K101 Final Exam Study Guide
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
1. In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
polar covalent bonds.
2. Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments demonstrated conclusively that
organic molecules can be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on early Earth.
3. What do the four 'elements of life' -carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen-have in common?
They all have unpaired electrons in their valence shells.
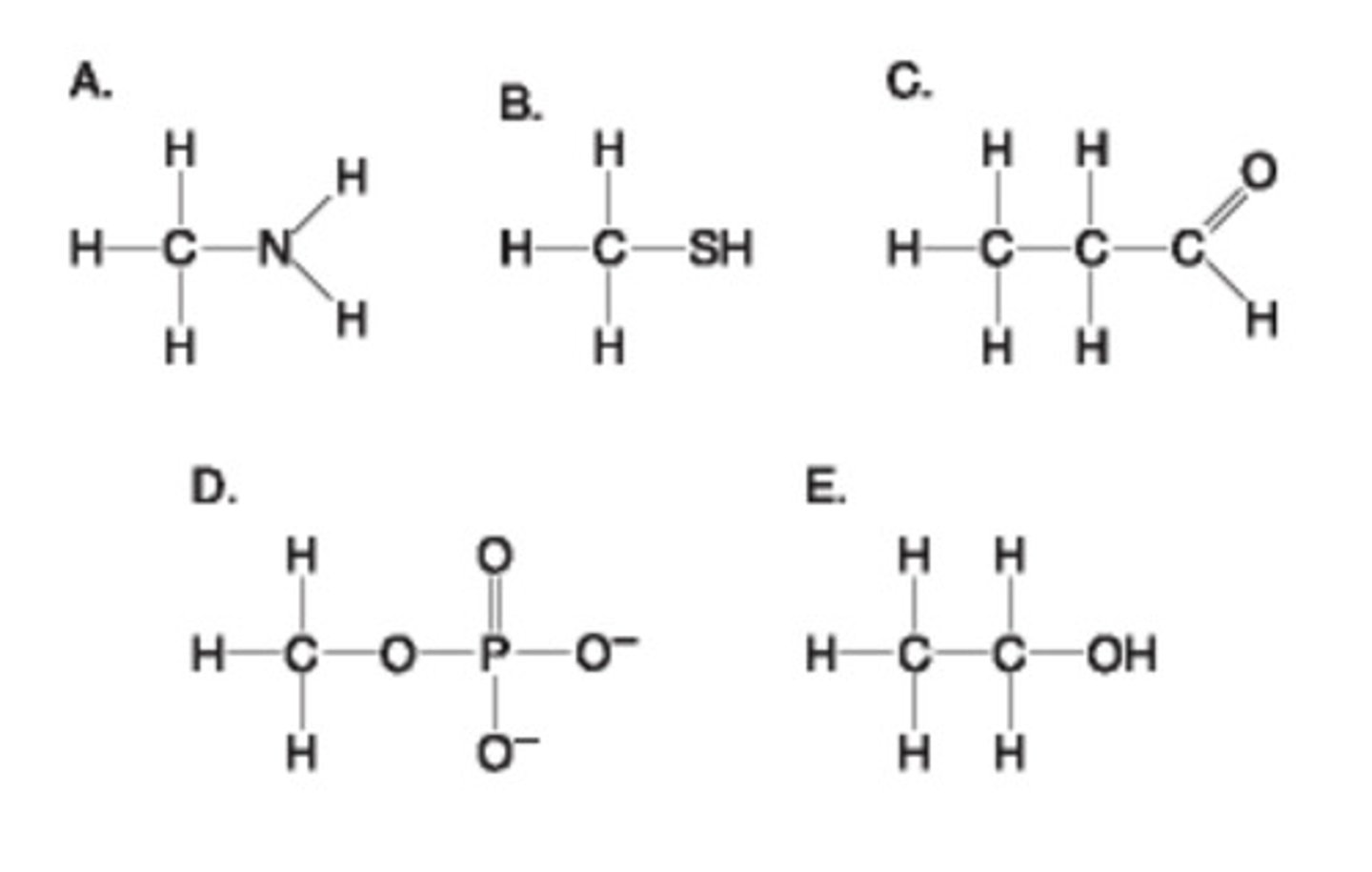
4. Using the functional group diagram at right answer A - E which of the following is incorrectly matched?:
A = amino group
B = thiol group
C = carbonyl (aldehyde)
D= organic phosphate
E= carboxyl group
E= carboxyl group
5. Water is able to form hydrogen bonds because
the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds
6. Which functional group shown at right is:
i) is an acidic functional group that can release H+ into a solution?
C. Carboxyl
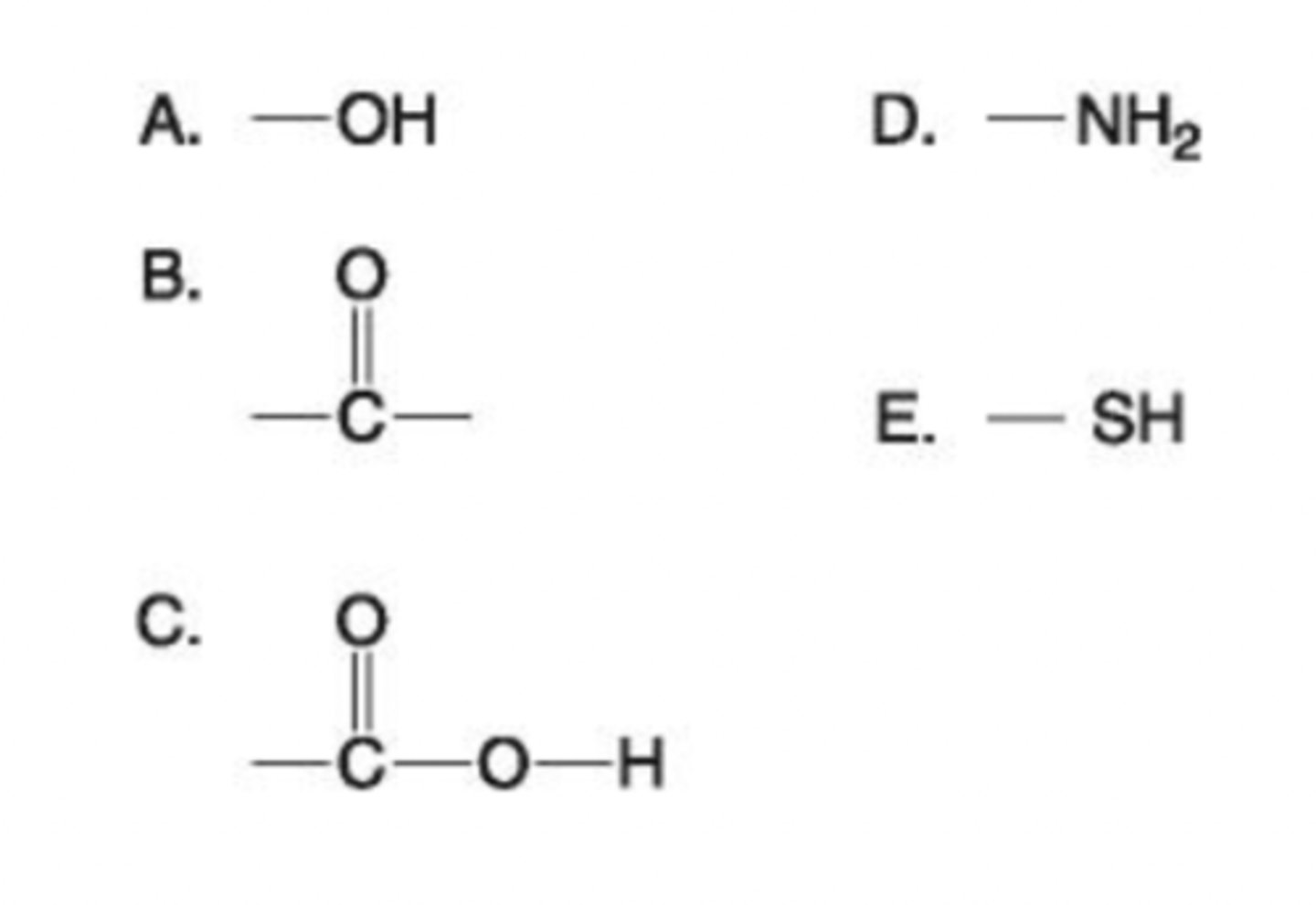
6. Which functional group shown at right is:
ii) a basic functional group that can accept H+?
D. Amine
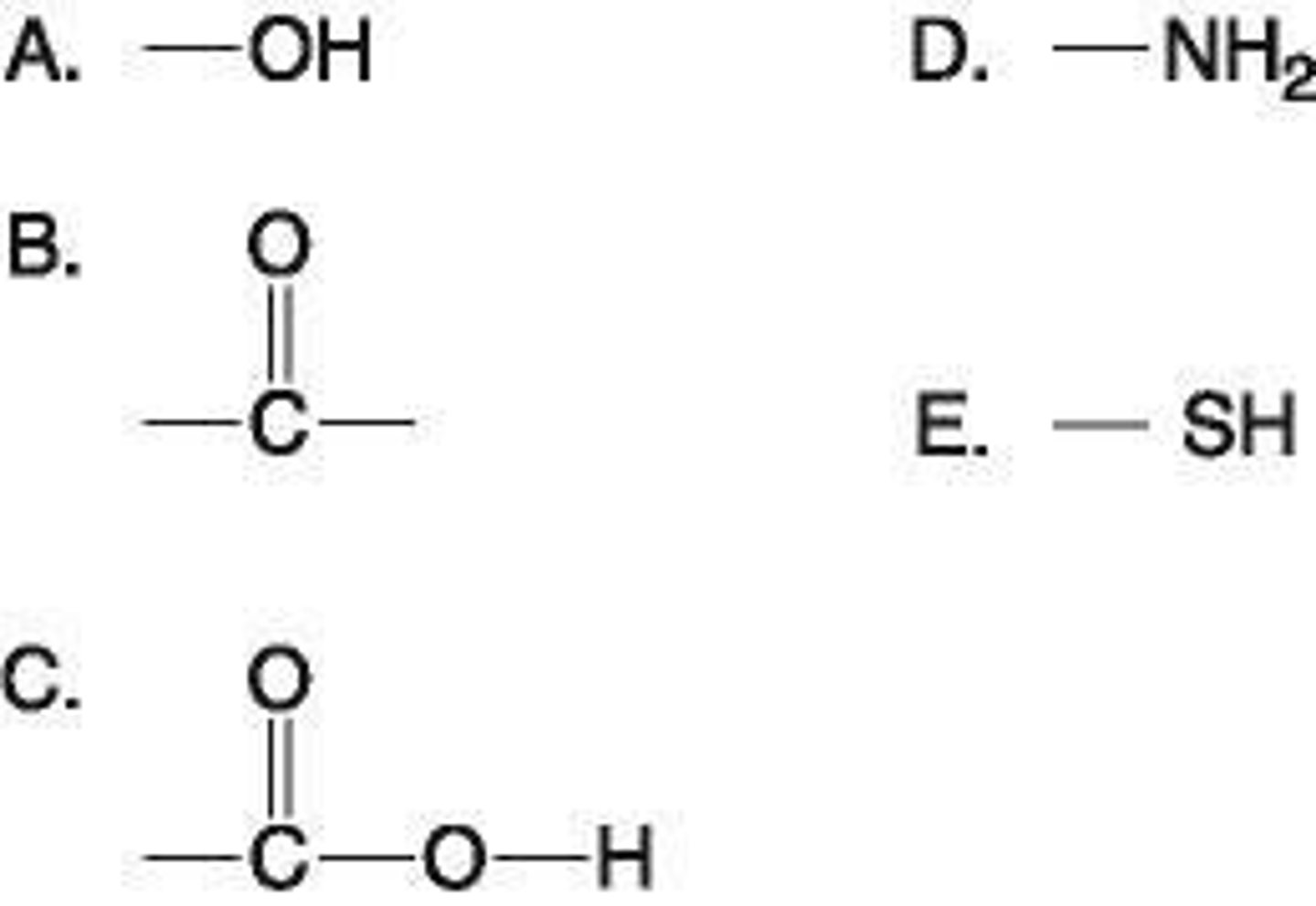
6. Which functional group shown at right is:
iii) can exist as a ketone or aldehyde configuration?
