DIET2003 QUIZ 2 (Weeks 4-7)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Describe the Australian agricultural landscape, its commodities and the concept of food security in relation to this (HORTICULTURE).
AUSTRALIAN AGRICULTURE
1% of the Australian population is farmer, managing 55% of Australia’s land mass for ag production
70% of food produced > exported
AUSTRALIAN COMMODITIES > Large Scale, Broad Acre Crops
North: tropical > mixed lifestyle, cropping
South: horticulture, dairy
West: agricultural technologies for cereal crops
Top 5 Commodities
Cattle
Wheat
Fruit & nuts
Sheep
Milk
FOOD SECURITY
Food security is human right > growing challenge
Food production needs to be increased by 60% to feed 10bn by 2030
Explain the impact of climate change on Australian agriculture, and the impact of Australian agriculture on climate change. Describe two possible approaches to combat this. (HORTICULTURE > bidirectional relationship).
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON AG
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change predicts a rise of at least 1.5C. Results in:
Lower yields: every 1C increase = 10% decrease in wheat yield, 6% decrease in net primary production
Decreased biosecurity: invasive species move with changing climate.
Increased drought risk: rainfall declined 16% since 1970
Floods: waterlogged/eroded soils, crop loss, fungal disease, livestock losses & bacterial infection, road closure and transport issues, power outages (reduced farm ops)
Bushfires: larger & hotter heatwaves, less hazard reduction
IMPACT OF AG ON CLIMATE CHANGE
Emissions: at contributes 17% emissions (livestock & machinery)
Land clearing: major emission source > 115 million tonnes annually, old land clearing & tillage practices = soil erosion, salinity
Water: at uses 70% of Australia’s water footprint
Biodiversity: monoculture susceptible to disease
SOLUTIONS?
Conservation Agriculture: Maintenance of permanent soil cover, minimum soil disturbance & diversification of plant species
No till cropping, cover cropping, mulching, crop rotations, summer fallow
Sustainable Intensification: Use of advanced technologies to optimise inputs & increase yield without adverse environmental impacts or cultivation of more land
Pesticides, agricultural biotechnology, digital tech, AI & robots
Describe the till vs no till argument in relation to conservation agriculture. Discuss the role of glyphosate in no till techniques (HORTICULTURE)
TILL/TILLAGE
Tillage (ploughing): method of turning over old crops to prepare soil for planting, resulting in:
Emissions from tillage machinery
Soil erosion and water sediment
Lower yields
Loss of nutrients, microbes, soil moisture
NO TILL
85% of Aus farms are no till, 90% prevention of soil erosion, 60% reduction of emissions from fossil fuels.
Most effective conservation soil system. Instead of tilling > glysophate is used & crops are planted directly into standing stubble of previous crop = soil undisturbed
Reduced soil erosion (from plowing & tilling), increased organic soil matter/strucure/microbes/moisture
ROLE/CONTROVERSIES OF GLYPHOSATE (ROUNDUP)
Key active factor of Glyphosate > enzyme inhibiting action
Used against invasive weeds
Controversy of use > cancer risk – traces in food not significant enough to cause significant health problems
Explain different inputs in sustainable intensification (HORTICULTURE)
Herbicides: Pesticides that kill invasive weeds competing for resources, also used in environmental land management & water conservation.
Insecticides: Controls insects & invasive pests that wipe out crops/infect them with disease. Globalization/climate = major threat
Fungicides: Protect plants from fungi disease exacerbated by humidity e.g., vegetables, fruit & nuts
Describe issues facing Australian farms: food loss & climate change. (HORTICULTURE)
FOOD LOSS ON FARMS
- 40% of crops are lost each year due to pests, weeds and diseases e.g., Irish Potato Famine
- 800m people are hungry, 10% of the global population & 1 million Australians are food insecure
- Fungal pathogens > biggest threat, resistant
CLIMATE CHANGE > BIGGEST BIOSECURITY THREAT
Global proliferation and expansion of fail armyworm has infested corn, rice & sorghum crops globally > most recently Australia
Causes ecosystem drift e.g., foot & mouth disease in livestock
Primary control: insecticides & border control
Describe some common soil conservation practices (HORTICULTURE)
Cover cropping: grasses/legumes planted to cover soil between crop rows = weed suppression, adds nitrogen, erosion control.
Crop rotation: different crops in same land plot over growing season = inc nutrients, reduced reliance on 1 nutrient, weed/pest resistance.
Summer fallow: essential dry land practice of resting crop land to conserve water & nutrients to grow crops not otherwise possible. Managed with glyphosate.
Explain the use of GPS, GIS (geographic information systems) and AI in Australian agriculture (HORTICULTURE)
Boundary mapping: accurate navigation for machinery, soil sampling, crop health monitoring
Compare variables: yield potential, crop health monitoring, soil moisture and irrigation.
Drones & robots: pest and weed killer identification and precise input application.
AI driven greenhouses: pest and weed identification and precise input application.
List some benefits of GM crops, and distinguish between GMO and GE crops. (HORTICULTURE)
GENETICALLY MODIFIED CROP BENEFITS
Climate change adaption e.g., heat, drought, flood and salt tolerance
Enables no till
Pest & disease resistant
Increased yield
Nitrogen use efficiency & reduced carbon emissions/chem inputs
Higher protein/nutrition content
2020: GM crops allow farmers to use 58 million less acres of land
GMOs vs GE
GMO technique: a foreign gene is inserted into the DNA strand
Crop takes on improved characteristics associated with the new gene & genetic modification can be detached.
GE (CRISPR) technique: gene is cut & it’s DNA is naturally modified during repair
Crops DNA is changed but tests cannot distinguish GE crop from traditional breeding techniques
GM CROPS: AUSTRALIA
99.5% of cotton grown in Australia > GM, grown since 1996
Bt cotton produces its own insecticide to combat it’s major pest – bollworm
Australian cotton: globally renowned as the most water efficient
List some upcoming innovations in the Australian agricultural industry (HORTICULTURE)
Biopesticides: dsRNA targets specific pest gene.
Precision fermentation: biotech to brew animal like proteins.
Synthetic biology: redesigning organisms through engineering
GM nutrition benefits: fortified fruits & veg with vitamins & antioxidants.
1 ha DHA canola = as much DHA as 10 tonnes of fish
Tomatoes high in antioxidant, GABA or Vit D
Wheat without gluten and less acrylamide
Describe the size, growth & industry value of the citrus industry. Explain how this is tracked. (CITRUS)
SIZE & GROWTH
29,000 hectares of commercial plantings, +800 commercial businesses, 900,000 tonnes of fruit per annum
30% increase in plantings over the last decade
30% growth of volume in citrus exports over the last decade
1/3 exported
INDUSTRY VALUE
3rd largest horticulture industry by value
Mildura, Victoria, thriving regional economic hub > citrus played important role in growth
Contributes 1 billion dollars to regional and domestic economy
TRACKING PRODUCTION → Australian Tree Census
Informing industry on national/regional plants, informing industry investment
Guiding growers in choosing varieties
Assisting citrus supply chain with packing, logistics and investment decisions
Directing market development research needs
Explain the national production patterns of citrus. (CITRUS)
1. Oranges (61% of national hectares) navel for eating, valencia for juice, 2. Mandarin & tangelo (28% of NH), 3. Lemon & lime (9% NH) 4. Grapefruit & pomelo (1% NH)
Grown commercially Australia wide > except Tasmania, major growing regions in Southern Australia – major region in the Riverina in NSW
Varieties grown in each region vary according to climate, harvest windows, soil profiles and pest pressure
Describe the first attempts to grow wheat (1790s-1820s) & it’s subsequent development as a staple crop in Australia (1850-1900) (GRAINS).
