CVA Axial Skeleton
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lessons 9 and 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Cranial most Sternum
manubrium
Caudal most sternum
xiphoid process
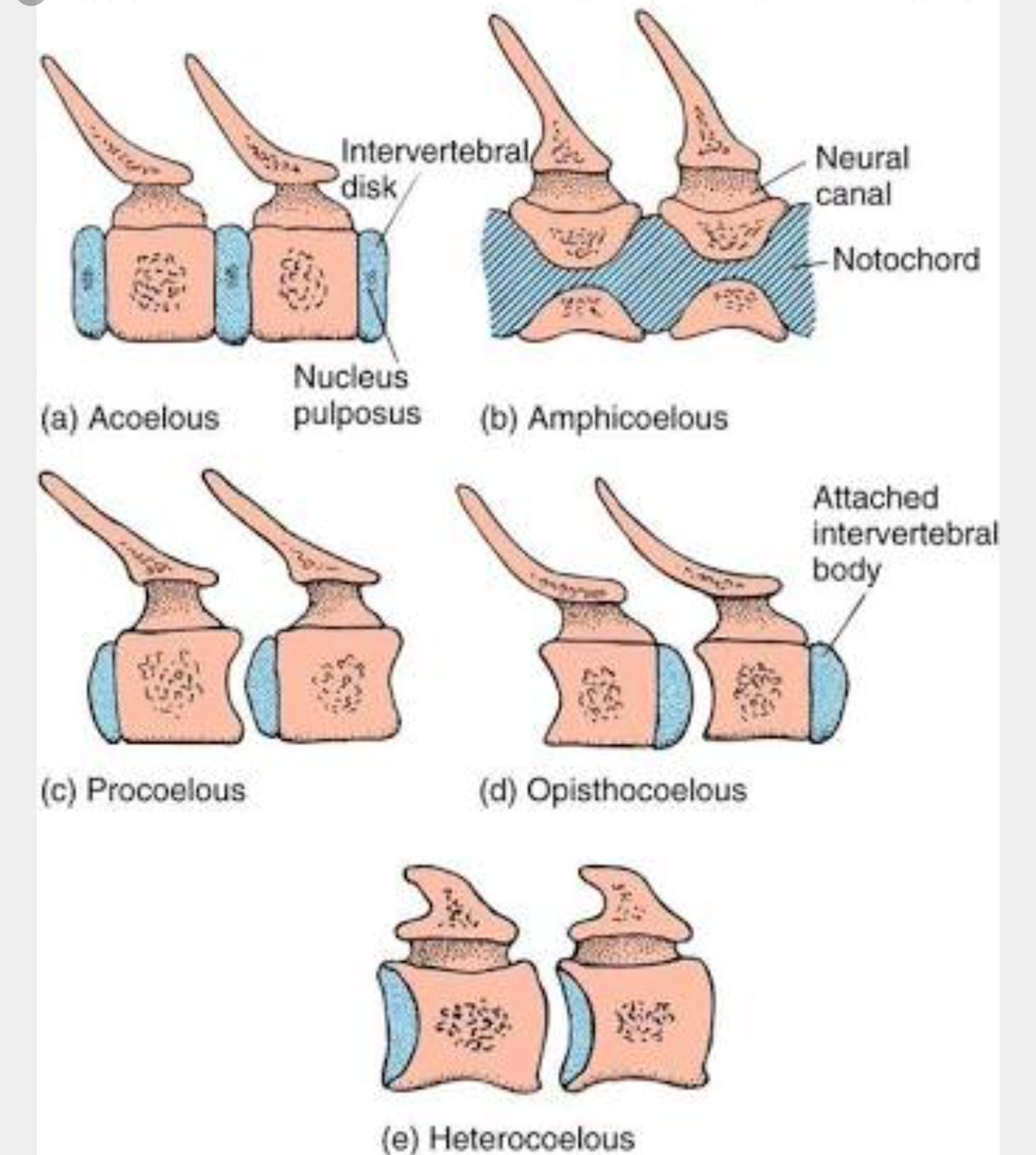
Acoelus
Ends of centrum are flat
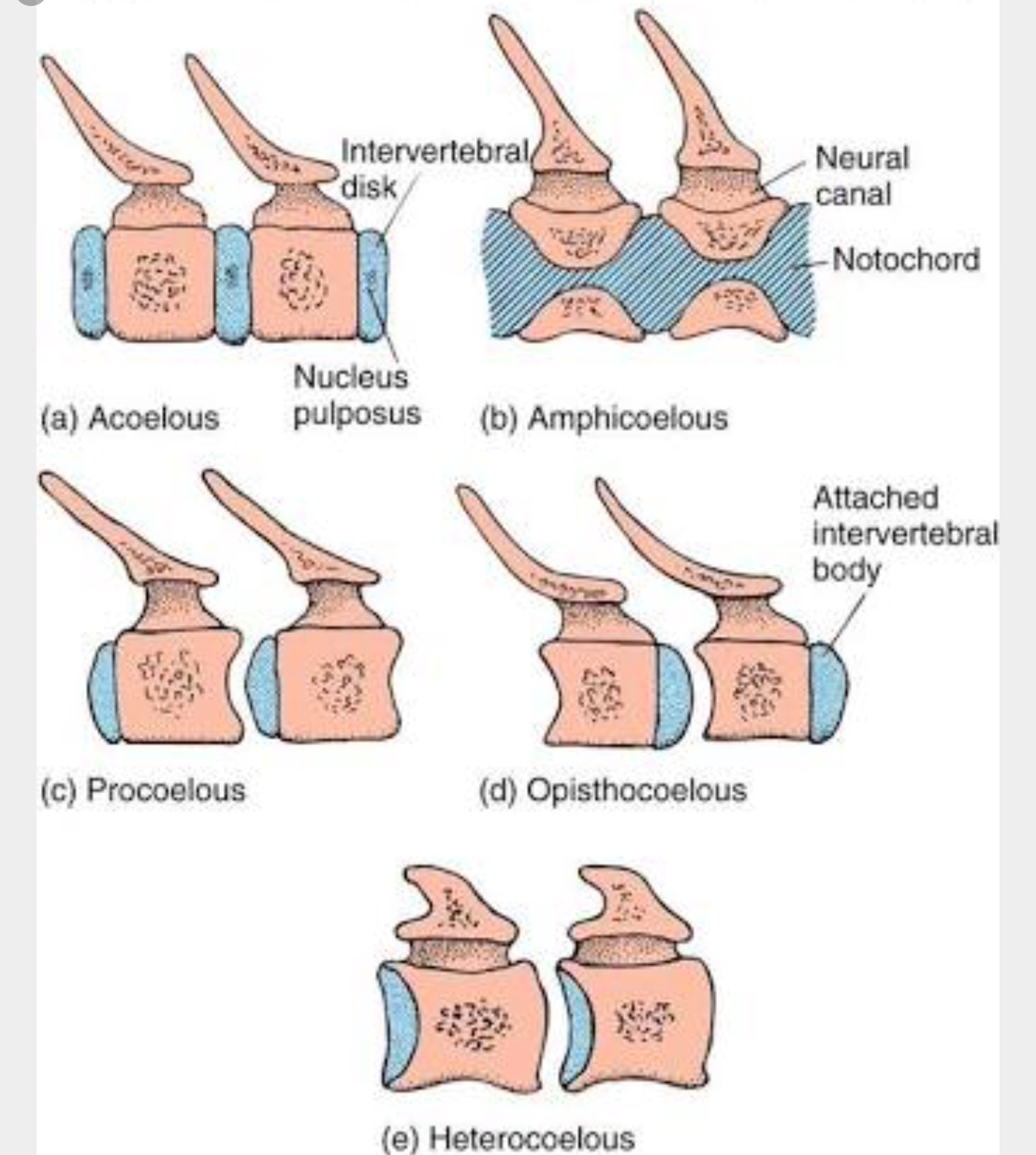
Amphicoelus
Both ends concave
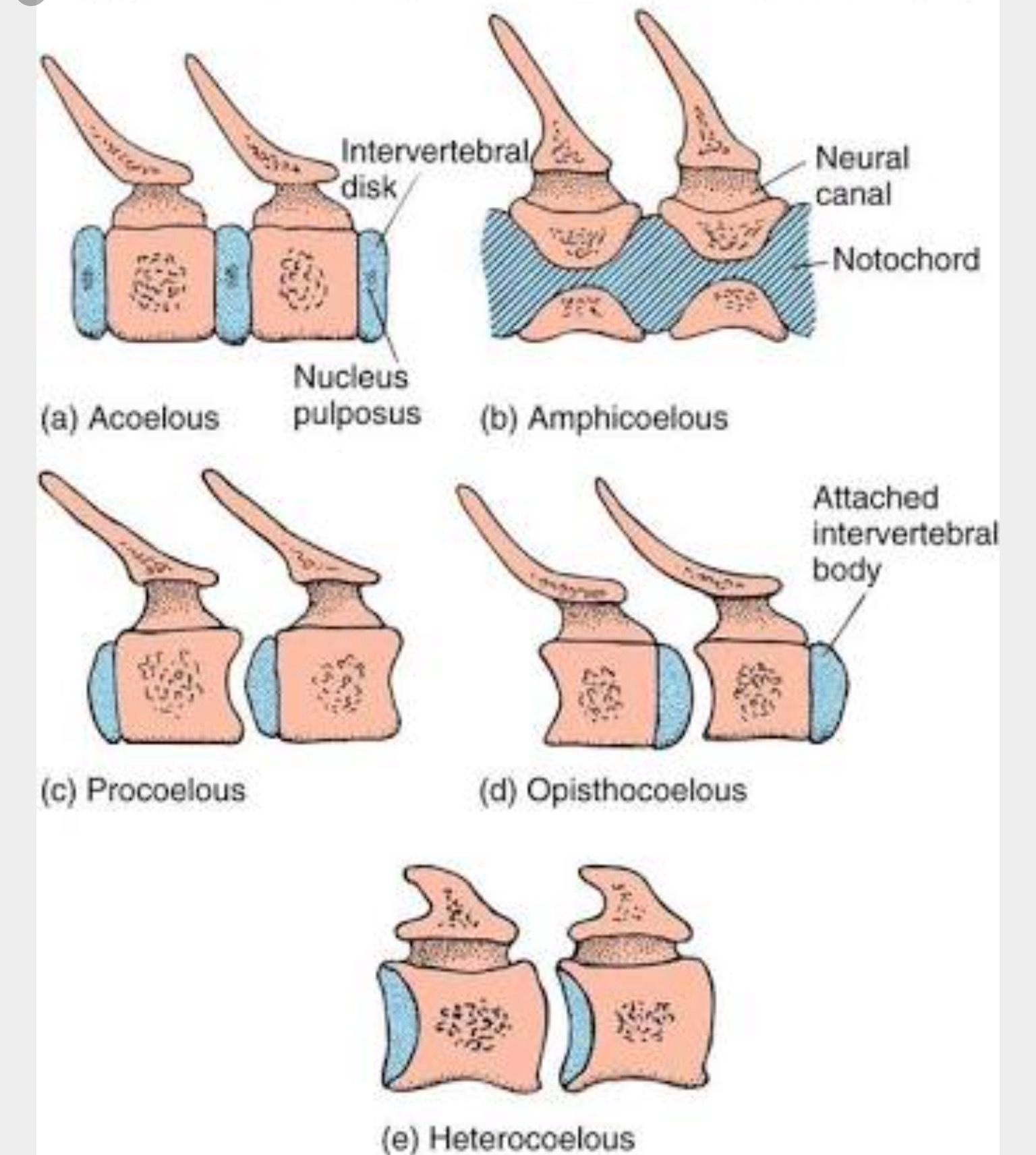
Procoelus
Cranial: concave Caudal: convex