B. Carbonyl
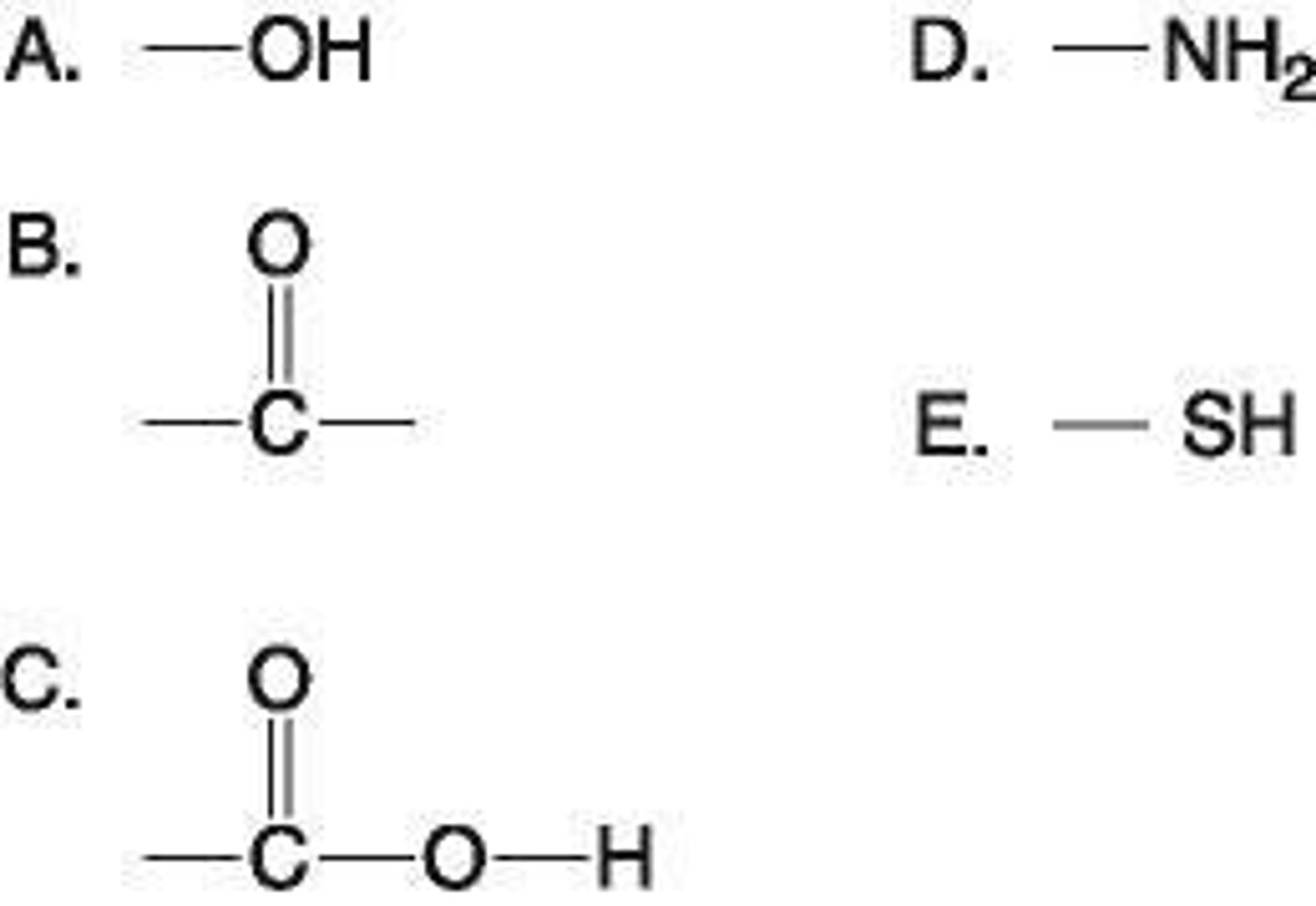
6. Which functional group shown at right is:
iv) a characteristic of alcohols?