FIRST ATTEMPTS (1790s-1820s)
Settlers had to adapt traditional farming practices to Australian environment = challenging (climate + seeds used)
First attempts at cereal cultivation = unsuccessful due to unfamiliar climate, soils + seasons
WHEAT AS A STAPLE (1850-1900):
Emerged as a significant cereal crop due to new varieties suited to Australian conditions
Improvements in farming techniques = growth of wheat farming
1870s: Australia exporting wheat to UK
1880s: agricultural college began - training people, ongoing research by William Farrer
Ensured better productivity & quality of wheat to mill into flour (palatability)
Manual process at every stage (planting to harvest)
WILLIAM FARRER (1880-1900):
Discovered European wheat varieties didn’t cope in Australian conditions (humidity or very hot + dry)
Early 1880s, Farrer travelled globally collecting different wheat seeds > planted the seeds (Canberra) to find varieties of wheat is best for Australian conditions
1886: cross-breeding the strongest varieties of wheat
1901: developed the Federation wheat variety > most successful breeding for Australia (but takes years)
Success in scientific breeding + farming practices for adaptation to local agricultural conditions > basis for food security for Australia
Describe the expansion & diversification of cereal crops (1890s-1910s) & the impact of the world wars. (GRAINS)
EXPANSION & DIVERSIFICATION (1890s-1910s)
Agriculture expanded; other cereal crops (oats, barely) cultivated
Improved transportation (railways) facilitated movement of grain: rural → urban areas
Federation wheat (+ improvements in farming techniques) = growth of wheat farming
IMPACT OF WARS (1915-1945)
Increased demand for wheat
Advancements in agricultural technology (use of tractors + combine harvesters)
Wartime + greater yields = flour exports > important part of the wheat industry
POST WWII BOOM (1945-1990)
After WWII = boom in cereal grain production → farmers embraced modern agricultural practices
Chemical fertilisers, pesticides + herbicides = increased yields
Government’s role: supporting agricultural sector through policies + subsidies
Describe the recent history and current challenges of growing cereal crops in Australia. (GRAINS)
CHALLENGES & INNOVATION (1990-present)
Issues (water scarcity, soil degradation, changing market dynamics) influenced farming practices
Technological advancements (precision farming + genetically modified crops) introduced to enhance productivity + sustainability
GLOBALISATION & EXPORT MARKETS (2000-present)
Major exporter of cereal grains (particularly wheat, also oil seeds) > mostly from WA (exports 90% wheat overseas)
Ability to produce high-quality grains + access international markets = key player in global grain trade
Australian wheat industry = export oriented + ships ~75% of nation’s total production to 50+ countries
Explain the focus on sustainability in cereal cultivation and strategies associated with sustainable cereal crop cultivation (GRAINS)
Growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture in Australia
Farmers adopting practices; conserve water, reduce environmental impact, ensure long-term viability of cereal grain production
Dramatic change = NO TILL
Removing practice (all farmers in Australia over last 30 years; leading in no-till farming) conserves more water + moisture in soil
Tillage/cultivating/ploughing = major cause of soil erosion
Removal of surface cover
Breakdown of soil structure
Wind erosion
Surface water runoff
BENEFITS OF A NO TILL SYSTEM
Decrease in: soil erosion + fuel use
Increase in: soil carbon, soil structure, soil moisture (very important in Australia), beneficial microbes
Catch: to carry out minimal soil disturbances = another way to manage weeds = glyphosate (efficient weed control > the most important synthetic compound in world ag.)
Glyphosate: systemic herbicide controlling weeds
Used widely since its launch as Roundup in 1970s
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Describe the future of Australian grain growing, and outline issues with biosecurity (GRAINS)
FUTURE OF AUSTRALIAN GRAIN GROWING
Reduction in Glyphosate
Weeds are genetically adapting + building resistance to glyphosate
Australia is well placed to economically benefit from new herbicides
Increase in temperature/climate
Average surface air temperature has increased from 1910 (data until 2020)
Growth of bugs = dependent on air temperature, moisture + pH
Fungal blast disease: grows on wheat + thrives/reproduces in hotter temperatures - kills the plant and is threatening species (biosecurity)
Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate - breed + develop a large population (climate change makes them even hungrier!)
Consequences: less edible food (biosecurity) + increased need for pesticides ( toxicity + sickness)
BIOSECURITY
Hitchhiker pests: risk of hitchhiker pests in Australia is increasing due to climate change, increased movement of people + products, + supply chain complexities
Mouse plague: post-drought + then heavy rain = large crop yields = mouse plague from extreme variation in climate in a short time
Outline the implementation of gene editing technology in cereal crops (GRAINS)
Gene editing technology (different to genetic modification):
Wheat adapted to longer root growth = attain more moisture + less likely to dry out = more biomass + higher yield
HB4 Wheat: genetically modified wheat, introducing sunflower genes to improve crop productivity
Key tool in adaptation of farming systems to extreme climates
Delivers more than 40% yield increase in environments under severe water stress
Wheat variety developed in Tasmania to cope with deep sewing of seeds (every seed has an optimum depth) = less reliant on hot dry climates
Explain the concept of the ‘Sustainability Framework’ behind Australian Grain. (GRAINS)
Australia's report card for agri sector: Behind Australian Grain:
Responsible stewardship (soil health, conservation, carbon footprint, water use, chemical use, biosecurity)
Building capacity + wellbeing (worker safety (aging farming population), capacity + leadership (increasing diversity + inclusion of skills across sector))
Consumer confidence (food safety (very high standards in Australia), responding to consumer needs, innovation (good research + development sector), trust + acceptance)
Success in scientific breeding + farming practices for adaptation to climate change will provide the basis for food security for Australia + Asia - William Farrer (1880-1900)
Explain influences on consumer buying behaviours regarding eggs & the role of food labelling (EGGS)
Knowledge of food production, cooking shows, culinary exploration, celebrity shows (Jamie Oliver revealed caged chickens primarily farmed for eggs → impacting people’s choices
Ethics can influence customers’ decision on consuming foods/brands: price, nutrition, religion/culture, carbon footprint/food mile, item’s country of origin, sustainability of farming system and packaging, animal welfare, fairtrade
Understanding processes of food production systems = informed decision about purchase impact
Population lacking knowledge due to urbanisation → don’t know how small the land is to intensively farm hens ⇒ unsustainable
Intensive farming systems can tighten security by minimising disease, managing waste, lessening environmental effects, streamlining the workforce + production system
Compromise growth of production over welfare of animals [*]
FOOD LABELLING
Food labelling and marketing catch costumer’s attention eg. organic, free-range, pasture-raised, hormone-free
Myth to bust: hormones haven’t been used in chickens for 30 years
Outline the process of egg production & different production environments. (EGGS)
EGG PRODUCTION
Laid eggs are transported to a packing shed
Eggs are washed and checked for cracks + packed according to size
Note: cracked eggs are used in cakes for example
Eggs might be sold by local farmer or distributed to larger manufacturers
