lec 4 - cell junctions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what sheets of epithelia need
control what passes between the cells
resist shearing forces
need to communicate
need polarity
types of cell junction
communicating junctions - gap
occluding junctions - tight
adhering junctions - adherens, desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, focal adhesions
what part of the cytoskeleton do cell junctions adhere to
desmosomes and hemidesmosomes link to cytokeratin
(most) others link to actin
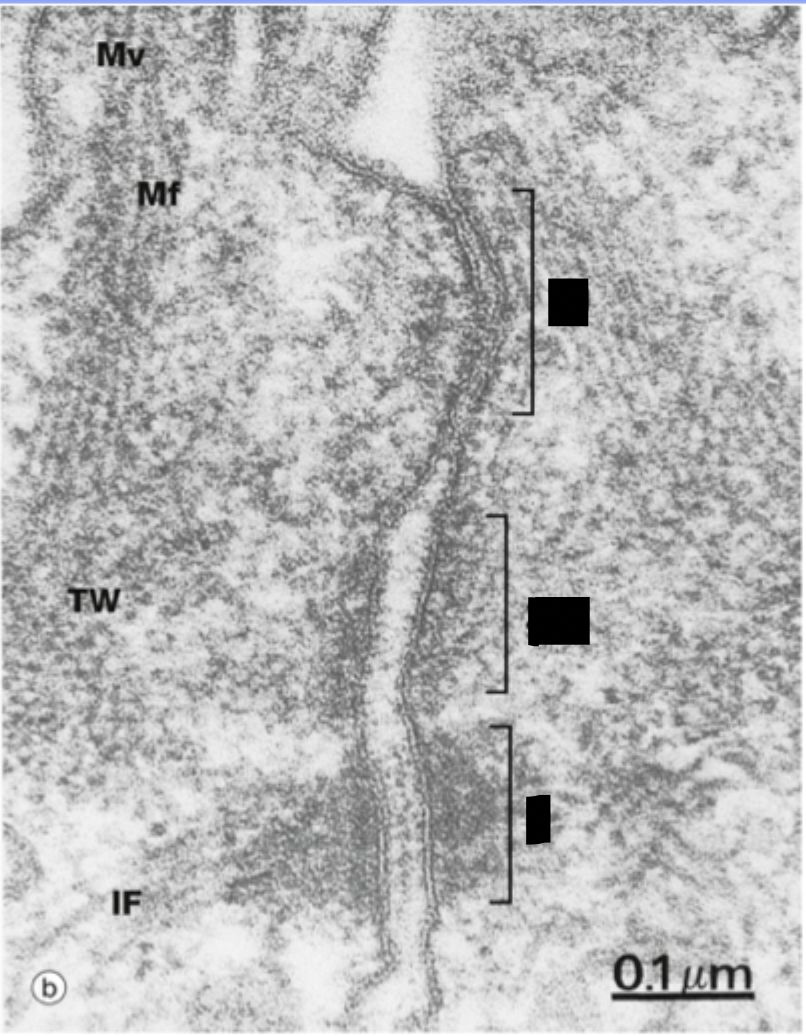
top: tight junction
middle: zonula adheren (or adherens junction)
bottom: desmosome
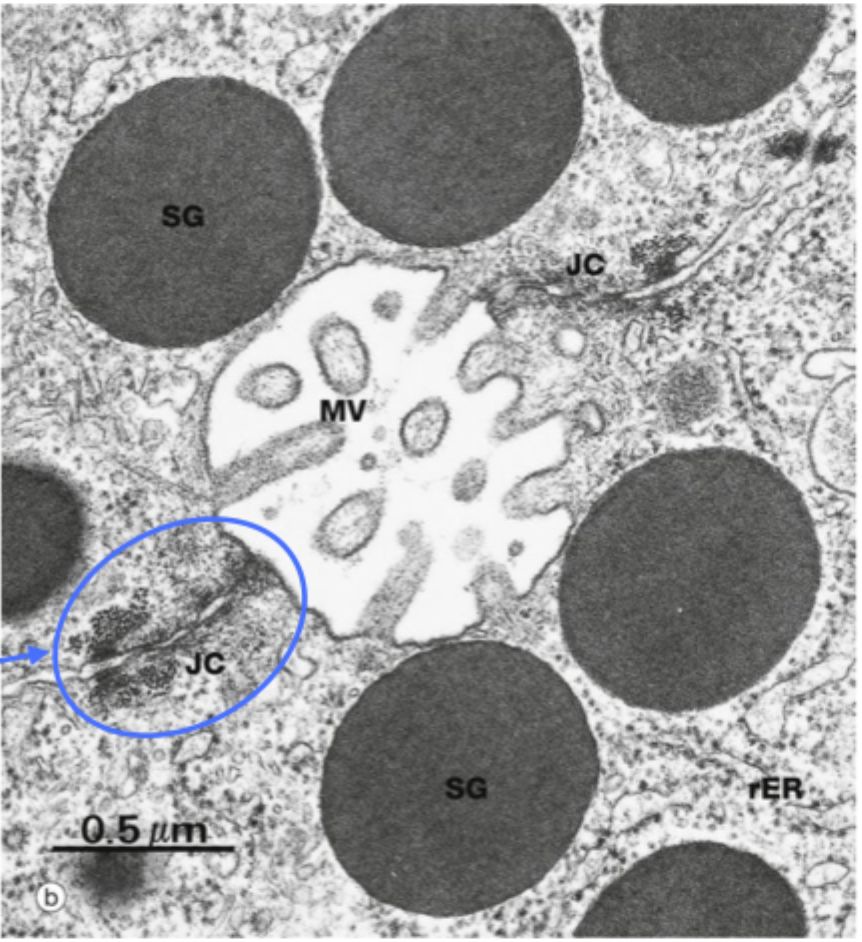
junctional complex
different junctions often form a junctional complex
gap junctions - what
membrane channels that bridge the gap between cells
allow direct cytoplasmic exchange (bidirectional)
rapid juxtacrine signalling - small molecules e.g. ions, ATP, second messengers, etc
gap junctions - proteins and structure
6 connexins make up a connexon (or hemichannel)
connexins have 4 transmembrane domains - linked by loops which allow the connexons from each connecting cell to dock to each other to form a gap junction
the channel twists to open - can only happen when correct docking has occured
location of gap junctions
in the cell membrane - basolateral surface between 2 adjacent cells with very little room between them
connexins synthesised in RER and oligomerize in golgi - then trafficked as connexons to plasma membrane
in the membrane near existing junctional complexes - need ZO-1
multiple channels cluster to form plaques
formation of gap junctions - when
after adherens and tight junctions (as needs ZO-1 proteins as anchors)
can be before or after desmosomes and hemidesmosomes - quick turnover as they are only really inserted into membrane as needed
tight junctions - what
zonula occludens
cell-cell adhesion complexes near apical membrane
selective barrier - controls paracellular pathway, maintains cell polarity, involved in signalling pathways
branching network of sealing strands
tight junction - proteins and structure
occludins
junctional adhesion molecules
claudins
scaffolding proteins
occludins:
4 transmembrane domains
stability and integrity
tightness not permeability
junctional adhesion molecules
transmembrane proteins
mediate cell-cell adhesions
interact with cytoskeleton and signalling proteins and scaffolding proteins
scaffolding proteins
link tight junctions to actin cytoskeleton
inclused ZO-1, 2, 3
claudins
involved in tight junctions
transmembrane proteins with 4 transmembrane domains
act as selective channels
each allows or restricts particular ions or molecules
claudin 1 blocks most ions and water
claudin 2 selective permeability to Na+, K+, Ca2+, water
claudin 1
blocks most ions and water
part of tight junctions in skin
claudin 2
selective permeability to Na+, K+, Ca2+, water
in tight junctions
tight junctions formation - how and when
initiated by adherens junctions (form afterward)
recruitment of polarity proteins -> claudins and occludens inserted into apical lateral memebrane -> JAMs dimerise and stabilise cell-cell contact -> ZO-1 binds claudins and occludins -> ZO-1 binds to f;actin
forms continuous circumferential belt
dysregulation of tight junctions