A. Hydroxyl
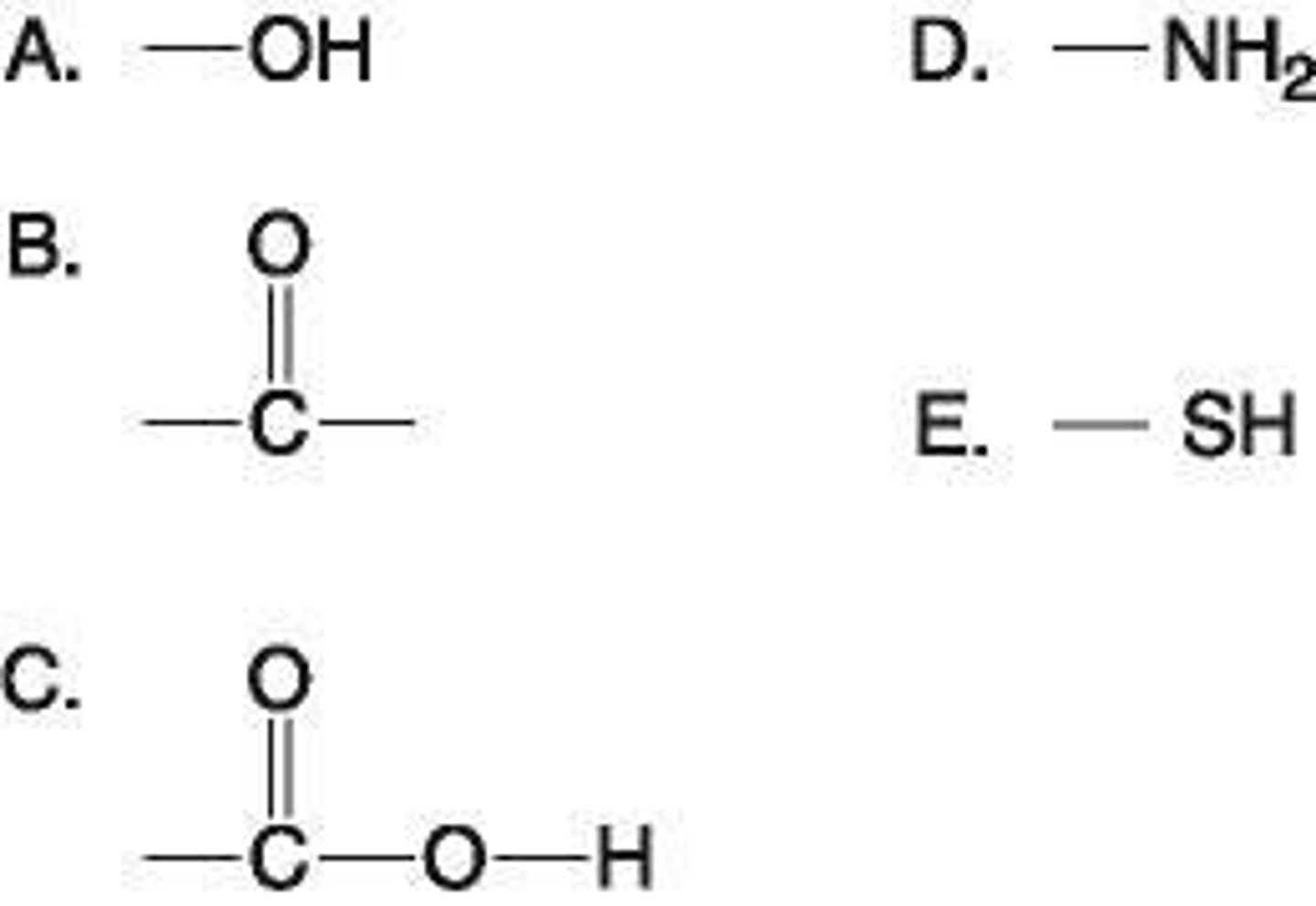
6. Which functional group shown at right is:
v) helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
E. Sulfhydryl
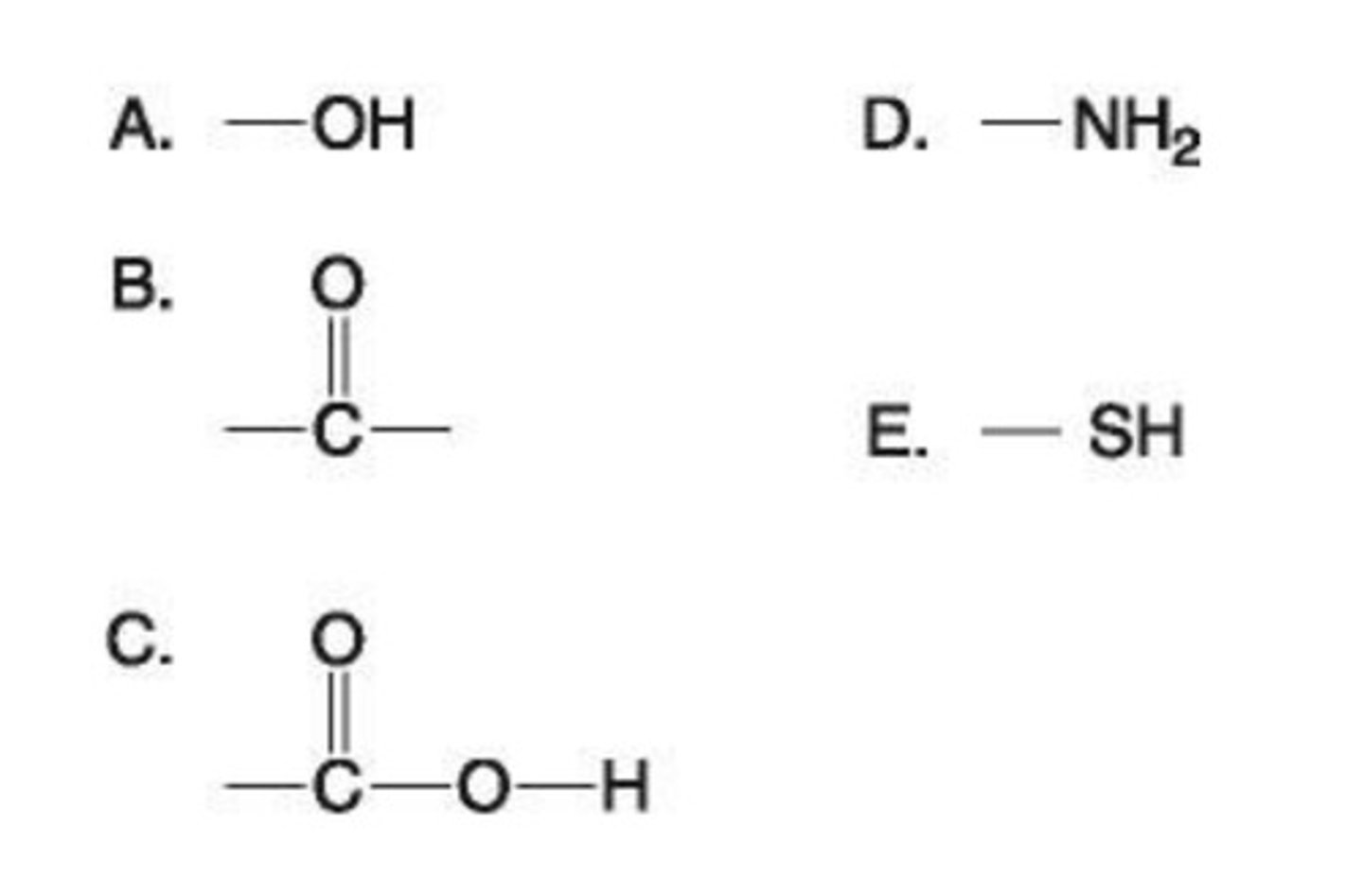
7. Which modifications of fatty acids will best keep triglycerides solid at warmer temperatures?
adding hydrogens to the fatty acids
8. A comparison of saturated and naturally occurring unsaturated fats reveals that the unsaturated fats are __________ at room temperature and have _______:
Liquids; cis double bonds
9. A molecule with four joined rings that is the precursor of vertebrate sex hormones (See Box 4.in figure below) and is also found in the vertebrate phospholipid bilayer is:
cholesterol
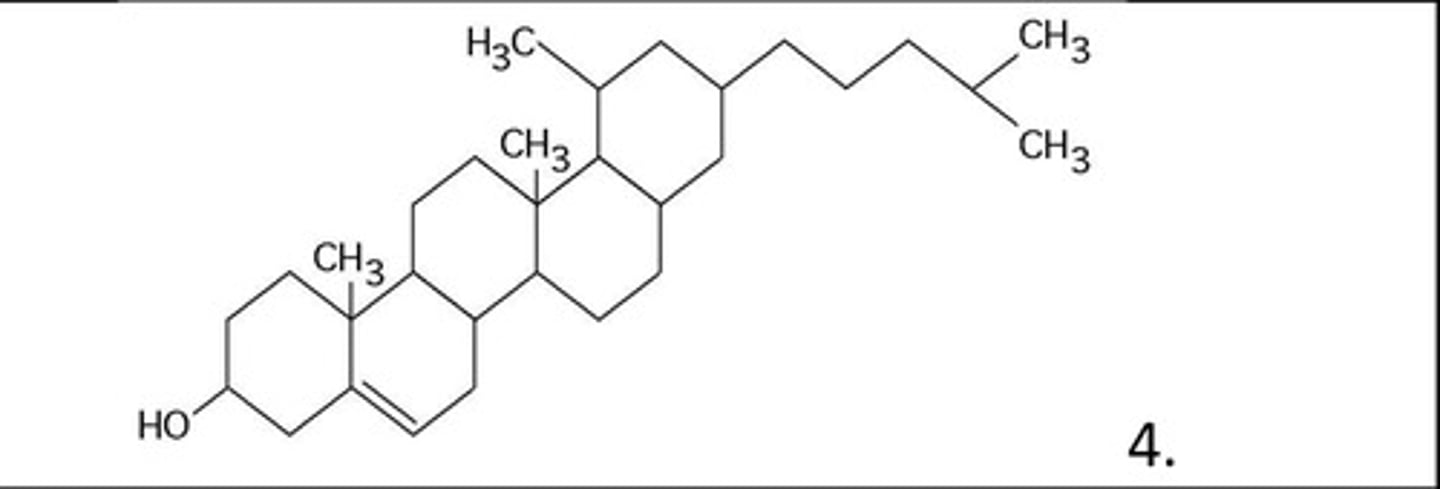
10. A molecule with the formula C18H36O2 is probably a __, where one with the formula C6H12O6 is probably a ___
fatty acid and monosaccharide, respectively
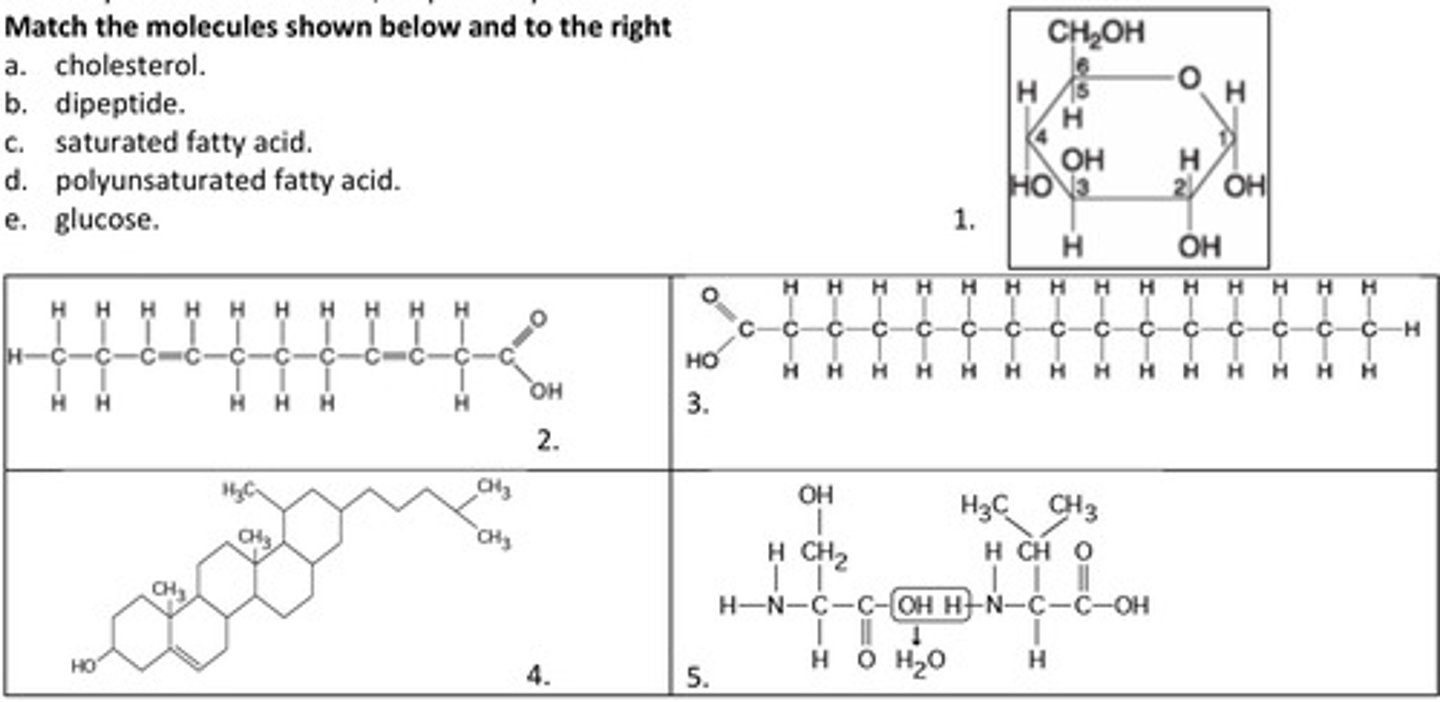
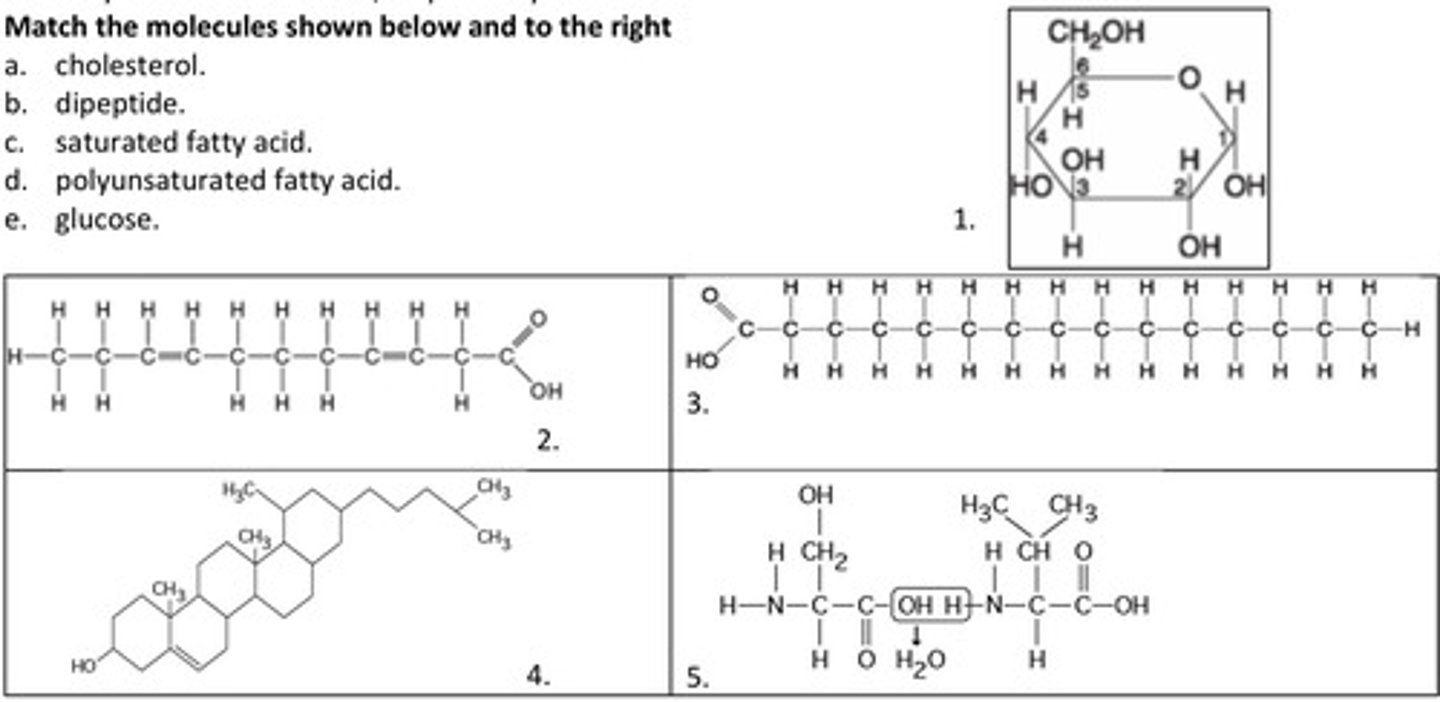
11. Match the molecules shown below and to the right
a. cholesterol.
4
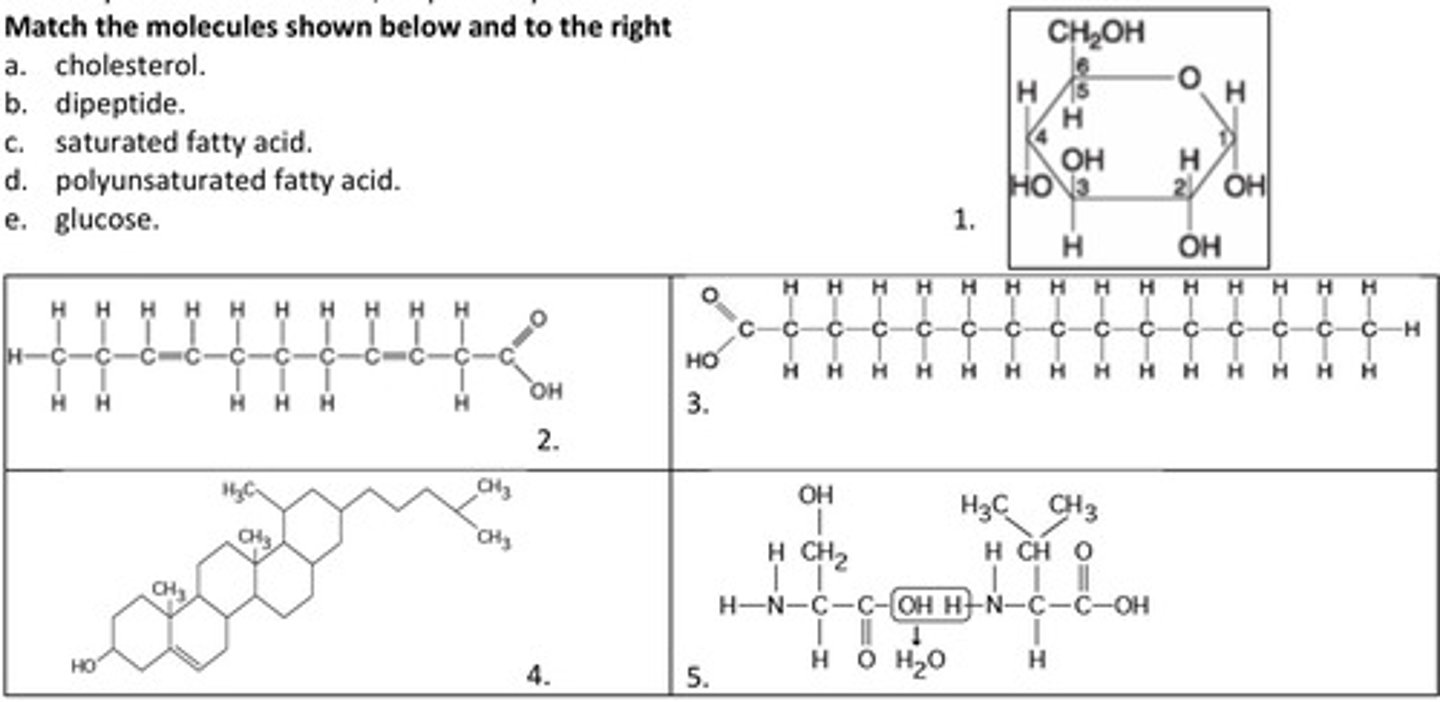
11. Match the molecules shown below and to the right
b. dipeptide.