After hens’ egg production ↓ their meat + bones may be used for stock, food or other animals, or fertilisers
PRODUCTION ENVIRONMENTS
Caged: hens are in small cages (less than A4 paper!!) to max egg production [*], predetors
Barned: hens can move around but limited to barn, interactions w/ other birds, nest boxing, perching, things to peck at + litter to sit on
Free-ranged: hens can move around outside, but are in barns during night + harsh weather [quality shelter for hen welfare → same quality as barned hens + good quality air], hens per m2 must be appropriate to avoid overcrowding
Explain the two main different hen farming systems. (EGGS)
Meat Chicken
Hens > farmed to be eaten
Live for 35 days; genetically selected to grow quickly (breast + muscle tissues) → transferred to be slaughtered
68% Aussies eat chicken meat at least twice a week
Layer Hens
Female hens farmed for eggs
Live for 70 weeks, laying 1-2 eggs per day
Important nutrients are fed through automatic systems, including:
Water
Carbohydrates + fats as laying eggs use lots of energy
Protein → amino acids → important in eggs
Fibre
Vitamins + minerals → build resistance to disease
Calcium → strong bones + quality egg shells
Outline the farm management in regards to oats. (OATS)
Crop rotation: annually change crop in each paddock to prevent disease buildup in soil + different plants can control weed resistance
Cereals → canola (break crop) → hay → legumes (nitrogen into soil)
In the same paddock but rotate each year
If a crop is low in commodity, farmers will grow that particular crop
Adapt nutrition (eg pH, phosphorus, micronutrients) of soil to different levels of rainfall → use rainfall to its full potential → nutrition transferred to grain
Being wise about where money should be spend: ie deficiencies in the soil
Sewing seeds in April or beginning of May (aka beginning of winter) is more beneficial than sewing in middle of winter because crops will continue to grow despite cold nights + less daylight as roots are intact
Sewing early also means less weeds + competition of weeds with crop
Because of crop rotation, the weed seeds of one paddock will not return to the same paddock
Describe changes in cropping systems and threat management in oat production. (OATS)
CHANGES IN CROPPING SYSTEMS
Switch from cultivating soil (dries soil + release carbon dioxide + breaks organic matter) to no-till (keeps moisture in soil, builds organic matter in soil)
No-till is like corrugated iron and the water easily germinates the seeds as the gaps easily run water down to the seeds
Flexibility: need to match up nutrition with the potential yield [set by rainfall] → applying what nutrition is lacking after
THREAT MANAGEMENT
Sustainably using natural rainfall
From markets: hedge (keep/protect) 50-70% of a certain seed every season to have supply when global markets are falling below ones break even price (equal of total cost and total revenue)
Give an overview of the olive oil industry, the history of trees and the execution of harvesting practices. (OLIVE OIL)
Cobram Estate Olives: >2.6 million olive trees across 7000 hectares of Victorian farmland.
306,500 trees planted on 552 hectares of leased, freehold properties in California
Olive Wellness Institute: science repository with information on nutrition, health and wellness of olives and olive products
Subject to extensive peer review & source of credible information
OLIVE TREES
One of the oldest horticulture crop > 5000 years of recorded history, dominates the Mediterranean
Over 70% of olives are cultivated using traditional model
Low planting density, low mechanisation and low yields
Mechanisation of olive harvest started 40yrs ago > expansion over the past few decades
Introduction of irrigation = higher and consistent yields
Olive flowers bloom from late October to early November: olives 6 months later
OLIVE HARVEST
Proprietary straddle harvesters pick olives and delivered to trailer
Taken to on-site mills (within 1-2 hours), and washed
Stainless steel crushers turn it into a paste
Machines knead olive oil paste, rests for 45-60 minutes → droplets of oil move to the top, enabling separation
Kneading infuses oil with healthy components and fruit flavour
Olive paste is pressed in a horizontal centrifuge to be separated from fruit pulp
Stored in stainless steel tanks (N, temp control) to protect freshness until packaged and dispatched to supermarket
Define high quality extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) & it’s health benefits and the different types of olive oils. (OLIVE OIL)
Natural Oils | Refined Oils |
Extra Virgin Olive Oil · Highest grade of olive oil, flavourful · Healthy, natural source of antioxidants | Refined Olive Oil · Obtained from natural oils, then refined · Higher in trans fats |
Virgin Olive Oil · Lower grade than EVOO · Less health benefits and flavour · Long period between picking and processing = undesirable fermentation | Olive Oil (pure, light, etc.) · Composition: EVOO and refined olive oil · Low in flavour · Higher in trans fats · No antioxidants |
Lampante Olive Oil · Not suitable for human consumption without heat and chemical treatment · 50% of olive oil around the world · Originally used to burn in lamps · Also caused due to fermentation |
HIGH QUALITY EVOO & HEALTH BENEFITS
Buy local, from trusted producer
Look for harvest date (don’t buy if longer than 12-14 months ago)
Health Benefits
Unsaturated oil fats account for 40g of Planetary health Diet
Mediterranean Diet, EVOO = main fat source & preferred cooking medium → 3 tablespoons of EVOO a day
Explain future focus in the olive industry, and the use of natural resources & impact on biodiversity. (OLIVE OIL)
FUTURE FOCUS & OLIVES
Feeding 10 billion people should use no additional agricultural land, conserve water usage, reduce phosphorus and nitrogen production, and reduce GHG emission
Olive Tree is capable of sustainably reducing atmospheric CO2
Producing 1kg of olive oil captures 6kg of atmospheric CO2
World-wide olive oil industry absorbs emissions of a city of 9 million people
Olive trees are evergreen and perennial - less intense fertilisers, no heat or chemicals needed for refinement
FRESHWATER USE
Olive stomata open during early morning and close during central hours of the day, = water-conserving adaptability (30-40% less water than standard grass needs)
More than annual crops but shorter growing cycles
NITROGEN/PHOSPHORUS FLOWS
Natural ecosystems → limited by availability
Fertilisers disrupt global nitrogen and phosphorus cycles
Nitrogen fertilizer production is highly intensive, emitting high levels of GHG
Soybean crop can fix atmospheric nitrogen
Phosphorus fertiliser = non-renewable, mined from phosphorus rock deposits – depletion in 50-100 years
BIODIVERSITY
14,000 edible plant species, 150-200 used by humans, & 3 (rice, maize, wheat) contribute 60% of calories consumed by humans
Similarly with edible oils: palm, soybean and rapeseed contribute to 68% of calories consumed
Oil crops harvested and replanted annually = strip organic nutrients from soil over time
Increases CO2 emissions
Olive oil trees stay over a year - higher levels of soiled carbon and nitrogen in the soil
Outline land systems change in the olive oil industry (OLIVE OIL)
LAND SYSTEM CHANGE
Food production = largest driver of land use and change e.g., burning biomass and clearing forests
2000-2014: Brazil lost 2.7 million hectares of land on average each year
Cultivated area of olives = constant, new orchids replace old ones or plantations are carried out in former grasslands or annually cultivated land
Measures taken to limit potential impact:
Implemented conservation plan since 2006
Irrigation system according to exhaustive soil mapping
Check-ins to prevent fertiliser leeching
Developing plan to plant up to 1000 hectares of new native bush
Outline the production process for meat → beef specific (LIVESTOCK).
