PHYSMOD_ ES FOR WOUND HEALING
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Electrical stimulation for tissue healing and repair / wound healing
______ regeneration
______ control
Improved _____
Tissue regeneration
Edema control
Improved circulation
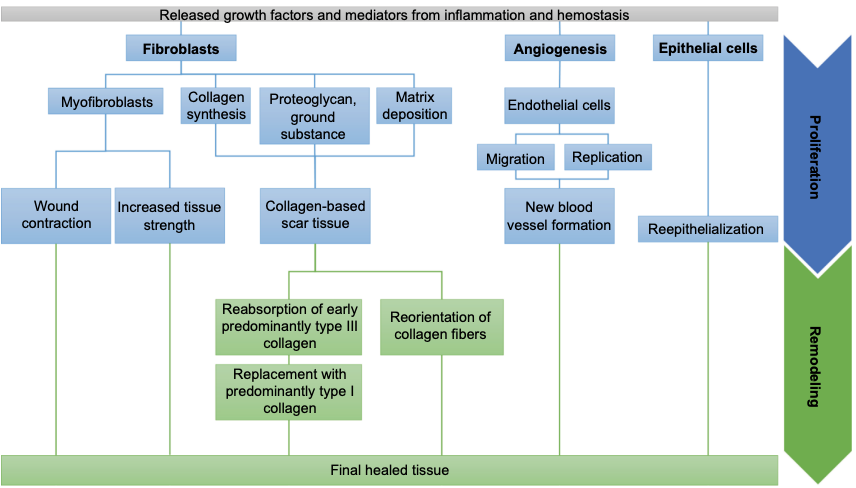
Wound Healing Process
HIPM
Homeostasis → Inflammation → Proliferation → Maturation
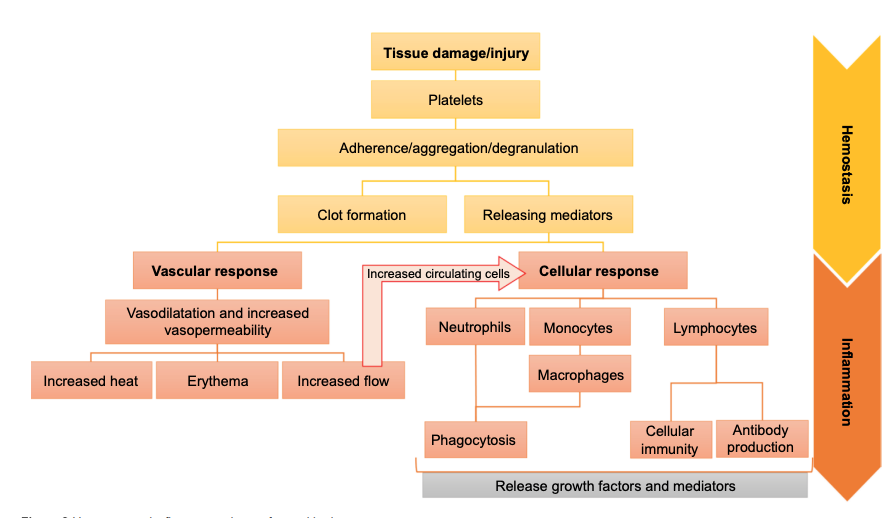
Wound Healing Process
Types of Currents used for wound healing:
MHRB
Microcurrents/ Low Intensity DC
High Voltage Pulsed Current
Russian Currents
Biphasic Pulsed Currents
Current
__________
Monophasic waveform that is continuous or pulsed modulated with polarity reversal
Peak amplitude of 999 uA/ < 1ma
Uses of Constant Current
Microcurrents/ Low Intensity DC
Current
__________
Twin-peak monophasic pulses
Peak voltage of 500V
10-100 USEC pulse duration
Uses Constant Voltage
HVPC
Current
__________
Continuous sine wave output of about 2500-5000Hz
Modulated to yield 50 bursts per second
Each burst is polyphasic time-modulated AC
MFBurstAC ( Russian Current)
Mother Fucker Burst AC = russian current
Current
__________
When muscle contraction is required to reduce edema
BPC
Biophysical Characteristics