5
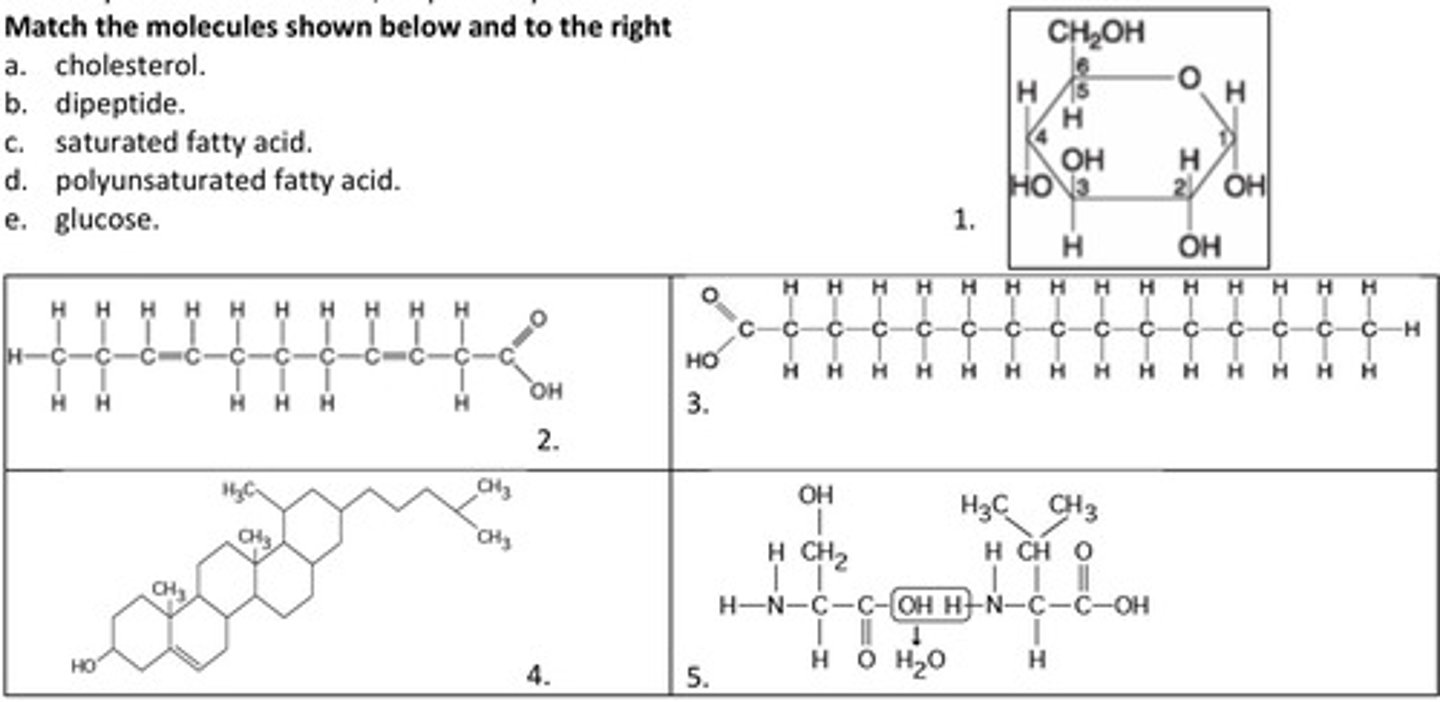
11. Match the molecules shown below and to the right
c. saturated fatty acid.
3
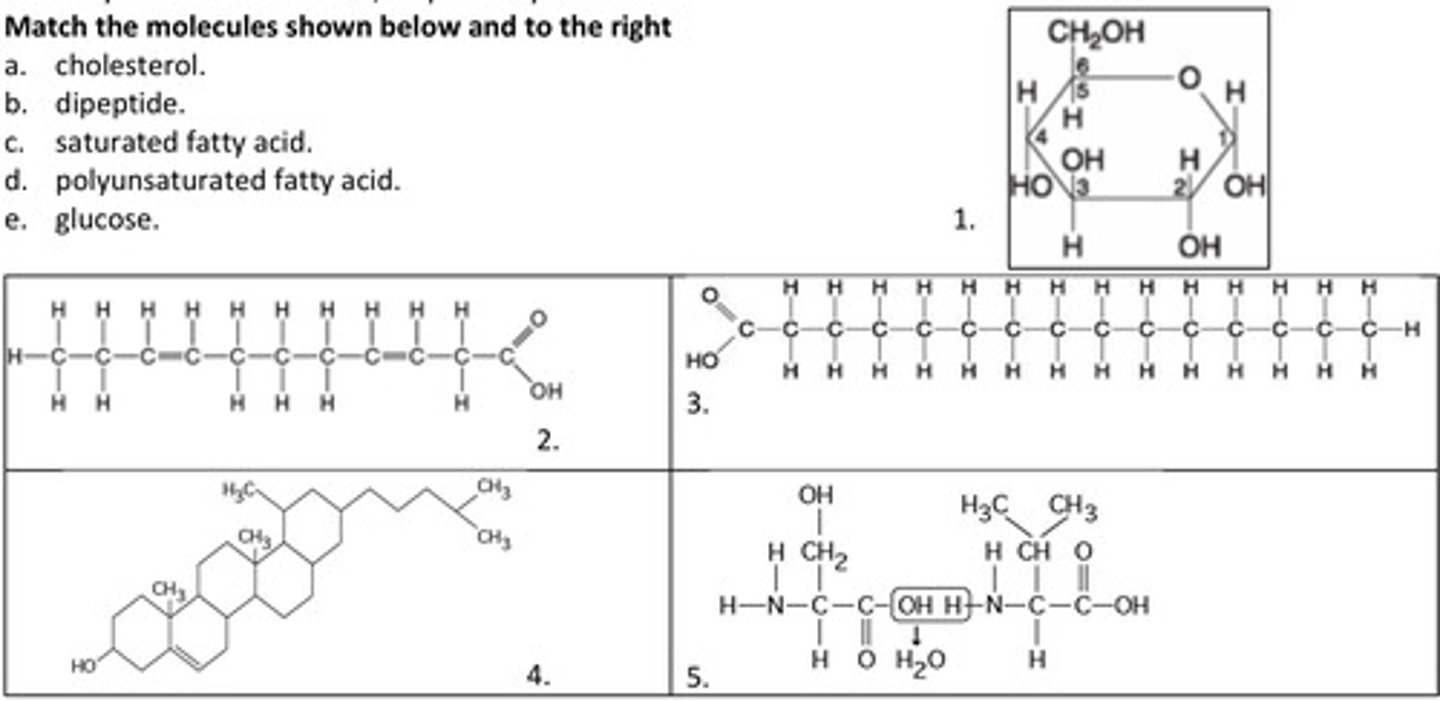
11. Match the molecules shown below and to the right
d. polyunsaturated fatty acid.
2
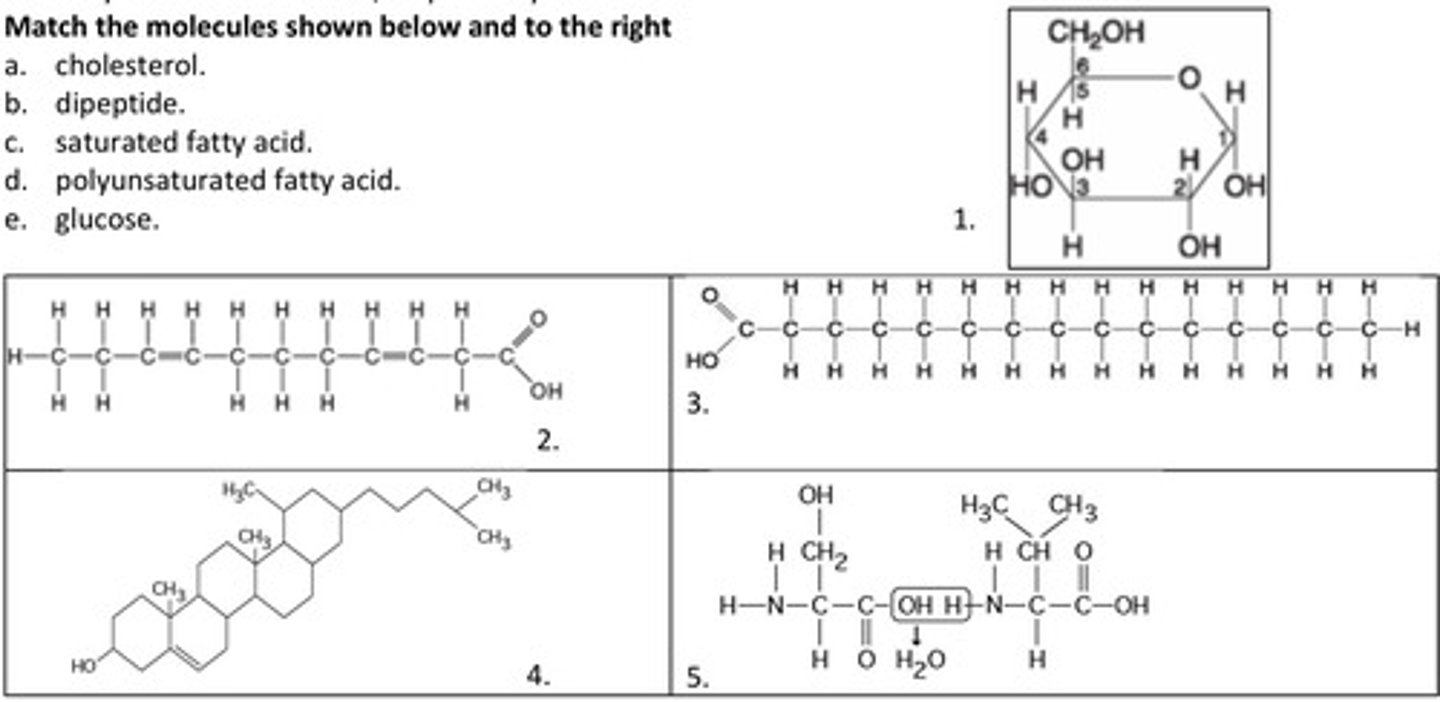
11. Match the molecules shown below and to the right
e. glucose.
1
12. Which of the following statements is/are true regarding chemical reaction (5) illustrated above?
It results in a peptide bond.
13. A bond that forms by joining monomers (such as nucleotides or amino acids) into polymers (such as DNA or insulin) is a(n):
Covalent bond
14. Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that they
are synthesized from subunits by dehydration reactions.