1. Final Wash and Cleanliness: The animal enters a shower area, ensuring it is clean and preventing contamination.
2. Ergonomically Designed Race: animal moves through an ergonomically designed race following the Model Code of Practice for animal welfare → quiet and orderly manner to minimise stress → animal is separated from others and the abattoir.
3. Stunning and Bleeding: The animal is quickly stunned, rendering it unconscious before the first cut, stops blood flow to the brain → Bleeding ends the life with minimal carcass damage & quickly removes blood.
4. Electrical Stimulation for Tenderness (Optional): Electrical current causes muscle contraction, hastening muscle-to-meat conversion → pH level of the carcass drops faster, and rigor mortis sets in sooner.
5. Hide Removal: The hide is removed with cuts at the legs, along the natural seams, to the flank, back, and rump.
6. Removal of Offal and Internal Organs: The carcass is opened to remove offal and internal organs → Everything from the carcass is used, including muscle, offal, co-products, and by-products → Edible offal includes tongue, tripe, cheek, liver, tail, tendons, heart, and kidney.
7. Splitting the Carcass: The body is split in two using a brisket splitter, making it easier to remove the spine and remaining organs, and allowing for inspection, storage, and further breakdown.
8. Ossification Range and MSA™ Grading: After splitting, the ossification range is determined → Key carcass attributes used by Meat Standards Australia™ (MSA) for grading → Other attributes: breed, color, fat depth, maturity, and ultimate pH.
9. Cleaning, Tagging, and Refrigeration: The carcass is sprayed down to remove bone dust, tagged for identification, and moved into refrigeration → Australian Standards for the Hygienic Production and Transportation of Meat specify the carcass internal temperature must reach no more than 7°C within 24 hours.
Explain the concept of ‘Meat Standards Australia’ and the steps to achieve an MSA product (LIVESTOCK).
MEAT STANDARDS AUSTRALIA
Beef Meat Standards Australia = world’s leading eating quality program for beef, launched in 1999
Widely adopted in Australia and internationally recognized → based on 1.7 million consumer taste tests by over 250,000 consumers from 13 countries → It takes into account all factors affecting eating quality from paddock to plate
MLA supports MSA program participants by creating opportunities for businesses to adopt eating quality principles.
Research shows stress-free cattle produce the best meat → MSA grading requires producers and processors to apply quality of life guidelines for: Welfare → Nutrition → Genetic improvement → Transport of livestock
MSA Grading Process: MSA graders collect information from producers and processors to ensure eligibility → assess important scientific characteristics of each cut to predict eating quality
Eligibility for MSA: MSA registered livestock must have MSA vendor declarations and transport documentation to verify they meet on-farm requirements.
STEPS FOR MSA
1. Ticket Scan: In the abattoir, as carcasses are processed, a ticket is attached and scanned to record production date, carcass weight, and individual number → ensures traceability along the supply chain.
2. Hump Height: All cattle breeds are eligible for MSA grading, but as tropical breed content increases, eating quality decreases → taken into account along with carcass weight to estimate the tropical breed effect
3. Eye Muscle Area: Eye Muscle Area is an indicator of yield and measures size of longissimus dorsi muscle in square centimeters
4. Ossification: Maturity is assessed through ossification: process of cartilage turning into bone in vertebrae → Using the AUSMEAT maturity reference standards, as ossification increases, tenderness decreases.
5. Marbling: Marbling, or intramuscular fat, impacts flavor and tenderness → MSA uses 2 systems to measure marbling:
AUSMEAT score for general indication of marbling → MSA score for the distribution and fleck size
6. Meat Colour: The rib-eye muscle color is assessed using AUSMEAT color chips and scored against the nationally approved standard
7. Fat Colour: assessed at the quartering site using AUSMEAT color chips
8. Rib Fat: Rib fat: measurement of subcutaneous or external fat at the quartering site → MSA required minimum is 3 millimeters → Requires even and adequate fat distribution to avoid toughness in the muscle
9. pH: pH measures lactic acid and is recorded with temperature → Measured in the rib-eye muscle with a pH meter, must be below 5.71 → High pH meat is coarse, less tender, and leads to cooking inconsistencies.
Data Capture: All measurements are entered into a handheld data capture unit → The carcass gets an overall value, and individual cuts are assigned eating quality grades → Only carcasses meeting all specifications are identified as MSA graded.
Feedback to Producers: measurements are shared with the producer to provide feedback, helping them adopt practices.
Cooking Methods: MSA graded cuts can be cooked in many ways → Each cut has a recommended cooking method designed to ensure consumer satisfaction
Give an overview of farming meat in Australia (LIVESTOCK).
Committed to sustainable and ethical production. Custodians of 47% of Australia's landmass, caring for approximately 25 million cattle and 68 million sheep.
Recognised globally for animal husbandry and farm management techniques.
Takes pride in its genetics & at the forefront of technological advancements in livestock production efficiency.
Progressive in areas such as:
Farm and pasture improvement.
Water management.
Focused on the highest possible food safety standards, supported by:
Traceability systems.
Quality assurance systems throughout the supply chain.
Industry = built by family-owned producers > committed to delivering world-class beef and lamb.
Legislation and Humane Treatment → Focus on maintaining quality and safety → All Australian processing plants must meet rigorous hygiene and safety standards → Australian meat processing sector is a world leader in beef and lamb dressing and fabrication.
Technology and Efficiency: Aus. abattoirs employ latest technologies to ensure continued production efficiency without sacrificing meat safety → While plants may differ in design (depending on markets and species processed), each uses innovative technology to ensure: Efficiency → Safety → Reliability
Outline goat, sheep & veal farming in Australia (LIVESTOCK)
GOAT
Goat production can be grouped into two categories:
Rangeland goats (a.k.a unmanaged, bush, or wild goats):
Combined breed adapted to survive in Australia's low rainfall, often arid rangelands → Majority are wild harvested for export
Recent years: more producers are domesticating these goats in rangeland environments, managing them as a component of businesses.
Farmed goats:
Prominence increased in 1994 with introduction of South African Boer breed. → renowned for meat quality → fast growth rate and solid muscle bulk
Boer goats were bred with Australian domestic herds to produce animals better suited to Australian conditions
Blending of breeds has led to Australian goat meat becoming less seasonal and more consistently available throughout the year.
