L1(transport)-Structure of cell surface membranes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1.What is a plasma membrane?
2.What is a cell surface membrane?
3.What are the 2 main purposes of the cell surface membrane?
1.All membranes around and within all cells (including those around organelles) that have the same basic structure.
2.Membranes that surround cells and separate the cytoplasm from the environment.
3.to allow different conditions to be established inside and outside of a cell.
It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
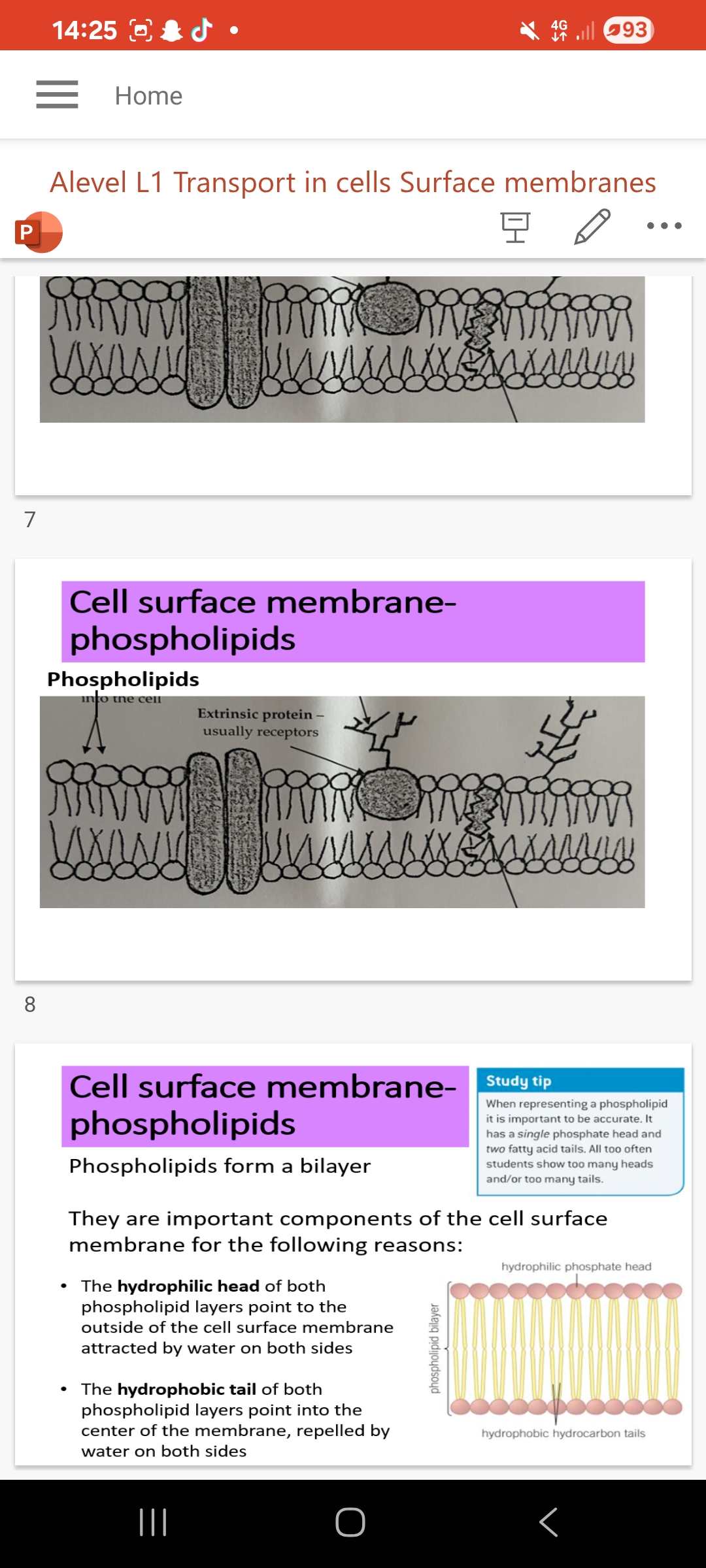
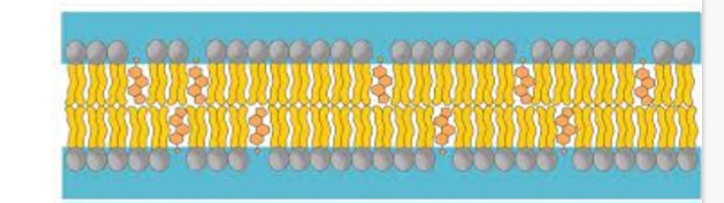
Phospholipids form a bilayer
They are important components of the cell surface membrane for the following reasons:
• The hydrophilic heads of both phospholipid layers point to the …1? of the cell surface membrane attracted by water on both sides
. The hydrophobic tail of both phospholipid layers point into the …2? of the membrane, repelled by water on both sides
Info:Lipid soluble material move through the membrane via the phospholipid portion.