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
i) Nucleus
C. Site transcription of mRNA and tRNA for protein synthesis
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its functioni)
ii) Mitochondria
E. Synthesis of ATP via oxidative phosphorylation
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
iii) Nucleolis
F. Site of rRNA for protein synthesis
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
iv) Rough ER
H. Synthesis of the insulin receptor, a transmembrane glycoprotein
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
v) Golgi apparatus
A. Sorting of proteins targeted for extracellular secretion
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
vi) Lysosome
G. Intercellular digestion
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
vii) Smooth ER
D. Synthesis of the steroid hormone testosterone
15. Match the following parts of the cell to its function
viii) Extracellular Matrix
B. Site of cell-cell adhesion and cell recognition
16. Proteins that are manufactured for secretion (export from the cell):
are made in the rough ER and packaged in transport vesicles
17. Mammalian blood contains the equivalent of 0.15 M NaCl. Seawater contains the equivalent of 0.45 M NaCl.
What will happen if red blood cells are transferred to seawater?
Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse.
18. All of the following are functions of integral membrane proteins except
Synthesis of hormones.
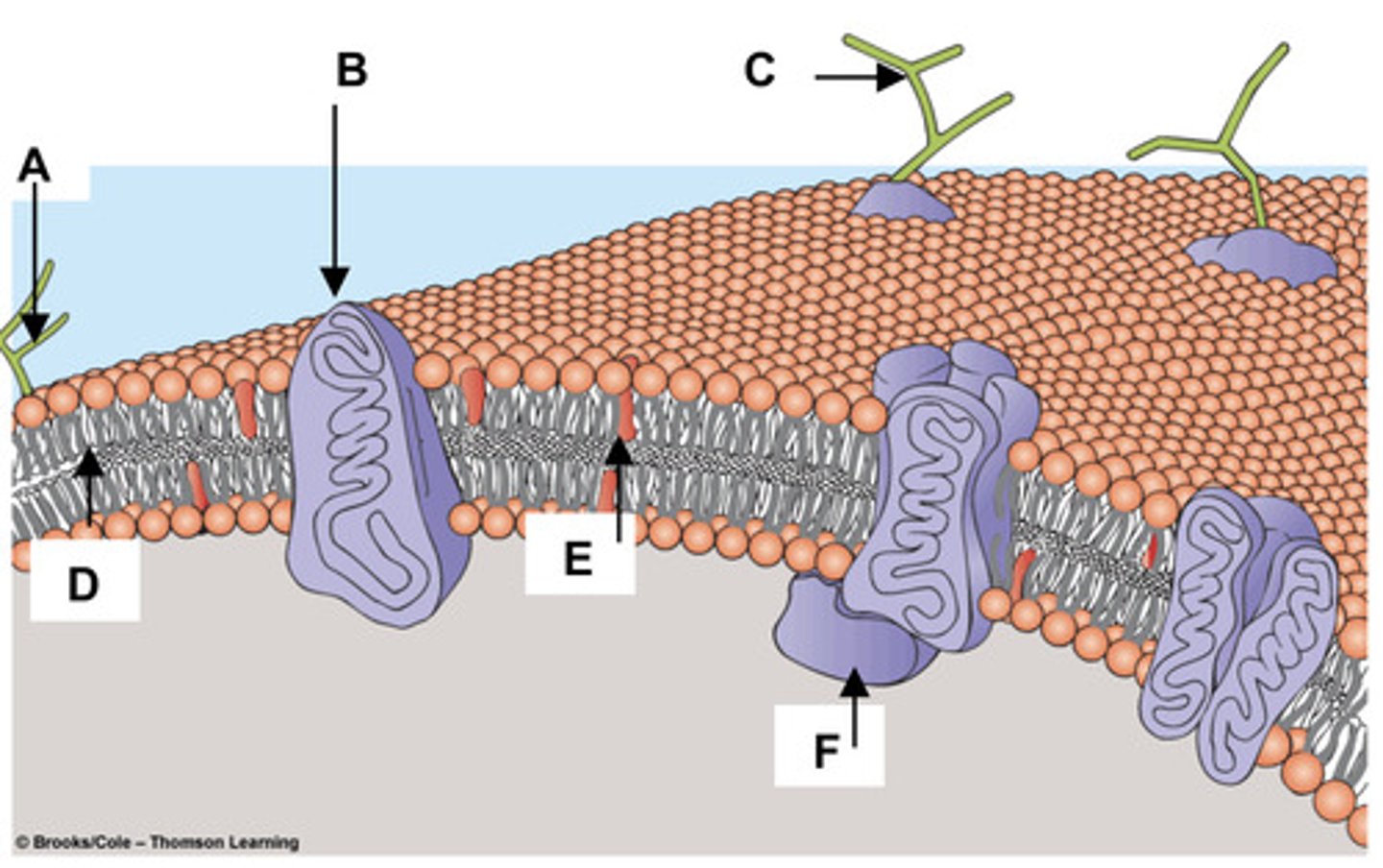
19. Match the components of the plasma membrane
with the letters in the figure at right.
a. Cholesterol -
E
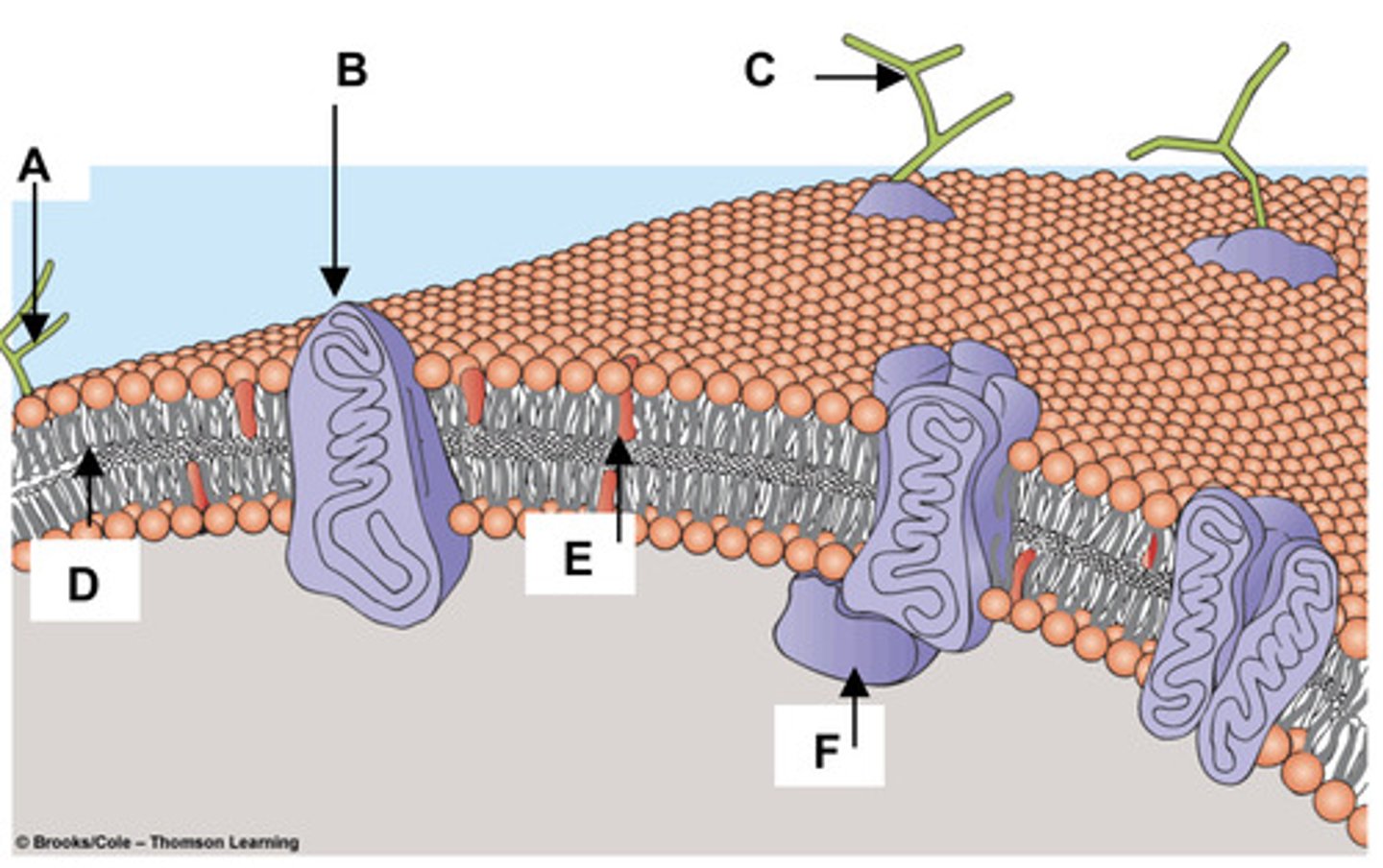
19. Match the components of the plasma membrane
with the letters in the figure at right.
b. Glycolipid -
A
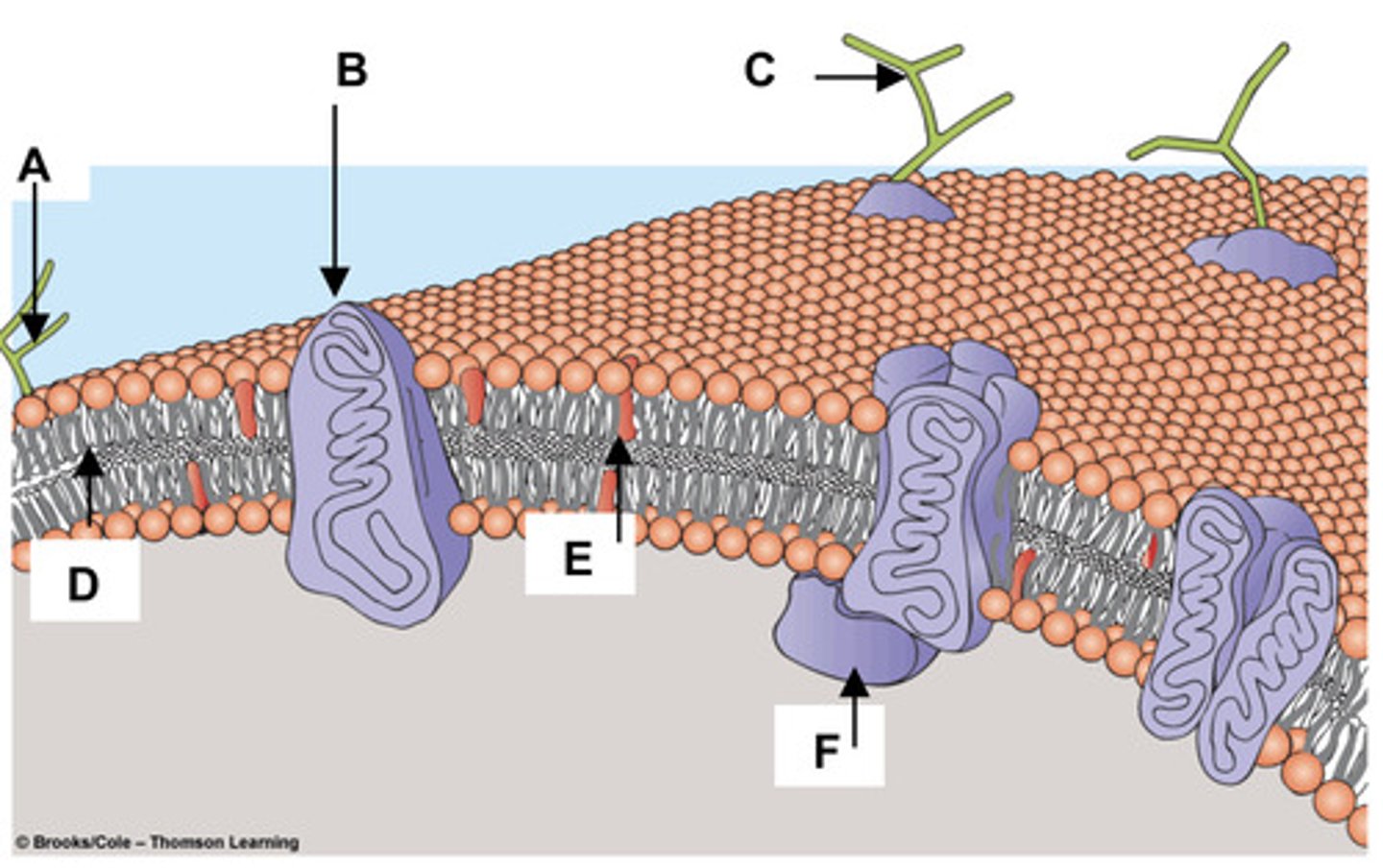
19. Match the components of the plasma membrane
with the letters in the figure at right.