Normal Skin battery
Found between stratum _____ and ______
_____ current bioelectrical system to maintain tissue health
Current flow shift to the _____ area → “Current of Injury”
_____ or _____ mimics and amplifies the weak human skin batteries at the wound site
Found between stratum corneum and dermis
Direct current bioelectrical system to maintain tissue health
Current flow shift to the injured area → “Current of Injury”
Microcurrent or HVPC mimics and amplifies the weak human skin batteries at the wound site
Physiological Basis
General Effects
________
Attraction of cells to an electrical
chargeElectrical stimulation promotes
tissue healing by ____ effects →
attract or repels charged particlesDue to ______
Galvatoxais
ionic
POLARITY
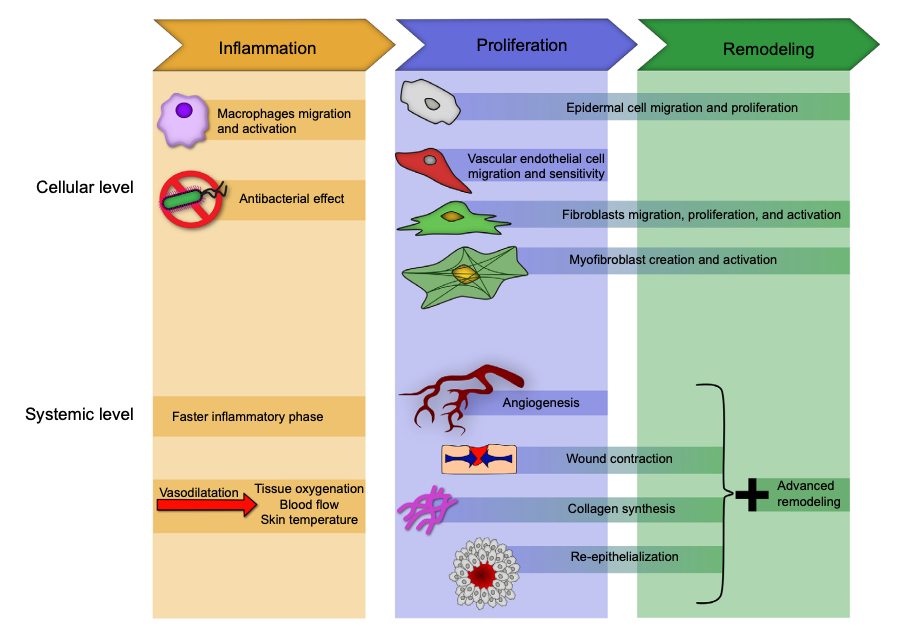
Physiological Basis
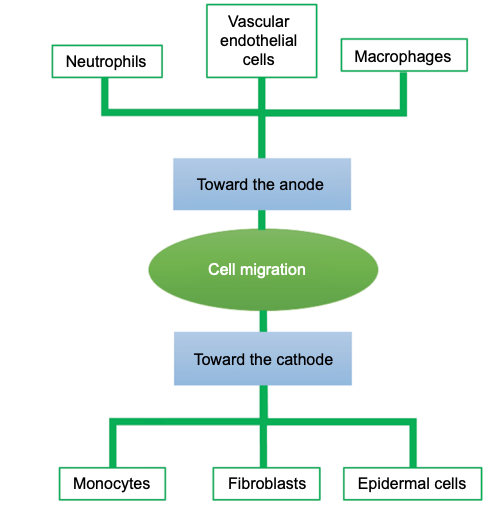
Physiological Basis: General Effects of Galvanotaxis
Physiological Basis: General Effects of Galvanotaxis
Phases of Wound Healing → Effects
Inflammation →______
Proliferative →_______
Maturation → ______
Anode (+) for Inflammation Phase; Cathode (-) for Proliferative & Maturation Phase
Inflammation → Phagocytosis & Autolysis
Proliferative → Fibroplasia
Maturation → Wound Contraction
Cont.