3.Name 3 functions of phospholipids in the membrane
1.outside. 2. Centre
3.• Alow lipid soluble substances to enter and leave the cell
• Prevent water soluble substances entering and leaving the cell
• Make the membrane flexible and self sealing
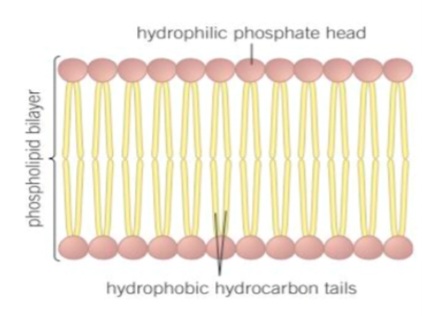
Info:Proteins are interspersed throughout the cell surface membrane and they are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer in two main ways: •Extrinsic •Intrinsic
Cell surface membrane- Proteins Extrinsic:
Extrinsic proteins occur on the …1? of the bilayer and NEVER extend completely through it.
They:
• Give mechanical support to the membrane
• Act as cell receptors, in conjunction with …2?, for molecules such as …3?
Cell surface membrane- Proteins intrinsic:
Intrinsic protein span the phospholipid bilayer from one side to the other.
Protein channels -…4? filled tubes which allow water soluble ions to …5? across the membrane
Carrier proteins - these …6? to ions or molecules like glucose and amino acids, then change …7? in order to move these molecules across the membrane
Surface. 2.glycoproteins 3.hormones. 4.water
5. Diffuse. 6.bind. 7.shape


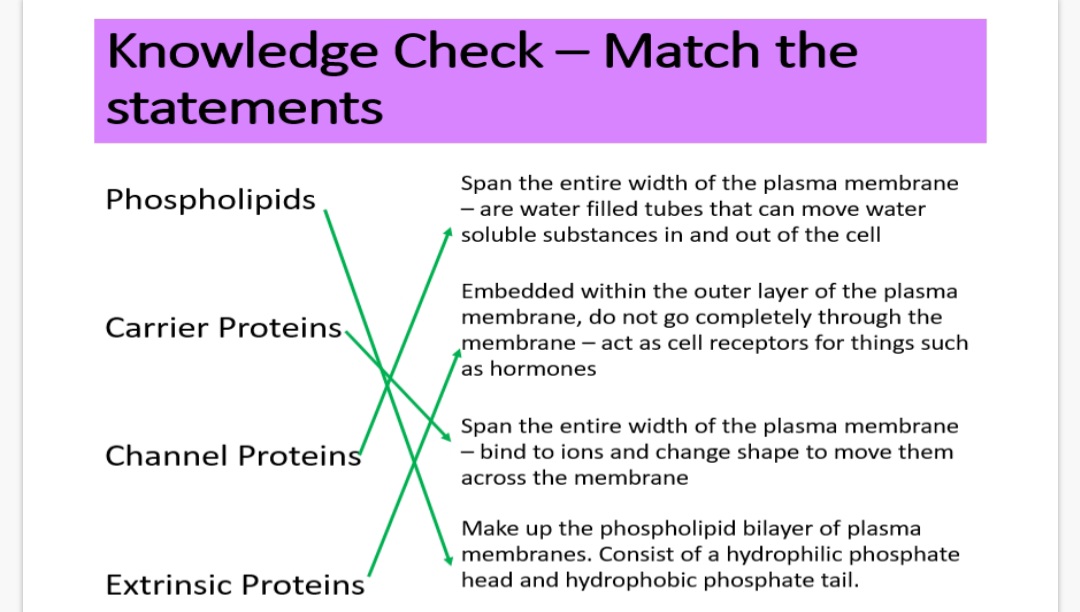
1.Match the defintions in the image:
Cell surface membrane - Proteins:
Info:
To summarise the function of the proteins in the membrane are:
• Provide …1? support
• Act as …2? transporting water soluble substances across the membrane
• Allow active …3? across the membrane through carrier proteins
• Form cell surface receptors for identifying cells
• Help cells adhere together
• Act as …4? -ie for hormones
Structural. 2.channels. 3.transport. 4.receptors
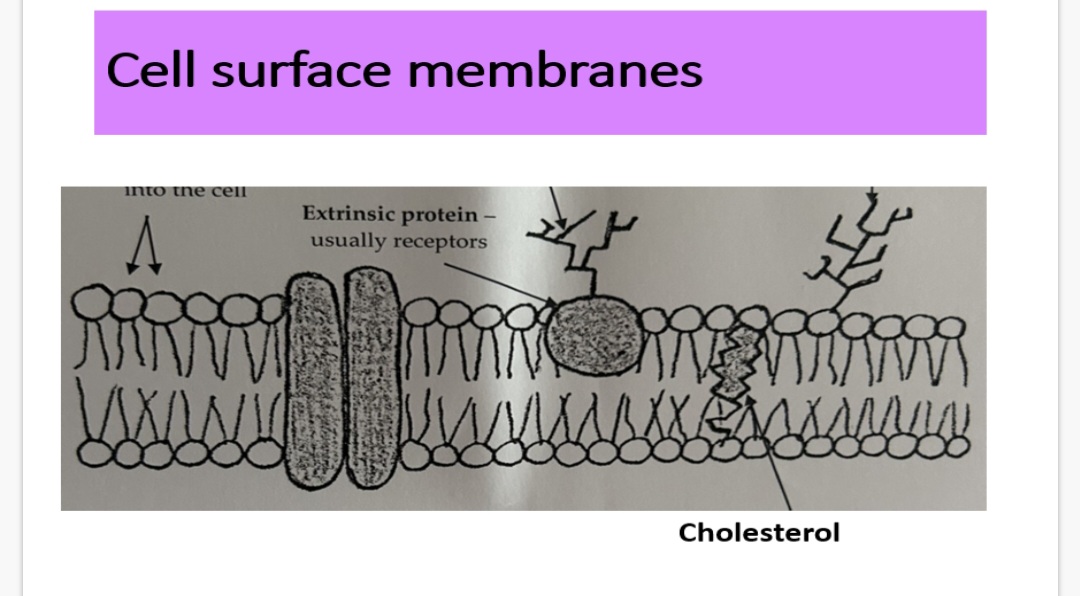
Cell surface membrane - cholesterol:
Cholesterol occurs within the …1? …2? of the cell surface membrane.
