Monetary policy
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is monetary policy?
Used to control money flow in an economy - uses interest rates and QE to influences levels of consumer spending and inflation
aim of monetary policy
low inflation and stable economic growth
What is expansionary monetary policy? (3)
increases economic activity by reducing I/r which increases consumption and AD
Increases investment
decreases exchange rate - increases exports - increased growth and AD
What is deflationary monetary policy?
decreases economic activity
increases MPS - decreases consumption
decreases investment
appreciation of exchange rate - increases imports - decreases AD
Effects of interest rates on the housing market
lower = lower mortgage payment = increased demand = increased consumption = increases AD = inflation
Evaluation example of monetary policy
covid decreased confidence and I/r were already near 0% so it was still not enough to stimulate demand
2008/9 deep recession - cut i/r from 5 to 0.5%
2007-11 cost pull inflation over 5% and recession
What is a liquidity trap?
when I/r are very low and monetary policy becomes ineffective
What is QE?
central banks increase money supply and use these electronically created funds to buy government bonds and other securities - used when I/r ineffective
increased supply of money to encourage banks to lend at a lower interest rates
money used to buy financial assets like from buying government bonds (maybe from commercial banks)
This increases the demand for bonds
increases price of bonds
decreases yield (I/r on bonds)
I/r for mortgages etc decrease
AD, C, I increase
Possible disadvantage of QE
cheaper mortgages increases house prices → wealth effect → increased wealth inequality
What type of policy is QE?
expansionary monetary policy
Role of the central bank
Monetary function - policy
financial stability
Lends to commercial banks/ manages liquidity
Debt management - gov debt
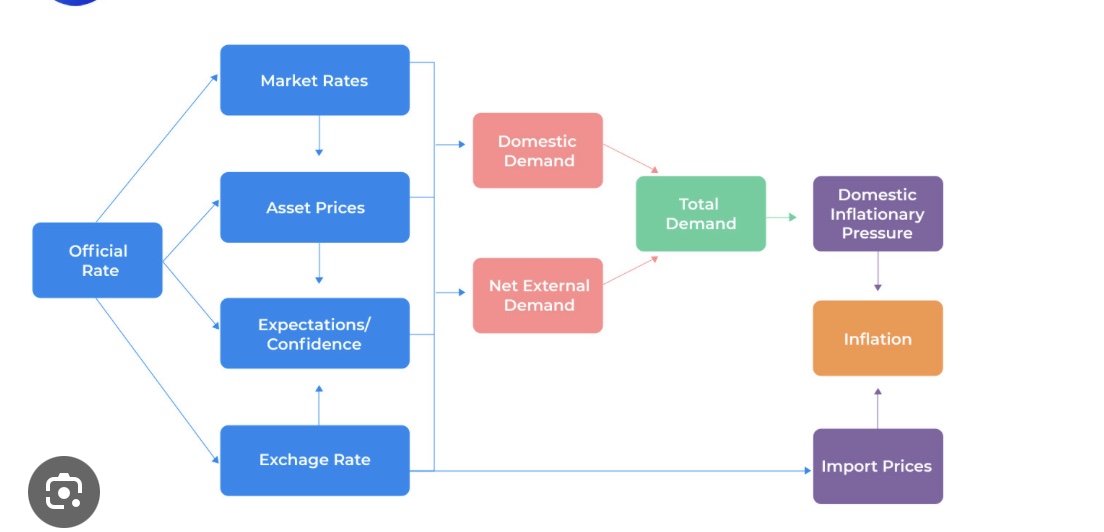
The transmission mechanism
Change in the base rate influences 4 primary factors
Market rate - mortgages and the bank lend rate
asset prices - house
Confidence - investment and spending
Exchange rate - SPICED
These all secondarily effect Net external and domestic demand which affects AD creating domestic inflationary pressures and inflation
Exchange rate effects import prices and therefore inflation
What is forward guidance?
Only in the SR there is an announcement for future plans of interest rate change to influence market expectations.
Thinking is that if commercial banks can be convinced that they can borrow overnight from BoE at a lower interest rate for a period of time then they may be willing to lend out money for the longer term at also a lower interest rate
Good and bad forward guidance
could lose credibility if promises are not kept
Helps influence LR interets rates
could reduce inflation expectations
Evaluate monetary policy
Time lags
Consider fiscal policy also - they may work against each other
QE depends on interest rates - must be close to 0