c. Integral Membrane Protein -
B
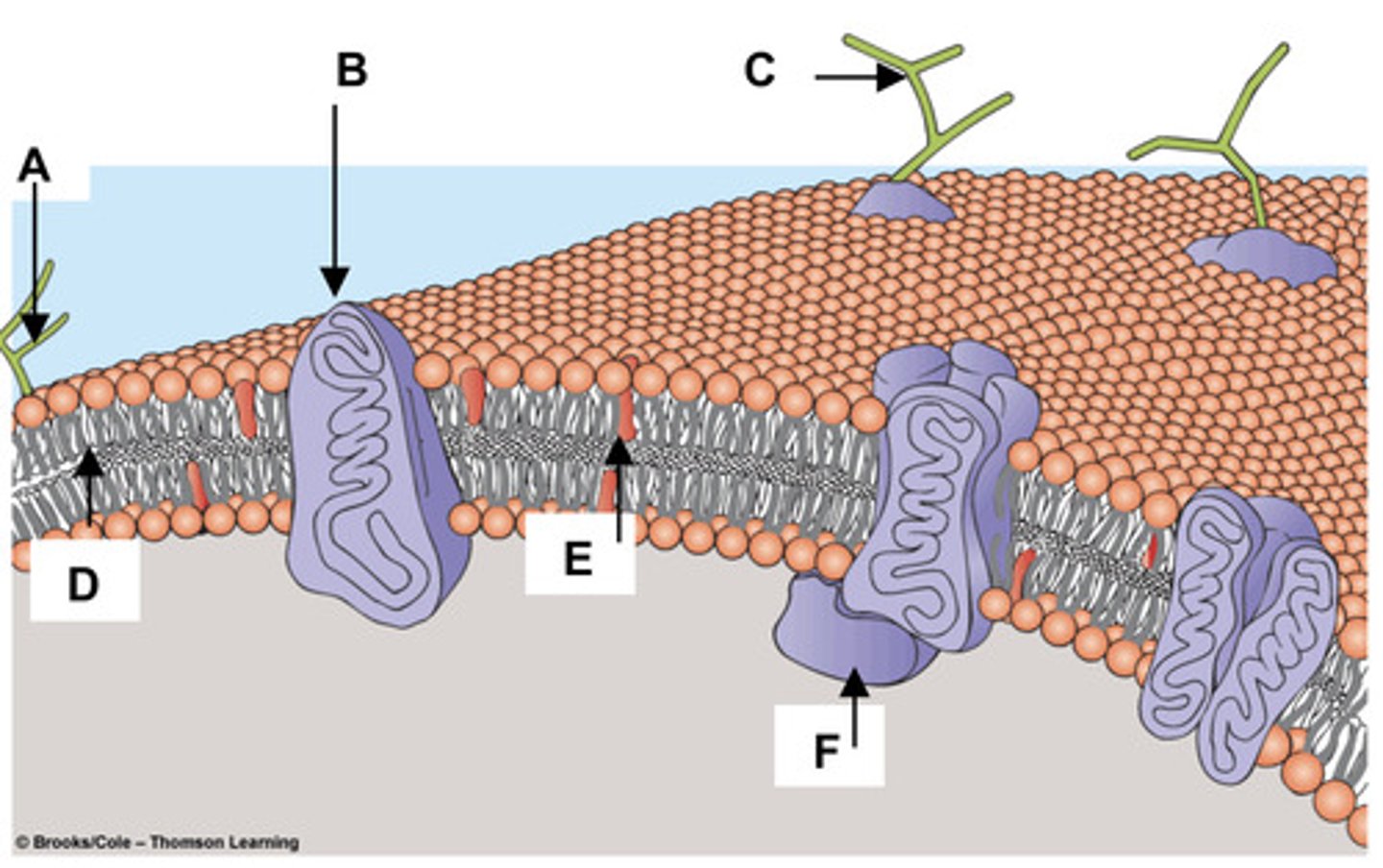
19. Match the components of the plasma membrane
with the letters in the figure at right.
d. Peripheral Membrane Protein -
F
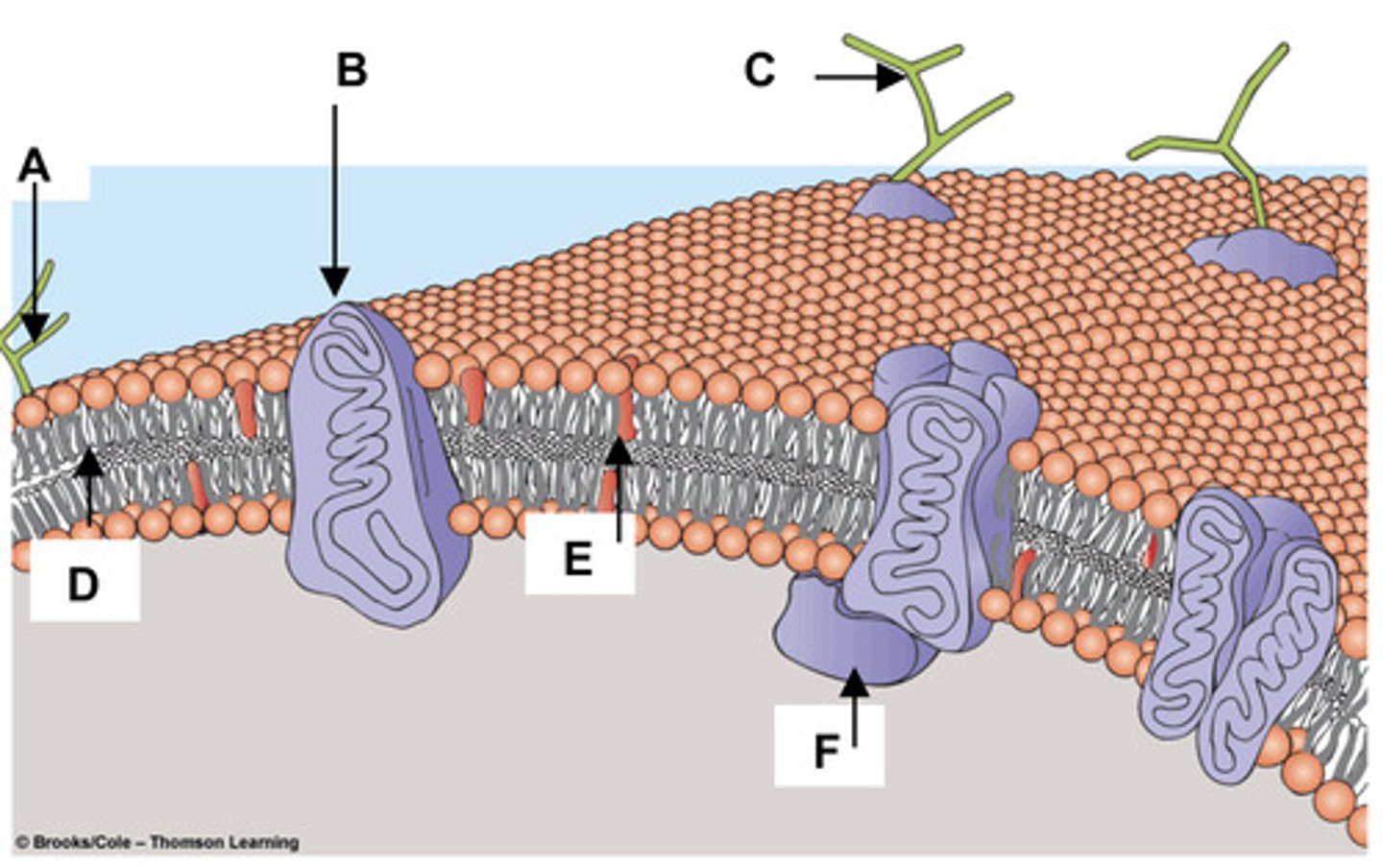
19. Match the components of the plasma membrane
with the letters in the figure at right.
e. Glycoprotein -
C
20. Which of the following types of reactions would decrease the entropy within a cell?
anabolic reactions
21. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
a. Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b. It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
c. Its terminal phosphate group has unusually strong covalent bonds that generate free energy.
a. Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b. It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
22. Increasing the substrate concentration in a reaction could overcome which of the following?
saturation of the enzyme activity
23. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: The primary way that cells do work is called energy coupling, using ATP. Which
statements below statements accurately defines energy coupling?
a. Anabolic reactions drive catabolic reactions.
b. Exergonic reactions drive endergonic reactions.
c. Endergonic reactions drive exergonic reactions.
d. ATP hydrolysis releases free energy that can be coupled to an endergonic reaction via the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
e. Endergonic and exergonic reactions occur independently of each other.
b. Exergonic reactions drive endergonic reactions.
d. ATP hydrolysis releases free energy that can be coupled to an endergonic reaction via the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
24. The general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein is
protein kinase
25. In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation
26. Why is the Calvin cycle said to be dependent on the light reactions?
The light reactions produce the ATP energy and NADPH for sugar production in the Calvin cycle.
27. One function of alcohol and lactic acid fermentation is to
oxidize NADH to NAD+.
28. When skeletal muscle cells undergo anaerobic respiration, they become fatigued and painful. This is now known to be caused by
buildup of lactate.
29. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Which of the 4
kinase enzymes in glycolysis might be the
enzyme shown below?
a. Hexokinase
b. Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
c. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
d. Phosphoglycerokinase (PGK)
b. Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
d. Phosphoglycerokinase (PGK)
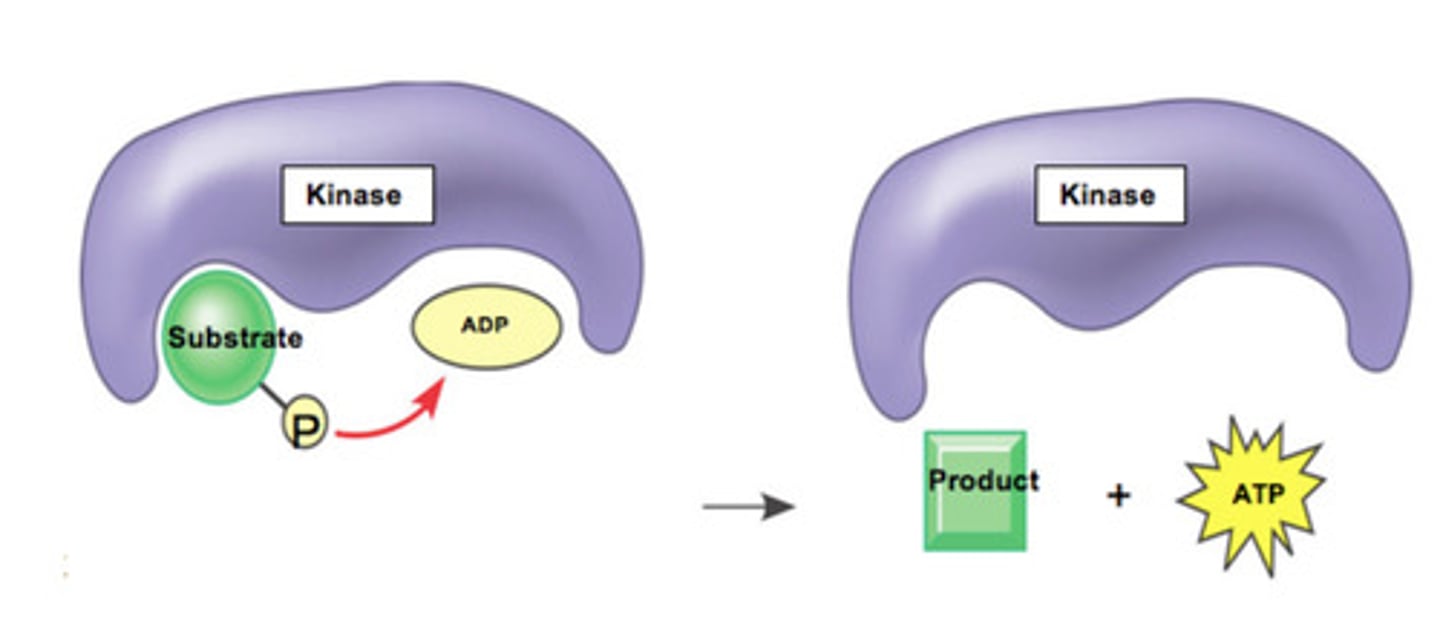
30. Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
a. Krebs cycle
v) Mitochondrial matrix
30. Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
b. Calvin cycle
iv) Chloroplast stroma
30. Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
c. Light reactions
i) Thylakoid membrane
30. Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
d. Proton Gradient in aerobic respiration
iii) Mitochondrial inner membrane space
30. Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
e. Proton Gradient in light reactions
ii) Thylakoid lumen
31. Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed during glycolysis?