Cholesterol molecules are very …3?(since they’re uncharged) so play an important role in preventing …4? loss and dissolved ions from leaving the cell.
They add strength to the membrane by pulling the fatty acid tails …5? to limit movement without making them rigid.
1 function of cholesterol is that it reduces lateral movement of other molecules including phospholipids.
6.State 2 other functions?
1 and 2. Phospholipid bilayer. 3.hydrophobic. 4. Water. 5.together
6.. Make the membrane less fluid at high temperatures
. Prevent leakage of water and dissolved ions from the cell
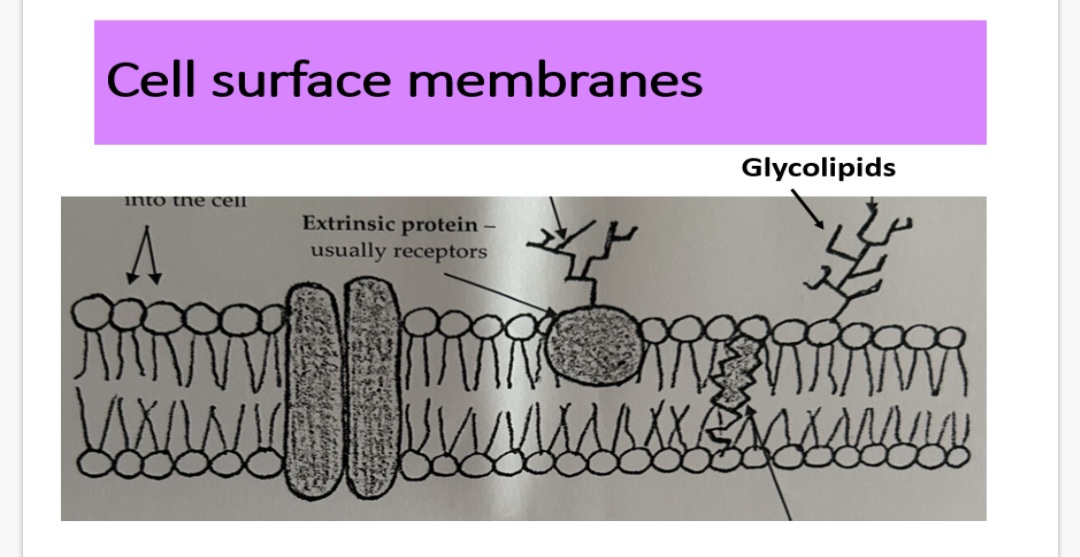
Cell surface membrane- Glycolipids:
Glycolipids are made up of carbohydrates …1? bonded with a lipid
The carbohydrate section extends from the …2? into the outside environment where it acts as a cell surface …3? for chemicals (human ABO blood)
4.State 3 functions of glycolipids?
Covalently. 2.bilayer. 3.receptor
4.◦ Act as recognition sites
• Help maintain the stability of the membrane
• Help cells to attach to one another to form tissues

Cell surface membrane- Glycoproteins:
Carbohydrate chains are attached to …1? proteins on the outer surface of the cell membrane.
These glycoproteins act as cell surface …2? for hormones and neuro…3?.
4.Name 3 glycoprotein functions?
Extrinsic. 2.receptors. 3.transmitters
4.◦ Act as recognition sites
• Help cells to attach to one another to form tissues
• Allow cells to recognise one another ie Lymphocytes can recognise an organisms own cells so it won’t attack
Cell surface membrane- permeability
Most molecules cannot freely diffuse across the membrane. Name 4 reasons why?
•Not soluble in lipids
• Too large to pass through the channels
. May be Electrically charged (polar). so have difficulty passing through nonpolar hydrophobic tails
Cell surface membrane- Fluid mosaic model
The arrangement is known as the fluid mosaic model because:
• Fluid-the individual phospholipids molecules can move relative to one another. This gives the membrane a …1? structure
• Mosaic - the proteins that are embedded in the bilayer vary in …2?, …3? and …4?
Flexible. 2,3 and 4. Size,shape and pattern