, and - if behind mirror
m is + for an upright image, and - for an inverted image
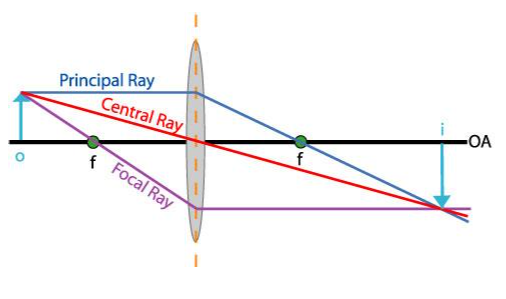
rules for drawing rays: CONVEX LENS
ray 1: leaves object parallel to axis, refracts,a ND goes through f on the other side
ray 2: goes through f on the same side, refracts, and goes parallel
ray 3: goes through midpoint of lens unrefracted
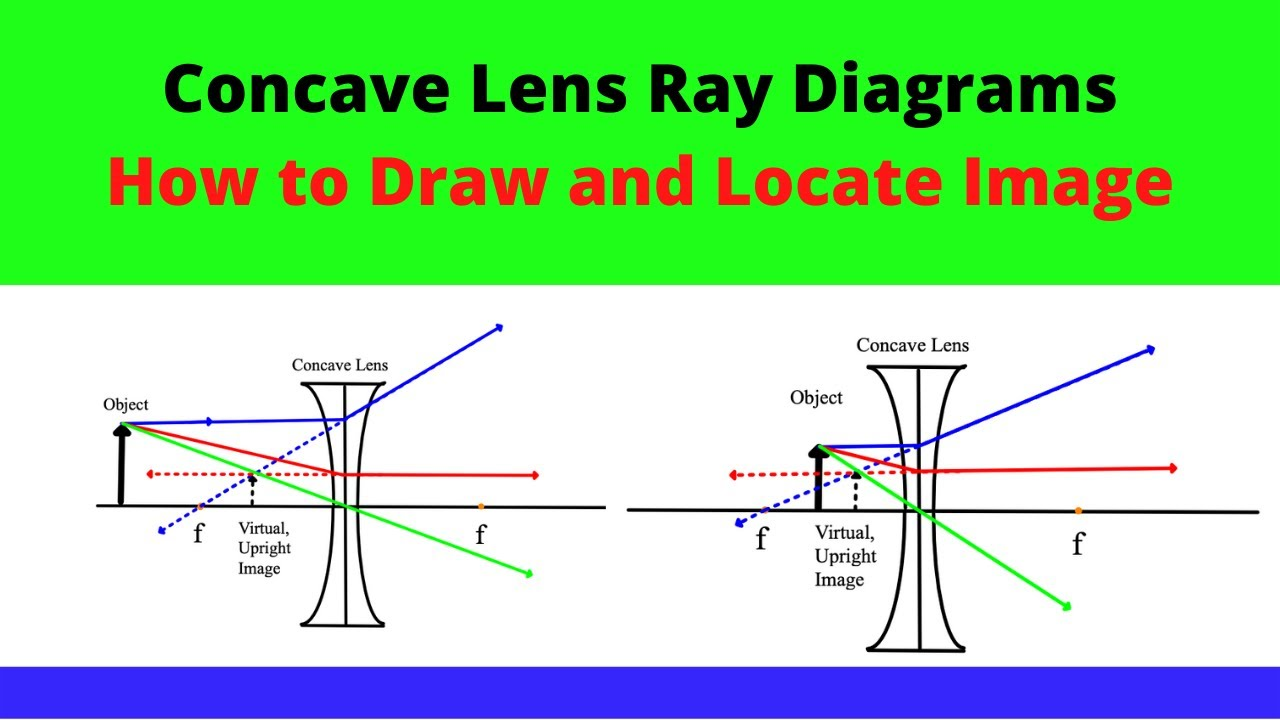
rules for drawing rays: CONCAVE LENS
ray 1: parallel to axis, refracts in a way that makes it seem that it came from f in the front
ray 2: goes towards f on the other side, and emerges parallel to axis
ray 3: goes through midpoint of lens unrefracted