100%
32. A C4 plant initially fixes CO2 into ____ where a C3 plant fixes CO2 into _______
Oxaloacetic acid using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco.
33. Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction? 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidized.
34. The oxygen consumed during aerobic cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
35. Which of the following is NOT true about Rubisco?
It is a kinase
36. Up to 60% of all medicines used today influence what structures in the cell membrane?
G-protein linked receptors
37. How does adenylyl cyclase help transmit signals within a cell?
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP, which then amplifies the signal throughout the cell.
38. MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
a. Epinephrine
Ligand
38. MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
b. Intergral membrane protein receptor
GPCR
38. MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
c. Intergral membrane protein enzyme
Adenylyl cyclase
38. MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
d. Peripheral membrane protein that binds GTP
G-Protein
38. MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
e. Second messenger generated from ATP
cAMP
39. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are found at high levels on various cancer cells. A protein, Herceptin, has
been found to bind to an RTK known as HER2 if which of the following is true?
If the patient's breast cancer cells have detectable HER2
40. MATCHING: Enzyme Roundup: Cell Signalling
a. Converts ATP to cAMP after G-protein signalling
Adenylyl Cyclase
40. MATCHING: Enzyme Roundup: Cell Signalling
b. Converts cAMP to AMP; inhibited by caffeine
Phosphodiesterase
40. MATCHING: Enzyme Roundup: Cell Signalling
c. Converts membrane lipids to IP3 and DAG
Phospholipase C
40. MATCHING: Enzyme Roundup: Cell Signalling
d. Phosphorylates relay molecules after activation and dimerization
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
41. The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (R-TKs) is always characterized by
Dimerization and auto-phosphorylation.
42. If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be
2x.
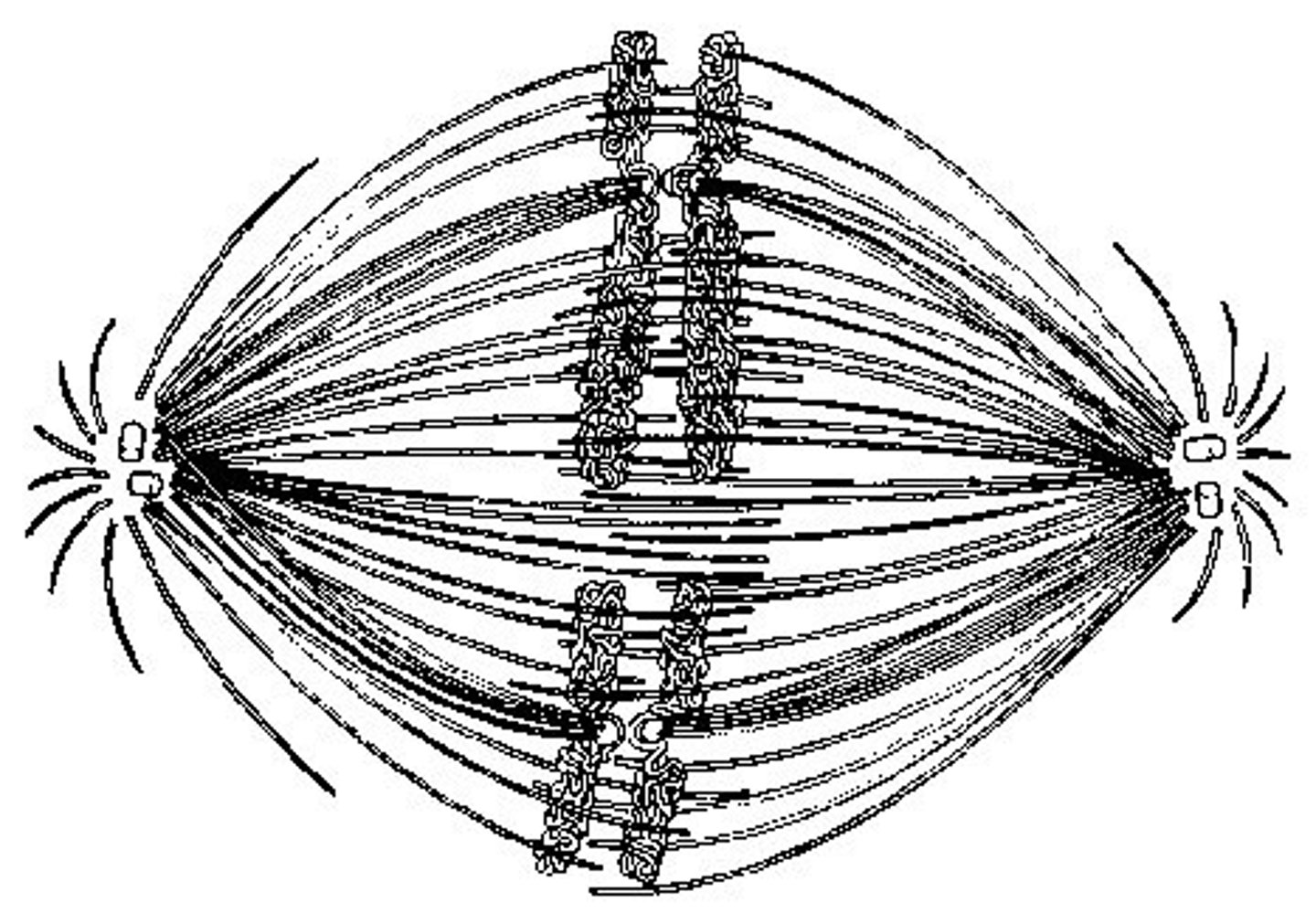
43. If the cell whose nuclear material is shown at right continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
formation of telophase nuclei
44. Observations of cancer cells in culture support the hypothesis that cancer cells _____
a. have altered plasma membranes and cytoskeletal proteins
b. have mutations or deletions in tumor suppressors like p53
c. have the ability to stimulate new blood vessel formation
d. do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition of growth
all of the above
45. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Which of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
a. The cells formed have the same combination of genes as found in the initial cell.
b. Homologous chromosomes separate.
c. The nuclear envelope disappears.
d. Sister chromatids undergo disjunction.
e. A spindle apparatus forms.
Homologous chromosomes separate.
46. In a plant with a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 46, how many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present in a cell that has just entered Meiosis II? (We want everyone correct!)
0
47. Using a microscope to examine the skin cells from a female, it is apparent that each nucleus has two Barr bodies. From this karyotype, it can be concluded that the woman's chromosomal condition is
47, XXX
48. At what stage of meiosis do cells become haploid?
Telophase I
49. After Telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
50. Homologous chromosomes synapse or pair during:
prophase I.
51. Mendel's law of independent assortment has its basis in which of the following events of meiosis?
alignment of tetrads at the equator in metaphase
52. In a population with two alleles for cystic fibrosis, C and c, the frequency the recessive allele is 0.6. What percent of the population would be heterozygous carriers for cystic fibrosis if the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
48%
53. Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbTt × BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
1/2
54. SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Blood Type: What are the probabilities for blood types in the offspring of individuals
who both have type AB blood?
a. Type A = 25%
b. Type B = 25%
c. Type AB = 25%
d. Type AB = 50%
e. Type O = 25%
a. Type A = 25%
b. Type B = 25%
d. Type AB = 50%
55. Epistasis: A black Labrador retriever (BbEe) is crossed with a chocolate Lab (bbEe). In a litter of 16 F1 puppies, what are the likely proportions of black, chocolate or yellow Labs?
6 Black, 6 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
56. Sex linkage: SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Hemophilia is an X-linked, recessive trait. If a male has hemophilia (XfY), and his spouse is heterozygous for blood clotting factors (XFXf),
a. There is a 50% chance that their sons will have hemophilia
b. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will have hemophilia
c. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will be carriers for hemophilia
d. All of their daughters will have hemophilia
e. All of their sons will have hemophilia
a. There is a 50% chance that their sons will have hemophilia
b. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will have hemophilia
c. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will be carriers for hemophilia
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
i) Marfan's
Autosomal dominant condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
ii) Tay Sachs
Autosomal recessive condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
iii) Cystic Fibrosis
Autosomal recessive condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
iv) Hemophilia
X-linked condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
v) Achondroplasia
Autosomal dominant condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
vi) Schizophrenia
Multifactorial condition
57. Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used
more than once
vii) Polydactyly
Autosomal dominant condition
58. Maize (corn) plants are tall if they have the genotype HH or Hh, and they are short if they have genotype hh. If a tall plant is mated with a short plant as a Test Cross, which outcome would indicate that the tall parent corn plant was heterozygous?
