Nursing 204: Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:08 PM on 2/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
clinical judgement: definition
an interpretation or conclusion about a patient’s needs, concerns, or health problems, and/or the decision to take action (or not), use or modify standard approaches, or improvise new ones as deemed appropriate by the patient’s response
2
New cards
clinical judgement attributes
notice, interpret, respond, reflect
3
New cards
assessment definition
health assessment is a systematic method of collecting data about a patient for the purpose of determining the patient’s current and ongoing health status, predicting risks to health, and identifying health promoting activities
4
New cards
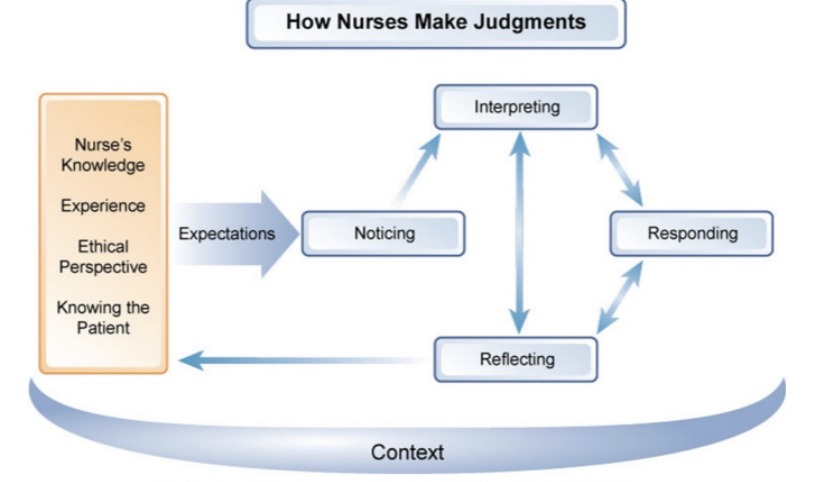
tanner’s model for clinical judgement
reflect on things after the fact, reflection-in-action
5
New cards
assessment attributes
subjective and objective, holistic assessment, evidence based screenings
6
New cards
ADPIE
assessment
diagnosis
planning
implementation
evaluation
diagnosis
planning
implementation
evaluation
7
New cards
objective data
can be detected by an observer or can be measured or tested again
8
New cards
objective data example
physical exam: vital signs
9
New cards
subjective data
symptoms, feelings or perceptions that can be described or verified only by the patient (you can’t see it, observe it, or prove it)
10
New cards
subjective data example
pain scale
11
New cards
nursing diagnosis
describe the human response or a patient’s physical, sociocultural, psychologic, and spiritual responses to an illness or a health condition
12
New cards
angina
a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart;
13
New cards
medical diagnoses
made by a licensed provider such as a physician, advanced practice nurse, or PA
14
New cards
PES format
Problem (what are the approved nursing diagnoses? what is the human response to illness?)
Etiology (what caused the problem? why is this response occurring?)
Signs/Symptoms (what are they? how does the nurse know? how might a nurse now?)
Etiology (what caused the problem? why is this response occurring?)
Signs/Symptoms (what are they? how does the nurse know? how might a nurse now?)
15
New cards
arm fracture medical diagnosis
simple, closed, radial ulnar fracture of the right arm
16
New cards
arm fracture nursing diagnosis
pain related to injury as evidenced by crying, risk for self care deficit
17
New cards
SMART goals
specific
measurable
attainable
relevant
time based
measurable
attainable
relevant
time based
18
New cards
UAP
unlicensed assistive personnel
(CNA’s, technicians)
(CNA’s, technicians)
19
New cards
temperature normal range
98\.6 (37)
97-99 (36.1=37.5)
97-99 (36.1=37.5)
20
New cards
what affects temperature
environment, time of day, health, activity levels, periods
21
New cards
what helps maintain a balance between heat lost and heat produced by the body
hypothalamus
22
New cards
areas to take temperature
sublingual (mouth/oral)
rectum (usually higher than oral)
axilla (armpit, usually lower than oral)
temporal artery (forehead)
tympanic membrane (eardrum, least accurate)
bladder (if a tube is already there)
esophagus (if a tube is already there)
rectum (usually higher than oral)
axilla (armpit, usually lower than oral)
temporal artery (forehead)
tympanic membrane (eardrum, least accurate)
bladder (if a tube is already there)
esophagus (if a tube is already there)
23
New cards
hypothermia
less than 36.5
24
New cards
normothermia
36\.5-37.3
25
New cards
hyperthermia
more than 37.3
26
New cards
fever
more than 38
27
New cards
shunting means what
flushing
28
New cards
places to take a pulse
temporal artery (temple)
facial artery (jaw)
common carotid artery
brachial artery
radial artery
femoral artery
popliteal artery (inside knee)
posterior tibial artery (ankle)
dorsalis pedis artery (top of foot)
facial artery (jaw)
common carotid artery
brachial artery
radial artery
femoral artery
popliteal artery (inside knee)
posterior tibial artery (ankle)
dorsalis pedis artery (top of foot)
29
New cards
pulse scale
3+ = bounding
2+ = normal
1+ weak
0 = none
2+ = normal
1+ weak
0 = none
30
New cards
brachycardia
less than 60 bpm
31
New cards
hypoxia
low oxygen in body tissues
32
New cards
normal pulse
60-100 bpm
younger/smaller children have faster resting HR
younger/smaller children have faster resting HR
33
New cards
newborn normal pulse
110-160 bpm
34
New cards
tachycardia
more than 100 bpm
35
New cards
inhalation
diaphragm moves down
36
New cards
exhalation
diaphragm moves up
37
New cards
apnea
no breathing
38
New cards
inspiration
inhaling air with oxygen into the lungs
\
\
39
New cards
diaphragm is attached to what nerve
T5
40
New cards
expiration
exhaling air with CO2 out of lungs
41
New cards
bradypnea
less than 12 breaths per min
42
New cards
eupnea
12-18 breaths per min
43
New cards
tachypnea
more than 18 breaths per min
44
New cards
blood pressure
pressure exerted by the circulating volume of blood on the arterial walls, veins, and chambers of the heart
45
New cards
systolic
represents ventricles contracting
46
New cards
diastolic
represents the pressure within the artery between beats
47
New cards
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic
48
New cards