SHEEP
Australia is the world’s largest exporter of sheep meat = 6.7% of global sheep meat production.
Produced across a wide range of climates, including:
Arid and semi-arid inland regions.
High rainfall areas of New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania, and the southwest corner of Western Australia.
New South Wales (NSW) = largest producer > 26 million of the national flock.
All Australian sheep are raised on pasture
Small proportion of sheep farmers (around 5%) grain-finish their lambs to optimise growth.
VEAL
Traditions of veal rearing and butchery vary > Australian veal different to Europe & America.
Strict code of animal welfare practices, ensuring:
Animals reared in the open.
Kept in small groups.
Fed a diet of milk and grass or grain.
Outline beef farming in Australia (LIVESTOCK)
Australia produces 3% of the world’s beef supply and is the third largest beef exporter in the world.
Produced in every state and territory in Australia but 50% of national herd is located in Queensland → 97% of Australia’s 28 million cattle are located on pasture based cattle properties and stations.
Northern Production:
Small number of large properties with high cattle numbers. Cominant cattle breeds: Bos Indicus (eg Brahman) or Bos Indicus cross (eg Droughtmaster) > better suited to harsh environment and ticks.
Natural fit for humid, tropical regions like northern Australia, larger frame and longer legs to cover large areas. Bos Indicus cattle > hump on their back that stores fat, large floppy ears, & saggy skin to keep them cool.
Southern Production:
Large number of smaller properties with lower cattle numbers. Dominant cattle breeds > Bos Taurus (eg Angus or Hereford) better suited to temperate environmental conditions a.k.a ‘British breeds’.
Thicker coats and a smaller frame, mature more quickly and grow muscle bulk more rapidly than Bos Indicus. Best known Bos Taurus breed is the Angus (originates from Scotland)
WAGYU
Japanese breed of cattle (Bos Tauru). Australia has largest wagyu heard outside Japan. Raised on pasture and then spend a considerable amount of time in feedlots –300 – 600 days.
Unsurpassed for its marbling = tender and juicy beef with rich texture and flavour. Softer fat composition and a finer meat texture than other beef.
Outline regen (regenerative) farming philosophy in relation to the live stock industry. (LIVESTOCK)
Positive of Regen Philosopy: stop conflicting with your land.
Higher sense of harmony > better balance e.g., more biodiversity + increased diversity e.g bird life coming back = birds are using reserves as nesting grounds
Native plants previously unseen have returned + seeing green leaf matter throughout and rehydrating
Focus on Carbon Emissions & Soil Carbon: Reducing CO2 emissions & improving soil carbon is crucial → Beef and grazing beef can be part of the solution to climate change.
Drought & System Collapse → drought exposed vulnerabilities → System collapsed = need for change.
Realisation of Inefficiency > Adapting to Change: Tried to intensify the system= lesser results → Two and a half years of fallow → no grass growth → Compacted soil → rain couldn’t penetrate well. New system..
Soil Restoration & Economic Considerations → focused on building topsoil back up → questioned the high-input system set up for maximum performance
Experimenting with Multi-Species Cover Crops/Sustainability: Contacted an expert to create a diverse mix of grasses, legumes, inc. tubers breaking into the compacted soil → Goal: enable plant access to deep soil nutrients instead of relying on inputs (increases organic carbon, maintains high soil health).
Rotational Grazing: essential to achieve maximum photosynthesis → Method: use machines or natural grazing—cattle → Cattle graze 1/3, leave 1/3, creating mulch that eventually turns into topsoil.
Introducing Species to Build Soil:Finding the perfect species takes time, started with grasses that would reseed and regrow naturally → letting nature decide which plants thrive each year, adding more plants for soil and cattle benefits.
Results of Multi-Species Pastures: Bulls on multi-species pastures gained 0.2 kg more per day compared to those on oats → fewer metabolic issues during weaning with animals raised on multi-species pastures.
Economic Benefits: savings: $60,000-$70,000 on seeds over $250,000 on superphosphate → Multi-species pastures are economically viable and sustainable.
Environmental and Long-Term Goals: regenerating soils, pastures, and trees, including creating wildlife corridors → Goal: leave the land better than we received it, ensuring a legacy.
Supporting Others in Regenerative Agriculture: starting regen farming can be overwhelming → books and local groups for support → joined MLA benchmarking group to establish a baseline & get help with procedures.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Impact: sequestering C from atmosphere & returning it to the soil → Goal = carbon neutral by 2030, ultimate mission to become a net carbon sink → Cattle play a crucial role in natural carbon cycling, helping photosynthesis capture carbon from the air & store in soil.
Outline the journey to sustainability and improved farming practices on a beef farm. (LIVESTOCK)
Land Condition & Early Struggles: Country was run down/dry (run of dry years compounding damage) > tried a few of old methods → ripped the country and seeded it, etc.
Turning Point: A New Approach
Family decision to do something different → started a journey 14 years ago.
Farming on the Western Downs, Southern Queensland → 5,200 hectares across 2 properties & wholesale beef brands in Brisbane, managed by Alistair.
Shifting Towards Sustainability
Understanding the system: Trying to replicate natural processes into land and animal operations
Went organic → unlocked MLA program (the MLA challenge)
Matthew took a dual role in the business side and production side → major shift when introducing measurements into the system.
Water Management & Grass Cover
Highly dependent on rainfall → critical factor
Set a benchmark: if no 30ml rain in fall, not worth farming. Good year = 4-5 events. Bad year = 1 event.
Realised need to operate with 10-15mls of rain → learned about smaller water cycle
Emphasis on how much grass and cover present → leads to healthy soil.
Soil Health & Functionality: Focus on understanding the soil → needs to be a functioning system. Rest = essential for grazing → training in rotation, cycling nutrients, and water.
Animal Health & Stock Management
Baseline soil testing and seasonal grass sampling to assess energy content.
Gut health focus: Induction program for cattle before putting them into paddocks.
AgriWebb: Digital tool for tracking animal history and movements across the property
C-Labs (Satellite Imaging): Determines dry matter in paddocks → decision-making based on data.
Grass Cover & Land Resilience:
Aiming to figure out the minimum grass cover needed for maximum results → Suggested balance: Take 30% out, leave 30%, and 30% standing → aiming for balance for land resilience → Discipline is key: Maintain 1,000 to 1,200 kg of grass cover → working on it for land sustainability.
Climate Variability & Adaptation:
Constant challenge, ranging from 250ml to 1,000ml of rainfall → Must prepare for cycles → sometimes dropping down to 20 acres of usable land
Importance of land cover: Helps with infiltration, microbial activity, and cooling land.
Rest as a Key Strategy: Rest introduced into system → remove set stocking → first step in building resilience.