The ratio of tall offspring to short offspring is 1:1. (50%:50%)
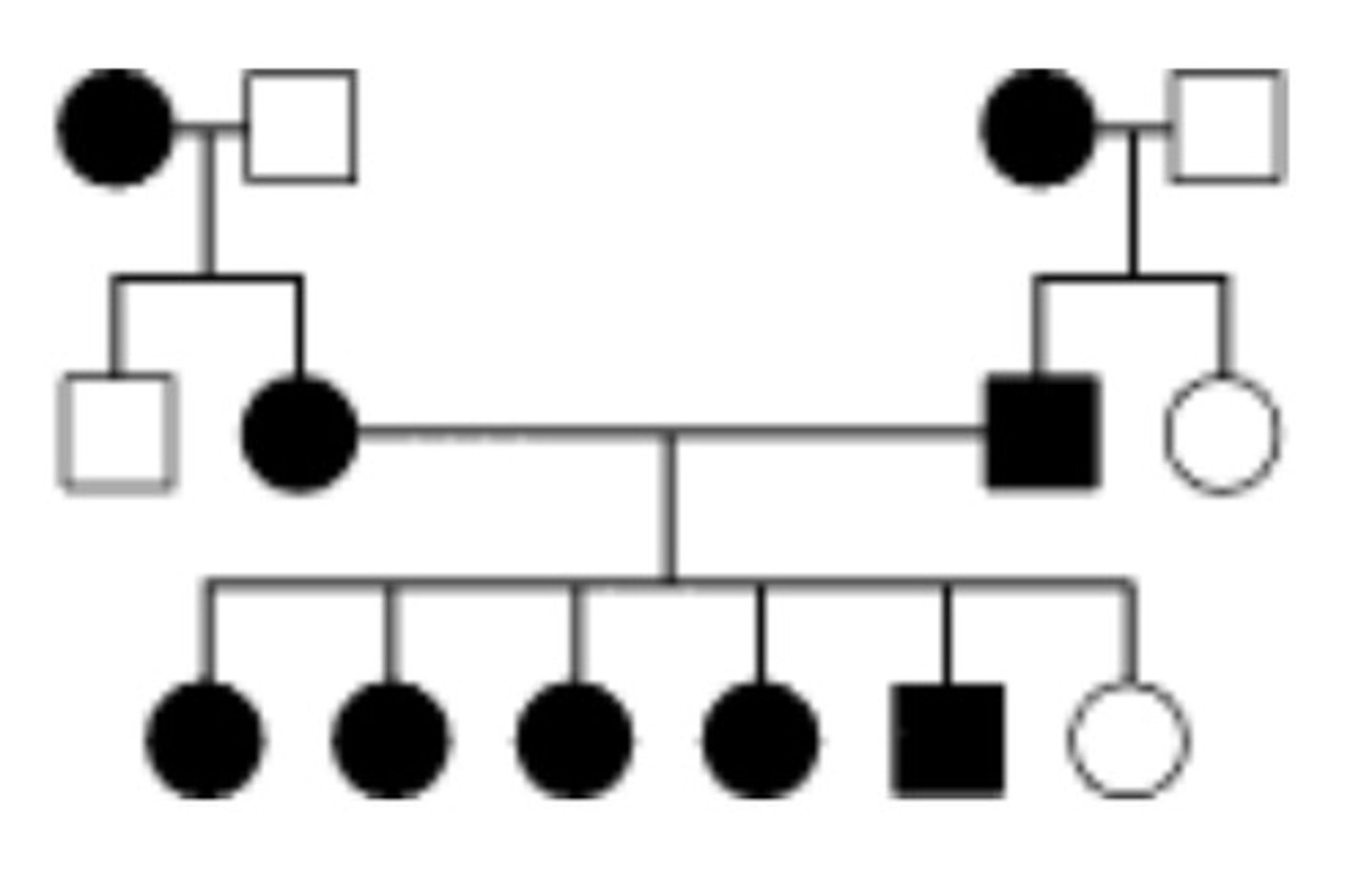
59. The trait found in the individuals is represented by the shaded symbols. Which of the following patterns of transmission for this gene is/are consistent with this pedigree?
autosomal dominant
60. Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive system, and other organs, resulting in a range of symptoms. Which of the following terms best describes this?
pleiotropy
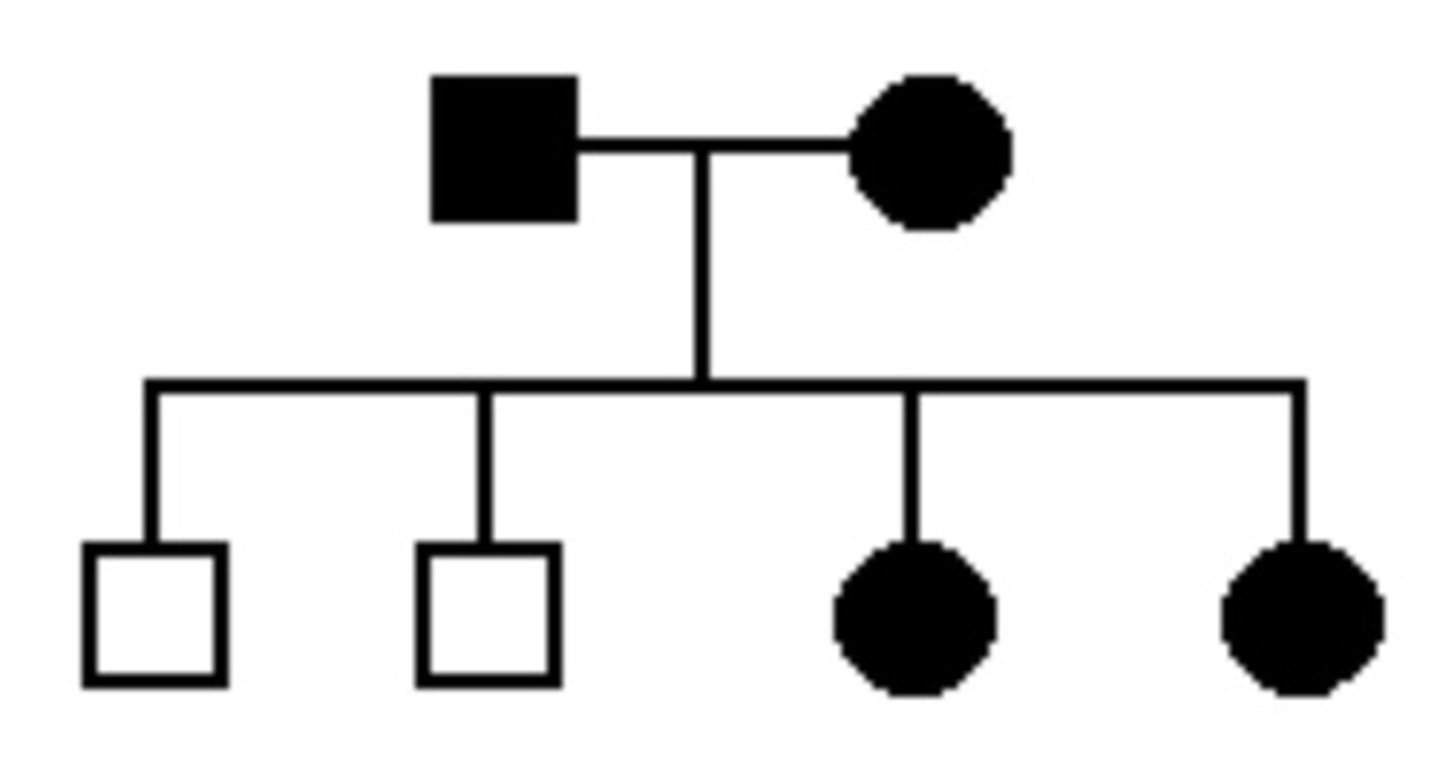
61. The pedigree at right shows a family with a disease pattern
indicated by shaded symbols. Which of the following patterns of
transmission for this gene are consistent with this pedigree?
autosomal dominant
62. A scientist removed the AAC nucleotides at the 3' end of the tRNA corresponding to the amino acid methionine. Which of the following describes the most likely result?
The amino acid methionine will not be able to bind to the tRNA.
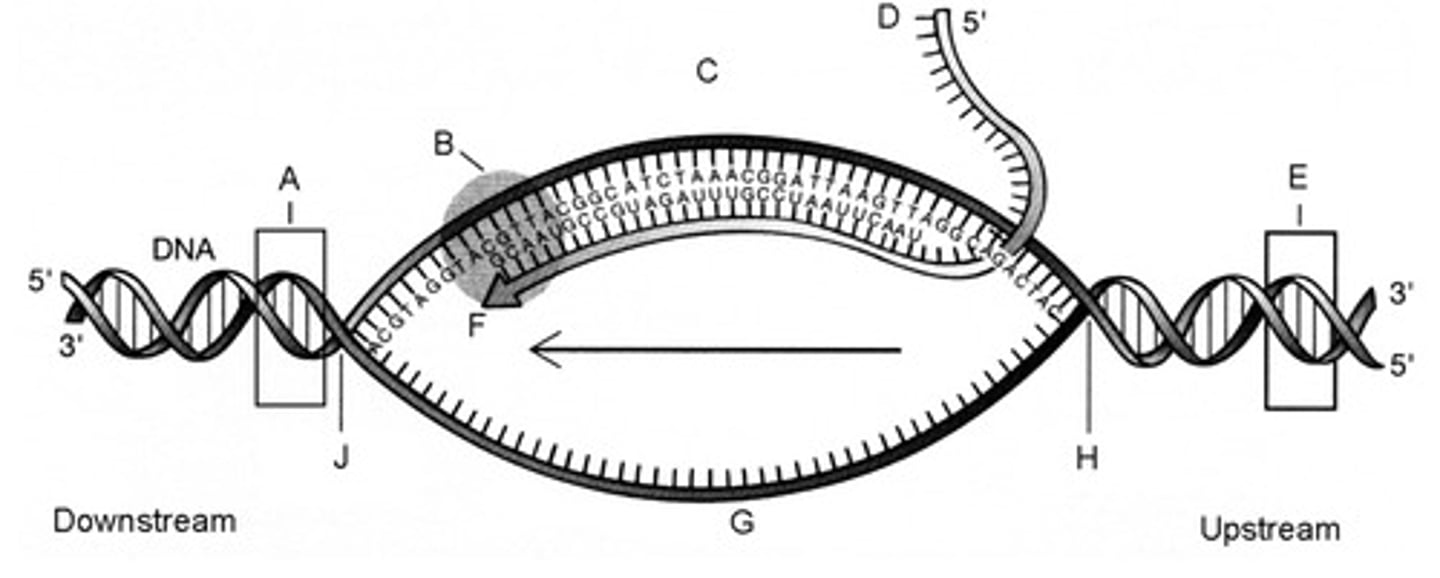
63. In the figure to the right, mRNA transcription process initiates at the area labeled _______, The messenger RNA transcript in the figure is labeled_____, and the template strand is labeled ______: fill up in the blank
E; D; C
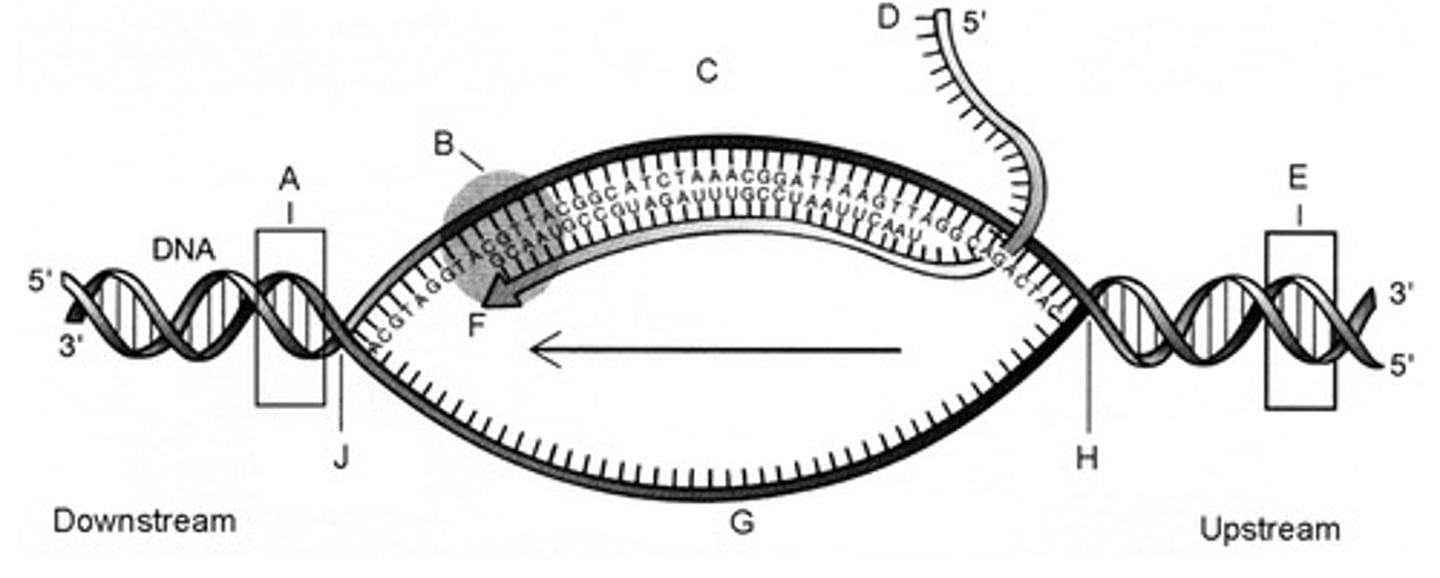
64. The component labeled B in the figure at right is:
RNA polymerase.