too small of a blood pressure cuff causes
a false high
49
New cards
too large of a blood pressure cuff causes
false low
50
New cards
orthostatic hypotension
from going to laying down to standing
* heart rate increases 30
* systolic drop of 20
* diastolic drop of 10
* cause: fluid volume deficit
* heart rate increases 30
* systolic drop of 20
* diastolic drop of 10
* cause: fluid volume deficit
51
New cards
fluid volume deficit
dehydration
52
New cards
hypotension
BP less than 90/60
53
New cards
normotension
BP of 90/60-120/80
* young children have lower
* young children have lower
54
New cards
hypertension
more than BP of 120/80
55
New cards
why does BP increase with age
vessels become less elastic
56
New cards
normal adult BP
less than 120 and less than 80
57
New cards
elevated adult BP
120-129 / less than 80
58
New cards
high BP stage 1 for adults
130-139 / 80-89
59
New cards
high BP stage 2 for adults
140+ / 90+
60
New cards
hypertensive crisis for adults
higher than 180 / higher than 120
61
New cards
hemorrhage increases or decreases BP
decrease
62
New cards
increased intercranial pressure increases or decreases BP
increases
63
New cards
acute pain increases or decreases BP
increases
64
New cards
end-stage renal disease increases or decreases BP
increase
65
New cards
general anesthesia increases or decreases BP
decrease
66
New cards
exercise postural change increases or decreases BP
decrease
67
New cards
smoking increases or decreases BP
increases
68
New cards
oxygen saturation
percentage of blood hemoglobin that is filled or saturated with oxygen
69
New cards
SpO2
saturation, peripheral of oxygen
70
New cards
desaturation
less than 95% on room air
71
New cards
normal saturation
95-100% on room air
72
New cards
high oxgen saturation
100% for patients on supplemental oxygen
73
New cards
in comparison to adults, children should have
* the same temperature
* higher HR
* higher RR
* lower BP
* same oxygen saturation
* higher HR
* higher RR
* lower BP
* same oxygen saturation
74
New cards
cardiac output
the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute
CO (ml/min) = HR (bmp) x SV (ml/beat)
CO (ml/min) = HR (bmp) x SV (ml/beat)
75
New cards
heart exam physical assessment
inspect appearance, color, scars, neck veins
76
New cards
pallor
pale
77
New cards
cyanosis
blueish color
* tells u oxygen levels have been low
* tells u oxygen levels have been low
78
New cards
murmers
sound of turbulent blood flow in the heart
* blood reverberates or bounces off the walls of the atrium or ventricles
* blood reverberates or bounces off the walls of the atrium or ventricles
79
New cards
bruits
sound of turbulent blood flow in the artery
80
New cards
thrills
the feeling of turbulent blood flow in the heart or arteries
81
New cards
extra heart sound S3 causes
* congestive heart failure
* left ventricular hypertrophy
* pulmonary edema
* heart attack
* sounds like Kentucky
* left ventricular hypertrophy
* pulmonary edema
* heart attack
* sounds like Kentucky
82
New cards
extra heart sound S4 causes
\
\
* ventricular hypertrophy
* long term hypertension
* sounds like tennessee
* long term hypertension
* sounds like tennessee
83
New cards
skin turgor explained
tight = more fluid under
normal
loose = tenting, less fluid underneath
normal
loose = tenting, less fluid underneath
84
New cards
edema
swelling due to fluid accumulation
85
New cards
peripheral temperature
warm if warm environment
86
New cards
capillary refill
should be 1-3 seconds
87
New cards
men heart attack symptoms
* nausea, vomiting
* jaw, neck, or back pain
* squeezing chest pressure or pain
* shortness of breath
* jaw, neck, or back pain
* squeezing chest pressure or pain
* shortness of breath
88
New cards
women heart attack symptoms
* nausea, vomiting
* jaw, neck, or back pain
* chest pain but not always
* pain or pressure in lower chest or upper abdomen
* shortness of breath
* fainting
* indigestion
* extreme fatigue
* jaw, neck, or back pain
* chest pain but not always
* pain or pressure in lower chest or upper abdomen
* shortness of breath
* fainting
* indigestion
* extreme fatigue
89
New cards
syncope
fainting
90
New cards
NANDA diagnosis
* activity intolerance/risk for activity intolerance
* decreased CO/risk for decreased CO
* risk for unstable BP
* risk for decreased cardiac tissue perfusion
* risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion
* ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion/risk for it
* decreased CO/risk for decreased CO
* risk for unstable BP
* risk for decreased cardiac tissue perfusion
* risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion
* ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion/risk for it
91
New cards
clubbing
tells oxygen levels have been low for a really long time
92
New cards
cadexia
extreme thinness
93
New cards
eupnea
normal breathing
94
New cards
dyspnea
difficulty brething
95
New cards
kussmaul
very shallow then fast
96
New cards
cheyne-stokes
no breathing, then deeper and deeper, then no breathing
97
New cards
vesicular lung sounds
normal
98
New cards
bronchovesicular lung sounds
normal
99
New cards
inspiratory stridor lung sounds
top, trachea, epiglottis
* obstruction in the airway
* obstruction in the airway
100
New cards
wheezes
high pitch bottom of chest