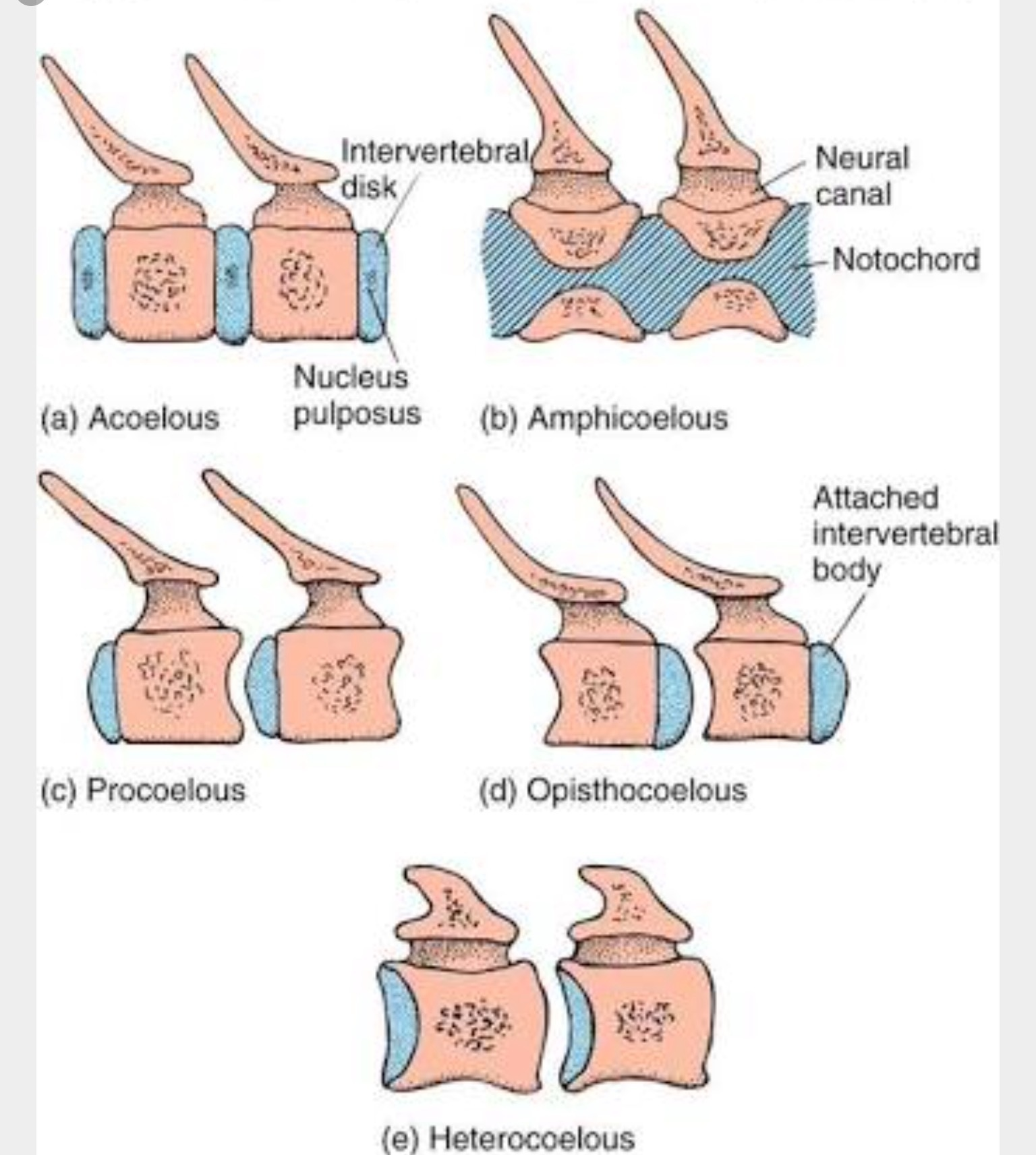
Opisthocoelus
Cranial: convex Caudal: concave
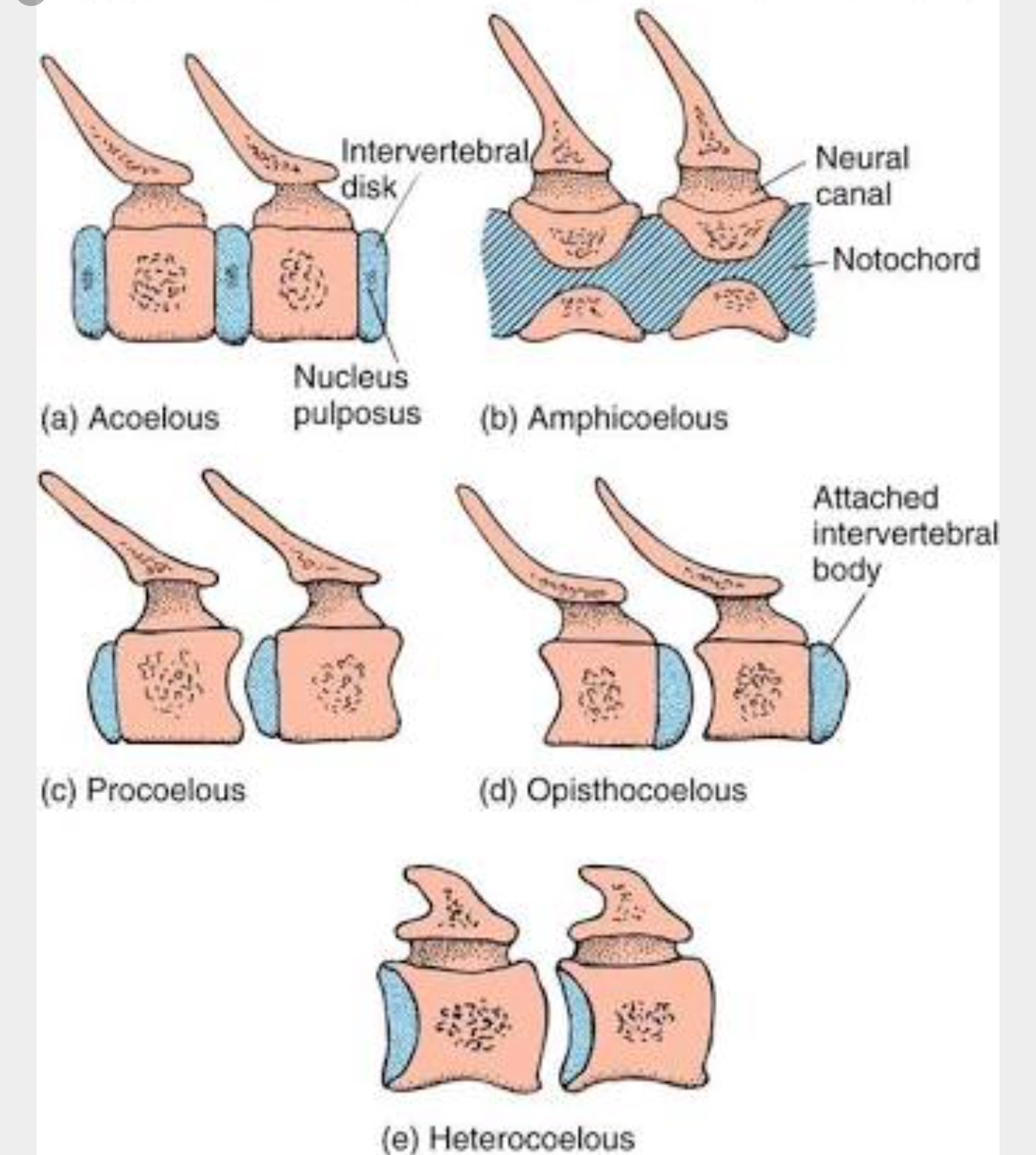
Heterocoelus
Saddle-shaped ends
True Rib
Meet with sternum at ventral aspect
False rib
Don’t articulate with sternum
Articulate with adjacent ribs
Floating Rib
Don’t articulate with anything ventrally
Trunk Rib
Open, spider-like shape
Caudal Rib (Fish Shape)
Elongated diamond
Dorsal Ribs