Ongoing Improvement & Future Prospects: No static results → better understanding of soil system, still have more potential
Outline the almond industry. (ALMONDS)
ZERO WASTE: “imperfect almonds” made into a paste → almond milk
“Perfect almonds” = snacking almonds
Growing almonds is a closed-loop, ie entire fruit is used; kernel, shell, hull
WATER EFFICIENCY: 90% drip irrigation
Science & data based: constant reviews and improvements to enhance yield eg use of water probes in soil and on trees
Water probes can conserve water by watering when necessary & monitor the soil moisture
ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Monitor soil + moisture for almond trees and whether irrigation is needed
Checking whether added nutrients are in the roots
Extra water from irrigation will be filtered and then reused
BEE & POLLINATION
Impacts almond health: almonds blossom in August & bees cross-pollinate almonds = increase variety
Nuts can only be grown when the flower is correctly pollinated → bees!
Almond pollen is good nutrition for bees and farmers plant filler flowers to vary the bees’ diet
ORCHARD RECYCLING: Recycling trees into the soil by turning them into mulch > Helps change characteristics of soil & maintain health
ALMOND HEALTH BENEFITS
30g/a handful of almonds per day
Heart health
High in mono and polyunsaturated fats
Low in saturated fat
contain fibre, phytosterols, plant protein, Vit E, & other unique cardioprotective nutrients
Diabetes prevention & management
Healthy weight + guts

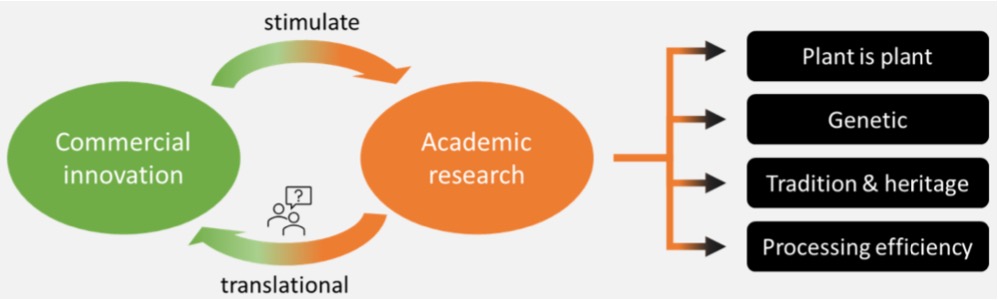
Describe the history of food processing, including the modern food processing industry.
EARLY DAYS: HUNTER GATHERERS
Nomadic tribes following herds and seasons of different berries and tubes growing in different planes.
Gather for about two to three weeks, and then they would hunt, have the kill and they eat that carcass for about a week or so, depending on how big their clan or their tribe was.
BEGINNING MODERN FOOD SUPPLY (Ancient Egyptian Agricultural Revolution – up until 1500s)
Egypt: cultivation for steady food supply over constant migration > planting crops and the base of the room and Nile, enabled development into cities and little communities
1500s
Explorers travelling for colonial powers to discover new land/cultures > discovered new flavours and spices and cocoa in the the Incas = broadened food supply.
Spice trade routes all across the world, transporting spices like cinnamon and cardamom, nutmegs, herbs, sugar etc.,
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: 1800s
Movement from manual labour to mechanisation e.g., sewing machines
Louis Pasteur ‘godfather of modern microbiology’, discovered pasteurisation as a way he treatment as a way to get rid of pathogenic bacteria.
Nutrition as a science was born.
Retort (originated in 1800s): pack it up with cans, fills with really, really, really hot water = temperature destroys the bacteria that could be in the products with cans in it.
Food safety has been an underlying, fundamental foundational principle of the food supply and the food industry ever since.
Fundamental and anyone who works in the food industry, food safety is everybody's business.
1970s
Food safety regulations revolution
Automation in food industry > inspired by motorcar industry
Decrease cost, increase productivity
Impact of WWI/II, Vietnam wars > need for food vouchers, food insecurity. Desire for safe, cheap accessible food food readily available
Automation for steady food supply
MODERN FOOD PROCESSING
Different trade agreements, variety of conflicts, emerging markets (developing nations > superpowers with significant buying purpose) = affects trade & agreements
Novel technologies e.g., artificial intelligence > used to understand consumer choices
Growing population > peak at about 10 billion in 2050, concerns for housing, infrastructure and the impact on food supply
Values have changed, but knowledge increased > generation of information & information access
What are some questions to consider when looking at food supply/processing and what are factors influencing food choices?
QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER
1. Why do people eat what they eat?
2. Why do we have the food that we have?
3. What are those factors that affect our food supply?
4. Why do we have the foods that we have?
FACTORS INFLUENCING FOOD CHOICE
Goes beyond marketing > food choice and ‘good’ vs ‘bad’ food choices are dependant on context & opinion e.g., microbiologist (pathogenic bacterial count) vs a dietitian (target individual, desired outcome)
Food supply
Socioeconomic status
Educational attainment > more disposable income
Location: rural vs urban → influences availability & cost
Cultural acceptability (accepted foods/eating practices)
Living environment
Food suitability
Food skills
Supermarket variety & availability e.g., alternative milks
Outline the historical nutritional composition of diets, including modern diet composition.
Hunter Gatherers: high % of starch e.g., tubers, roots, vegetables & berries from foraging. Small percentages of fat & protein
Ancient Egyptians: lots of starch, protein reduced, fat reduced, increased refined sugar & salt. Meat = expensive.
Modern affluent societies: huge component of diet is based on refined fat, refined sugar. Small proportion of starch. Moderate intake of protein, low fibre intake.
AGHE: differences in intake dictated by sex, age, height, weight, activity level, etc.,
Poor ADG adherence: 2 ½ serves of vegetables, 3.8 serves of grains, 1.8 serves of meat/protein, 1.8 serves of dairy
High % of discretionary choices > public health & education for consumers = vital.
Obesity as a clinical health condition & need to consider other chronic illnesses – dietary intake is only one slice of the pie e.g., looking at prevention, why is the rate of colon cancer so high?
We eat food, not nutrients – primary source of nutrition (food industry plays role in providing that)
Food provides us with culture and enjoyment and pleasure > 50,000 taste buds on our tongue, because it's such a pleasurable experience
Outline the NOVA classification system & examples of foods in each classification group.
Created in 2010 by a epidemiologist, Montero in South America.
GOAL: classify foods based on their degree of processing.
GROUP 1: Unprocessed or minimally processed foods e.g., cut orange = unprocessed food, orange juice = minimally processed product.
GROUP 2: culinary ingredients > foods transformed into an ingredient e.g., wheat made into flour, cocoa made into cocoa powder, vanilla beans.
GROUP 3: processed foods e.g., bread, corn flakes, weetbix
GROUP 4: ultra processed foods e.g., baby formula, jelly snakes & ice cream.
UPF: SPAM
One most processed food products in world invented by American Defence Force post WWI
Solution to spillage & shelf life, alternative to jerky
Issues with malnourishment in soldiers
Good quality protein, easy to transport & eat, no refrigeration
UPF: BABY FORMULA
Origins: roughly 1905/1906, British paediatrician
Previous method: otter/cow milk, or sugar water = mass infant mortality >3 months
Paediatrician created baby formula off milk powder, sugar, vitamins & minerals = decrease in morality rate, if reached 6mth mark > greater indication of survival
Modern: 20-30 ingredients in 1 tin, extremely processed due to underdeveloped digestive tract.