Phases of Wound Healing → Cell Polarity
Inflammation →______
Proliferative →_______
Maturation → ______
Macrophages (-); Neutrophils (-)
Fibroblasts (+)
Keratinocytes (+), Epidermal Cells (+)
Physiological Basis: General Effects in Inflammation Phase
Initiates the ____ repair process by its effect on the current of injury
INC ____ flow
Promotes _____
Enhances tissue _____
Controls ____
Solubilizes ____ products including ____ tissue
Initiates the wound repair process by its effect on the current of injury
Increases blood flow
Promotes phagocytosis
Enhances tissue oxygenation
Controls infection
Solubilizes blood products including necrotic tissue
Physiological Basis: General Effects in Proliferative Phase
Stimulates ____ and _____ cells
Stimulates DNA and protein _____
_____ ATP generation
Improves ____ transport
Produces better _____ matrix organization
Stimulates wound _____
Stimulates fibroblasts and epithelial cells
Stimulates DNA and protein synthesis
Increases ATP generation
Improves membrane transport
Produces better collagen matrix organization
Stimulates wound contraction
Physiological Basis: General Effects in Maturation Phase
Stimulates _____ cell reproduction and migration
Produces a ____, ___ scar
Stimulates epidermal cell reproduction and migration
Produces a smoother, thinner scar
Physiological Basis: General Effects in Germicidal Effect
Inhibiting the growth of action of microorganisms
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staphylococcus aureus
Conflicting evidences whether anode or cathode
just read it ;)
Physiological Basis: General Effects for Edema Control
Due to ____
Electrical stimulation is indicated
Due to _____
Electrical stimulation is indicated
Due to ____ disorders
Electrical stimulation is contraindicated
Clue: IIS
Due to inflammation
Electrical stimulation is indicated
Due to immobility
Electrical stimulation is indicated
Due to systemic disorders
Electrical stimulation is
contraindicated
Physiological Basis: General Effects for Edema Control
Due to Inflammation
ES to retard ____ formation
ES CANNOT DEC _____
Use of ____ → repels negatively charged proteins back to blood vessels & reduces pore size in microvessel walls
_____ at sensory level stimulation
Due to Inflammation
ES to retard edema formation
ES cannot decrease edema
Use of cathode → repels negatively charged proteins back to blood vessels & reduces pore size in microvessel walls
HVPC at sensory level stimulation
Physiological Basis: General Effects for Edema Control
Due to immobility
Muscle contraction → _____ effect
ES should be used together with ____ elevation and followed by
_____
Due to immobility
Muscle contraction → Pumping effect
ES should be used together with limb elevation and followed by
compression
Physiological Basis: General Effects for Improving Circulation
Conflicting evidences in improving circulation via muscle contraction
womp
Indications
____und healing
Burns
Ulcers (pressure, vascular or
neuropathic)
Surgical wounds
_____
Retardation of ____
Reduction of _____
_____ blood flow
Wound healing
Burns
Ulcers (pressure, vascular or
neuropathic)
Surgical wounds
Infections
Retardation of edema
Reduction of edema
Increase blood flow
Considerations
Electrode Placement
Over the wound
Around the wound
Infection control
Wrap electrodes with sterile gauze pads; saturate pads with normal saline
solutionObserve proper aseptic techniques (use of gloves, mask, gown and goggles)
Electrodes
Should be warmer than the wound but not warmer than 380C
Dosimetry Wound Healing
Parameters → LIDC → HVPC
Waveform →
Mode
Polarity →
Pulse Frequency →
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Treatment Time →
LIDC
Waveform → LIDC
Mode → Continuous Pulsed
Polarity → Negative (cells); use anode ;Positive (cells); use cathode
Pulse Frequency → Continuous: 0 Hz ;Pulsed: 1-200 Hz
Pulse Duration → NA
Amplitude → Comfortable tingling (1-999 μA)
Treatment Time → 30-90 min
Dosimetry Wound Healing
Parameters → LIDC → HVPC
Waveform →
Mode
Polarity →
Pulse Frequency →
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Treatment Time →
HVPC
Waveform → HVPC
Mode → Pulsed
Polarity → Negative (cells); use anode ;Positive (cells); use cathode
Pulse Frequency → 60-125 pps/Hz , 1-200 Hz
Pulse Duration → 40-100 usec
Amplitude → Comfortable tingling (150-500 μA)
Treatment Time → 45-60 min, 30-90min
Dosimetry Edema Control
Parameters → Inflammation
Waveform →
Mode
Polarity →
Pulse Frequency →
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Treatment Time →
Inflammation
Waveform → HVPC
Mode → Pulsed
Polarity → Negative (cells); use anode
Pulse Frequency → 100-120 pps/Hz
Pulse Duration → 40-100 usec
Amplitude → Comfortable tingling
Treatment Time → 20-30min
Dosimetry Edema Control
Parameters → Immobilization
Waveform →
Mode
Polarity →
Pulse Frequency →
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Treatment Time →
Imobilization
Waveform → BPC
Mode → Pulsed
Polarity → NA
Pulse Frequency → 30-50 pps / Hz; 2-5 sec equal on:off time
Pulse Duration → 150-350 usec
Amplitude → Visible Contraction
Treatment Time → 20-30min
Dosimetry INC BLOOD FLOW
Parameters → Circulation
Waveform →
Mode →
Polarity →
Pulse Frequency →
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Treatment Time →
Waveform → BPC
Mode → Pulsed
Polarity → NA
Pulse Frequency → 30-50 pps/Hz; 1-2 sec equal on:off time
Pulse Duration →150-350 usec
Amplitude → Visible Contraction
Treatment Time → 20-30 min