Pin bones
Costo-Chondral Junction
Meeting place of ventral and sternal rib
Tuberculum
Dorsal portion of vertebral rib
Capitulum (Head)
Ventral portion of vertebral rib
Facet
Portion of vertebral body where rib articulates
Atlas
Controls nodding movement, wing shaped
Axis
Controls side to side movement, long tube shape
Pygostyle
Fused - most caudal vertebra
Cervical
Articulates vertebral column with head
• Atlas / Axis
Thoracic
Facets articulate with ribs
Lumbar
Between thoracic and sacral
Sacral
Near pelvis
Caudal
Comprises tail
Invertebral Bodies
Cushions between vertebrae
In mammals:
• Annulus fibrosis (fibrocartilage) surrounding
• Nucleus pulposus (notochord remnant)
3 origins of plastron
Clavicles (Epiplastrons), Interclavicle (Entoplastron), Gastralia (Hypoplastron and Xiphiplastron)
Uncinate Processes
Extend from rib caudally
Muscle attachment
Teleost Vertebrae - trunk
Neural spines
Ribs
No hemal spines
Teleost Vertebrae – caudal/tail
neural spine
hemal spines
no ribs
Turtle ribs and vertebrae
Thoracic vertebrae and ribs fused with carapace
Heterocoelus cervical vertebrae → movement of neck
Zygopophyses
Zygosphene and Zygantrum interlock to prevent excess twisting
Synsacrum
caudalmost thoracic
- all lumbar
- all sacral
- first caudal
Innominate Bone