Explain the difference between food processing and processed food.
Technology → process of transformation.
Outcome = product.
Food processing is the technology > processed foods are outcome
FOOD PROCESSING & CHANGING STRUCTURES
Modifying architecture for purpose > similar to food processing
Range of technology utilised to change the structure = different food outcomes, can affect nutritional composition.
Fresh fruits and veggies → three main components for water category, but the structural framework is largely based on the dietary fibre. And then we've also got all the nutrients, macros, micros and phytonutrients that are located within the different cells.
Modifying structure → release nutrients for bioavailability, BUT ability to negatively affect it.
EXAMPLE: tomatoes. Cooking for jams/sauces improves bioavailability of lycopene, but kills Vitamin C
Outline some of the new food products available due to food processing, and novel technologies.
NEW FOOD PRODUCTS
Rnge of different food products
Alternative foods e.g., alternate minces/cheese
Hybrid products e.g., dairy products, with finer sterols added to milk to help decrease cholesterol in patients with elevated blood cholesterol.
Foods catering to dysphasia patients
Swallowing food, some leaks into the front passage & heads towards lungs
Trisco: company in Brisbane ‘Precise’ range - sold internationally > thickeners for water/coffee/tea/beer & thickened juices
NOVEL TECH IN THE FOOD INDUSTRY
High pressure processing: unique, used extensively.
Placed in chamber & treated with extremely high pressure > doesn’t require additives/heat treatment e.g., Presha Apple Juice – triangular bottle withstands pressure in the tanks
Pulse electric field technology: expensive, not used commercially.
Zapped with electricity to kill pathogenic bacteria and increase shelf life.
3D Printed technologies
Chefs and scientists using 3D printers to create delicate suites, geometrically designed meats
Netherlands: the government has implemented 3D printers in old age homes to 3D print food > easy for elderly people to chew and swallow, nutritionally designed for that individual person
Technology monitoring shelf life in real time > best buy dates obsolete?
Describe new trends in food processing.
Upcycling /Waste Reduction
Seven Brothers Brewery (UK): taken cereal normally be wasted, dumped in landfill or given to a pig farmer e.g., Kellogg's Coco Pops, cornflakes and Rice bubbles -> into beer
Fever tree lemonade (Italy): lemon pomace from lemon used (perfume byproduct)
Natural purple Berry brightening serum (UK): Source purple Berry from the byproduct of Robina Berry cordial.
Describe a nutritional approach to food processing.
How much nutrients are released in the digestive tract? How much of the nutrients that are in there is released?
Which part of the digestive tract are the nutrients released and where does the rest end up? Where is it actually being absorbed?
What is its direct impact on health from manufacturing my DNA through to function, Wellness, etc.,
EXAMPLE: PerkI, probiotic drink, invention from researchers from the University of Queensland: micro-encapsulation. Bacteria is in a little cage or or a protective shell around each bacterial forming unit. Once it arrives at the colon, my gut bacteria have to eat the little shell → designed specifically to reach the colon for beneficial health aspect.
Outline a brief history (with example) of food processing.
→ Food processing – one of the oldest industries
→ Fertile Crescent: upper region of Egypt, to Mesopotamia through to the Persian Gulf > MULTIPLE food based processes were created and discovered.
E.g., Egyptians took papyrus > flour and created bread.
7000 BC: CHEESE → ANCIENT ITALY
Archaeologist in the 1960s and 1970s discovered pottery fragments in Poland > pot with holes, chemistry assessment indicated chemistry content for dairy, protein, fat and lactose from various animals – holes were for creating yogurt & cheese
ANCIENT IRANIANS: BEER
Storing barley in big vats covered in water to stave off rats = beer, retained liquid as it was nutritionally rich
24000 BC: GHERKINS, MESOPOTAMIA
Hanging gardens of Babylon → where the Gerkins found their life.
Cucumbers = short shelf life > discovered it could be extended if soaked in water or brine.
ABRAHAM LINCOLN & FOOD SAFETY (MILK)
Abraham Lincoln’s mother died of milk poisoning: issue > toxic weed that the cattle were eating, toxin accumulated in its milk.
Milk poisoning predominantly effected the immunocompromised e.g., pregnant women, the elderly, children or babies
Removal of weed + Louis Pasteur's pasteurisation = milk safety → developed into school milk feeding programme (beneficial for kids & growing bones)
Outline the two main methods for classifying food
Nutrient based classification (nutrient profiling) > categorisation from nutritional composition e.g., ADGs > core foods vs discretionary foods, Health Star ratings, the 5 food groups
Food-processing based classification e.g., NOVA
Explain the concept of the NOVA classification system and it’s origins.
Developed in Brazil in 2009 > Professor Carlos Montero
First to introduce UPFs
Groups food according to nature, extent & purposes of industrial processes undergone.
1 of 4 groups:
1. Unprocessed/Minimally Processed 2. Processed Culinary Ingredients. 3. Processed Foods. 4. Ultra Processed Foods
DOES NOT consider food nutrient content > degree of processing affects health impact of food more than nutrients
Outline the first three NOVA classification groups and examples within each.
GROUP 1: Unprocessed/Minimally Processed
Unprocessed (or natural foods): edible parts of plants (fruit, leaves, stems, seeds, roots) or from animals (muscle, offal, eggs, milk), fungi, algae and water, after separation from nature.
Minimally processed foods: Natural foods altered by methods to make them suitable for storage, or make them safe/edible/pleasant to consume.
Methods: drying, crushing, grinding, powdering, roasting, boiling, non-alcoholic fermentation, pasteurisation, chilling and freezing.
GROUP 2: Processed Culinary Ingredients
Examples: Oils, butter, lard, sugar & salt.
Used to prepare, season & cook Group 1 foods
Rarely consumed in isolation > used in combination
GROUP 3: Processed Foods
Made by adding salt, oil sugar/other substances from group 2 to group 1 foods.
Most processed foods have two or three ingredients & recognisable as modified versions of group 1 foods.
Processes: canning and bottling using oils, sugars or salt; preservation e.g., salting, salt-pickling, smoking, and curing; non-alcoholic fermentation (breads and cheeses).
Explain the Group 4 category in the NOVA classification.
GROUP 4: Ultra Processed Foods
“Formulations of ingredients, mostly of exclusive industrial use, made by a series of industrial processes, many requiring sophisticated equipment and technology” = ‘ultra processed’
Complex food manufacturing techniques e.g., extraction → Hydrolysis, hydrogenation → extrusion, moulding and pre-frying → added colours, flavours, emulsifiers → attractive packaging (using synthetic materials).
Highly profitable, convenient and hyper- palatable (low-cost ingredients, long shelf-life, well branded, ready-to- consume).