inflammatory bowel disease: reduced claudin 1 and 2, increased claudin 3 = leaky barrier
loss of claudin 4 and 7 and occludins: linked to invasive and metastatic GI cancers
claudin 16 and 19 mutations: impaired reabsorption of Mg2+ and Ca2+
salmonella: effector proteins disrupt tight junctions and allow bacterial invasion
adherins junction what
belt like adhesion complexes
basal to tight junctions
strong cell-cell adhesion
mechanical adhesion - tensile strength
involved in signalling anf establishing cell polarity
adherens structure and proteins
transmembrane proteins: E-cadherins form dimers with neighbouring cells, Ca2+ dependant
intracellular proteins: catenins link cadherins to actin cytoskeleton, involved in regulating junction stability and signalling
formation of adherens junctions - how and when
cadherins on adjacent cells form homodimers (Ca2+ dependant)
cadherin cytoplasmic tails recruit catenins which connect to actin
junctions form a continuous circumferential belt
dysfunction of adherins junctions
E-cadherins essential for intestinal epithelial integrity - mutation or loss = increased intestinal permeability
E-cadherins encoded by CDH1 gene - mutations linked to cancers
desmosomes what
spot-like intercellular junctions - link to cytoskeleton
strong mechanical adhesion
abundant where high mechanical/shearing force
desmosomes protein/structure
desmosomal intermediate filament complex (DIFC): extracellular core, dense plaques
transmembrane proteins: desmosomal cadherins - desmogleins and desmocollins
intracellular proteins: plakoglobin and desmoplakin (connect the transmembrane proteins to intermediate filaments)
desmosomes formation - how and when
forms after adherens junctions and tight junctions have formed
desmogleins and desmocollins on adjacent cells bind
cytoplasmic tails recruit plakoglobin
plakoglobin binds to desmoplakin
desmoplakin connects to cytokeratin
hemidesmosomes what
anchor epithelial to basement membrane
hemidesmosomes protein and structure
transmembrane protein: integrin
intracellular protein: plectin
extracellular protein: laminin (lamina lucida)
hemidesmosomes formation - how and when
form after desmosomes have formed
integrin heterodimers inserted into basal membrane
binds laminin - binds to basal lamina components
integrin binds to plectin - links integrin to keratin
hemidesmosomes cluster to form dense adhesion sites
focal adhesions what
highly dynamic multi protein complexes
mediate attachment of cell to ECM, connect to actin
more plastic than hemidesmosomes
involved in cell migration and signalling
focal adhesions - structure and proteins
transmembrane proteins: integrins
adaptor proteins: e.g. talin
focal adhesion kinase (FAK) regulates adhesion turnover
focal adhesions formation
integrins bind to ECM components (fibronectin, collagen)
recruitment of adaptor proteins
link to actin
cell junction complex formation order
initial cell to cell contact
adherens junctions assemble - E-cadherin clustering, actin remodeling, polarity initiated
tight junction formation - recruitment and positioning of polarity determining complexes, includes recruitment of ZO-1
desmosome formation
hemidesmosomes and focal adhesions form
gap junctions form after adherens and tight junctions, as needed. Rapid turnover to meet cellular needs