COMPSCI 1210 LAB A
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:33 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
A programming language that can be directly understood and obeyed by a machine or computer without any translation.
Machine Language
2
New cards
a low-level programming language for a computer or other programmable device specific to a particular computer architecture in contrast to most high level programming languages, which are generally portable across multiple systems.
Assembly language
3
New cards
simple computer model
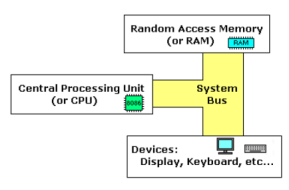
4
New cards
The __ connects the various components of a computer.
system bus (shown in yellow)
5
New cards
The __is the heart of the computer, most of the computations occur inside the CPU.
CPU
6
New cards
__ is a place to where the programs are loaded in order to be executed.
RAM
7
New cards
Why Assembly Language? (enumerate all the benefits)
* Speed
* Space
* Capability
* Knowledge
* Space
* Capability
* Knowledge
8
New cards
Assembly language programs are generally the fastest programs around.
Speed
9
New cards
Assembly language programs are often the smallest
SPACE
10
New cards
You can do things in assembly which are difficult or impossible in HLLs
Capability
11
New cards
Your knowledge of assembly language will help you write better programs, even when using HLLs
Knowledge
12
New cards
Representation of Numbers in Binary
* **1 BIT** - (either 1 or 0)
* **NIBBLE(4)** - 1 nibble is equal to four bits or half a byte (maximum value of Fh, 15 decimal).
* **1 BYTE(8) -**
1 byte is equal to 8 bits or 2 nibbles
(maximum value FFh, 255 decimal)
* **1 WORD (16) -**
1 word is equal to 2 bytes
* **NIBBLE(4)** - 1 nibble is equal to four bits or half a byte (maximum value of Fh, 15 decimal).
* **1 BYTE(8) -**
1 byte is equal to 8 bits or 2 nibbles
(maximum value FFh, 255 decimal)
* **1 WORD (16) -**
1 word is equal to 2 bytes

13
New cards
__ are a place in the CPU where a **number can be** **stored and manipulated.**
Registers
14
New cards
There are three sizes of registers
* 8-bit intel 8008,
* 16-bit 8086 architechture,
* 32-bit 80386 architecture.
* 16-bit 8086 architechture,
* 32-bit 80386 architecture.
15
New cards
4 different types of registers;
* General Purpose
* Segment
* Stack
* Index
* Segment
* Stack
* Index
16
New cards
General Purpose Registers
* AX
* BX
* CX
* DX
* SI
* DI
* BP
* SP
* BX
* CX
* DX
* SI
* DI
* BP
* SP
17
New cards
the accumulator register (divided into AH / AL). ·
AX
18
New cards
the base address register (divided into BH / BL). ·
BX
19
New cards
\- the count register (divided into CH / CL). ·
CX
20
New cards
* the data register (divided into DH / DL). ·
DX
21
New cards
destination index register.
· DI
22
New cards
source index register
**SI**
23
New cards
\- base pointer.
· BP -
24
New cards
\- stack pointer
SP
25
New cards
* Sometimes called pointer registers
* **Mainly used for string instructions**
* **Mainly used for string instructions**
Index Registers
26
New cards
Index Registers:
* SI
* DI
* IP
* DI
* IP
27
New cards
__are used as source index for string operation
Source index
28
New cards
__are also used for string operation
Destination index
29
New cards
___cannot be manipulated directly because it stores the address of the next instruction
Instruction pointer
30
New cards
Stack Registers:
* • BP
* SP
* SP
31
New cards
__ is similar to BX, generally used to address and access local variables in a process.
– Base pointer
32
New cards
__maintains the program stack for arithmetic computations
Stack pointer
33
New cards
specific areas defined in a program for containing data, code and stack.
Segment Register
34
New cards
**three main segments** of Segment register:
* Code Segment
* Data Segment
* Stack Segment
* Data Segment
* Stack Segment
35
New cards
It contains all the instructions to be executed.
Code Segment
36
New cards
It contains data, constants and work areas.
Data Segment −
37
New cards
It contains data and returns addresses of procedures or subroutines.
Stack Segment −
38
New cards
* an area of memory which you can save and restore values too.
* This is an area of memory that is like a stack of plates
* This is an area of memory that is like a stack of plates
stack
39
New cards
__ like data structure in the memory in which data can be stored
Stack
40
New cards
the last one you put on is the first one that you take off.
LIFO or FILO
41
New cards
If another piece of data is put on the stock, it grows __.
downward
42
New cards
the stack starts at a __ and grows downwards.
high address
43
New cards
The element that is higher in the stock have ___than those on the bottom
lower address
44
New cards
Stock is comprised of elements that are added and removed with **t**wo operations
Push and Pop
45
New cards
PUTS A PIECE OF DATA ONTO THE TOP OF THE STACK.
Push
46
New cards
PUTS THE PIECE OF DATA FROM THE TOP OF THE STACK INTO
A SPECIFIED REGISTER OR VARIABLE.
A SPECIFIED REGISTER OR VARIABLE.
Pop
47
New cards
syntax for push

48
New cards
syntax for pop
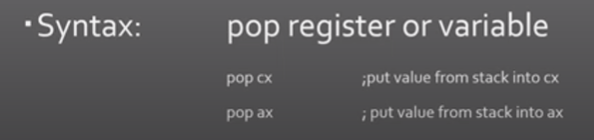
49
New cards
3 types of operand
* Immediate
* register
* memory
* register
* memory
50
New cards
___is a number which will be known at compilation and will always be the same
Immediate operand
51
New cards
___ any general purpose or index register. Example AX or SI.
Register operand
52
New cards
___is a variable which is stored in memory.
Memory operand
53
New cards
ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION
54
New cards
Most instructions are made up of **three characters**
* operand
* comma
* another operand
* comma
* another operand

55
New cards
moves a value from one place to another.
MOV

56
New cards
__ calls a DOS or BIOS function which are subroutines to do things that we would rather not write a function
INT

57
New cards
Most interrupts have more than__, this means that you have to pass a number to the function you want.
one function
58
New cards
How to declare a data
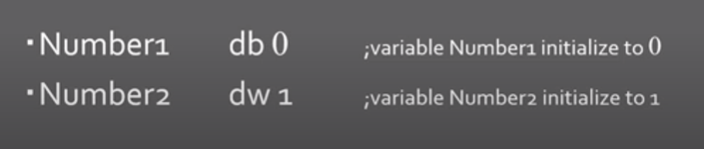
59
New cards
You can only put bytes into __ registers and word into _ registers
* 8-bit
* 16-bit
* 16-bit
60
New cards
add the contents of one number to another
ADD -

61
New cards
subtract one number from another
SUB —

62
New cards
multiplies two unsigned integers (always +)
MUL -

63
New cards
multiplies two signed integers (either + or -)
IMUL —

64
New cards
divides two unsigned integers (always +)
DIV -

65
New cards
divides two signed integers (either + or -)
IDIV —