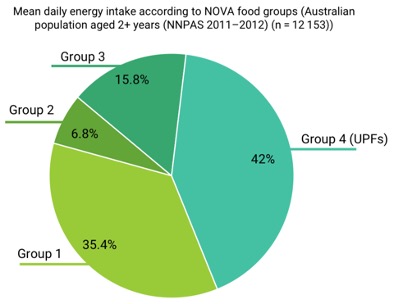
Outline consumption patterns of UPFs in the Australian population landscape.
CONSUMPTION OF UPFs (AUS)
1. Mass-produced packaged breads (4.8% of total daily energy intake)
2. Frozen and shelf stable ready meals (3.7%)
3. Fast food dishes (3.5%)
4. Pastries, buns and cakes (3.3%)
5. Breakfast cereal (3.2%)
Identify additives exclusive to UPFs (cosmetic & food substances)
Cosmetic additives: Flavours/flavour enhancers, colours, emulsifiers/Emulsifying salts, artificial sweeteners, thickeners and foaming, bulking, carbonating, gelling and glazing agents.
Food substances: hydrolysed proteins/soya protein isolate/whey protein, gluten, casein, fructose/high-fructose corn syrup/‘fruit juice concentrate’, maltodextrin/dextrose, lactose, soluble or insoluble fibre.
Explain the adverse health effects associated with UPF intake.
Majority of evidence -> published in the last couple of years (2020 onwards)
Overwhelming volume > go back to hierarchy of evidence (NRMHC)
Associated within increased risk of:
All cause mortality, overweight/obesity, chronic diseases (T2D, CVD, CAD), mental health disorders
Large categories of UPFs > easier to establish significant link
Predominately observational studies – cannot with 100% certainty say they are negative for health
We don’t know why UPFs can lead to adverse outcomes & WG
Outline possible hypotheses that explain the negative impacts of UPFs.
Lower Nutritional Quality: Increased amounts of salt, sugar, saturated fats, and energy, and decreased amounts of fibre, vitamins, and micronutrients.
Changes in Food Matrix & Texture: Impact on digestibility
Contact Materials: packaging material contaminants e.g., bisphenol, mineral oils, phthalates.
Contaminants from Processing: industrial trans fatty acids, advanced glycation end productions, acrolein, furans, acrylamide.
Food Additives & Industrial Ingredients: colouring agents, sweeteners, emulsifiers, flavouring agents, corn syrup, modified starches & maltodextrin.
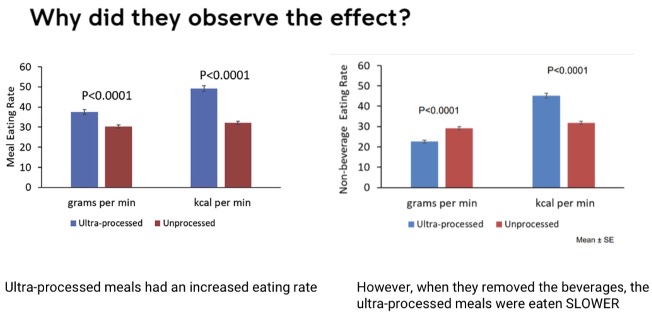
Describe the design and results of the randomised control trial compared an unprocessed and an UPF diet.
STUDY DESIGN
20 adults; consumed ultra processed and unprocessed diets for 14 days each
All foods provided by researchers
Diets matched for total calories, sugar, fat, dietary fibre and macronutrients.
RESULTS
UPF diet still led to an increase in calorie intake over the time period.
Participants gained 0.9 kg at the end of the 2 wk on UPF diet & lost 0.9 kg, mostly body fat, by the end of non UPF diet
Describe the concept of the ‘impossible triangle’ of food processing.
TASTE + NUTRITION + COST = ‘perfect food’
Difficult to balance all 3.
Consider: convenience, safety, brand loyalty, advertisement, brand vs customer etc.,
Outline traditional food processing techniques and common machinery utilised in this process.
DRYING: Removal of water from a product > one of the oldest methods of food preservation
Used widely in large quantities to add value e.g., wheat & Australian exports > reduced mould & pest risk, best long term storage, increased grain storage
Drying & Water Activity (aW)
A measure of availability of water:
Amount available for transport/reaction
Effect of viscosity at low aw (diffusion process is reduced at higher viscosity)
Purpose of Drying
Control aw (NOT moisture!) > varies between 0 (dry) and 1
aw different from moisture content -> correlates to chemical and biological processes
Water is bound by dipole-dipole forces, ionic bonds & hydrogen bonding
Types of Hot Air Dryers
Bin dryers: storage bin with perforated floor and blower to generate air flow (ambient or heated)
Applications: vegetables, grains
Conveyor or belt dryers: continuous dryers with control over drying conditions and high production rates (up to 5.5 ton/h). Co-current, counter-current, crossflow, or centre exhaust air flow arrangement. Food can be dried up to 10-15% moisture content before secondary drying.
Vacuum belt dryers: liquid food converted into stable foam and spread thinly on a perforated belt to dry before grounded into free flowing powders.
Applications: fruit, milk, nuts, biscuits, purées.
Spray drying: a dispersion of pre-concentrated food is atomised into a fine mist of droplets sprayed into a co-current or counter-current hot air. Dryer selection depends on properties of feed material & required properties of product.
Applications: dairy & food powders.
FREEZE DRYING: Water in food product is frozen & converted into vapour by sublimation under reduced pressure (vacuum)
Advantages: superior quality and minimal shrinkage.
Disadvantages: high energy costs vs hot air drying.
Describe why the food processing industry is moving in the direction of plant based meats. List some consumer concerns with plant based meats/foods.
FACTORS DRIVING PB FOOD INDUSTRY
Growing Population: projected 10 billion by 2050 → current agricultural system insufficient to meet production demand & quality = food security crisis
Livestock & Agricultural Emissions: 60% of agricultural emissions from meat & dairy production.
Australia = Plant Based Leader?: poised to be global leader, 3rd fastest growing market for PB foods > $13 billion by 2030.
Example of PB meat industry → Beyond Meat, listed in 2019.
CONCERNS WITH PB MEAT
Cost: increased production & purchase cost.
Safety Concern: long ingredient list & ultra processed > extrusion technology.
Outline novel food processing techniques.
INFRARED/MICROWAVE HEATING
Radiation: heat transfer by emission and absorption of electromagnetic waves (e.g. microwave, infrared, etc).
- No airflow in infrared drying -> important for spices e.g., chilli.
IR Heating in Freeze Drying
Energy consumption down
Reduced processing time
Reduce cost (vs mechanical processing)
Differentiate advanced food processing vs advanced food engineering. List reasons for food processing related to the SDGS
ADVANCED FOOD PROCESSING
Developed over time
Technology difficult to separate from product → process and product very intertwined and integrated in modern systems e.g., milk
ADVANCED FOOD ENGINEERING
Creating products with the use of specialised machinery e.g., Ferraro Rocher
Technologies used in new ways/combinations
FOOD PROCESSING & SDGs
Reduces food insecurity → increased availability and affordability
Reduces resource use
Can promote good health & wellbeing through engineered foods